そもそも偶奇性(Evenness)とは一体何なのでしょう?
偶数(Even)と奇数(Odd)
偶数(Even)=2n
c0<-seq(-5,5,length=11)
c1<-c0*2
# 出力結果
> c1
[1] -10 -8 -6 -4 -2 0 2 4 6 8 10
奇数(Odd)=2n+1
c0<-seq(-5,5,length=11)
c1<-c0*2+1
# 出力結果
> c1
[1] -9 -7 -5 -3 -1 1 3 5 7 9 11
加算(Addition)
- 偶数+偶数=偶数
- 偶数+奇数=奇数
- 奇数+奇数=偶数
乗算(Multiply)
- 奇数×奇数=奇数
- 奇数×偶数=偶数
- 偶数×偶数=偶数
偶数とは要するに「素因数分解した時、要素に素数2を含む数」であり、素数2は以下の操作によってその数の要素から生滅する訳ですね。
【Rで九九】どうして36個の数字しか使われないのか?
- 奇数の加算によって滅っする(2n+2n+1→2m+1)。
- 奇数同士の加算によって生じる((2n+1)+(2n+1)→2m+2→2m)。
- 偶数に奇数を掛けても生じる((2n+1)×2n=2m+2n=2l)
従って奇数同士の掛け算の結果は自明の場合(Trival Case)として奇数となるのです。
偶関数(Even Function)と奇関数(Odd Function)
数学上の定義はこうなってます。
偶関数と奇関数の意味,性質などまとめ
- 任意の実数xに対してf(x)=f(−x)を満たす関数を偶関数(Even Function)という。なお数値積分integrate(f(x),lower=-a,upper=a)の結果は2*integrate(f(x),upper=0,lower=a)となる。
- 任意の実数xに対してf(x)=−f(−x)を満たす関数を奇関数(Odd Function)という。なお数値積分integrate(f(x),lower=-a,upper=a)の結果は0となる。
加算(Addition)
- 偶関数+偶関数=偶関数
- 奇関数+奇関数=奇関数
乗算(Multiply)
- 奇関数×奇関数=偶関数
- 奇関数×偶関数=奇関数
- 偶関数×偶関数=偶関数
ちなみに「対称的なものと交代的(反対称的)なものに分解するための恒等式」x=(x+y)/2+(x-y)/2を用いると任意の関数を偶関数と奇関数の和に分解できます。
行列・関数・多項式に共通する有名な性質
オイラーの公式(Eulerean Formula)」e^Θi=cos(Θ)+sin(Θ)iを導出したマクローリン級数 (Maclaurin series) 概念の出発点?
【Rで球面幾何学】オイラーの公式を導出したマクローリン級数の限界?

偶関数(Even Function)の代表例Cosine波(Cosine Wave)

# グラフ化してみる。
plot(cos,xlim=c(-pi,pi),ylim=c(-1,1),main="Cosine Wave")
abline(h=0,col=rgb(1,0,0))
abline(v=0,col=rgb(1,0,0))
数値積分の結果
> integrate(cos,lower=-pi,upper=pi)
4.359836e-16 with absolute error < 4.5e-14
> round(4.359836e-16,digit=8)
[1] 0
> integrate(cos,lower=0,upper=pi)
4.402787e-17 with absolute error < 2.2e-14
> round(4.402787e-17,digit=8)
[1] 0
> 0*2
[1] 0
奇関数(Odd Function)の代表例Sine波(Sine Wave)

plot(sin,xlim=c(-pi,pi),ylim=c(-1,1),main="Sine Wave")
abline(h=0,col=rgb(1,0,0))
abline(v=0,col=rgb(1,0,0))
数値積分の結果
> integrate(sin,lower=-pi,upper=pi)
0 with absolute error < 4.4e-14
ちなみにSine波/Cosine波の数値積分の別区間は以下。
【初心者向け】半径・直径・円周長・円の面積・球の表面積・球の体積の計算上の往復
偶奇性(Evenness)概念の起源について。
「原始座標群(Primitive Coordinate Group)=距離も方角も観測不能な極座標系(Polar Coordinate System)」概念から出発します。この段階ではまだ偶奇性(Evenness)概念は存在しません。
【無限遠点を巡る数理】原始座標群なる「事象の墓場」概念の設定

①Inf(inty)/Inf(inty)=1の概念を追加すると、かかる演算(Operation)の敷衍結果として、これを中点(Midpoint)とする半分の概念、およびこの操作の相似形としての2倍の概念が同時追加されます。禁止が解除になる感覚?
| Index | Harf | Base | Double | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | -Inf | 1/(2^Inf):=0 | 1/(2^Inf):=0 | 1/(2^Inf):=0 |
| 2 | … | … | … | … |
| 3 | -3 | 1/(2^4)=1/16 | 1/(2^3)=1/8 | 1/(2^2)=1/4 |
| 4 | -2 | 1/(2^3)=1/8 | 1/(2^2)=1/4 | 1/(2^1)=1/2 |
| 5 | -1 | 1/(2^2)=1/8 | 1/(2^1)=1/2 | 2/2=1 |
| 6 | 0 | 1/2 | 2/2=1 | 2^1=2 |
| 7 | 1 | 2/2=1 | 2^1=2 | 2^2=4 |
| 8 | 2 | 2^1=2 | 2^2=4 | 2^3=8 |
| 9 | 3 | 2^2=4 | 2^3=8 | 2^4=16 |
| 10 | … | … | … | … |
| 11 | Inf | 2^Inf:=Inf | 2^Inf:=Inf | 2^Inf:=Inf |
library('xtable')
target_index<-c("-Inf","…","-3","-2","-1","0","1","2","3","…","Inf")
target_base<-c("1/(2^Inf):=0","…","1/(2^3)=1/8","1/(2^2)=1/4","1/(2^1)=1/2","2/2=1","2^1=2","2^2=4","2^3=8","…","2^Inf:=Inf")
target_harf<-c("1/(2^Inf):=0","…","1/(2^4)=1/16","1/(2^3)=1/8","1/(2^2)=1/8","1/2","2/2=1","2^1=2","2^2=4","…","2^Inf:=Inf")
target_double<-c("1/(2^Inf):=0","…","1/(2^2)=1/4","1/(2^1)=1/2","2/2=1","2^1=2","2^2=4","2^3=8","2^4=16","…","2^Inf:=Inf")
Regula_falsi00<-data.frame(Index=target_index,Harf=target_harf,Base=target_base,Double=target_double)
library(xtable)
print(xtable(Regula_falsi00),type = "html")
- すなわち0を加法単位元(Additive Identity)とする加法整数群Zn(n=-Inf→0→Inf){-Inf,…,-3,-2,-1,0,1,2,3,…,Inf}概念が使用可能になると同時に(これを添字集合とする)1を乗法単位元(Multiplicative Identity)とする群(Group)2n(n=-Inf→0→Inf){1/Inf:=0,…,1/(2^3)=1/8,1/(2^2)=1/4,1/2,2/2=1,2,2^2=4,2^3=8,…,Inf/1:=Inf}およびそのデカルト積(Cartesian product)の概念もまた使用可能となるのである。
- 同時に「周期の問題」として偶数系(Even System)と奇数系(Odd System)の概念も自明的な場合(Trival Case)として使用可能となる。
-
近代数学史(およびコンピューター開発)の歴史が「対数表の発表合戦」に遡るのは決して偶然ではなかった?
【数理考古学】常用対数表(Table of Common Logarithms)を使った計算 - ただしここから「ネイピア数の発見→自然指数/対数関数(Natural Exponential/Logarithmic Function)の発見」を経てオイラーの公式(Eulerian Formula)e^πi=cos(θ)+sin(θ)iに至る道は決して平坦ではなかったのである。
【初心者向け】指数・対数関数の発見とそれ以降の発展について。 - そして、もししかしたら群(Group)の成立条件に結合条件(Join Condition)が入っているのって、こうやって数列(Number Sequance)を組んだりデカルト積(Cartesian Product)が求められる様にする必要があるからかもしれない。
【初心者向け】群論概念の根幹
共役関係(Conjugated Relation)概念の導入
共役関係(Conjugated Relation)は、この際に導入されるのがただの素数2ではなく、群(Group)2n(n=-Inf→-3,-2,-1,0,1,2,3→Inf){0,…,1/8,1/4,1/2,1,2,4,8,…,Inf}である事から生じるのです。
【初心者向け】複素共役のアニメーション表示について。
2次元上の見え方

3次元上の見え方



この数理は当然「既存関数では半円しか描けない」問題とも関係してきます。
【Rで球面幾何学】「半円しか描けなかった」世界の思い出?
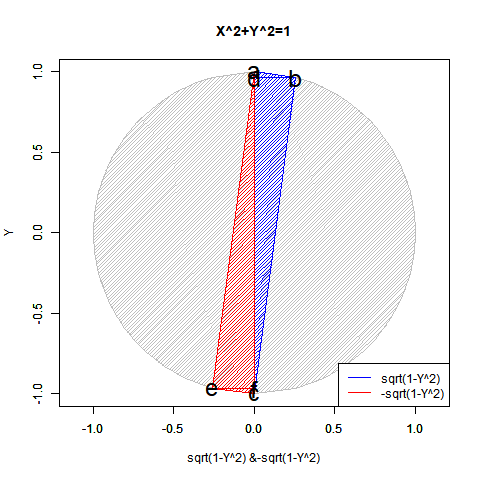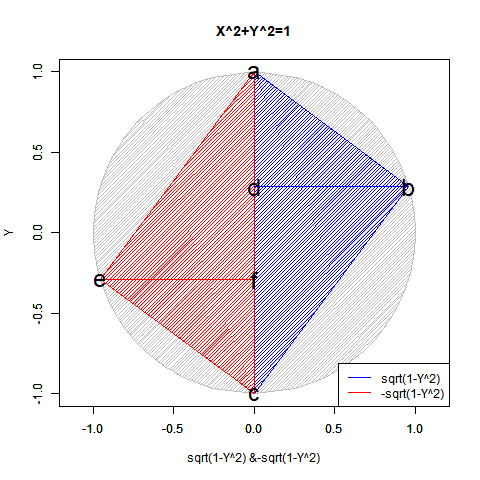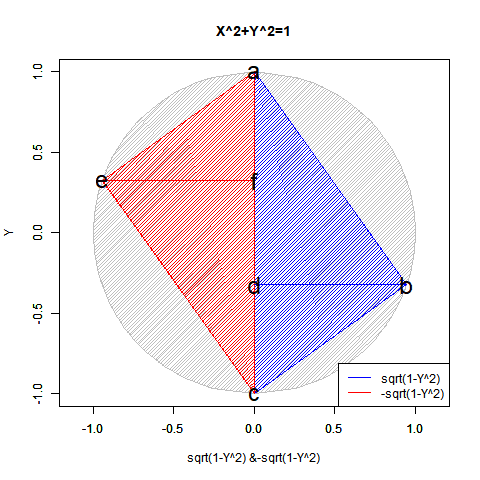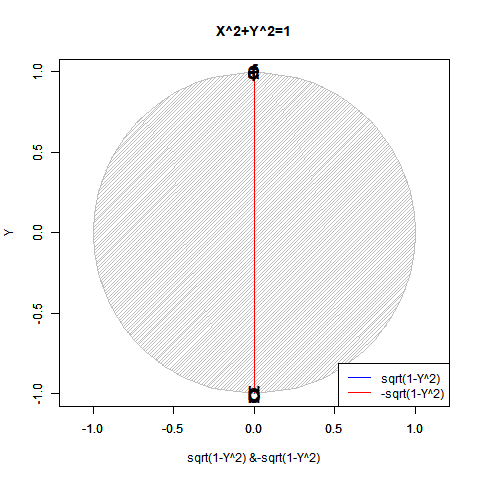
実は「半分」になるだけでなく「倍」となるケースもあります。地球上の座標を表す経緯度法(Longitude and Latitude)で緯度(Latitude,-90度~90度)が経度(Longitude,-180度~180度)の半分なのは何故でしょう? 三次元極座標系(Polar Coordinate System)において緯度に対応する角度θ(0~π)が経度に対応する角度φ(0~2π)の半分なのは何故でしょう? 全周分使うと球面上を2周してしまうからなんですね。
二次元空間(円弧)におけるデカルト座標系(x,y)と極座標系(r,φ)の相互変換
- 原点(0,0)からの距離r=sqrt(x^2+y^2)
- φ=-(atan2(x,y)-pi/2)
- x=r×cos(φ)
- y=r×sin(φ)
三次元空間(球面)におけるデカルト座標系(x,y,z)の極座標系(r,φ,θ)の相互変換
- 原点(0,0,0)からの距離r=sqrt(x^2+y^2+z^2)
- φ=-(atan2(x,y)-pi/2)
- θ=-(atan2(sqrt(x^2+y^2+z^2),z)-pi/2))
- x=r×sin(θ)cos(φ)
- y=r×sin(θ)sin(φ)
- z=r*cos(θ)
【初心者向け】半径・直径・円周長・円の面積・球の表面積・球の体積の計算上の往復
メルカトル図法 - Wikipedia

とりあえず、偶奇性(Evenness)概念と共役関係(Conjugated Relation)概念の連続性について示せたので以下続報…

