初めに
初めまして.大学院を修了してからのほうが勉強している時間が長くなった新社会人です.ゲーム会社で新人プログラマしてます.
今回取り組むのは以下の3種類です.
- 光芒
- まつ毛によるグレア
- ハロ
今回取り組むにあたり,畳み込みとそれを高速に実行するために高速フーリエ変換(FFT)を使用していますが,この部分の解説をしているサイト・記事ならいくらでもあるのでここでは説明しません.その点ご留意ください.また計算に関しては全てコンピュートシェーダでやっています.これいいですね.速い!!!
*ここに記載している画像は記事2のものよりも新しくなりました.記事2も編集したいのですが,編集時に内容が消えており更新すると吹き飛んでしまいます.そのため更新していません.南無阿弥陀仏.
レンズによる回折
ここではまずレンズのフーリエ変換作用(光学的フーリエ変換)について簡単に解説します.先にまとめると**「レンズを通過した平行光は焦点距離において,通過した形状のフーリエ変換像(周波数スペクトル)になる」というものです.そして,「波長によってフーリエ変換像の大きさが変わる」**ということです.ここだけ確認して次に進んでいただいてよいです.
フラウンホーファー回折
レンズによる回折を説明するにあたり,フラウンホーファー回折という回折理論について触れておきます.
今以下のように平行光が開口を通過する場合を考えます.
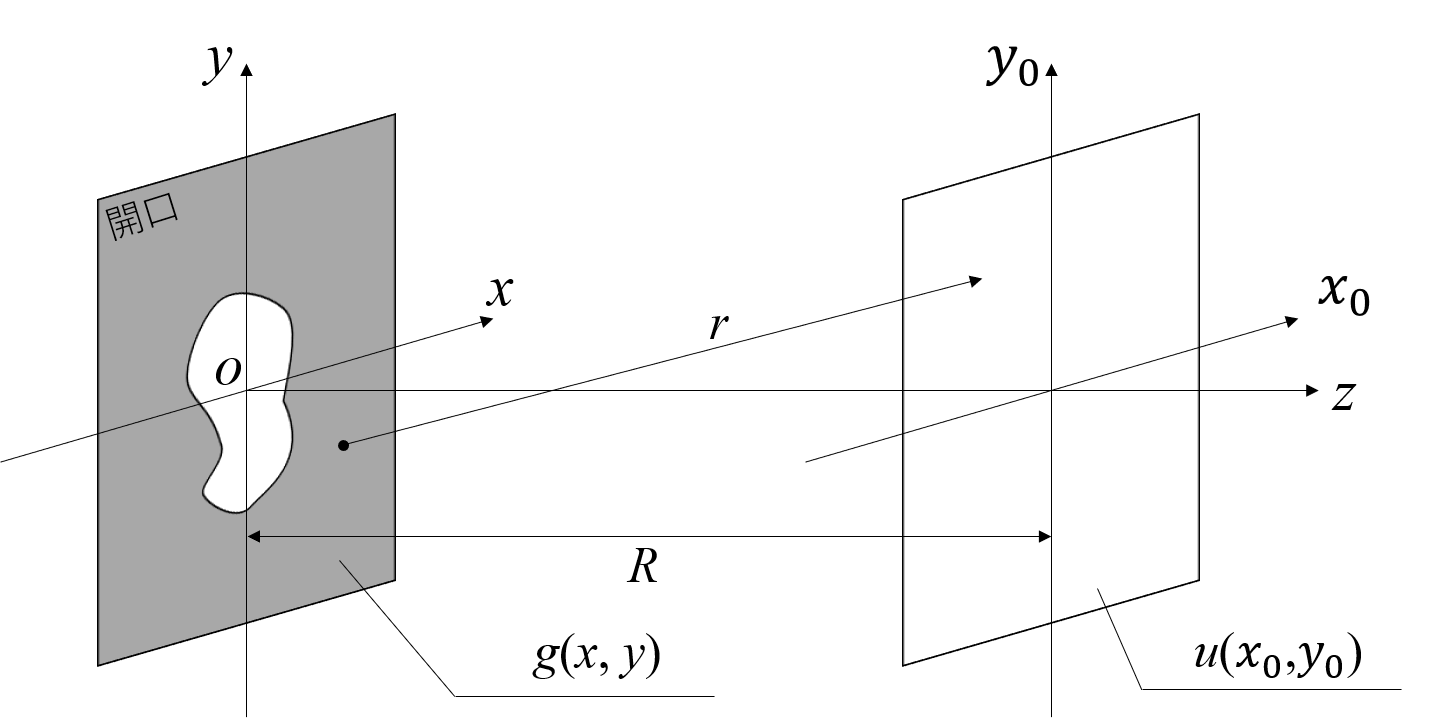
キルヒホッフの回折理論により,開口から距離$R$離れた位置での光波分布は,開口面での各点における素元波同士の干渉として記述され,以下のようになります.
u(x_0,y_0) = \frac{1}{i\lambda}\iint g(x,y)\frac{A\exp[ikr]}{r}dxdy
ここで,$\frac{A\exp[ikr]}{r}$は素元波,$k$は波数,$r\equiv\sqrt{R^2+(x-x_0)^2+(y-y_0)^2}$であり,$g(x,y)$は開口を表す関数です.
g(x,y) = \left\{
\begin{array}{ll}
1 & (\text{Inside of Aperture}) \\
0 & (\text{Outside of Aperture})
\end{array}
\right.
最初の積分の式だけではよくわからんという人もいると思いますので,ざっくり説明しますと**「平行光が開口$g(x,y)$にさえぎられて,空いている部分から飛んできた素元波は$\frac{A\exp[ikr]}{r}$で表される.この素元波をスクリーン上で全部足すと干渉を再現することになり,その結果がスクリーンにおける光の分布になる」**となります.
ここで,開口のサイズと比較してスクリーンまでの距離が十分長いとみなせる場合,近軸近似により以下が成り立ちます.
\frac{1}{r}\simeq\frac{1}{R}
次に指数の肩の$r$ですが,フラウンホーファー回折では次のように近似します.
r\simeq R+\frac{{x_0}^2+{y_0}^2}{2R}-\frac{xx_0+yy_0}{R}
これらと,元の積分式から以下を得ます.
u(x_0,y_0) = A^{'}\iint g(x,y)\exp[-i(\nu_x x+\nu_y y)]dxdy = A^{'}\mathcal{F}[g(x,y)]
ここで,$\mathcal{F}[\cdot]$はフーリエ変換を表します.また,
A^{'}\equiv \frac{A}{i\lambda R}\exp\left[ik\left(R + \frac{{x_0}^2+{y_0}^2}{2R}\right)\right]\\
\nu_x\equiv\frac{k}{R}x_0=\frac{2\pi}{\lambda R}x_0,\; \nu_y\equiv\frac{k}{R}y_0=\frac{2\pi}{\lambda R}y_0
です.以上でわかることは,**「開口を通過した光の伝搬自体がフーリエ変換の作用を持っている」ということと,「波長に応じて像の大きさが変化する」**ということです.上式の$u$と$v$は空間周波数であり,スペクトル(ここでは像)の大きさはこれに基づき変化し,波長により変化することが式により明らかなので前述のことが言えます.
レンズのフーリエ変換作用
今前節と同様以下のように,開口$g(x,y)$から距離$R$離れた位置での回折波の光波分布を計算することを考えます.
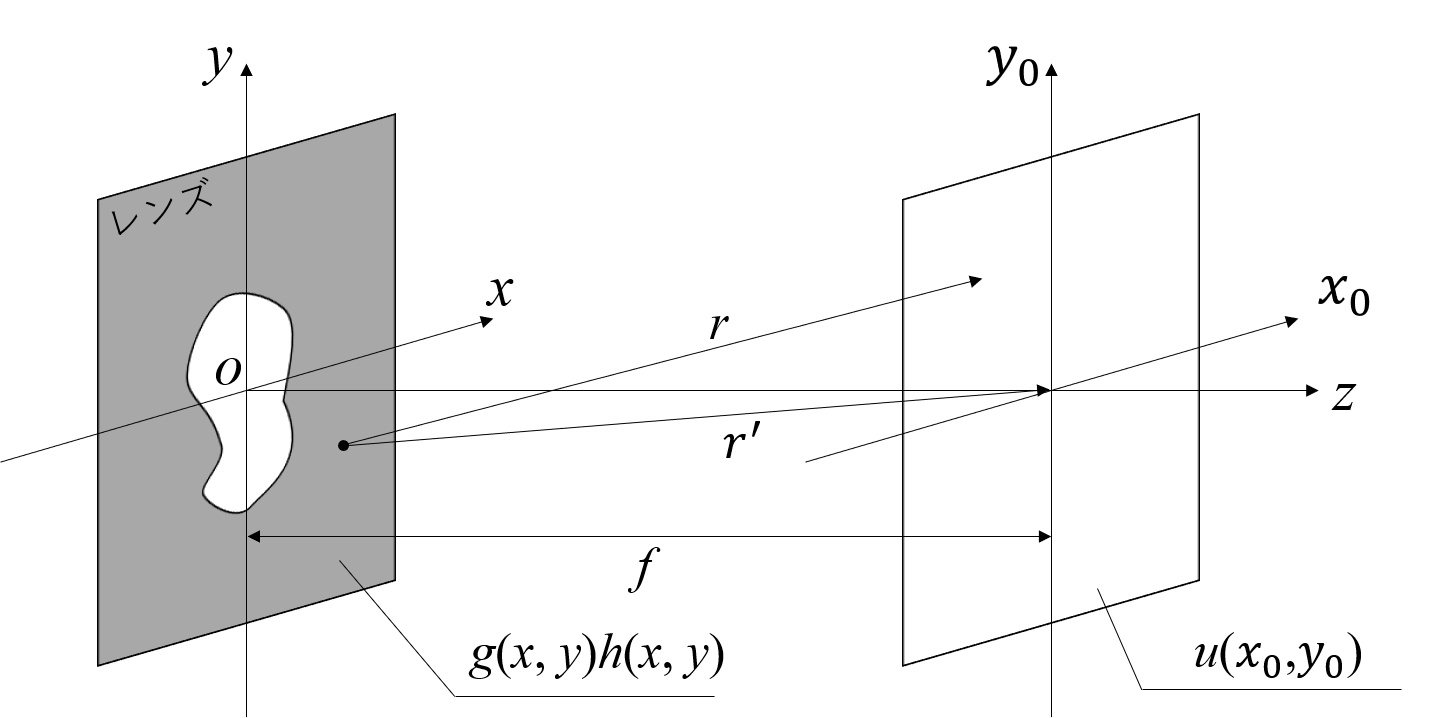
ここで$h(x,y)$は開口面のある点$(x,y)$から焦点までの距離$r^{'}=\sqrt{f^2+x^2+y^2}$に応じて波の位相をずらす性質を持ちます.この関数は焦点距離$f$のレンズ中心を基準として
h(x,y)=\exp[-ik(r^{'}-f)]
と表されます.この時,距離$R$での分布は
u(x_0,y_0) = \frac{1}{i\lambda}\iint g(x,y)\frac{A\exp[ik(r-r^{'}+f)]}{r}dxdy
となります.また,$R=f$のとき,次の近似を使用します.
r\simeq f+\frac{{x-x_0}^2+{y-y_0}^2}{2f}\\
r^{'}\simeq f+\frac{{x}^2+{y}^2}{2f}
以上により以下を得ます.
u(x_0,y_0) = A^{'}\iint g(x,y)\exp[-i(\nu_x x+\nu_y y)]dxdy = A^{'}\mathcal{F}[g(x,y)]
また,先ほどと同様に
A^{'}\equiv \frac{A}{i\lambda f}\exp\left[ik\left(f + \frac{{x_0}^2+{y_0}^2}{2f}\right)\right]\\
\nu_x\equiv\frac{k}{f}x_0=\frac{2\pi}{\lambda f}x_0,\; \nu_y\equiv\frac{k}{f}y_0=\frac{2\pi}{\lambda f}y_0
です.結局,フーリエ変換すれば結像面での分布が得られるわけです.
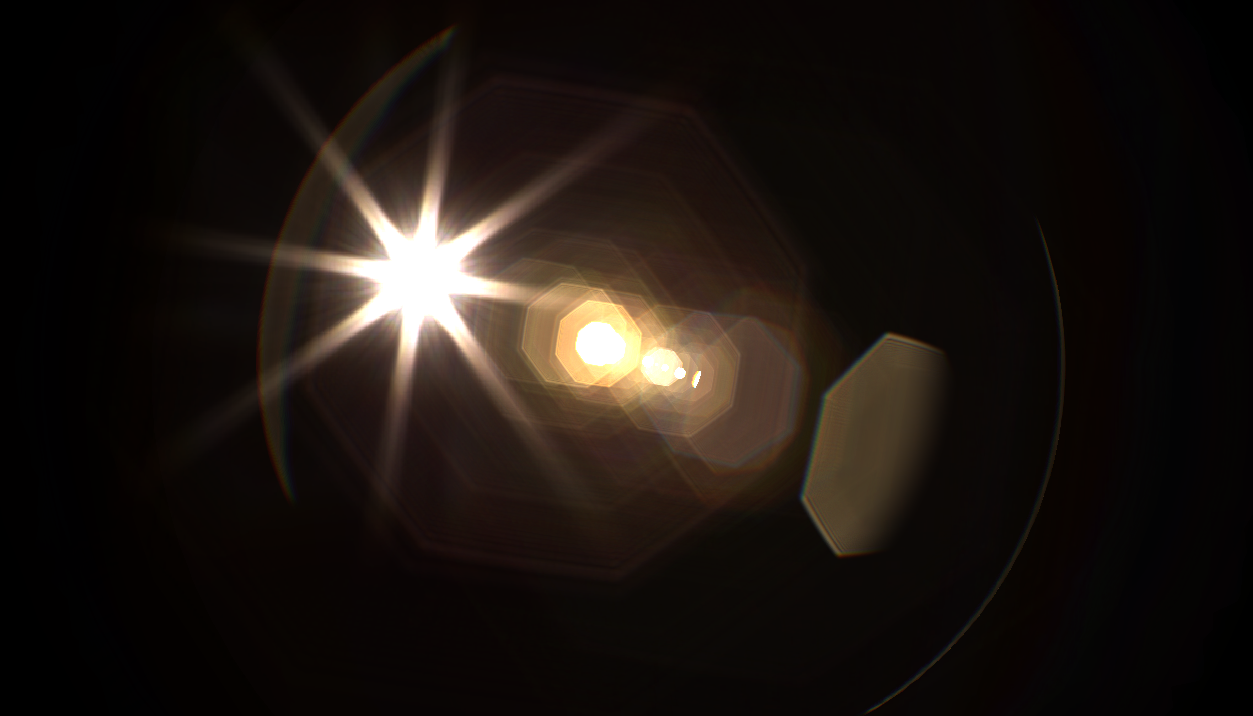
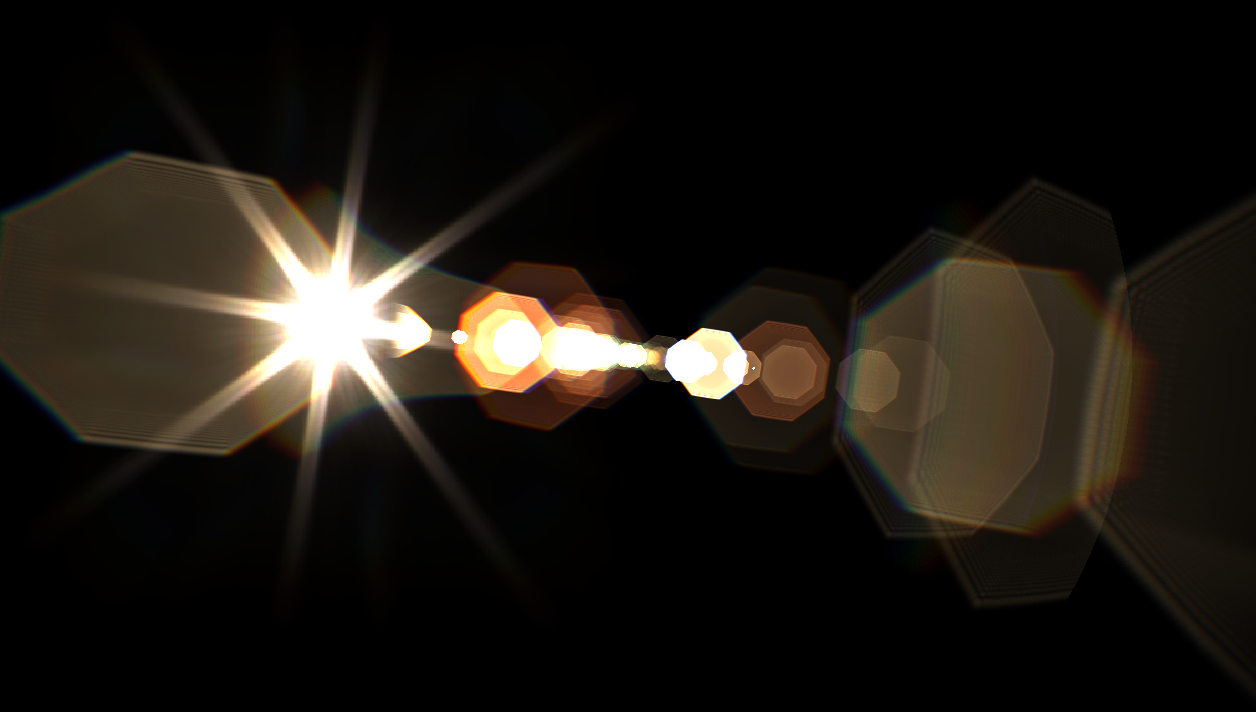
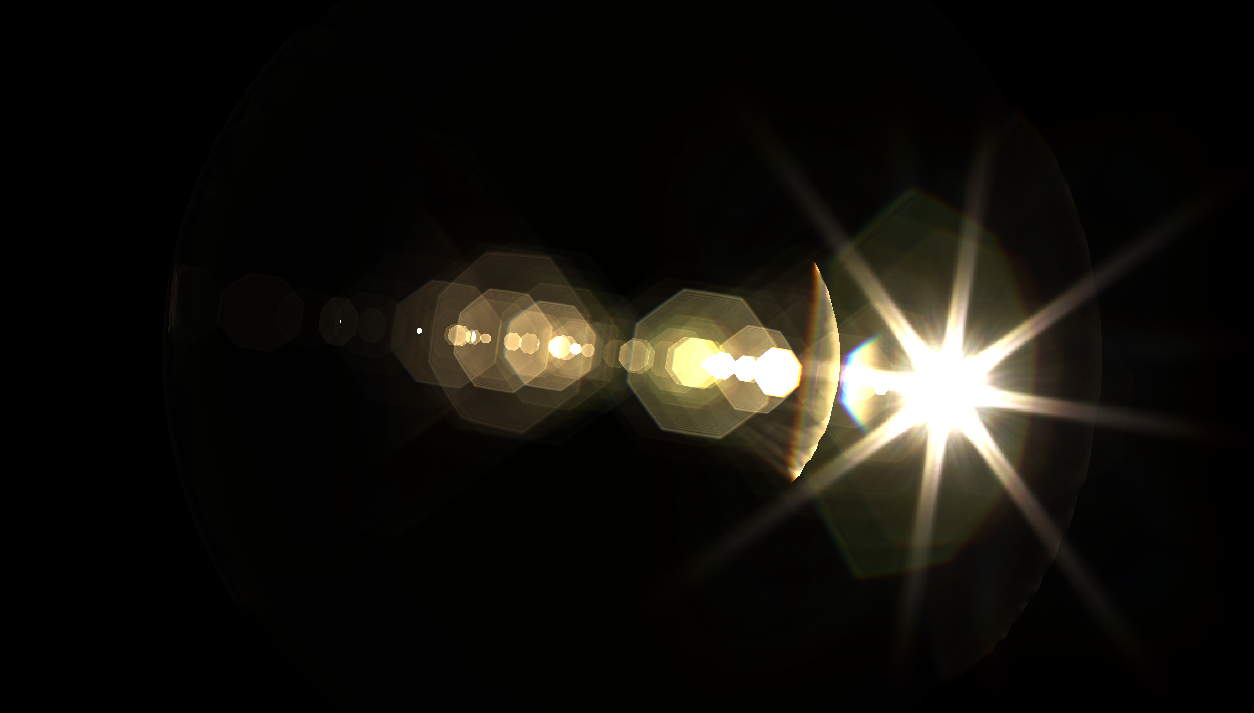
光芒

カメラで強い光や点光源を撮影すると,上図のように光源から放射状に光線が伸びたような写真になるときがあります.これは絞り羽根の重複部分の隙間から回折してきた光の映り込みによって生じます.より精密な物理ベースレンズフレアに関してはこちらをご確認ください.
以降カメラを簡単に以下のような構造であると考えます.
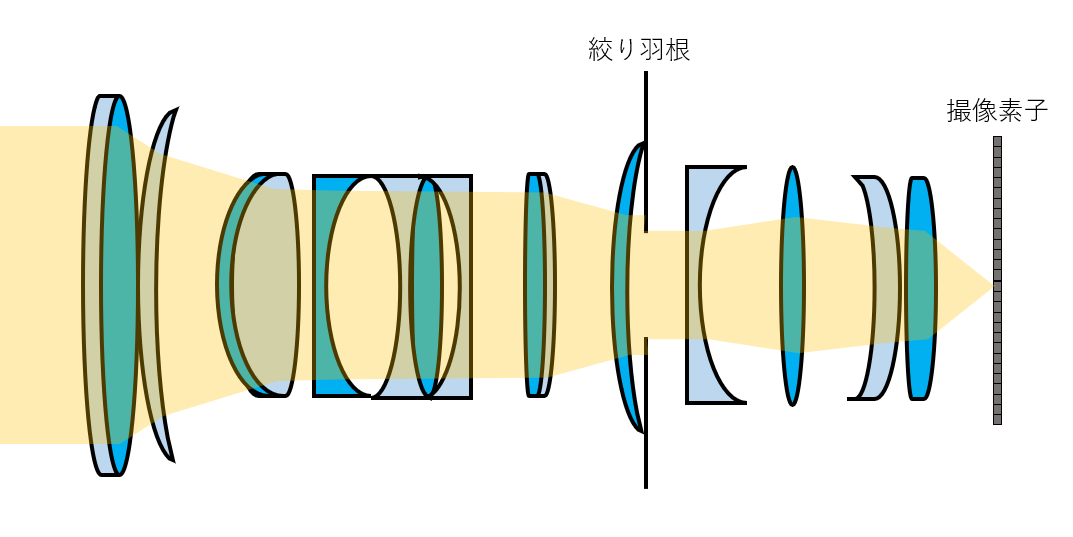
この構造で行けば,光芒は光がレンズを通り絞りばねで大きく回折し撮像素子上に結像された結果と考えてよいでしょう.
また,さらにレンズと絞り羽根の間の回折を考えず,先に絞り羽根の影響を受けてレンズを光が通過したと考えることにします.
この設定で行けば,計算すべきは絞り羽根形状の開口画像をフーリエ変換した結果が光芒になるからです.
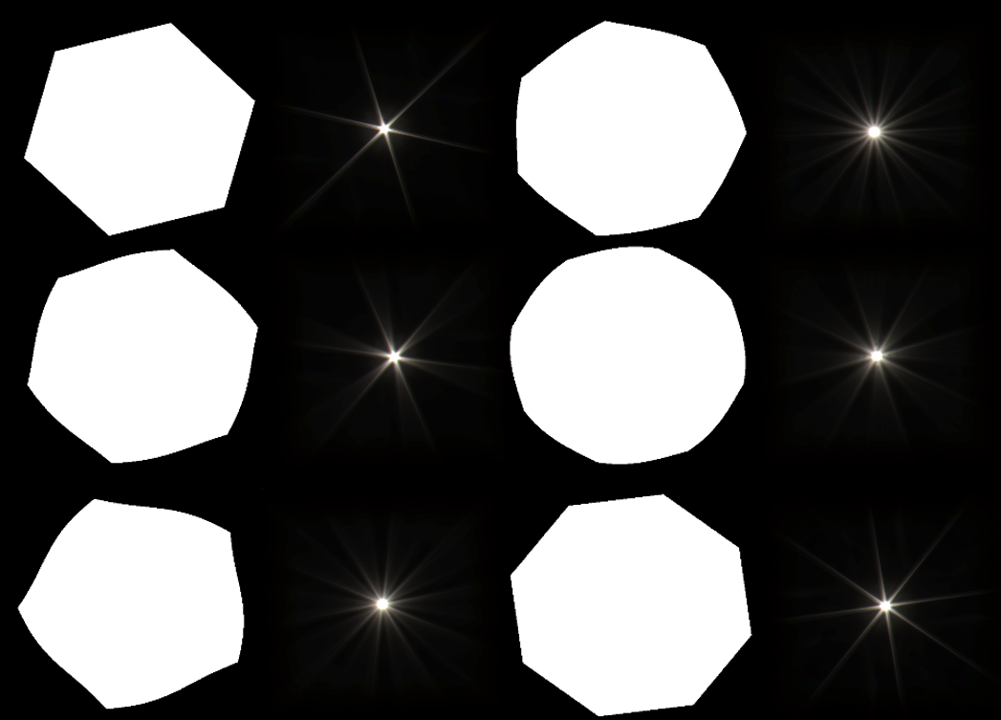
以下に左側に示した絞り羽根開口のフーリエ変換像から計算されるバーストを右に示します.より詳細はこちら
まつ毛によるグレア
夜中,まぶしい街灯や車のライトを見たときに,光源から毛が生えたように見えた経験はないでしょうか.結構あれ好きなのですが.これもカメラと同様に,まつ毛にさえぎられた光が水晶体によって集光され,網膜上に結像すると考えればよいと思います.
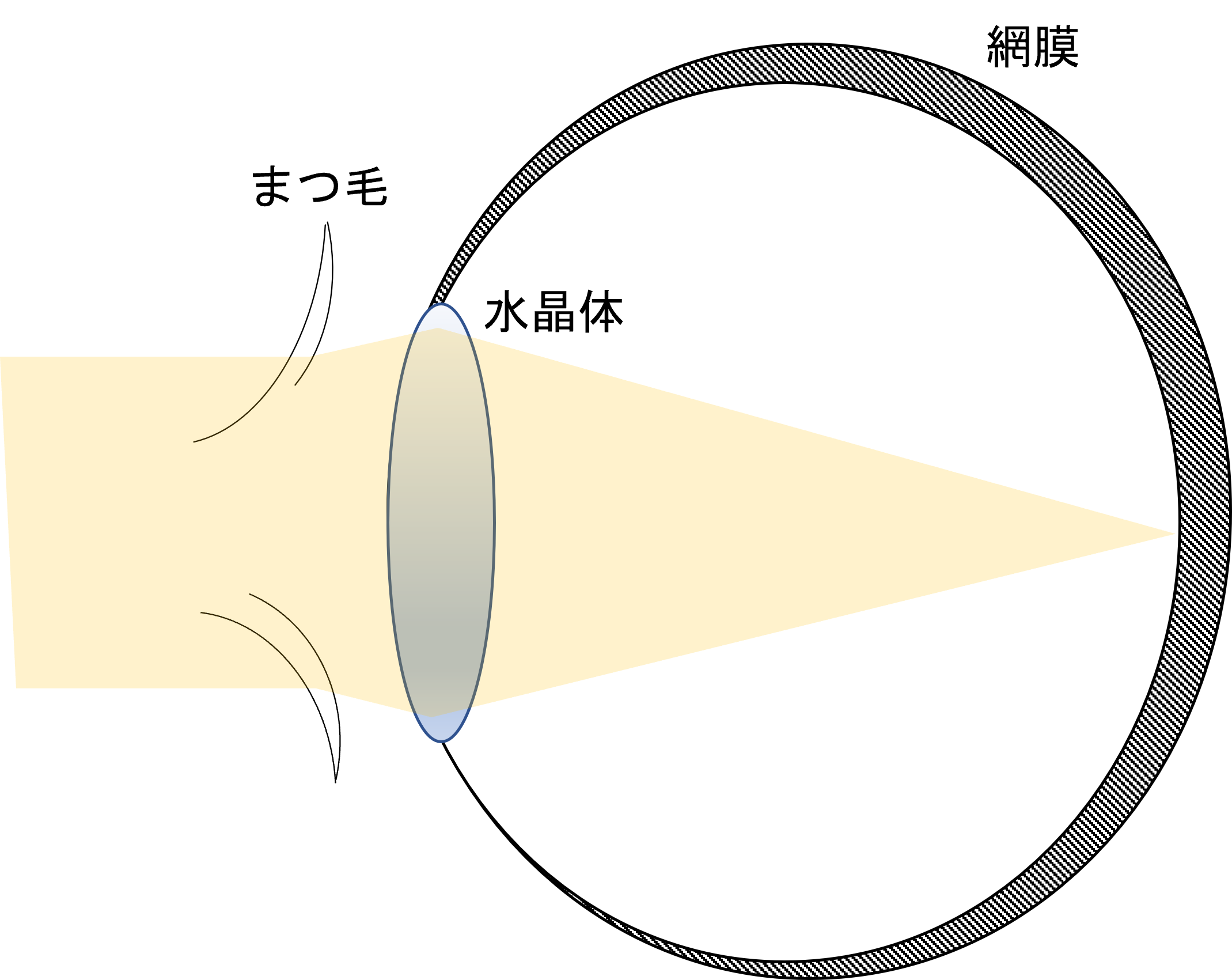
要するにこれに関してもまつ毛の画像を用意してフーリエ変換です.(まつ毛はめちゃくちゃ適当です.すみません.)
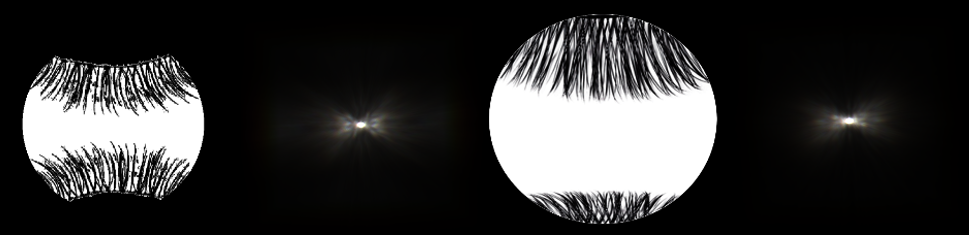
ハロ
光源の周りに傘状の光がみられる現象です.調べていただければいくらでも画像出てきます.このあたり
これはゾーンプレートで回折しなかった光が光源の周りにボケを作ることで発生すると考えられています.ゾーンプレートとは同心円状のモノクロの濃淡によって,微視的な回折を利用することで光線の屈折を実現するレンズの効果を持ったものです.
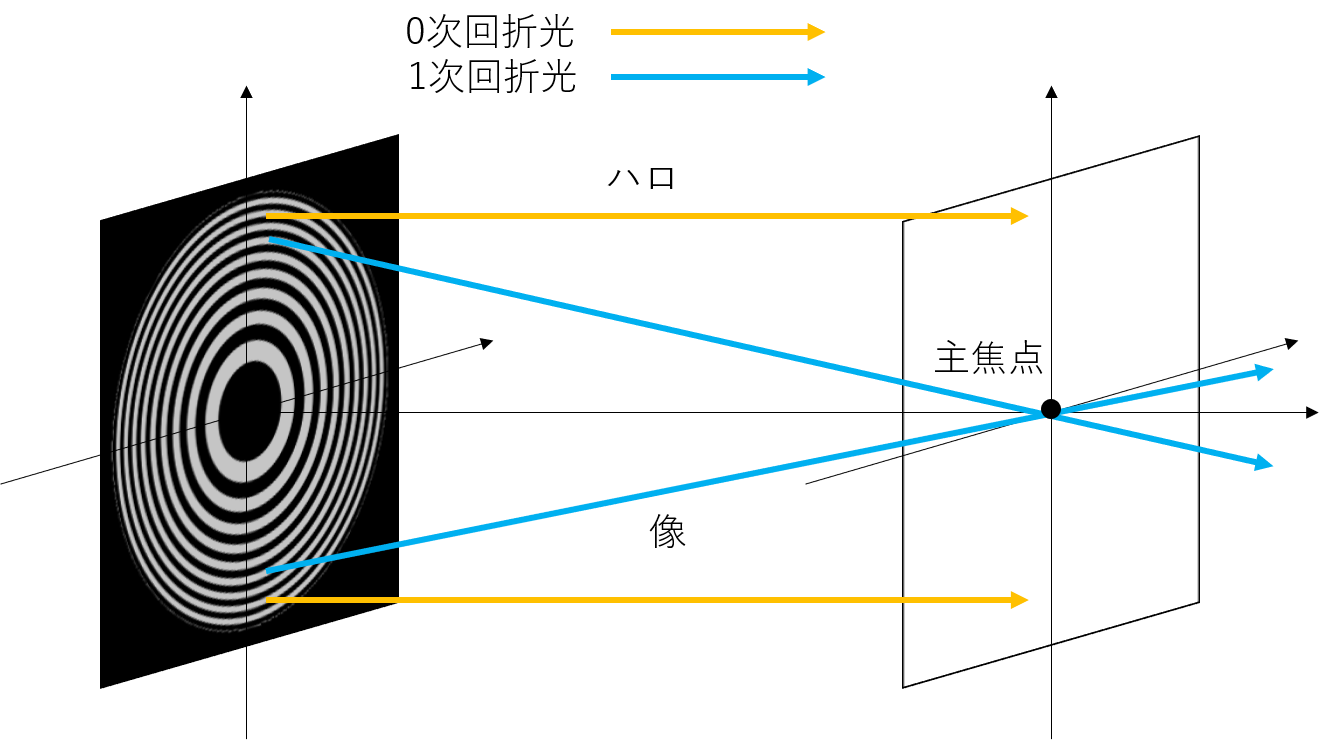
伝搬自体がフーリエ変換ですから,1次の回折光はレンズによる回折としてのフーリエ変換,0次の回折光は伝搬としてのフーリエ変換と考えればよいでしょう.なのでこれも単純にフーリエ変換してしまいます.

エフェクトをかける
上記で紹介したエフェクトは全て光源中心に発生するものですから,エフェクトを対象全体にかけるのではなく,対象画像の高輝度部分(白い部分)にかけるべきです.今回はエフェクトをかける対象として以下の画像を用意しました.

グレア系統は夜に見やすいですから雰囲気もいい感じです.
画像の前に説明しておきますが,以降の画像はFFTを使用した畳み込みを用いており,4倍拡張という操作をしていないので折り返し雑音というノイズが発生しています.そのため,若干色味が変化していたり,画像端からもエフェクトが発生しているように見えます.この部分は回避できますので安心してください(こちらを参考にしていただければと思います.記事にも書いていますし,コメントで回答している質問のあたりを見ていただければ.).
ならなぜしていないのかという話ですが,メモリを2~4倍消費するためFFTを行う際に使用しているgroupsharedな配列のサイズがやばいことになるからです.
では今回のエフェクトのかけ方を見ていきましょう.以下に大まかなプロセスを示します.
ミソは波長に基づいてスケーリングする部分です.これがあるだけで色収差を考慮することになるのでかなりマシに見えます.
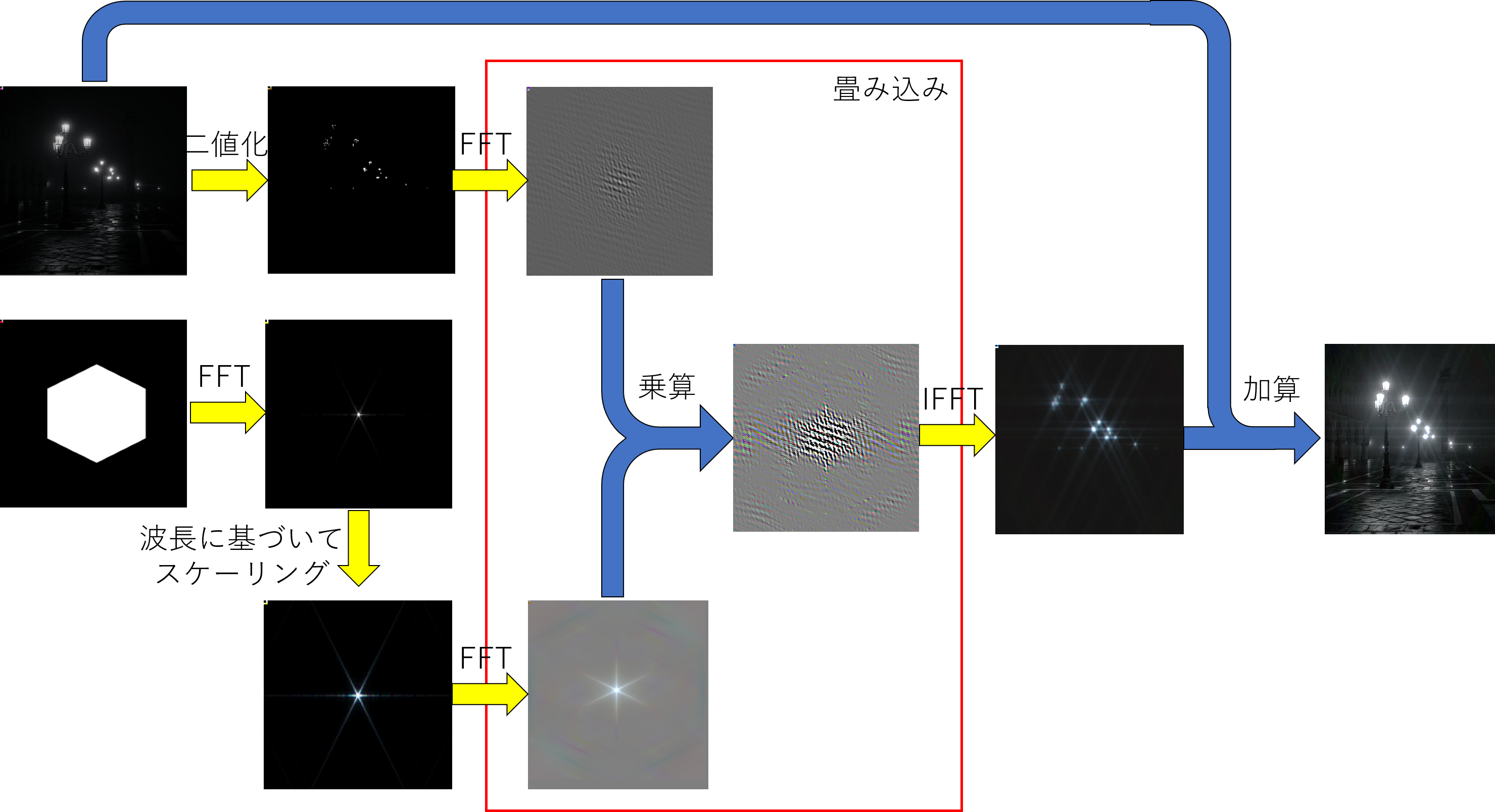
FFTをかけた後の画像は値がゆうに1を超えますし,負の数・浮動小数点数を含みますので,計算過程で使用するテクスチャとして浮動小数点画像を使用してください.ちなみに私はDXGIのフォーマットとしてDXGI_FORMAT_R16G16B16A16_FLOATを使用しています.
以降,エフェクトをかけた結果を載せます.順に8枚絞り・まつ毛・ゾーンプレートです.
ここまでのまとめ
コード
長すぎるので初めて折り畳みを使います.
Cpp
定数バッファになる構造体.
struct ComputeParameters
{
float lambdaR = 633e-9;
float lambdaG = 532e-9;;
float lambdaB = 466e-9;
float glareintensity = 0.8;
float threshold = 0.8;
};
この関数ですべてのエフェクトを扱います.
int ComputeFilterApp::ExecuteGlareCommand()
{
ComputeParameters cp;
cp.lambdaR = 633e-9;
cp.lambdaG = 532e-9;
cp.lambdaB = 466e-9;
cp.glareintensity = m_glareintensity;
cp.threshold = m_threshold;
WriteToUploadHeapMemory(m_mainComputeCB[0].Get(), sizeof(cp), &cp);
ExecuteCopyCommand(m_RfullsizeTex.at(0), m_RWfullsizeTex.at(0));//グレアがかかる画像
ExecuteBinaryThresholdCommand(m_RWfullsizeTex.at(0), m_RWfullsizeTex.at(1));
ExecuteClearCommand(m_RWfullsizeTex.at(2));
//グレア用画像
switch (m_glaremode)
{
case GlareMode_EyeRush:
ExecuteCopyCommand(m_RfullsizeTex.at(1), m_RWfullsizeTex.at(3));
break;
case GlareMode_Cross1:
ExecuteCopyCommand(m_RfullsizeTex.at(2), m_RWfullsizeTex.at(3));
break;
case GlareMode_Cross2:
ExecuteCopyCommand(m_RfullsizeTex.at(3), m_RWfullsizeTex.at(3));
break;
case GlareMode_Cross3:
ExecuteCopyCommand(m_RfullsizeTex.at(4), m_RWfullsizeTex.at(3));
break;
case GlareMode_Halo:
ExecuteCopyCommand(m_RfullsizeTex.at(5), m_RWfullsizeTex.at(3));
break;
default:
ExecuteCopyCommand(m_RfullsizeTex.at(1), m_RWfullsizeTex.at(3));
break;
}
ExecuteClearCommand(m_RWfullsizeTex.at(4));
ExecuteFFTCommand(m_RWfullsizeTex.at(3), m_RWfullsizeTex.at(4));//グレア生成
ExecuteCalcurateAmplitudeCommand(
m_RWfullsizeTex.at(3), m_RWfullsizeTex.at(4)
, m_RWfullsizeTex.at(5), m_RWfullsizeTex.at(6));
ExecuteCalcMaxMinCommand(m_RWfullsizeTex.at(5), m_RWmaxminTex.at(0), m_RWmaxminTex.at(1));
ExecuteDivideMaxAmpCommand(
m_RWmaxminTex.at(0), m_RWmaxminTex.at(1)
, m_RWfullsizeTex.at(5), m_RWfullsizeTex.at(6)
, m_RWfullsizeTex.at(3), m_RWfullsizeTex.at(4));
ExecuteRaiseRICommand(
m_RWfullsizeTex.at(3), m_RWfullsizeTex.at(4)
, m_RWfullsizeTex.at(5), m_RWfullsizeTex.at(6));//グレアの輝度を底上げ
ExecuteSpectrumScalingCommand(
m_RWfullsizeTex.at(5), m_RWfullsizeTex.at(6)
, m_RWfullsizeTex.at(3), m_RWfullsizeTex.at(4));//波長スケーリング
ExecuteCopyCommand(m_RWfullsizeTex.at(3), m_RWfullsizeTex.at(7));//表示用に退避
//return 3;//ここで返すとグレア単体
//二値化画像とグレア画像を畳み込む
ExecuteConvolutionCommand(
m_RWfullsizeTex.at(1), m_RWfullsizeTex.at(2)
, m_RWfullsizeTex.at(3), m_RWfullsizeTex.at(4)
, m_RWfullsizeTex.at(5), m_RWfullsizeTex.at(6));
ExecuteCalcurateAmplitudeCommand(
m_RWfullsizeTex.at(5), m_RWfullsizeTex.at(6)
, m_RWfullsizeTex.at(0), m_RWfullsizeTex.at(1));
ExecuteCalcMaxMinCommand(m_RWfullsizeTex.at(0), m_RWmaxminTex.at(0), m_RWmaxminTex.at(1));
ExecuteDivideMaxAmpCommand(
m_RWmaxminTex.at(0), m_RWmaxminTex.at(1)
, m_RWfullsizeTex.at(0), m_RWfullsizeTex.at(1)
, m_RWfullsizeTex.at(3), m_RWfullsizeTex.at(4));
ExecuteCopyCommand(m_RfullsizeTex.at(0), m_RWfullsizeTex.at(0));
ExecuteAddCommand(m_RWfullsizeTex.at(0), m_RWfullsizeTex.at(3), m_RWfullsizeTex.at(1));
return 1;
}
上記関数内で使用されている関数について示します.AutoTransitionTextureというクラスが使用されていますが,リソースバリアを勝手に張るテクスチャだと思ってください.(2020/12/05追記 逆FFTの関数を書き忘れていたので追加.)
void ComputeFilterApp::ExecuteCopyCommand(TextureData& In, AutoTransitionTexture& Out)
{
m_commandList->SetComputeRootConstantBufferView(0, m_mainComputeCB[0]->GetGPUVirtualAddress());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(1, In.handleRead);
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(3, Out.WriteState());
m_commandList->SetPipelineState(m_pipelines["copyCS"].Get());
m_commandList->Dispatch(1, m_texheight, 1);
}
void ComputeFilterApp::ExecuteBinaryThresholdCommand(AutoTransitionTexture& In, AutoTransitionTexture& Out)
{
m_commandList->SetComputeRootConstantBufferView(0, m_mainComputeCB[0]->GetGPUVirtualAddress());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(1, In.ReadState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(3, Out.WriteState());
m_commandList->SetPipelineState(m_pipelines["BTCS"].Get());
m_commandList->Dispatch(1, m_texheight, 1);
}
void ComputeFilterApp::ExecuteClearCommand(AutoTransitionTexture& Tex)
{
m_commandList->SetComputeRootConstantBufferView(0, m_mainComputeCB[0]->GetGPUVirtualAddress());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(3, Tex.WriteState());
m_commandList->SetPipelineState(m_pipelines["clearCS"].Get());
m_commandList->Dispatch(1, m_texheight, 1);
}
void ComputeFilterApp::ExecuteFFTCommand(AutoTransitionTexture& Real, AutoTransitionTexture& Image)
{
//縦方向
m_commandList->SetComputeRootConstantBufferView(0, m_mainComputeCB[0]->GetGPUVirtualAddress());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(1, Real.ReadState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(2, Image.ReadState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(3, m_RWfullsizeInnerTex.at(2).WriteState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(4, m_RWfullsizeInnerTex.at(3).WriteState());
m_commandList->SetPipelineState(m_pipelines["fftCS_ROW"].Get());
m_commandList->Dispatch(1, m_texheight, 1);
//横方向
m_commandList->SetComputeRootConstantBufferView(0, m_mainComputeCB[0]->GetGPUVirtualAddress());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(1, m_RWfullsizeInnerTex.at(2).ReadState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(2, m_RWfullsizeInnerTex.at(3).ReadState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(3, Real.WriteState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(4, Image.WriteState());
m_commandList->SetPipelineState(m_pipelines["fftCS_COL"].Get());
m_commandList->Dispatch(1, m_texwidth, 1);
}
void ComputeFilterApp::ExecuteIFFTCommand(AutoTransitionTexture& Real, AutoTransitionTexture& Image)
{
//縦方向
m_commandList->SetComputeRootConstantBufferView(0, m_mainComputeCB[0]->GetGPUVirtualAddress());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(1, Real.ReadState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(2, Image.ReadState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(3, m_RWfullsizeInnerTex.at(2).WriteState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(4, m_RWfullsizeInnerTex.at(3).WriteState());
m_commandList->SetPipelineState(m_pipelines["ifftCS_ROW"].Get());
m_commandList->Dispatch(1, m_texheight, 1);
//横方向
m_commandList->SetComputeRootConstantBufferView(0, m_mainComputeCB[0]->GetGPUVirtualAddress());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(1, m_RWfullsizeInnerTex.at(2).ReadState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(2, m_RWfullsizeInnerTex.at(3).ReadState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(3, Real.WriteState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(4, Image.WriteState());
m_commandList->SetPipelineState(m_pipelines["ifftCS_COL"].Get());
m_commandList->Dispatch(1, m_texwidth, 1);
}
void ComputeFilterApp::ExecuteCalcurateAmplitudeCommand(AutoTransitionTexture& InReal, AutoTransitionTexture& InImage, AutoTransitionTexture& OutReal, AutoTransitionTexture& OutImage)
{
m_commandList->SetComputeRootConstantBufferView(0, m_mainComputeCB[0]->GetGPUVirtualAddress());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(1, InReal.ReadState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(2, InImage.ReadState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(3, OutReal.WriteState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(4, OutImage.WriteState());
m_commandList->SetPipelineState(m_pipelines["ampCS"].Get());
m_commandList->Dispatch(1, m_texheight, 1);
}
void ComputeFilterApp::ExecuteCalcMaxMinCommand(AutoTransitionTexture& Tex, AutoTransitionTexture& OutOnePixReal_MAX, AutoTransitionTexture& OutOnePixImage_MIN)
{
//最大値最小値の計算
m_commandList->SetComputeRootConstantBufferView(0, m_mainComputeCB[0]->GetGPUVirtualAddress());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(1, Tex.ReadState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(3, m_RWlineInnerTex.at(0).WriteState());
m_commandList->SetPipelineState(m_pipelines["maxminfirstCS"].Get());
m_commandList->Dispatch(m_texwidth, 1, 1);
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(1, m_RWlineInnerTex.at(0).ReadState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(3, OutOnePixReal_MAX.WriteState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(4, OutOnePixImage_MIN.WriteState());
m_commandList->SetPipelineState(m_pipelines["maxminsecondCS"].Get());
m_commandList->Dispatch(1, 1, 1);
}
void ComputeFilterApp::ExecuteDivideMaxAmpCommand(AutoTransitionTexture& OutOnePixReal_MAX, AutoTransitionTexture& OutOnePixImage_MIN, AutoTransitionTexture& InReal, AutoTransitionTexture& InImage, AutoTransitionTexture& OutReal, AutoTransitionTexture& OutImage)
{
//最大振幅による除算
m_commandList->SetComputeRootConstantBufferView(0, m_mainComputeCB[0]->GetGPUVirtualAddress());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(1, OutOnePixReal_MAX.ReadState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(2, OutOnePixImage_MIN.ReadState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(3, InReal.ReadState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(4, InImage.ReadState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(5, OutReal.WriteState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(6, OutImage.WriteState());
m_commandList->SetPipelineState(m_pipelines["divByMaxAMPCS"].Get());
m_commandList->Dispatch(1, m_texheight, 1);
}
void ComputeFilterApp::ExecuteRaiseRICommand(AutoTransitionTexture& InReal, AutoTransitionTexture& InImage, AutoTransitionTexture& OutReal, AutoTransitionTexture& OutImage)
{
m_commandList->SetComputeRootConstantBufferView(0, m_mainComputeCB[0]->GetGPUVirtualAddress());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(1, InReal.ReadState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(2, InImage.ReadState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(3, OutReal.WriteState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(4, OutImage.WriteState());
m_commandList->SetPipelineState(m_pipelines["raiseRICS"].Get());
m_commandList->Dispatch(1, m_texheight, 1);
}
void ComputeFilterApp::ExecuteSpectrumScalingCommand(AutoTransitionTexture& InReal, AutoTransitionTexture& InImage, AutoTransitionTexture& OutReal, AutoTransitionTexture& OutImage)
{
m_commandList->SetComputeRootConstantBufferView(0, m_mainComputeCB[0]->GetGPUVirtualAddress());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(1, InReal.ReadState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(2, InImage.ReadState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(3, OutReal.WriteState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(4, OutImage.WriteState());
m_commandList->SetPipelineState(m_pipelines["spectrumScalingCS"].Get());
m_commandList->Dispatch(1, m_texheight, 1);
}
void ComputeFilterApp::ExecuteConvolutionCommand(AutoTransitionTexture& InReal0, AutoTransitionTexture& InImage0, AutoTransitionTexture& InReal1, AutoTransitionTexture& InImage1, AutoTransitionTexture& OutReal, AutoTransitionTexture& OutImage)
{
//一方のFFT
ExecuteFFTCommand(InReal0, InImage0);
//もう一方のFFT
ExecuteFFTCommand(InReal1, InImage1);
//乗算
ExecuteMultiplyCommand(InReal0, InImage0, InReal1, InImage1, OutReal, OutImage);
//逆FFT
ExecuteIFFTCommand(OutReal, OutImage);
}
void ComputeFilterApp::ExecuteMultiplyCommand(AutoTransitionTexture& InReal0, AutoTransitionTexture& InImage0, AutoTransitionTexture& InReal1, AutoTransitionTexture& InImage1, AutoTransitionTexture& OutReal, AutoTransitionTexture& OutImage)
{
m_commandList->SetComputeRootConstantBufferView(0, m_mainComputeCB[0]->GetGPUVirtualAddress());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(1, InReal0.ReadState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(2, InImage0.ReadState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(3, InReal1.ReadState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(4, InImage1.ReadState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(5, OutReal.WriteState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(6, OutImage.WriteState());
m_commandList->SetPipelineState(m_pipelines["mulCS"].Get());
m_commandList->Dispatch(1, m_texheight, 1);
}
void ComputeFilterApp::ExecuteAddCommand(AutoTransitionTexture& Tex1, AutoTransitionTexture& Tex2, AutoTransitionTexture& Out)
{
m_commandList->SetComputeRootConstantBufferView(0, m_mainComputeCB[0]->GetGPUVirtualAddress());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(1, Tex1.ReadState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(2, Tex2.ReadState());
m_commandList->SetComputeRootDescriptorTable(3, Out.WriteState());
m_commandList->SetPipelineState(m_pipelines["AddCS"].Get());
m_commandList->Dispatch(1, m_texheight, 1);
}
またパイプラインの中での名前とHLSLでの名前は次のように結び付けます.
void ComputeFilterApp::getNameAtShaderAndPipeline(vector<pair<wstring, string>>& name)
{
name.push_back(make_pair(L"mainMULTIPLY", "mulCS"));
name.push_back(make_pair(L"mainFFT", "fftCS_ROW"));
name.push_back(make_pair(L"mainFFT", "fftCS_COL"));
name.push_back(make_pair(L"mainFFT", "ifftCS_ROW"));
name.push_back(make_pair(L"mainFFT", "ifftCS_COL"));
name.push_back(make_pair(L"mainAMPLITUDE", "ampCS"));
name.push_back(make_pair(L"mainDivByMaxAMP", "divByMaxAMPCS"));
name.push_back(make_pair(L"mainAdd", "AddCS"));
name.push_back(make_pair(L"mainBinaryThreshold", "BTCS"));
name.push_back(make_pair(L"mainCopy", "copyCS"));
name.push_back(make_pair(L"mainClear", "clearCS"));
name.push_back(make_pair(L"mainSpectrumScaling", "spectrumScalingCS"));
name.push_back(make_pair(L"mainRaiseBottomRealImage", "raiseRICS"));
name.push_back(make_pair(L"mainMAXMINfirst", "maxminfirstCS"));
name.push_back(make_pair(L"mainMAXMINsecond", "maxminsecondCS"));
}
こんな感じでコンパイル時に対応付けしています.
...何か処理
vector<pair<wstring, string>> nameAtPipeline;
getNameAtShaderAndPipeline(nameAtPipeline);
std::vector<std::wstring> flags;
std::vector<Shader::DefineMacro> defines;
for (auto& p : nameAtPipeline)
{
//動的にヘッダ生成
if (p.second == "fftCS_ROW")
{
createHeaderHLSL(m_texwidth, m_texheight, true, false);
}
else if (p.second == "fftCS_COL")
{
createHeaderHLSL(m_texwidth, m_texheight, false, false);
}
else if (p.second == "ifftCS_ROW")
{
createHeaderHLSL(m_texwidth, m_texheight, true, true);
}
else
{
createHeaderHLSL(m_texwidth, m_texheight, false, true);
}
Shader shader;
shader.load(L"ComputeFilter.hlsl", Shader::Compute, p.first, flags, defines);//エントリポイント
D3D12_COMPUTE_PIPELINE_STATE_DESC computeDesc{};
computeDesc.CS = CD3DX12_SHADER_BYTECODE(shader.getCode().Get());
computeDesc.pRootSignature = m_csSignature.Get();
PipelineState pipeline;
hr = m_device->CreateComputePipelineState(&computeDesc, IID_PPV_ARGS(&pipeline));
ThrowIfFailed(hr, "CreateComputePipelineState failed.");
m_pipelines[p.second] = pipeline;
}
HLSL側で使用するWIDTHやHEIGHTの値を定めたヘッダhlsl(param.hlsl)の生成
int ComputeFilterApp::inv2pow(int n) {
int m = 0;
m = static_cast<int>(log(static_cast<double>(n)) / log(2.0));
return m;
}
void ComputeFilterApp::createHeaderHLSL(UINT width, UINT height, bool raw, bool inv)
{
ofstream file("param.hlsl");
if (!file) {
cerr << "Error: file not opened." << endl;
exit(0);
}
file << "#define" << " " << "WIDTH" << " " << width << "\n";
file << "#define" << " " << "HEIGHT" << " " << height << "\n";
file << "#define" << " " << "PI" << " " << 3.14159265 << "\n";
file << "#define" << " " << "RAD" << " " << "PI / 180.0" << "\n";
if (raw)
{
file << "#define" << " " << "ROW" << " " << "1" << "\n";
file << "#define" << " " << "LENGTH" << " " << "WIDTH" << "\n";
file << "#define" << " " << "BUTTERFLY_COUNT" << " " << inv2pow(width) << "\n";
}
else
{
file << "#define" << " " << "ROW" << " " << "0" << "\n";
file << "#define" << " " << "LENGTH" << " " << "HEIGHT" << "\n";
file << "#define" << " " << "BUTTERFLY_COUNT" << " " << inv2pow(height) << "\n";
}
if (inv)
{
file << "#define" << " " << "INVERSE" << " " << "1" << "\n";
}
else
{
file << "#define" << " " << "INVERSE" << " " << "0" << "\n";
}
file.close();
}
出力するとこんな感じです.
//param.hlsl
# define WIDTH 512
# define HEIGHT 512
# define PI 3.14159
# define RAD PI / 180.0
# define ROW 0
# define LENGTH HEIGHT
# define BUTTERFLY_COUNT 9
# define INVERSE 1
HLSL
複素数計算のための関数
float2 complex_conjugate(float2 cmp)
{
return float2(cmp.x, -cmp.y);
}
float complex_sqr(float2 cmp)
{
return cmp.x * cmp.x + cmp.y * cmp.y;
}
float complex_norm(float2 cmp)
{
return sqrt(complex_sqr(cmp));
}
float2 complex_add(float2 cmp1, float2 cmp2)
{
return float2(cmp1.x + cmp2.x, cmp1.y + cmp2.y);
}
float2 complex_sub(float2 cmp1, float2 cmp2)
{
return float2(cmp1.x - cmp2.x, cmp1.y - cmp2.y);
}
float2 complex_mul(float2 cmp1, float2 cmp2)
{
return float2(cmp1.x * cmp2.x - cmp1.y * cmp2.y, cmp1.y * cmp2.x + cmp1.x * cmp2.y);
}
float2 complex_div(float2 cmp1, float2 cmp2)
{
float2 cmp = complex_mul(cmp1, complex_conjugate(cmp2));
float sqr = complex_sqr(cmp2);
return float2(cmp.x / sqr, cmp.y / sqr);
}
float2 complex_polar(float amp, float phase)
{
return float2(amp * cos(phase), amp * sin(phase));
}
定数バッファなど
struct ComputeParameters
{
float lambdaR;
float lambdaG;
float lambdaB;
float glareintensity;
float threshold;
};
ConstantBuffer<ComputeParameters> computeConstants : register(b0);
Texture2D<float4> sourceImageR : register(t0);
Texture2D<float4> sourceImageI : register(t1);
RWTexture2D<float4> destinationImageR : register(u0);
RWTexture2D<float4> destinationImageI : register(u1);
RWTexture2D<float4> destinationImageR1 : register(u2);
RWTexture2D<float4> destinationImageI1 : register(u3);
Cpp側で呼ばれるもの
//copyCSに対応
[numthreads(WIDTH, 1, 1)]
void mainCopy(uint3 dispatchID : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
float2 index = dispatchID.xy;
destinationImageR[index] = sourceImageR[index];
}
//BTCSに対応
[numthreads(WIDTH, 1, 1)]
void mainBinaryThreshold(uint3 dispatchID : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
float2 index = dispatchID.xy;
float3 input = sourceImageR[index].rgb;
float3 col = float3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
float r = 0;
float g = 0;
float b = 0;
if ((input.r + input.g + input.b) / 3.0 > computeConstants.threshold)
{
col = float3(1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
}
destinationImageR[index] = float4(col, 1.0f);
}
//clearCSに対応
[numthreads(WIDTH, 1, 1)]
void mainClear(uint3 dispatchID : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
float2 index = dispatchID.xy;
destinationImageR[index] = float4(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
}
//fftCS_シリーズで使用される
void ComputeSrcID(uint passIndex, uint x, out uint2 indices)
{
uint regionWidth = 2 << passIndex;
indices.x = (x & ~(regionWidth - 1)) + (x & (regionWidth / 2 - 1));
indices.y = indices.x + regionWidth / 2;
if (passIndex == 0)
{
indices = reversebits(indices) >> (32 - BUTTERFLY_COUNT) & (LENGTH - 1);
}
}
void ComputeTwiddleFactor(uint passIndex, uint x, out float2 weights)
{
uint regionWidth = 2 << passIndex;
sincos(2.0 * PI * float(x & (regionWidth - 1)) / float(regionWidth), weights.y, weights.x);
weights.y *= -1;
}
# define REAL 0
# define IMAGE 1
# ifdef DOUBLE//メモリに余裕があるとき
groupshared float3 ButterflyArray[2][2][LENGTH];
# define SharedArray(tmpID, x, realImage) (ButterflyArray[(tmpID)][(realImage)][(x)])
# else
groupshared float3 ButterflyArray[2][LENGTH];
# define SharedArray(tmpID, x, realImage) (ButterflyArray[(realImage)][(x)])
# endif
//fftCS_シリーズで使用される
void ButterflyWeightPass(uint passIndex, uint x, uint tmp, out float3 resultR, out float3 resultI)
{
uint2 Indices;
float2 Weights;
ComputeSrcID(passIndex, x, Indices);
float3 inputR1 = SharedArray(tmp, Indices.x, REAL);
float3 inputI1 = SharedArray(tmp, Indices.x, IMAGE);
float3 inputR2 = SharedArray(tmp, Indices.y, REAL);
float3 inputI2 = SharedArray(tmp, Indices.y, IMAGE);
ComputeTwiddleFactor(passIndex, x, Weights);
#ifndef DOUBLE
GroupMemoryBarrierWithGroupSync();//ダブルバッファでない場合は格納の完了を保証する必要がる
#endif
# if INVERSE
resultR = (inputR1 + Weights.x * inputR2 + Weights.y * inputI2) * 0.5;
resultI = (inputI1 - Weights.y * inputR2 + Weights.x * inputI2) * 0.5;
# else
resultR = inputR1 + Weights.x * inputR2 - Weights.y * inputI2;
resultI = inputI1 + Weights.y * inputR2 + Weights.x * inputI2;
# endif
}
void initializeFFT_SharedArray(uint bufferID, inout uint2 texPos)
{
texPos = (texPos + LENGTH / 2) % LENGTH;
SharedArray(0, bufferID, REAL) = sourceImageR[texPos].xyz;
# if ROW && !INVERSE
SharedArray(0, bufferID, IMAGE) = (0.0).xxx;
# else
SharedArray(0, bufferID, IMAGE) = sourceImageI[texPos].xyz;
# endif
}
void ButterflyPass(in uint bufferID, out float3 real, out float3 image)
{
for (int butterFlyID = 0; butterFlyID < BUTTERFLY_COUNT - 1; butterFlyID++)
{
GroupMemoryBarrierWithGroupSync();
ButterflyWeightPass(butterFlyID, bufferID, butterFlyID % 2,
SharedArray((butterFlyID + 1) % 2, bufferID, REAL),
SharedArray((butterFlyID + 1) % 2, bufferID, IMAGE));
}
GroupMemoryBarrierWithGroupSync();
ButterflyWeightPass(BUTTERFLY_COUNT - 1, bufferID, (BUTTERFLY_COUNT - 1) % 2,
real, image);
}
//fftCS_シリーズに対応
[numthreads(LENGTH, 1, 1)]
void mainFFT(uint3 dispatchID : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
const uint bufferID = dispatchID.x;
# if ROW
uint2 texPos = dispatchID.xy;
# else
uint2 texPos = dispatchID.yx;
# endif
initializeFFT_SharedArray(bufferID, texPos);
float3 r_result = 0, i_result = 0;
ButterflyPass(bufferID, r_result, i_result);
destinationImageR[texPos].rgb = r_result;
destinationImageI[texPos].rgb = i_result;
}
//ampCSに対応
[numthreads(WIDTH, 1, 1)]
void mainAMPLITUDE(uint3 dispatchID : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
float2 index = dispatchID.xy;
float3 inputR = sourceImageR[index].rgb;
float3 inputI = sourceImageI[index].rgb;
float r = inputR.r * inputR.r + inputI.r * inputI.r;
float g = inputR.g * inputR.g + inputI.g * inputI.g;
float b = inputR.b * inputR.b + inputI.b * inputI.b;
float3 col = float3(sqrt(r), sqrt(g), sqrt(b));
destinationImageR[index] = float4(col, 1.0f);
destinationImageI[index] = float4(col, 1.0f);
}
//maxminfirstCSに対応
[numthreads(1, 1, 1)]
void mainMAXMINfirst(uint3 dispatchID : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
uint2 index = dispatchID.xy;
float3 color_max = sourceImageR[float2(0, 0)].xyz;
float3 color_min = color_max;
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < HEIGHT; i++)
{
uint2 indexx = uint2(index.x, i);
float3 color = sourceImageR[indexx].xyz;
color_max = max(color_max, color);
color_min = min(color_min, color);
}
destinationImageR[float2(index.x, 0)] = float4(color_max, 1.0f);
destinationImageR[float2(index.x, 1)] = float4(color_min, 1.0f);
}
//maxminsecondCSに対応
[numthreads(1, 1, 1)]
void mainMAXMINsecond(uint3 dispatchID : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
uint2 index = dispatchID.xy;
float3 color_max = sourceImageR[float2(0, 0)].xyz;
float3 color_min = color_max;
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < HEIGHT; i++)
{
uint2 index1 = uint2(i, 0);
uint2 index2 = uint2(i, 1);
float3 colormax = sourceImageR[index1].xyz;
float3 colormin = sourceImageR[index2].xyz;
color_max = max(color_max, colormax);
color_min = min(color_min, colormin);
}
destinationImageR[float2(0, 0)] = float4(color_max, 1.0f);
destinationImageI[float2(0, 0)] = float4(color_min, 1.0f);
}
//divByMaxAMPCSに対応
[numthreads(WIDTH, 1, 1)]
void mainDivByMaxAMP(uint3 dispatchID : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
float2 index = dispatchID.xy;
float2 zero = float2(0.0, 0.0);
//sourceImageRに最大値格納したテクスチャをセットしておく
float3 color_max = sourceImageR[zero].rgb;
//destinatinImageR/Iに正規化したいテクスチャをセットしておく
float3 colorR = destinationImageR[index].rgb;
float3 colorI = destinationImageI[index].rgb;
colorR = colorR / color_max;
colorI = colorI / color_max;
float col_max_per = color_max.r;
col_max_per = max(col_max_per, color_max.g);
col_max_per = max(col_max_per, color_max.b);
float3 ratio = color_max / col_max_per;
colorR = colorR * ratio;
colorI = colorI * ratio;
destinationImageR1[index] = float4(colorR, 1.0f);
destinationImageI1[index] = float4(colorI, 1.0f);
}
//raiseRICSに対応
[numthreads(WIDTH, 1, 1)]
void mainRaiseBottomRealImage(uint3 dispatchID : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
float2 index = dispatchID.xy;
float3 inputR = sourceImageR[index].rgb;
float3 inputI = sourceImageI[index].rgb;
float3 amplitude = float3(sqrt(inputR.r * inputR.r + inputI.r * inputI.r)
, sqrt(inputR.g * inputR.g + inputI.g * inputI.g)
, sqrt(inputR.b * inputR.b + inputI.b * inputI.b));
if ((amplitude.r + amplitude.g + amplitude.b) / 3.0f < 0.9)
{
/*inputR = inputR * 10.0f;
inputI = inputI * 10.0f;*/
inputR = inputR * computeConstants.glareintensity;
inputI = inputI * computeConstants.glareintensity;
}
if ((inputR.r + inputR.g + inputR.b) / 3.0f >= 1.0)
{
inputR = float3(1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
}
if ((inputI.r + inputI.g + inputI.b) / 3.0f >= 1.0)
{
inputI = float3(1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
}
destinationImageR[index] = float4(inputR, 1.0);
destinationImageI[index] = float4(inputI, 1.0);
}
//spectrumScalingCSに対応
[numthreads(WIDTH, 1, 1)]
void mainSpectrumScaling(uint3 dispatchID : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
float2 indexR = dispatchID.xy;
float ratioRG = computeConstants.lambdaG / computeConstants.lambdaR;
float ratioRB = computeConstants.lambdaB / computeConstants.lambdaR;
float2 uvR = indexR - float2(0.5 * WIDTH, 0.5 * HEIGHT);
float2 uvG = uvR * ratioRG;
float2 uvB = uvR * ratioRB;
float2 indexG = uvG + float2(0.5 * WIDTH, 0.5 * HEIGHT);
float2 indexB = uvB + float2(0.5 * WIDTH, 0.5 * HEIGHT);
float r = sourceImageR[indexR].r;
float g = sourceImageR[indexG].g;
float b = sourceImageR[indexB].b;
destinationImageR[indexR] = float4(r, g, b, 1.0);
r = sourceImageI[indexR].r;
g = sourceImageI[indexG].g;
b = sourceImageI[indexB].b;
destinationImageI[indexR] = float4(r, g, b, 1.0);
}
//mulCSに対応
[numthreads(WIDTH, 1, 1)]
void mainMULTIPLY(uint3 dispatchID : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
float2 index = dispatchID.xy;
float3 color_real1 = sourceImageR[index].rgb;//元1 実部
float3 color_image1 = sourceImageI[index].rgb;//元1 虚部
float3 color_real2 = destinationImageR[index].rgb;//元2 実部
float3 color_image2 = destinationImageI[index].rgb;//元2 虚部
//各色からの複素数生成
float2 compR1 = float2(color_real1.r, color_image1.r);
float2 compG1 = float2(color_real1.g, color_image1.g);
float2 compB1 = float2(color_real1.b, color_image1.b);
float2 compR2 = float2(color_real2.r, color_image2.r);
float2 compG2 = float2(color_real2.g, color_image2.g);
float2 compB2 = float2(color_real2.b, color_image2.b);
//各色毎に乗算
float2 mulcompR = complex_mul(compR1, compR2);
float2 mulcompG = complex_mul(compG1, compG2);
float2 mulcompB = complex_mul(compB1, compB2);
//代入用の複素数作成
float3 colorREAL = float3(mulcompR.x, mulcompG.x, mulcompB.x);
float3 colorIMAGE = float3(mulcompR.y, mulcompG.y, mulcompB.y);
destinationImageR1[index] = float4(colorREAL, 1.0f);
destinationImageI1[index] = float4(colorIMAGE, 1.0f);
}
//AddCSに対応
[numthreads(WIDTH, 1, 1)]
void mainAdd(uint3 dispatchID : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
float2 index = dispatchID.xy;
float3 input1 = sourceImageR[index].rgb;
float3 input2 = sourceImageI[index].rgb;
float3 col = input1 + input2;
destinationImageR[index] = float4(col, 1.0f);
}
おわりに
お疲れさまでした.フーリエ変換すごい使えますよね.学部生の時に始まり,大学院を修了し就職した今も,フーリエ変換のことを想わなかったときはありません.ウェーブレット変換に浮気する可能性はありますが,これからも仲良くしていきたいものです.
もし質問等ありましたらコメントにお願いします.ではまたどこかで.
追記)こちらもご覧ください.以下のようなレンズフレアについての記事です.





