はじめに
GMOコネクトの永田です。
今回は(Python版ではなく)Node.jsのTensorflow.jsを使ってみました。
前回と同じくGANを試そうとしたのですが、JavaScript版では調べても情報がなく、LLMでも動作するアウトプットがでてこなかったので、試行錯誤で苦労しました。
まとめ
-
optimizer.minimize()を使おう-
model.trainableWeights.map(v => v.val)で、generator、discriminatorの勾配を明に指定しよう
-
- ドキュメントがなければ、ソースコードやdumpを見ればいいじゃない
tf.variableGrads() でつまずく
最初、Python版GANと同じような実装にしようと考えていました。
Python版GANの抜粋
def train_step(images, generator, discriminator, generator_optimizer, discriminator_optimizer, noise_dim, batch_size):
"""Executes one training step."""
noise = tf.random.normal([batch_size, noise_dim])
with tf.GradientTape() as gen_tape, tf.GradientTape() as disc_tape:
generated_images = generator(noise, training=True)
real_output = discriminator(images, training=True)
fake_output = discriminator(generated_images, training=True)
gen_loss = generator_loss(fake_output)
disc_loss = discriminator_loss(real_output, fake_output)
gradients_of_generator = gen_tape.gradient(gen_loss, generator.trainable_variables)
gradients_of_discriminator = disc_tape.gradient(disc_loss, discriminator.trainable_variables)
generator_optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradients_of_generator, generator.trainable_variables))
discriminator_optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradients_of_discriminator, discriminator.trainable_variables))
return gen_loss, disc_loss
しかしいくら学習を進めても勾配が思ったように更新されず、色々と検索した結果、みんな大好きstack overflowには辿り着きました。
It looks like because of the python syntax that with tf.GradientTape() is using, it's not quite possible to have the same syntax.
I'm working on doing the GAN example in JS myself, will update this post with a github link if I manage it.
なんか課題がありそうなことは分かったのですが、解決までには至っていないようでした😭
公開されているTensorflow.js版のGANで動くものを探す
こんな時は動くものをベースにするのが手っ取り早いので、探します。
結果、次の二つが見つかりました。(ソース公開してくれていてありがたいです😊)
Tensorflow.js GANサンプル1
どうやら学習のコア部分はこの辺りのようです。
tfjs-ganのモデル定義部分(generator側のみ抜粋)
tfjs-ganの学習部分(batch毎のロジックのgenerator側のみ抜粋)
上記より分かることは、以下の通りです。
- 学習対象の値を
tf.variable型の引数で明に定義している - optimizer.minimizeで、更新したい値を明に指定している(この例だとgeneratorの値のみ明に指定)
Tensorflow.js GANサンプル2
同じくソースをみます。
どうやら学習のコア部分はこの辺りのようです。
ganlabのモデル定義部分(generator側のみ抜粋)
// Generator.
const gfc0W = tf.variable(tf.randomNormal([this.noiseSize, this.numGeneratorNeurons], 0, 1.0 / Math.sqrt(2)));
const gfc0B = tf.variable(tf.zeros([this.numGeneratorNeurons]));
this.gVariables.push(gfc0W);
this.gVariables.push(gfc0B);
for (let i = 0; i < this.numGeneratorLayers; ++i) {
const gfcW = tf.variable(tf.randomNormal([this.numGeneratorNeurons, this.numGeneratorNeurons], 0, 1.0 / Math.sqrt(this.numGeneratorNeurons)));
const gfcB = tf.variable(tf.zeros([this.numGeneratorNeurons]));
this.gVariables.push(gfcW);
this.gVariables.push(gfcB);
}
const gfcLastW = tf.variable(tf.randomNormal([this.numGeneratorNeurons, 2], 0, 1.0 / Math.sqrt(this.numGeneratorNeurons)));
const gfcLastB = tf.variable(tf.zeros([2]));
this.gVariables.push(gfcLastW);
this.gVariables.push(gfcLastB);
// (略)
generator(noiseTensor) {
const gfc0W = this.gVariables[0];
const gfc0B = this.gVariables[1];
let network = noiseTensor.matMul(gfc0W)
.add(gfc0B)
.relu();
for (let i = 0; i < this.numGeneratorLayers; ++i) {
const gfcW = this.gVariables[2 + i * 2];
const gfcB = this.gVariables[3 + i * 2];
network = network.matMul(gfcW)
.add(gfcB)
.relu();
}
const gfcLastW = this.gVariables[2 + this.numGeneratorLayers * 2];
const gfcLastB = this.gVariables[3 + this.numGeneratorLayers * 2];
const generatedTensor = network.matMul(gfcLastW)
.add(gfcLastB)
.tanh();
return generatedTensor;
}
ganlabの学習部分(batch毎のロジックのgenerator側のみ抜粋)
const gCost = this.model.gOptimizer.minimize(() => {
const noiseBatch = this.noiseProvider.getNextCopy();
const pred = this.model.discriminator(this.model.generator(noiseBatch));
return this.model.gLoss(pred);
}, true, this.model.gVariables);
先ほどのtfjs-ganと同じような感じですね。
- 学習対象の値を
tf.variable型の引数で明に定義している - optimizer.minimizeで、更新したい値を明に指定している(この例だとgeneratorの値のみ明に指定)
Sequential Modelからtf.variableの取得
上記2個のサンプルからは、
- 学習対象の値を
tf.variable型の引数で明に定義している - optimizer.minimizeで、更新したい値を明に指定している
という方針が分かりました。
次に、Sequential Modelからtf.variableを取り出す方法を調べます。
・・・そもそもドキュメントが見つからないですね😇
とりあえず、tfjs-ganのgenerator相当をSequentialで書いてみます。
// Sequential model version
const generator = tf.sequential(
{
layers: [
tf.layers.dense({ units: 140, inputShape: [SEED_SIZE] }),
tf.layers.leakyReLU(),
tf.layers.dense({ units: 80 }),
tf.layers.leakyReLU(),
tf.layers.dense({ units: INPUT_SIZE, activation: 'tanh' })
]
});
__________________________________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Input Shape Output shape Param #
==========================================================================================
dense_Dense1 (Dense) [[null,40]] [null,140] 5740
__________________________________________________________________________________________
leaky_re_lu_LeakyReLU1 (Lea [[null,140]] [null,140] 0
__________________________________________________________________________________________
dense_Dense2 (Dense) [[null,140]] [null,80] 11280
__________________________________________________________________________________________
leaky_re_lu_LeakyReLU2 (Lea [[null,80]] [null,80] 0
__________________________________________________________________________________________
dense_Dense3 (Dense) [[null,80]] [null,784] 63504
==========================================================================================
Total params: 80524
Trainable params: 80524
Non-trainable params: 0
Trainable paramsがありこれを取り出そうと、console.log で雑にダンプしたりPython版のAPI名を参考に試したところ、以下が利用できそうでした。
generator.trainableWeights
[
LayerVariable {
dtype: 'float32',
shape: [ 40, 140 ],
id: 1,
originalName: 'dense_Dense1/kernel',
name: 'dense_Dense1/kernel',
trainable_: true,
constraint: null,
val: Variable {
kept: false,
isDisposedInternal: false,
shape: [Array],
dtype: 'float32',
size: 5600,
strides: [Array],
dataId: [Object],
id: 25,
rankType: '2',
trainable: true,
name: 'dense_Dense1/kernel'
}
},
LayerVariable {
dtype: 'float32',
shape: [ 140 ],
id: 2,
originalName: 'dense_Dense1/bias',
name: 'dense_Dense1/bias',
trainable_: true,
constraint: null,
val: Variable {
kept: false,
isDisposedInternal: false,
shape: [Array],
dtype: 'float32',
size: 140,
strides: [],
dataId: [Object],
id: 27,
rankType: '1',
trainable: true,
name: 'dense_Dense1/bias'
}
},
...
val だけ取れれば期待したものになりそうです。
// tfjs-ganのminimizeの引数で指定したvariable
console.log([G1w, G1b, G2w, G2b, G3w, G3b])
// Sequential版の同等のvariable
console.log(generator.trainableWeights.map(v => v.val))
上記で取得できる配列が、tfjs-ganと同等であることが確認できましたので、tfjs-ganを早速Sequential版に改造していきます。
Sequential版tfjs-gan
ということで、元のソースコードをなるべく残しつつ、出来上がったのがこちらです。(主要な差分のみ抜粋)
// Network arch for generator with sequential
const generator = tf.sequential({
layers: [
tf.layers.dense({ units: 140, inputShape: [SEED_SIZE] }),
tf.layers.leakyReLU(),
tf.layers.dense({ units: 80 }),
tf.layers.leakyReLU(),
tf.layers.dense({ units: INPUT_SIZE, activation: 'tanh' })
]
});
// Network arch for discriminator with sequential
const discriminator = tf.sequential({
layers: [
tf.layers.dense({ units: 200, inputShape: [INPUT_SIZE] }),
tf.layers.leakyReLU(),
tf.layers.dense({ units: 90 }),
tf.layers.leakyReLU(),
tf.layers.dense({ units: 1, activation: 'sigmoid' })
]
});
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// GAN functions
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
function gen(xs) {
return generator.predict(xs);
}
function disReal(xs) {
return discriminator.predict(xs);
}
function disFake(xs) {
return disReal(gen(xs));
}
// Single batch training
async function trainBatch(realBatch, fakeInputSeed) {
// Training discriminator
const dcost = dOptimizer.minimize(() => {
const outputReal = disReal(realBatch);
const outputFake = disFake(fakeInputSeed);
let lossReal = tf.metrics.binaryCrossentropy(ONES, outputReal);
let lossFake = tf.metrics.binaryCrossentropy(ZEROS, outputFake);
return lossReal.add(lossFake).mean();
}, true, discriminator.trainableWeights.map(v => v.val));
// Training generator
const gcost = gOptimizer.minimize(() => {
const outputFake = disFake(fakeInputSeed);
const lossFake = tf.metrics.binaryCrossentropy(ONES, outputFake);
return lossFake.mean();
}, true, generator.trainableWeights.map(v => v.val));
return [dcost, gcost];
}
Sequential版での学習結果
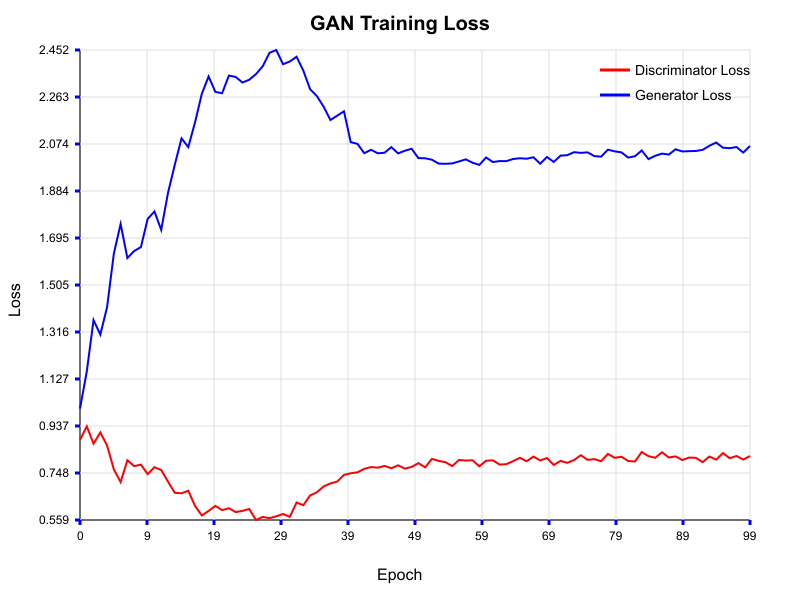
では、Sequential版でもGANの学習を試してみます。いつも通りMNISTデータのうち40,000件を利用します。
Epoch=50ぐらいで収束しており、期待通り学習が出来ていそうですね!
(再掲)まとめ
-
optimizer.minimize()を使おう-
model.trainableWeights.map(v => v.val)で、generator、discriminatorの勾配を明に指定しよう
-
- ドキュメントがなければ、ソースコードやdumpを見ればいいじゃない
弊社では、機械学習・AI・LLMなどを使ったサービスの開発や技術支援をはじめ、幅広い支援を行っておりますので、何かありましたらお気軽にお問合せください。