0. はじめに
この記事は Houdini Advent Calendar 2024 の20日目の記事です。
0-1. 動作環境
OS: RedHat Enterprise Linux 9.4
Houdini: 20.5.410 Py3.11 (最新の Production Build) Education Edition
0-2. 免責
この記事をもとに被った不利益について私は一切責任を負いません.
1. GasAdd DOPについて
GasAdd DOP は HDK の SIM 系のサンプルの一つとして $HFS/toolkit/sample/SIM/ 以下にあるのでまずはビルドして使ってみたいと思います。
先のディレクトリに行き、 hcustom ./SIM_GasAdd.C と打ってビルドします。
成功すると DOP コンテキストに GasAdd DOP が追加されています。

このノードの機能はシンプルで Source Field に指定した FieldをDest Field に指定した Field に加算します。
Volume Source DOP の Add みたいなイメージです。
1-1. GasAdd.h
このヘッダファイルにはノードを作成するために必要な関数などの宣言が含まれています。細かい実装はGasAdd.Cの方に書かれています。
以下はサンプルプログラムのヘッダの全文です。
/*
* Copyright (c) 2024
* Side Effects Software Inc. All rights reserved.
*
* Redistribution and use of Houdini Development Kit samples in source and
* binary forms, with or without modification, are permitted provided that the
* following conditions are met:
* 1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice,
* this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
* 2. The name of Side Effects Software may not be used to endorse or
* promote products derived from this software without specific prior
* written permission.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY SIDE EFFECTS SOFTWARE `AS IS' AND ANY EXPRESS
* OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES
* OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN
* NO EVENT SHALL SIDE EFFECTS SOFTWARE BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT,
* INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT
* LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA,
* OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF
* LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING
* NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE,
* EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
*
*----------------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
#ifndef __SIM_GasAdd_h__
#define __SIM_GasAdd_h__
#include <GAS/GAS_SubSolver.h>
#include <GAS/GAS_Utils.h>
namespace HDK_Sample {
/// A simple field manipulation class that will add fields
/// together.
class SIM_GasAdd : public GAS_SubSolver
{
public:
/// These macros are used to create the accessors
/// getFieldDstName and getFieldSrcName functions we'll use
/// to access our data options.
GET_DATA_FUNC_S(GAS_NAME_FIELDDEST, FieldDstName);
GET_DATA_FUNC_S(GAS_NAME_FIELDSOURCE, FieldSrcName);
protected:
explicit SIM_GasAdd(const SIM_DataFactory *factory);
~SIM_GasAdd() override;
/// Used to determine if the field is complicated enough to justify
/// the overhead of multithreading.
bool shouldMultiThread(const SIM_RawField *field) const
{ return field->field()->numTiles() > 1; }
/// The overloaded callback that GAS_SubSolver will invoke to
/// perform our actual computation. We are giving a single object
/// at a time to work on.
bool solveGasSubclass(SIM_Engine &engine,
SIM_Object *obj,
SIM_Time time,
SIM_Time timestep) override;
/// Add two raw fields together. Use UT_ThreadedAlgorithm's macros
/// to define the addFields method that will invoke addFieldPartial()
/// on each worker thread.
THREADED_METHOD2(SIM_GasAdd, shouldMultiThread(dst),
addFields,
SIM_RawField *, dst,
const SIM_RawField *, src);
void addFieldsPartial(SIM_RawField *dst, const SIM_RawField *src, const UT_JobInfo &info);
private:
/// We define this to be a DOP_Auto node which means we do not
/// need to implement a DOP_Node derivative for this data. Instead,
/// this description is used to define the interface.
static const SIM_DopDescription *getDopDescription();
/// These macros are necessary to bind our node to the factory and
/// ensure useful constants like BaseClass are defined.
DECLARE_STANDARD_GETCASTTOTYPE();
DECLARE_DATAFACTORY(SIM_GasAdd,
GAS_SubSolver,
"Gas Add",
getDopDescription());
};
} // End HDK_Sample namespace
#endif
コードの解説です。
class SIM_GasAdd : public GAS_SubSolver
独自のマイクロソルバのクラスは GAS_SubSolver クラスを継承して作られます。
public:
// getFieldDstName 関数と getFieldSrcName 関数を作成
// 下の定義が内部的にあるので置き換えられる
// #define GAS_NAME_FIELDDEST "fielddst"
// #define GAS_NAME_FIELDSOURCE "fieldsrc"
GET_DATA_FUNC_S(GAS_NAME_FIELDDEST, FieldDstName);
GET_DATA_FUNC_S(GAS_NAME_FIELDSOURCE, FieldSrcName);
これらは Option レコードにアクセスするための getter 関数を定義するためのマクロです。
マクロの具体的な実装は以下です。
#define GET_DATA_FUNC_S(DataName, FuncName) \
const UT_StringHolder &get##FuncName() const { \
static constexpr UT_StringLit dname(DataName); \
return getOptions().getOptionS(dname.asRef()); \
} \
void get##FuncName(UT_String &value) const { \
value = get##FuncName(); \
}
そして GET_DATA_FUNC_S(fieldsrc, FieldSrcName); の対して展開したものが以下です。
const UT_StringHolder& getFieldSrcName() const {
// UT_StringLit 型の dname を宣言し "fieldsrc" を格納する
static constexpr UT_StringLit dname("fieldsrc");
// dname.asRef() で UT_StringLit のメソッドをコールしパラメータ名を UT_StringHolder の参照で受け取る
// マイクロソルバのパラメータの内容は solve サブデータのオプションレコードにパラメータをフィールド名として入ってる
// SIM_Options::getOptionS() メソッドをつかって fieldsrc フィールド(つまり fieldsrc パラメータ)に
// 設定されている source field の名前を UT_StringHolder で受け取る
// SIM_OptionsUser::getOptions() ->SIM_Options&
// SIM_Options::getOprionS(const UT_StringHolder& name) -> const UT_StringHolder&
return getOptions().getOptionS(dname.asRef());
}
//これで getFieldSrcName() メソッドをコールすると fieldsrc パラメータに設定されている field 名を取得できる
void getFieldSrcName(UT_String& value) const {
value = getFieldSrcName();
}
ここでやっていることはノードの fieldsrc パラメータに設定されている field 名を取得する getFieldSrcName() というメソッドを定義することです。
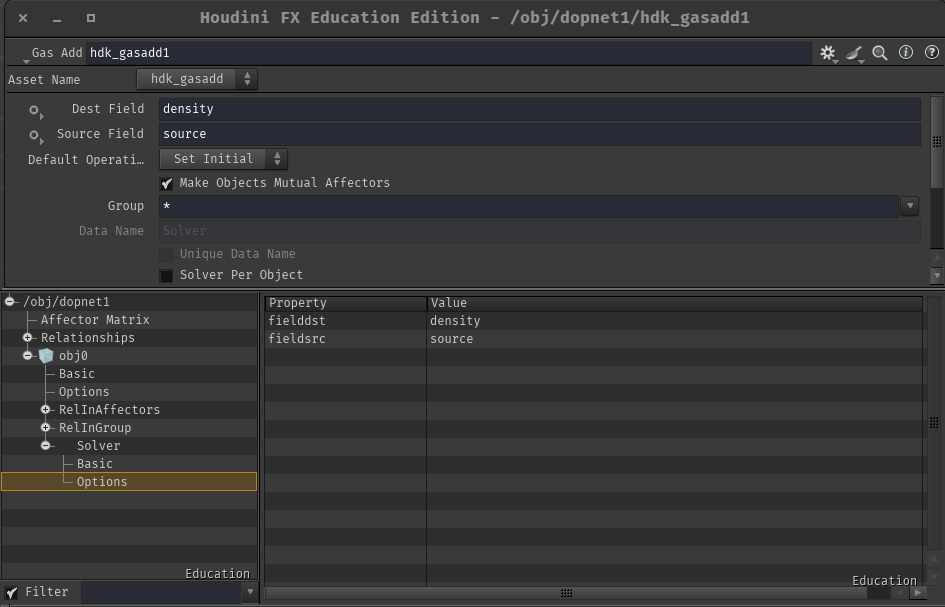
画像と通り、 fieldsrc , fielddst パラメータの情報は solver サブデータの Option レコードの各パラメータ名のフィールドに格納されているので、 SIM_Options::getOptionS() メソッドを用いて処理で実際に使用するfieldの名前を取得できます。
なので、取得して UT_StringHolder クラスの参照で返す getFieldSrcName() メソッドを定義しています。
protected:
// コンストラクタとデストラクタの宣言
explicit SIM_GasAdd(const SIM_DataFactory* factory);
~SIM_GasAdd() override;
// フィールドがマルチスレッドを使用するべきかどうかを判断する
bool shouldMultiThread(const SIM_RawField* field) const {
/*
SIM_RawField::field() -> const UT_VoxelArray<fpreal32>*
DOPs の field を表現する SIM_RawField クラスの field() メソッドは、
より抽象的な UT_VoxelArray クラスのオブジェクトのポインタを返す
UT_VoxelArray<T>::numTiles -> const int
UT_VoxelArray クラスの numTiles() メソッドはタイル数を int で返す
タイルの数が2以上かどうか
16*16*16 ボクセルの範囲で1タイル
UT_VoxelArray は thread safty 上、タイルごとにスレッドを割り当てるので
処理するタイル数が1ならマルチスレッドにする必要がない
*/
return field->field()->numTiles() > 1;
}
// GAS_SubSolverが実際の計算を行うために呼び出すコールバックのoverrideの宣言
bool solveGasSubclass(SIM_Engine& engine, SIM_Object* obj, SIM_Time time, SIM_Time timestep) override;
// 各スレッドがマルチスレッドの有無に応じて然るべき JobInfo オブジェクトを持って addFieldPartial メソッドをコールすることができる効率的な
// addField メソッドを定義する
THREADED_METHOD2(SIM_GasAdd, shouldMultiThread(dst), addFields, SIM_RawField*, dst, const SIM_RawField*, src);
// addFieldで呼び出されるaddFieldPartialを宣言する
void addFieldsPartial(SIM_RawField* dst, const SIM_RawField* src, const UT_JobInfo& info);
一番下のマクロは加算の処理を並列で行う addFieldPartial() メソッドをマルチスレッディングのジョブ情報を持ってコールする addField() メソッドを定義しています。
具体的な実装は以下です。
#define THREADED_METHOD2(CLASSNAME, DOMULTI, METHOD, PARMTYPE1, PARMNAME1, PARMTYPE2, PARMNAME2) \
THREADED_METHOD2_INTERNAL( , CLASSNAME, DOMULTI, METHOD, PARMTYPE1, PARMNAME1, PARMTYPE2, PARMNAME2) \
#define THREADED_METHOD2_INTERNAL(ISCONST, CLASSNAME, DOMULTI, METHOD, PARMTYPE1, PARMNAME1, PARMTYPE2, PARMNAME2)\
void METHOD ## NoThread(PARMTYPE1 PARMNAME1, PARMTYPE2 PARMNAME2) ISCONST { \
METHOD ## Partial(PARMNAME1, PARMNAME2, UT_JobInfo(0, 1, 0)); \
} \
\
void METHOD(PARMTYPE1 PARMNAME1, PARMTYPE2 PARMNAME2) ISCONST { \
\
if (!(DOMULTI)) { \
METHOD ## NoThread(PARMNAME1, PARMNAME2); \
return; \
} \
\
auto functor = [&](const UT_JobInfo &info) { \
METHOD ## Partial(PARMNAME1, PARMNAME2, info); \
return 0; \
}; \
\
UT_ThreadedAlgorithm alg; \
alg.run(functor); \
\
}
そして THREADED_METHOD2(SIM_GasAdd, shouldMultiThread(dst), addFields, SIM_RawField*, dst, const SIM_RawField*, src); の対して展開したものが以下です。
void addFieldNoThread(SIM_RawField*, dst, const SIM_RawField*, src) {
// NoThread 版は Partial にジョブ数1インデックス0の UT_JobInfo クラスのジョブ情報を与えて実行している
addFieldPartial(dst, src, UT_JobInfo(0, 1, 0));
}
void addField(SIM_RawField* dst, const SIM_RawField* src) {
// DOMULTI はマルチスレッドで計算するかどうかの bool
if(!(DOMULTI)) {
addFieldNoThread(dst, src);
return;
}
auto functor = [&](const UT_JobInfo& info) {
addFieldPartial(dst, src, info);
return 0;
}
UT_ThreadedAlgorithm alg;
// void UT_ThreadedAlgorithm::run(UT_Functor1<int, const UT_JobInfo&> functor, UT_Lock* lock = 0)
alg.run(functor);
}
上のコードは addFieldParcial() メソッドをマルチスレッドで処理する方法を提供する addField() メソッドを定義してます。
private:
// SIM_DopDescription のコンストラクタの宣言
// データファクトリ登録時にコールされる
// リファレンスから
// つまり、このデータに対して DOP_Node 派生を実装する必要はありません
// 代わりに、この記述を使用してインタフェースを定義します
static const SIM_DopDescription *getDopDescription();
// これらのマクロはノードをファクトリーにバインドし、 BaseClass のような有用な定数が定義されていることを確認するために必要
DECLARE_STANDARD_GETCASTTOTYPE();
// リファレンスから
// SIM_DataFactory は SIM_Data オブジェクトを作成したり破棄したりする手段を提供します。
// SIM_Data オブジェクトについては、データ型名以外何も知る必要はありません。
// DECLARE_DATAFACTORY マクロや IMPLEMENT_DATAFACTORY マクロで使用されるデフォルトの実装に依存するのではなく、
// サブクラスを派生させて使用することも可能です。しかし、一般的にはこれらのマクロで十分です。
DECLARE_DATAFACTORY(SIM_GasAdd, GAS_SubSolver, "Gas Add", getDopDescription());
DECLARE_STANDARD_GETCASTTOTYPE の実装
#define DECLARE_STANDARD_GETCASTTOTYPE() \
protected: \
void *getCastToType(const UT_StringRef &totype) const override { \
\
if( classname() == totype ) { \
return (void *)this; \
} \
return BaseClass::getCastToType(totype); \
\
}
上のコードは指定された型にキャストできるか調べて適切なポインタを返す getCastToType() メソッドを定義します。
DECLARE_DATAFACTORY の実装
#define DECLARE_DATAFACTORY(DataClass, SuperClass, Description, DopParms) \
public: \
\
class DataClass##Factory : public SIM_DataFactory { \
public: \
DataClass##Factory(SIM_Engine* engine) : SIM_DataFactory( \
SYS_CONCAT(#DataClass,_UTsh), \
SYS_CONCAT(Description,_UTsh), \
DataClass::getDataTypeSuperclasses, \
DataClass::constructor, \
DataClass::destructor, \
DataClass::DopParms, \
engine \
) { \
} \
}; \
\
static void createDataFactory(SIM_Engine *engine) { \
SIM_DataFactory* factory; \
factory = new DataClass##Factory(engine); \
SIM_DataFactoryCreator::addDataFactory(engine, factory); \
} \
\
friend class DataClass##Factory; \
\
private: \ \
DECLARE_CLASSNAME(DataClass, SuperClass); \
static SIM_Data* constructor(const SIM_DataFactory *factory) { \
return (BaseClass*) \
new DataClass(factory); \
} \
static void destructor(SIM_Data *data) { \
delete (DataClass*) \
data->getPointerToType(#DataClass); \
}
そして DECLARE_DATAFACTORY(SIM_GasAdd, GAS_SubSolver, "Gas Add", getDopDescription()); に対して展開したものが以下です。
public:
// SIM_GasAddFactory クラスの定義
class SIM_GasAddFactory : public SIM_DataFactory {
public:
//SIM_DataFactory のコンストラクタ
//SIM_DataFactory::SIM_DataFactory( const UT_StringHolder& datatype,
// const UT_StringHolder& description,
// SIM_GetSuperclasses get_superclasses,
// SIM_DataConstructor constructor,
// SIM_DataDestructor destructor,
// const SIM_DopDescription* dopdesc,
// const SIM_Engine* engine
// )
//SYS_CONCAT は ## のエイリアス
SIM_GasAddFactory(SIM_Engine *engine) : SIM_DataFactory(
SYS_CONCAT("SIM_GasAdd", _UTsh),
SYS_CONCAT("Gas Add", _UTsh),
SIM_GasAdd::getDataTypeSuperclasses,
SIM_GasAdd::constructor,
SIM_GasAdd::destructor,
SIM_GasAdd::getDescription(),
engine
) {
}
};
// createDataFactory メソッドの定義
// SIM_Engine から DataFactory を新たに作り取り付ける
static void createDataFactory(SIM_Engine* engine) {
//DataFactory を作る
SIM_DataFactory* factory;
factory = new SIM_GasAddFactory(engine);
//SIM_Engine に DataFactory を取るつける
SIM_DataFactoryCreator::addDataFactory(engine, factory);
//static void SIM_DataFactoryCreator::addDataFactory(SIM_Engine* engine, SIM_DataFactory* factory)
}
friend class SIM_GasAddFactory;
private:
// 指定されたクラス名を文字列として返す classname() という static method を定義するマクロ
DECLARE_CLASSNAME(SIM_GasAdd, GAS_SubSolver);
// コンストラクタの定義
static SIM_Data *constructor(const SIM_DataFactory *factory) {
return (GAS_SubSolver *) new SIM_GasAdd(factory);
}
// デストラクタの定義
static void destructor(SIM_Data *data) {
delete (SIM_GasAdd *) data->getPointerToType("SIM_GasAdd");
}
このコードでは SIM_Data サブクラスの SIM_DataFactory を宣言するために必要なすべての static method と SIM_DataFactory を継承した SIM_GasAddFactoryの定義を行っています。
上のコードで使われている DECLARE_CLASSNAME マクロの実装は以下です。
#define DECLARE_CLASSNAME(DataClass, SuperClass) \
private: \
typedef SuperClass BaseClass; \
typedef DataClass ThisClass; \
\
public: \
static inline const UT_StringHolder &classname() { \
static constexpr UT_StringLit theType(#DataClass); \
return theType.asHolder(); \
} \
\
private: \
const UT_StringHolder &getDataTypeSubclass() const override { \
return classname(); \
} \
\
protected: \
static void getDataTypeSuperclasses(UT_StringArray& classes) { \
static constexpr UT_StringLit theSuperType(#SuperClass); \
classes.append(theSuperType.asHolder()); \
SuperClass::getDataTypeSuperclasses(classes); \
} \
そして DECLARE_CLASSNAME(SIM_GasAdd, GAS_SubSolver); に対して展開したものが以下です。
private:
// SuperClass を BaseClass として、 DataClass を ThisClass として型定義
typedef GAS_SubSolver BaseClass;
typedef SIM_GasAdd ThisClass;
public:
// クラス名を返す静的メソッド
static inline const UT_StringHolder &classname() {
// クラス名 SIM_GasAdd を格納する定数オブジェクト theType を定義
static constexpr UT_StringLit theType("SIM_GasAdd");
// UT_StringHolder 型に変換して返す
return theType.asHolder();
}
private:
// クラス名を取得する仮想メソッドをオーバーライド
const UT_StringHolder &getDataTypeSubclass() const override {
// クラス名を返す
return classname();
}
protected:
// 継承階層のクラス名を取得する静的メソッド
static void getDataTypeSuperclasses(UT_StringArray& classes) {
// 親クラス名 GAS_SubSolver を格納する定数オブジェクト theSuperType を定義
static constexpr UT_StringLit theSuperType("GAS_SubSolver");
// UT_StringHolder 型に変換して追加
classes.append(theSuperType.asHolder());
// 親クラスの継承階層も追加
SuperClass::getDataTypeSuperclasses(classes);
}
このコードでは DataClass に classname() メソッドと getDataTypeSuperClasses() メソッドを実装し、 getDataTypeSubClass() メソッドをオーラーライドしています。
これでヘッダファイルの主な処理が終わります。
基本的にはコアとなるクラスやメソッドの宣言とノードの utility 的なメソッドの定義がこおなわれており、ノードのメインの処理や体裁は .C の方に記述されています。
1-2. SIM_GasAdd.C
以下が.Cファイルの全文です。
/*
* Copyright (c) 2024
* Side Effects Software Inc. All rights reserved.
*
* Redistribution and use of Houdini Development Kit samples in source and
* binary forms, with or without modification, are permitted provided that the
* following conditions are met:
* 1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice,
* this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
* 2. The name of Side Effects Software may not be used to endorse or
* promote products derived from this software without specific prior
* written permission.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY SIDE EFFECTS SOFTWARE `AS IS' AND ANY EXPRESS
* OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES
* OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN
* NO EVENT SHALL SIDE EFFECTS SOFTWARE BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT,
* INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT
* LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA,
* OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF
* LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING
* NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE,
* EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
*
*----------------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
#include "SIM_GasAdd.h"
#include <UT/UT_DSOVersion.h>
#include <UT/UT_Interrupt.h>
#include <PRM/PRM_Include.h>
#include <SIM/SIM_PRMShared.h>
#include <SIM/SIM_DopDescription.h>
#include <SIM/SIM_FieldSampler.h>
#include <SIM/SIM_ScalarField.h>
#include <SIM/SIM_VectorField.h>
#include <SIM/SIM_MatrixField.h>
#include <SIM/SIM_Object.h>
#include <GAS/GAS_SubSolver.h>
using namespace HDK_Sample;
///
/// This is the hook that Houdini grabs from the dll to link in
/// this. As such, it merely has to implement the data factory
/// for this node.
///
void
initializeSIM(void *)
{
IMPLEMENT_DATAFACTORY(SIM_GasAdd);
}
/// Standard constructor, note that BaseClass was crated by the
/// DECLARE_DATAFACTORY and provides an easy way to chain through
/// the class hierarchy.
SIM_GasAdd::SIM_GasAdd(const SIM_DataFactory *factory)
: BaseClass(factory)
{
}
SIM_GasAdd::~SIM_GasAdd()
{
}
/// Used to automatically populate the node which will represent
/// this data type.
const SIM_DopDescription *
SIM_GasAdd::getDopDescription()
{
static PRM_Name theDstFieldName(GAS_NAME_FIELDDEST, "Dest Field");
static PRM_Name theSrcFieldName(GAS_NAME_FIELDSOURCE, "Source Field");
static PRM_Template theTemplates[] = {
PRM_Template(PRM_STRING, 1, &theDstFieldName),
PRM_Template(PRM_STRING, 1, &theSrcFieldName),
PRM_Template()
};
static SIM_DopDescription theDopDescription(
true, // Should we make a DOP?
"hdk_gasadd", // Internal name of the DOP.
"Gas Add", // Label of the DOP
"Solver", // Default data name
classname(), // The type of this DOP, usually the class.
theTemplates); // Template list for generating the DOP
return &theDopDescription;
}
bool
SIM_GasAdd::solveGasSubclass(SIM_Engine &engine,
SIM_Object *obj,
SIM_Time time,
SIM_Time timestep)
{
SIM_ScalarField *srcscalar, *dstscalar;
SIM_VectorField *srcvector, *dstvector;
SIM_MatrixField *srcmatrix, *dstmatrix;
SIM_DataArray src, dst;
int i, j, k;
getMatchingData(src, obj, GAS_NAME_FIELDSOURCE);
getMatchingData(dst, obj, GAS_NAME_FIELDDEST);
// Now for each pair of source and dst fields, we want to add
// src to dst. We want to support scalar, vector, and matrix fields,
// but only compatible operations. We can determine what type we
// have via casting.
for (i = 0; i < dst.entries(); i++)
{
// Check to see if we exceeded our src list.
if (i >= src.entries())
{
addError(obj, SIM_MESSAGE, "Fewer source fields than destination fields.", UT_ERROR_WARNING);
break;
}
// Try each casting option.
dstscalar = SIM_DATA_CAST(dst(i), SIM_ScalarField);
srcscalar = SIM_DATA_CAST(src(i), SIM_ScalarField);
dstvector = SIM_DATA_CAST(dst(i), SIM_VectorField);
srcvector = SIM_DATA_CAST(src(i), SIM_VectorField);
dstmatrix = SIM_DATA_CAST(dst(i), SIM_MatrixField);
srcmatrix = SIM_DATA_CAST(src(i), SIM_MatrixField);
if (dstscalar && srcscalar)
{
addFields(dstscalar->getField(), srcscalar->getField());
}
if (dstvector && srcvector)
{
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++)
addFields(dstvector->getField(j), srcvector->getField(j));
}
if (dstmatrix && srcmatrix)
{
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++)
for (k = 0; k < 3; k++)
addFields(dstmatrix->getField(j, k), srcmatrix->getField(j, k));
}
// Make sure we are flagged as dirty
if (dstscalar)
dstscalar->pubHandleModification();
if (dstvector)
dstvector->pubHandleModification();
if (dstmatrix)
dstmatrix->pubHandleModification();
}
// Successful cook
return true;
}
void
SIM_GasAdd::addFieldsPartial(SIM_RawField *dst, const SIM_RawField *src, const UT_JobInfo &info)
{
UT_VoxelArrayIteratorF vit;
UT_Interrupt *boss = UTgetInterrupt();
// Initialize our iterator to run over our destination field.
vit.setArray(dst->fieldNC());
// When we complete each tile the tile is tested to see if it can be
// compressed, ie, is now constant. If so, it is compressed.
vit.setCompressOnExit(true);
// Restrict our iterator only over part of the range. Using the
// info parameters means each thread gets its own subregion.
vit.setPartialRange(info.job(), info.numJobs());
// Create a sampler for the source field.
SIM_ScalarFieldSampler srcsampler(dst, src);
float srcval;
// Visit every voxel of the destination array.
for (vit.rewind(); !vit.atEnd(); vit.advance())
{
if (vit.isStartOfTile())
{
if (boss->opInterrupt())
break;
// Check if both source and destination tiles are constant.
if (vit.isTileConstant() &&
srcsampler.isTileConstant(vit, srcval))
{
// If both are constant, we can process the whole tile at
// once. We call skipToEndOfTile() here so that the loop's
// call to advance() will move us to the next tile.
vit.getTile()->makeConstant( vit.getValue() + srcval );
vit.skipToEndOfTile();
continue;
}
}
// Write out the sum of the two fields. Instead of using the
// iterator, we could also have built a UT_VoxelRWProbeF.
float srcval = srcsampler.getValue(vit);
vit.setValue( vit.getValue() + srcval );
}
}
コードの解説です。
// Houdiniがリンクするためにdllから取得するフック
void initializeSIM(void*) {
// このノードのデータファクトリを実装する
IMPLEMENT_DATAFACTORY(SIM_GasAdd);
}
マクロを使ってDataFactoryの実装を行っています。
マクロの実装は以下です。
#define IMPLEMENT_DATAFACTORY(DataClass) \
static SIM_DataFactoryCreator DataClass##Creator(DataClass::createDataFactory); \
そして IMPLEMENT_DATAFACTORY(SIM_GasAdd); に対して展開したのものが以下です。
// SIM_DataFactoryCreatorクラスのcreateDataFactoryメソッドを宣言する
static SIM_DataFactoryCreator SIM_GasAddCreator(SIM_GasAdd::createDataFactory);
// SIM_GasAddのコンストラクタを定義する
// BaseClass(つまりGAS_SubSolver)から継承し、factoryを渡してコンストラクタをコールする
SIM_GasAdd::SIM_GasAdd(const SIM_DataFactory* factory) : BaseClass(factory){
}
// SIM_GasAddのデストラクタを定義する
SIM_GasAdd::~SIM_GasAdd() {
}
ここでコンストラクタとデストラクタの定義を行っています。
// getDopDescriptionメソッドの定義
const SIM_DopDescription* SIM_GasAdd::getDopDescription() {
// 下の定義があるので置き換えられる
// #define GAS_NAME_FIELDDEST "fielddst"
// #define GAS_NAME_FIELDSOURCE "fieldsrc"
//PRM_Name::PRM_Name(const char* theToken, const char* theTable = nullptr, int theFlags = 0)
static PRM_Name theDstFieldName(GAS_NAME_FIELDDEST, "Dest Field");
static PRM_Name theSrcFieldName(GAS_NAME_FIELDSOURCE, "Source Field");
//パラメータテンプレートの配列を作成
static PRM_Template theTemplates[] = {
PRM_Template(PRM_STRING, 1, & theDstFieldName),
/*
今回使われているPRM_Templateのコンストラクタ
PRM_Template::PRM_Template( PRM_Type thetype,
PRM_TypeExtended thetype_ext,
PRM_Export theexportlevel,
int thevectorsize = 1,
PRM_Name* thenameptr = 0,
PRM_Default* thedefaults = 0,
PRM_ChoiceList* thechoicelistptr = 0,
PRM_Range* therangeptr = 0,
PRM_Callback thecallbackfunc = 0,
PRM_SpareData* thespareptr = 0,
int theparmgroup = 1,
const char* thehelptext = 0,
PRM_ConditionalBase* thecondptr = 0
)
*/
PRM_Template(PRM_STRING, 1, & theSrcFieldName),
//最後に空のテンプレートを入れる
PRM_Template()
};
//このノードのdescriptionの作成
static SIM_DopDescription theDopDescription(
true, //DOPを作るべきか
"hdl_gasadd", //DOPの内部名
"Gas Add", //DOPのラベル
"Solver", //取り付けるサブデータのデフォルトの名前
classname(), //このDOPのタイプ、通常はクラス。
//ヘッダファイル内のDECLARE_DATAFACTORYマクロ内のDECLARE_CLASSNAMEマクロで、
//クラス名を文字列で返すclassname()メソッドが定義されている
theTemplates //テンプレートのリスト
);
return &theDopDescription;
}
ノードのパラメータや名前を内包した SIM_DopDescription を返す getDopDescription() メソッドの定義を行っています。
// solveGasSubclass()を実装する
bool SIM_GasAdd::solveGasSubclass(SIM_Engine& engine, SIM_Object* obj, SIM_Time time, SIM_Time timestep) {
//field変数の宣言
SIM_ScalarField* srcscalar;
SIM_ScalarField* dstscalar;
SIM_VectorField* srcvector;
SIM_VectorField* dstvector;
SIM_MatrixField* srcmatrix;
SIM_MatrixField* dstmatrix;
SIM_DataArray src, dst;
int i, j, k;
getMatchingData(src, obj, GAS_NAME_FIELDDEST);
getMatchingData(dst, obj, GAS_NAME_FIELDSOURCE);
/*
nameで指定したSIM_Dataをすべて取得する
void GAS_SubSolver::getMatchingData(SIM_DataArray& data,
SIM_Object* obj,
const char* name,
bool silent = false
)
*/
for(i = 0; i < dst.entries(); i++){
// UT_Array<T>::entries() -> const i64で配列サイズを返す
// SIM_DataArray - UT_ValArray<SIM_Data *> - UT_Array
// UT_Array::entries() -> exint
// exint - i64
//dstのサイズのほうが大きければ警告を出す
if(i >= src.entries()) {
addError(obj, SIM_MESSAGE, "Fewer source fields than destination fields.", UT_ERROR_WARNING);
/*
void SIM_Data::addError(const SIM_RootData * root,
int errorcode,
const char * errorparm,
UT_ErrorSeverity severity
)
SIM_MESSAGE = 0
*/
break;
}
//castする
dstscalar = SIM_DATA_CAST(dst(i), SIM_ScalarField);
srcscalar = SIM_DATA_CAST(src(i), SIM_ScalarField);
dstvector = SIM_DATA_CAST(dst(i), SIM_VectorField);
srcvector = SIM_DATA_CAST(src(i), SIM_VectorField);
dstmatrix = SIM_DATA_CAST(dst(i), SIM_MatrixField);
srcmatrix = SIM_DATA_CAST(src(i), SIM_MatrixField);
/*
安全にキャストできるかチェックしたあと、型のキャストをする
#define SIM_DATA_CAST(Data, DataClass) \
((DataClass *)(SIM_Data::castPointerToType(static_cast<SIM_Data *>(Data), #DataClass))) \
実際に展開したあと
((SIM_MatrixField *)(SIM_Data::castPointerToType(static_cast<SIM_Data *>(src(i)), "SIM_MatrixField")));
*/
// fieldをaddする
if(dstscalar && srcscalar) {
addFields(dstscalar->getField(), srcscalar->getField());
}
if(dstvector && srcvector) {
for(j = 0; j < 3; j++){
addFields(dstvector->getField(j), srcvector->getField(j));
}
}
if(dstmatrix && srcmatrix) {
for(j = 0; j < 3; j++){
for(k = 0; k < 3; k++){
addFields(dstmatrix->getField(j, k), srcmatrix->getField(j, k));
}
}
}
// dirty flagをたてる
// 外部から編集されたことをfieldに知らせる
if(dstscalar){
dstscalar->pubHandleModification();
//ScalarField::pubHandleModification()
}
if(dstvector) {
dstvector->pubHandleModification();
//VectorField::pubHandleModification()
}
if(dstmatrix) {
dstmatrix->pubHandleModification();
//MatrixField::pubHandleModification()
}
}
// Successful cook
return true;
}
実際にソルバの処理において呼ばれる solveGasSubclass() を実装しています。
呼ばれる順は solverGasSubclass() -> addFields() -> addFieldsPartial()で、役割は
-
solverGasSubclass(): DOP Objectを受け取ってsrc field, dst fieldを作りaddFieldsをコールする。クック全体を管理する。 -
addFields(): THREADED_METHOD2マクロ内で定義される。ジョブ情報を作成して、マルチスレッドを使ってaddFieldsPartialをコールする。 -
addFieldsPartial(): 実際にボクセルの値を読み書きして加算を行う。
です。
// addFieldsPartial()を実装する
void SIM_GasAdd::addFieldsPartial(SIM_RawField *dst, const SIM_RawField *src, const UT_JobInfo &info)
実際に値を読み書きする addFieldsPartial() メソッドを定義します。
// VoxelArray にアクセスするためのイテレータを宣言する
UT_VoxelArrayIteratorF vit;
UT_VoxelArray にアクセスするためのイテレータを宣言します。
ボクセルを表現する UT_VoxelArray にアクセスする方法がいくつかあります。
1つ目は下のように for を3回ネストして3方向に走査する方法です。
UT_VoxelArrayF* voxel;
int x, y, z;
float total = 0.0;
for (z = 0; z < voxel->getZRes(); z++)
for (y = 0; y < voxel->getYRes(); y++)
for (x = 0; x < voxel->getXRes(); x++)
total += (*voxel)(x, y, z);
この方法は最適ではありません。なぜなら、コードが冗長になるのはもちろんのこと軸ごとに走査するとタイルをまたぐので定数データの書き込み時のタイルの圧縮性を利用することができずメモリ効率が低下するからです。
また、UT_VoxelArray::getValue() はインデックスを用いてコールするたびに、そのボクセルが所属するタイルの情報をクエリするので軸ごとに走査するするとタイル境界を行き来してオーバーヘッドが大きくなります。
下の動画は仮想的な Voxel とその配列の配置を示したした様子です。各四角がボクセル、色がタイルを示しています。
Array の方を見るとタイルの境界を何度もまたいでいることがわかります。

変わりにタイルごとに平坦化されたような構造の UT_VoxelArrayIterator クラスが用意されています。
下の動画は仮想的な Voxel と UT_VoxelArrayIterator に配置を示した様子です。
それぞれのタイル間は1度しかまたいでいないことがわかります。

これを用いるを以下のように書けます。
UT_VoxelArrayF* voxel;
UT_VoxelArrayIterator voxelIter;
voxelIter.setArray(voxel);
for (voxelIter.rewind(); !voxelIter.atEnd(); voxelIter.advance())
total += voxelIter.getValue();
UT_VoxelArrayIterator::rewind() で最初のボクセルが取得でき、UT_VoxelArrayIterator::advance() で次のボクセルを取得できます。
UT_VoxelArrayIterator::advance() が新しいタイルに移動するたび古いタイルの圧縮性がテストされ、定数データの書き込み時メモリが1タイル分を超えて拡張する必要がないことが保証されています。
タイル内の走査順は z -> y -> x で変更不可です。
// おそらくinterruptオブジェクトを取得する
UT_Interrupt* boss = UTgetInterrupt();
UT_Interrupt::UTgetInterrupt() メソッドはドキュメントに実装が見つけられなかったので、よくわかりません。
// dst fieldからVoxelArrayIteratorを作る
vit.setArray(dst->fieldNC());
UT_VoxelArray オブジェクトの dst field から UT_VoxelArrayIteratorF を作ります。
SIM_RawField::fieldNC()はfieldを受けてgridをクリアしてfieldを返すメソッドです。
SIM_RawField にはアトリビュート UT_VoxelArrayF* myField と CE_Grid* myGrid がいます。
GridとFieldの関連性がよくわからない...
メソッドの実装は以下です。
UT_VoxelArrayF* fieldNC() const {
if (myGrid) {
clearGrid();
}
return myField;
}
vit.setCompressOnExit(true);
タイル内の最後のボクセルの書き込みが完了したとき、そのタイルが定数タイルか判定し、そうであれば圧縮します。
vit.setPartialRange(info.job(), info.numJobs());
並列処理のためのJob情報に従って Iterator の範囲を制限します。
例えば3つのスレッドを使って処理するなら Voxel Iterator を3分割し、現行のスレッドの範囲を返します。
// ソースフィールドのサンプラーを作成する
SIM_ScalarFieldSampler srcsampler(dst, src);
float srcval;
// dst field のボクセルのうちこのジョブが処理する範囲のボクセルを走査する
for(vit.rewind(); !vit.atEnd(); vit.advance()){
if(vit.isStartOfTile()){
// 現行のボクセルがタイルの最初か
if(boss->opInterrupt()){
// UT_Interruptは時間がかかる処理をするときにつかう
// opStart() -> opInterrupt(進捗を示す0-100の数字 デフォルトは-1)1回以上 -> opEnd() の順で使う
// opInterrupt()は操作を続行する場合は0を返し、終了要求がきたなら1を返す。
// つまりここでは Esc キーが押されたときにループを抜ける処理が実装されている。
break;
}
// source tile と dst tile が両方定数タイルか
if(vit.isTileConstant() && srcsampler.isTileConstant(vit, srcval)){
// SIM_ScalarFieldSampler::isTileConstant(const UT_VoxelArrayIteratorF& iter, float& val) -> bool
// source field の iterator がいるタイルが定数タイルか
// 両方定数タイルなら、タイル全体を一度に処理できる。
vit.getTile()->makeConstant(vit.getValue() + srcval);
// iterator からタイルを取得する
// UT_VoxelArrayIterator<T>::getTile() -> UT_VoxelTile<T>*
// このタイルを与えられた値の定数タイルに変える
// UT_VoxelTile<T>::makeConstant(T t)
// 現行の値と src の値を足す
// UT_VoxelArrayIterator<T>::getValue() -> T
// skipToEndOfTile() をコールしタイルの最後のボクセルまで移動し、ループの advance() が次のタイルに移動するようにする
vit.skipToEndOfTile();
continue;
}
}
// タイルの最初のボクセルじゃないとき(つまり定数タイルじゃないタイルに差し掛かったとき)
// 2つのフィールドの合計を書き出す。
// イテレータを使う代わりに、UT_VoxelRWProbeF で行うこともできる
// UT_VoxelRWProbeF を使うことでタイルへのクエリを16回に1回しか行わないので、
// UT_VoxelArray::setValue() より効率的
// 今回は iterator を使っているのでそこまで非効率的ではない(と思う)
// dst field から source field をサンプリングする
float srcval = srcsampler.getValue(vit);
// SIM_ScalarFieldSampler::getValue(const UT_VoxelArrayIteratorF& iter) -> float
// iterator の現行位置における値をサンプリングする
// dst field と src field を足して値を書き込む
vit.setValue(vit.getValue() + srcval);
// UT_VoxelArrayIterator<T>::setValue(T t) -> void
// iterator の現行位置のボクセルに値を格納する
}
以上がサンプルのソースコードの解説です。
2. おわりに
余談ですが最後に、Variational Stokes: A Unified Pressure-viscosity Solver for Accurate Viscous Liquids という論文を紹介します。
この論文の言っていることは、従来の流体ソルバでは粘性と圧力を別のステージで計算するので精度的な問題で、高い粘性の流体を扱ったときにサーフェスのディテールが失われるので、統一的に扱うことでディテールを保つようにしたよということです。実際の比較動画があります。
Variational Stokes: A Unified Pressure-Viscosity Solver for Accurate Viscous Liquids (SIGGRAPH 2017)
そしてこの論文を著者が HDK を使って実装したマイクロソルバが下のリポジトリです。
Stokes Variational Micro-Solver Plugin DOP for Houdini
気になる方は覗いてみてください。
本当はこれを Rust でラップするところまで書きたかったのですが、間に合いそうにないので今回はここまでです。
HDK のマイクロソルバに関する情報があまり出てこないので少し詳しめに書いてみました。誰かの助けになれば幸いです。
最後まで読んでいただきありがとうございました!