目的
本記事では、FSK方式を使ってASCIIコードの文字列を波形に変換し、その波形をWAV形式で保存します。その後、WAVファイルを読み込んで元の文字列を復元する方法を紹介します。
本来は電波を使って実験を行いたいところですが、任意の電波を生成する装置がなく、又電波が飛んでいても肉眼で確認できないため、WAV形式を採用しました。
音声形式ではありますが、いずれも波形である点では同じように扱えます。
FM(周波数変調) とFSK(周波数偏移変調)の違い
紛らわしいので以下2つの違いを説明しておきます。
どちらも周波数の変化で情報を表すという点では同じです。
FM(周波数変調) - アナログ方式
入力:連続的なアナログ信号(音声など)
出力:連続的に変化する周波数
周波数
↑
| ___ ___ _ 滑らかに変化
| / \ / \ / \
| / \_/ \_/ \
|_/________________________→ 時間
FSK(周波数偏移変調) - デジタル方式
入力:離散的なデジタル信号(0と1)
出力:2つ(または数個)の決まった周波数だけを使う
周波数
↑
| 2000Hz 2000Hz 2000Hz 段階的変化
| _______ _______ _______
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
|____| |____| |_______|_____→ 時間
1000Hz 1000Hz
変調方式
├── アナログ変調(連続信号伝送)
│ ├── AM(振幅変調)
│ ├── FM(周波数変調)← アナログ版
│ └── PM(位相変調)
│
└── デジタル変調(離散信号伝送)
├── ASK(振幅偏移変調)
├── FSK(周波数偏移変調)← デジタル版
└── PSK(位相偏移変調)
FSKで情報を伝達する大まかな流れ
情報源 → [エンコーダ] → 通信路 → [デコーダ] → 情報復元
↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
"A" 周波数パターン 波 "A"に復元
FSKの具体例
データ: 10110
ビット時間: 0.1秒
周波数: 0=1000Hz, 1=2000Hz
時間 0.0-0.1s 0.1-0.2s 0.2-0.3s 0.3-0.4s 0.4-0.5s
ビット 1 0 1 1 0
周波数 2000Hz 1000Hz 2000Hz 2000Hz 1000Hz
状態 高い音を 低い音を 高い音を 高い音を 低い音を
0.1秒間 0.1秒間 0.1秒間 0.1秒間 0.1秒間
維持 維持 維持 維持 維持
周波数
↑
| 2000Hz 1000Hz 2000Hz 2000Hz 1000Hz
| _______ _______ _______
| | | | | | |
| | 1 | 0 | 1 | | 1 | 0
|__| |_______| |_| |_______
|
+-------------------------------------------→ 時間
0.1s 0.2s 0.3s 0.4s 0.5s
ビット列をASCIIコードにすることで文字列を波として表現できます。
C言語で検証
構成
[文字列] → [ASCII変換] → [FSK変調] → [WAV出力]
↓
[WAV入力] → [FSK復調] → [ビット判定] → [文字列復元]
本来は、WAV音声を再生し、それを録音して文字列を復元したいところですが、録音すると雑音が入る可能性があります。これにより、波形が崩れて誤り検出やビットの開始位置の判定が必要になり、処理が複雑になります。そのため、今回は出力したWAVファイルをそのまま読み込んで復元する方法を選びました。
WAVを生成
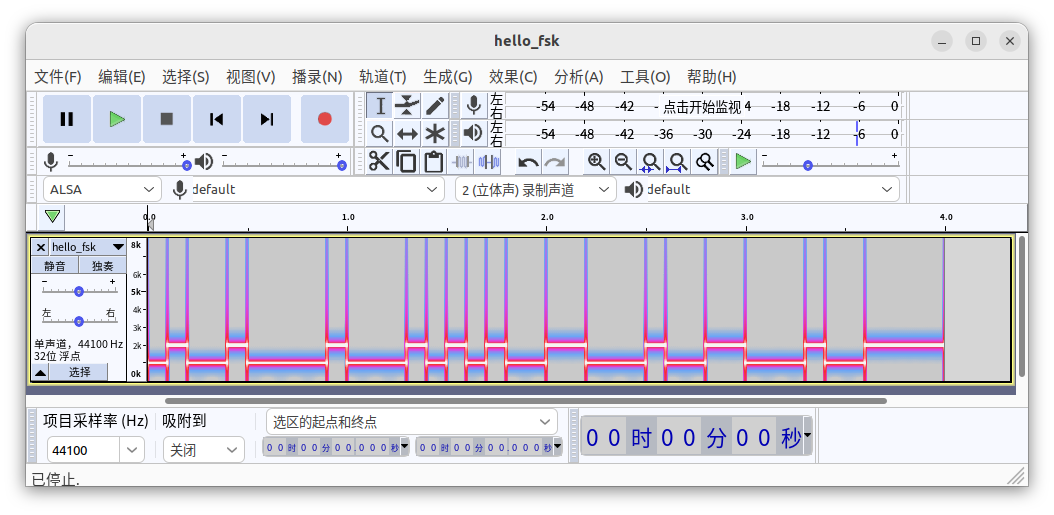
以下はAudacityというソフトを用いて生成したWAVファイルを解析し、横軸を時間、縦軸を周波数として図にしたものです。
0の部分は低く、1の部分は高くなっています。
test@test-fujitsu:~/kaihatsu/butsuri$ gcc -o fsk_encoder fsk_encoder.c -lm
test@test-fujitsu:~/kaihatsu/butsuri$ ./fsk_encoder
=== FSKエンコーダ ===
変換する文字列: "HELLO"
パラメータ:
サンプリングレート: 44100 Hz
ビット時間: 0.1秒
周波数(0): 1000 Hz
周波数(1): 2000 Hz
サンプル数/ビット: 4410
文字 'H' (ASCII 72) -> ビット列: 01001000
文字 'E' (ASCII 69) -> ビット列: 01000101
文字 'L' (ASCII 76) -> ビット列: 01001100
文字 'L' (ASCII 76) -> ビット列: 01001100
文字 'O' (ASCII 79) -> ビット列: 01001111
WAVファイル生成完了: hello_fsk.wav
文字数: 5
総ビット数: 40
総サンプル数: 176400
ファイルサイズ: 352844 bytes
再生時間: 4.00秒
WAVファイル 'hello_fsk.wav' が生成されました。
このファイルをオーディオプレーヤーで再生すると、FSK変調された音が聞けます。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <stdint.h>
// WAVヘッダーの構造体
typedef struct {
char chunkID[4]; // "RIFF"
uint32_t chunkSize; // ファイルサイズ - 8
char format[4]; // "WAVE"
char subchunk1ID[4]; // "fmt "
uint32_t subchunk1Size; // 16 (PCMの場合)
uint16_t audioFormat; // 1 (PCM)
uint16_t numChannels; // 1 (モノラル)
uint32_t sampleRate; // 44100
uint32_t byteRate; // sampleRate * numChannels * bitsPerSample/8
uint16_t blockAlign; // numChannels * bitsPerSample/8
uint16_t bitsPerSample; // 16
char subchunk2ID[4]; // "data"
uint32_t subchunk2Size; // データサイズ
} WavHeader;
// パラメータ設定
#define SAMPLE_RATE 44100
#define BIT_DURATION 0.1 // 1ビットあたりの時間(秒)
#define SAMPLES_PER_BIT (int)(SAMPLE_RATE * BIT_DURATION)
#define FREQ_0 1000 // ビット0の周波数
#define FREQ_1 2000 // ビット1の周波数
#define AMPLITUDE 16000 // 振幅(16ビットなので最大32767)
// 文字を8ビットのバイナリに変換
void char_to_binary(char c, int* bits) {
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
bits[7 - i] = (c >> i) & 1;
}
}
// サイン波を生成(指定した周波数で)
double generate_sine_wave(double frequency, int sample_index) {
double angle = 2.0 * M_PI * frequency * sample_index / SAMPLE_RATE;
return sin(angle);
}
// FSK信号を生成してWAVファイルに保存
void generate_fsk_signal(const char* text, const char* filename) {
int text_len = strlen(text);
int total_bits = text_len * 8;
int total_samples = total_bits * SAMPLES_PER_BIT;
// サンプルデータを格納するバッファ
int16_t* samples = (int16_t*)malloc(total_samples * sizeof(int16_t));
if (!samples) {
printf("メモリ割り当てエラー\n");
return;
}
int sample_index = 0;
// 各文字を処理
for (int char_index = 0; char_index < text_len; char_index++) {
char current_char = text[char_index];
int bits[8];
// 文字を8ビットに変換
char_to_binary(current_char, bits);
printf("文字 '%c' (ASCII %d) -> ビット列: ", current_char, current_char);
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
printf("%d", bits[i]);
}
printf("\n");
// 各ビットに対してサイン波を生成
for (int bit_index = 0; bit_index < 8; bit_index++) {
int bit = bits[bit_index];
double frequency = (bit == 1) ? FREQ_1 : FREQ_0;
// 1ビット分のサンプルを生成
for (int i = 0; i < SAMPLES_PER_BIT; i++) {
double sample_value = generate_sine_wave(frequency, sample_index);
samples[sample_index] = (int16_t)(sample_value * AMPLITUDE);
sample_index++;
}
}
}
// WAVヘッダーを作成
WavHeader header;
memcpy(header.chunkID, "RIFF", 4);
memcpy(header.format, "WAVE", 4);
memcpy(header.subchunk1ID, "fmt ", 4);
memcpy(header.subchunk2ID, "data", 4);
header.subchunk1Size = 16;
header.audioFormat = 1; // PCM
header.numChannels = 1; // モノラル
header.sampleRate = SAMPLE_RATE;
header.bitsPerSample = 16;
header.blockAlign = header.numChannels * header.bitsPerSample / 8;
header.byteRate = header.sampleRate * header.blockAlign;
header.subchunk2Size = total_samples * sizeof(int16_t);
header.chunkSize = 36 + header.subchunk2Size;
// WAVファイルを書き出し
FILE* file = fopen(filename, "wb");
if (!file) {
printf("ファイルオープンエラー: %s\n", filename);
free(samples);
return;
}
// ヘッダー書き込み
fwrite(&header, sizeof(WavHeader), 1, file);
// サンプルデータ書き込み
fwrite(samples, sizeof(int16_t), total_samples, file);
fclose(file);
free(samples);
printf("\nWAVファイル生成完了: %s\n", filename);
printf("文字数: %d\n", text_len);
printf("総ビット数: %d\n", total_bits);
printf("総サンプル数: %d\n", total_samples);
printf("ファイルサイズ: %ld bytes\n", sizeof(WavHeader) + total_samples * sizeof(int16_t));
printf("再生時間: %.2f秒\n", (double)total_samples / SAMPLE_RATE);
}
// テスト用メイン関数
int main() {
const char* text = "HELLO";
printf("=== FSKエンコーダ ===\n");
printf("変換する文字列: \"%s\"\n", text);
printf("パラメータ:\n");
printf(" サンプリングレート: %d Hz\n", SAMPLE_RATE);
printf(" ビット時間: %.1f秒\n", BIT_DURATION);
printf(" 周波数(0): %d Hz\n", FREQ_0);
printf(" 周波数(1): %d Hz\n", FREQ_1);
printf(" サンプル数/ビット: %d\n", SAMPLES_PER_BIT);
printf("\n");
generate_fsk_signal(text, "hello_fsk.wav");
printf("\nWAVファイル 'hello_fsk.wav' が生成されました。\n");
printf("このファイルをオーディオプレーヤーで再生すると、FSK変調された音が聞けます。\n");
return 0;
}
生成したWAVから文字列を復元
test@test-fujitsu:~/kaihatsu/butsuri$ gcc -o fsk_decoder fsk_decoder.c -lm
test@test-fujitsu:~/kaihatsu/butsuri$ ./fsk_decoder
復元結果: HELLO
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
// WAVヘッダー構造体
typedef struct {
char chunkID[4];
uint32_t chunkSize;
char format[4];
char subchunk1ID[4];
uint32_t subchunk1Size;
uint16_t audioFormat;
uint16_t numChannels;
uint32_t sampleRate;
uint32_t byteRate;
uint16_t blockAlign;
uint16_t bitsPerSample;
char subchunk2ID[4];
uint32_t subchunk2Size;
} WavHeader;
// パラメータ
#define SAMPLE_RATE 44100
#define BIT_DURATION 0.1
#define SAMPLES_PER_BIT (int)(SAMPLE_RATE * BIT_DURATION)
#define FREQ_THRESHOLD 1500
// ゼロクロス検出で周波数推定
double estimate_frequency_zero_crossing(const int16_t* samples, int num_samples) {
int zero_crossings = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < num_samples; i++) {
if ((samples[i-1] <= 0 && samples[i] > 0) ||
(samples[i-1] >= 0 && samples[i] < 0)) {
zero_crossings++;
}
}
return (zero_crossings * SAMPLE_RATE) / (2.0 * num_samples);
}
// 閾値を元に周波数からビット判定
int detect_bit(double frequency) {
return (frequency > FREQ_THRESHOLD) ? 1 : 0;
}
// 8ビットから文字に変換
char binary_to_char(const int* bits) {
char result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
result = (result << 1) | bits[i];
}
return result;
}
// WAVをデコードして文字列を復元
char* decode_fsk_signal(const char* filename) {
FILE* file = fopen(filename, "rb");
if (!file) {
printf("ファイルを開くのに失敗: %s\n", filename);
return NULL;
}
WavHeader header;
if (fread(&header, sizeof(WavHeader), 1, file) != 1) {
printf("ヘッダー読み込みエラー\n");
fclose(file);
return NULL;
}
int total_samples = header.subchunk2Size / sizeof(int16_t); // WAVの標本総数
int total_bits = total_samples / SAMPLES_PER_BIT; // FSK でエンコードされたビットの総数
int text_len = total_bits / 8; // 伝送する文字列の長さ
int16_t* samples = (int16_t*)malloc(total_samples * sizeof(int16_t));
if (!samples) { fclose(file); return NULL; }
if (fread(samples, sizeof(int16_t), total_samples, file) != total_samples) {
printf("サンプルデータ読み込みエラー\n");
free(samples);
fclose(file);
return NULL;
}
fclose(file);
char* decoded_text = (char*)malloc(text_len + 1);
if (!decoded_text) { free(samples); return NULL; }
//復元する文字の数だけループ HELLO→5回
for (int char_index = 0; char_index < text_len; char_index++) {
int bits[8];
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
int start = (char_index * 8 + i) * SAMPLES_PER_BIT; // 今解析する「ビット」の開始位置を計算
double freq = estimate_frequency_zero_crossing(&samples[start], SAMPLES_PER_BIT);
bits[i] = detect_bit(freq);
}
decoded_text[char_index] = binary_to_char(bits);
}
decoded_text[text_len] = '\0';
free(samples);
return decoded_text;
}
int main() {
const char* filename = "hello_fsk.wav";
char* decoded_text = decode_fsk_signal(filename);
if (decoded_text) {
printf("復元結果: %s\n", decoded_text);
free(decoded_text);
}
return 0;
}