公式ドキュメント
キャスト
以下はどちらもまったく同じである:
SELECT '2023-09-15 12:34:56'::timestamp;
SELECT CAST('2023-09-15 12:34:56' AS timestamp);
タイムゾーン表示
タイムゾーンはセッション毎に設定される。
postgres=# show timezone;
TimeZone
----------
UTC
タイムゾーン変更
カレントセッションのみ変更
set timezone to 'Asia/Tokyo';
postgresql.confでグローバルに設定
timezone = 'Asia/Tokyo'
データベースごとにデフォルト値を設定
-- 変更
ALTER DATABASE db1 SET timezone TO 'Asia/Tokyo';
-- この後db1に接続し直すと反映される
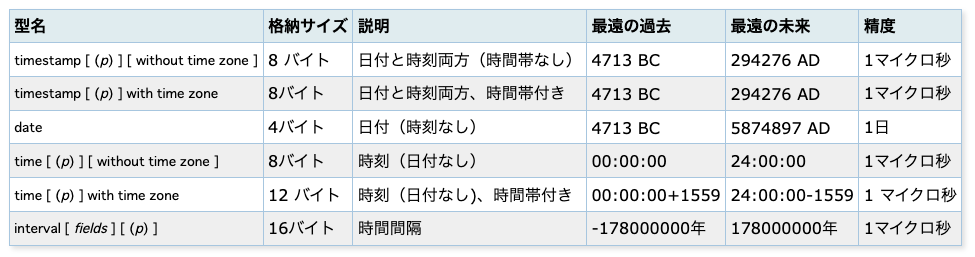
日付のデータ型
timestamp with time zoneはtimestamptzと略記できる(PostgreSQLの拡張であり標準SQLには無い)。
timestamp型の内部構造
timestamp型は2000-01-01 00:00:00から経過したマイクロ秒としてint64で保持されている。
https://dba.stackexchange.com/a/288936
timestampとtimestamptzの違い
- timestamptzは現在のセッションのタイムゾーンに変換して表示される
- timestampは変換されず、文字列のごとく記録されたHH:MM:SSがそのまま表示される
postgres=# create table t (a timestamp, b timestamptz);
CREATE TABLE
時間: 6.300 ミリ秒
postgres=# insert into t (a, b) values ('2023-09-06 01:02:03', '2023-09-06 01:02:03+09:00');
INSERT 0 1
時間: 2.058 ミリ秒
postgres=# insert into t (a, b) values ('2023-09-06 01:02:03', '2023-09-06 01:02:03+03:00');
INSERT 0 1
時間: 1.199 ミリ秒
postgres=# select * from t;
a | b
---------------------+------------------------
2023-09-06 01:02:03 | 2023-09-06 01:02:03+09
2023-09-06 01:02:03 | 2023-09-06 07:02:03+09
(2 行)
すべての時間帯付きの日付と時刻はUTCで内部的に保存されます。
https://www.postgresql.jp/document/13/html/datatype-datetime.html#DATATYPE-TIMEZONES
timestamptzからtimestampへのキャスト
単純にタイムゾーン部分が無視された日時となる。
postgres=# select * from t;
a | b
---------------------+------------------------
2023-09-06 01:02:03 | 2023-09-06 01:02:03+09
2023-09-06 01:02:03 | 2023-09-06 07:02:03+09
(2 行)
postgres=# select a, b::timestamp from t;
a | b
---------------------+---------------------
2023-09-06 01:02:03 | 2023-09-06 01:02:03
2023-09-06 01:02:03 | 2023-09-06 07:02:03
(2 行)
timestampからtimestamptzへのキャスト
単純に現在のセッションのタイムゾーンが付与される。
postgres=# select a::timestamptz, b from t;
a | b
------------------------+------------------------
2023-09-06 01:02:03+09 | 2023-09-06 01:02:03+09
2023-09-06 01:02:03+09 | 2023-09-06 07:02:03+09
(2 行)
日付を文字列化
SELECT to_char(now(), 'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS.US');
to_char
----------------------------
2024-06-29 22:57:18.231684
日付のパース
::timestampまたは::timestamptzでキャストするのが簡単。
postgres=# SELECT '2021-02-03T04:05:06.789012+09:00'::timestamptz;
timestamptz
-------------------------------
2021-02-02 19:05:06.789012+00 -- DBのタイムゾーンはUTCなので、正常にパースできている
postgres=# SELECT '2021-02-03 04:05:06 +09:00'::timestamptz;
timestamptz
------------------------
2021-02-02 19:05:06+00 -- DBのタイムゾーンはUTCなので、正常にパースできている
(1 row)
postgres=# SELECT '2021-02-03 04:05:06 +09:00'::timestamp;
timestamp
---------------------
2021-02-03 04:05:06 -- +09:00が無視されてしまっている
postgres=# SELECT to_timestamp('2021-02-03T04:05:06+09:00', 'YYYY-MM-DD"T"HH24:MI:SS');
to_timestamp
------------------------
2021-02-03 04:05:06+00 -- +09:00が無視されてしまっている
日付の加算減算
加算
SELECT now() + '9 hours'::interval;
減算
SELECT now() - '3 days'::interval;
::interval を省略して + '9 hours' でも可だが、 - '9 hours' のようにマイナスはエラーになるので注意。+ '-9 hours' は可。
month を指定した場合、存在しない日付は月末になる
postgres=# select '2023-01-31'::date + '1 month'::interval;
?column?
---------------------
2023-02-28 00:00:00 -- 2月31日は存在しないので月末になる
(1 行)
日付の差
単純に引き算すれば良い。結果はinterval型になる。
select '2023-09-05 13:00:00'::timestamp - '2023-09-05 12:00:00'::timestamp;
?column?
----------
01:00:00
日付を切り詰める(date_trunc('second', timestamp))
postgres=# select date_trunc('day', '2021/2/14 01:23:45.678912'::timestamp);
date_trunc
---------------------
2021-02-14 00:00:00
(1 row)
Time: 2.529 ms
postgres=# select date_trunc('second', '2021/2/14 01:23:45.678912'::timestamp);
date_trunc
---------------------
2021-02-14 01:23:45
(1 row)
Time: 1.151 ms
postgres=# select date_trunc('minute', '2021/2/14 01:23:45.678912'::timestamp);
date_trunc
---------------------
2021-02-14 01:23:00
(1 row)
interval型を秒に変換
postgres=# select extract(epoch from '1 hour'::interval);
date_part
-----------
3600
interval型を日数に変換
postgres=# SELECT floor(EXTRACT(epoch FROM (SELECT ('2023-09-15 12:00:00'::timestamp - '2023-09-13 19:00:00'::timestamp))) / 86400);
floor
-------
1 -- floorは小数点切り捨て
postgres=# SELECT ceil(EXTRACT(epoch FROM (SELECT ('2023-09-15 12:00:00'::timestamp - '2023-09-13 19:00:00'::timestamp))) / 86400);
ceil
-------
2 -- ceilは小数点切り上げ
timestamp型をUNIXエポック秒に変換
postgres=# select extract(epoch from '2023-09-05 12:00:00'::timestamp);
date_part
------------
1693915200