この記事はなに?
私は現在2x2x2ルービックキューブを解くロボットを開発中です。これはそのロボットのプログラムの解説記事集です。
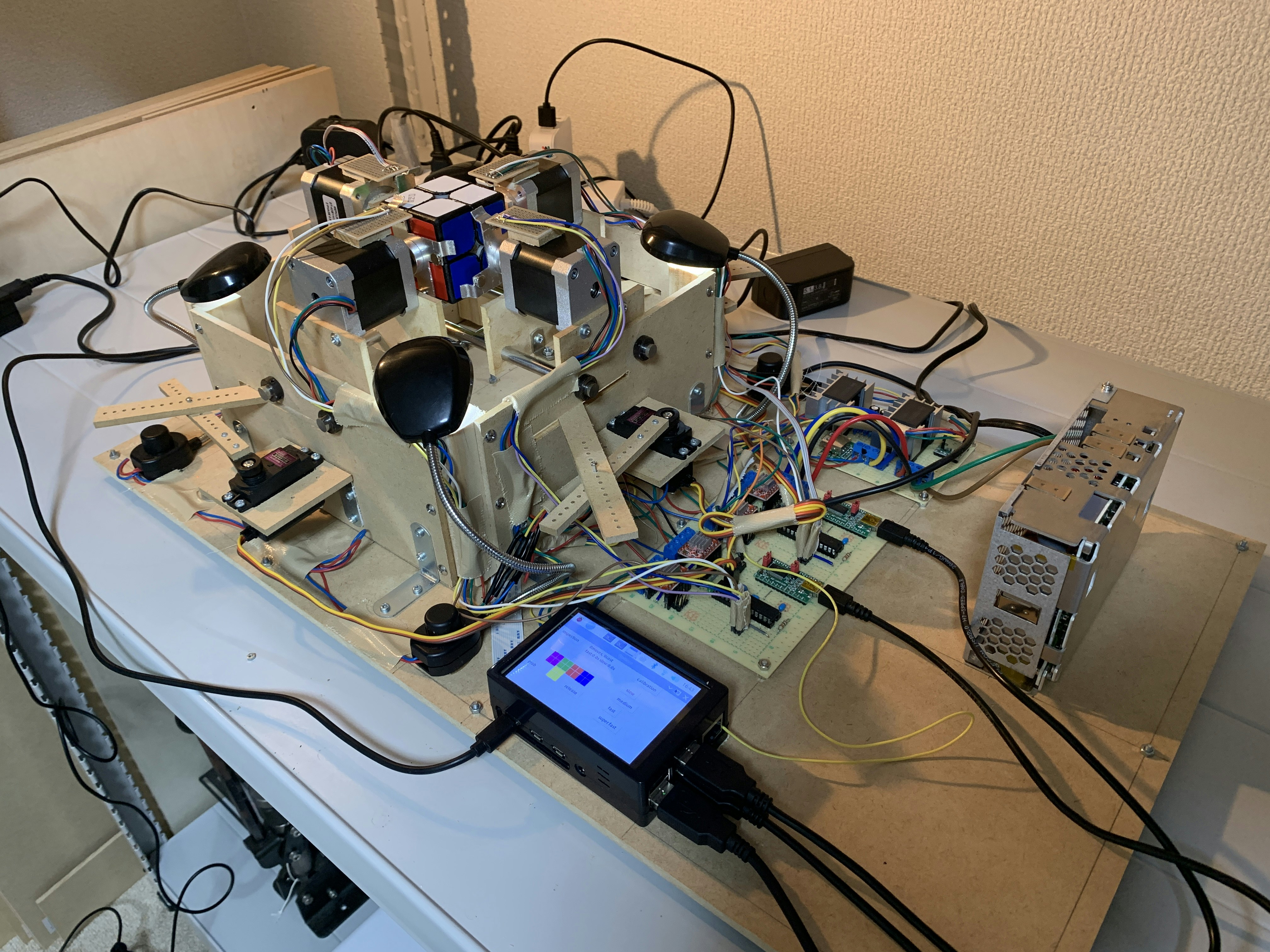
かつてこちらの記事に代表される記事集を書きましたが、この時からソフトウェアが大幅にアップデートされたので新しいプログラムについて紹介しようと思います。
該当するコードはこちらで公開しています。
関連する記事集
「ルービックキューブを解くロボットを作ろう!」
ルービックキューブロボットのソフトウェアをアップデートした
- 基本関数
- 事前計算
- 解法探索
- 状態認識
- 機械操作(Python)
- 機械操作(Arduino)
- 主要処理(本記事)
今回は主要処理編として、main.pyを紹介します。
モジュールのインポート
使うモジュールをインポートします。
import tkinter
from time import sleep
from basic_functions import *
from solver import solver
from controller import controller, grab_p, release_p, calibration, move_actuator
from detector import detector
Bluetoothの設定
このロボットはBluetoothで他のPCの画面上にリアルタイムで解いている経過時間を表示できます。そのための設定です(普段は使いません)。
# bluetoothを使うなら行う処理
bluetoothmode = False
if bluetoothmode:
subprocess.call(['sh', 'bluetooth_script.sh'])
PORT = 1
server_socket=bluetooth.BluetoothSocket( bluetooth.RFCOMM )
print("connect...")
server_socket.bind( ("",PORT ))
server_socket.listen(1)
client_socket,address = server_socket.accept()
print("connection success!!")
GUI
画面表示周りです。tkinterを使いました。
# GUIを作る
root = tkinter.Tk()
root.title("Soltvvo")
root.geometry("400x250")
grid = 20
offset = 50
entry = [[None for _ in range(8)] for _ in range(6)]
for i in range(6):
for j in range(8):
if 1 < i < 4 or 1 < j < 4:
entry[i][j] = tkinter.Entry(master=root, width=2, bg='gray')
entry[i][j].place(x = j * grid + offset, y = i * grid + offset)
inspection = tkinter.Button(root, text="inspection", command=inspection_p)
inspection.place(x=0, y=0)
solutionvar = tkinter.StringVar(master=root, value='')
solution = tkinter.Label(textvariable=solutionvar)
solution.place(x=120, y=0)
solvingtimevar = tkinter.StringVar(master=root, value='')
solvingtime = tkinter.Label(textvariable=solvingtimevar)
solvingtime.place(x=120, y=20)
grab = tkinter.Button(root, text="grab", command=grab_p)
grab.place(x=0, y=150)
release = tkinter.Button(root, text="release", command=release_p)
release.place(x=150, y=150)
calib = tkinter.Button(root, text='calibration', command=calibration)
calib.place(x=300, y=0)
start_slow = tkinter.Button(root, text="slow", command=start_slow_p)
start_slow.place(x=300, y=50)
start_medium = tkinter.Button(root, text="medium", command=start_medium_p)
start_medium.place(x=300, y=90)
start_fast = tkinter.Button(root, text="fast", command=start_fast_p)
start_fast.place(x=300, y=130)
start_superfast = tkinter.Button(root, text="super fast", command=start_superfast_p)
start_superfast.place(x=300, y=170)
root.mainloop()
パズルの認識から解法探索まで
パズルの認識と解法探索、採用する解法の選定です。ここで一つ留意点があります。このロボットは4つのアームでパズルを回します。よって、初期のパズルの向きによって速く解けるか否かが変わります。細かい話を割愛すると、2つの適切に選んだ向きで解法をそれぞれ探索し、よりコストの低い(速く解ける)解を採用すれば良いです。これを実装しました
''' インスペクション '''
''' Inspection '''
def inspection_p():
global solution
# 初期化
solution = []
solutionvar.set('')
for i in range(6):
for j in range(8):
if 1 < i < 4 or 1 < j < 4:
entry[i][j]['bg'] = 'gray'
# 通常の向きで色情報を取得、一度解法探索
colors0 = detector()
for i in range(6):
for j in range(8):
if 1 < i < 4 or 1 < j < 4:
if colors0[i][j] != '':
entry[i][j]['bg'] = dic[colors0[i][j]]
else:
entry[i][j]['bg'] = 'gray'
with open('log.txt', mode='w') as f:
f.write(str(colors0) + '\n')
solution0, cost0 = solver(colors0)
if solution0 == -1:
print('cannot solve!')
solutionvar.set('cannot solve!')
return
# パズルを90度回転させてもう一度解法探索
colors1 = rotate_colors(colors0)
solution1, cost1 = solver(colors1)
# コストの低い解を採用
if cost0 <= cost1:
solution = solution0
cost = cost0
with open('log.txt', mode='a') as f:
f.write('0\n')
else:
solution = solution1
cost = cost1
with open('log.txt', mode='a') as f:
f.write('1\n')
move_actuator(0, 0, -90, 200)
move_actuator(1, 0, 90, 200)
sleep(0.3)
if solution == -1:
solution = []
print('cannot solve!')
solutionvar.set('cannot solve!')
return
with open('log.txt', mode='a') as f:
f.write(str(cost) + '\n')
f.write(str(solution) + '\n')
# コストと想定タイムの表示
solutionvar.set('cost: ' + str(cost) + ' ex: ' + str(round(cost * 0.083, 2)) + 's')
# パズルを回す準備
grab = solution[0][0][0] % 2
for j in range(2):
move_actuator(j, grab, 1000)
sleep(0.2)
for j in range(2):
move_actuator(j, (grab + 1) % 2, 2000)
print(solution)
パズルを90度回転させるときに出てきたrotate_colors関数は以下です。この関数を使って色の情報を置換し、パズル全体の回転を表現します。
''' パズルを仮想的に回転させる '''
''' Rotate puzzle (don't rotate it in real world) '''
def rotate_colors(colors):
# 色の情報を置換する
replace = [
[[-1, -1], [-1, -1], [2, 2], [2, 3], [-1, -1], [-1, -1], [-1, -1], [-1, -1]],
[[-1, -1], [-1, -1], [3, 2], [3, 3], [-1, -1], [-1, -1], [-1, -1], [-1, -1]],
[[2, 1], [3, 1], [4, 2], [4, 3], [3, 4], [2, 4], [1, 3], [1, 2]],
[[2, 0], [3, 0], [5, 2], [5, 3], [3, 5], [2, 5], [0, 3], [0, 2]],
[[-1, -1], [-1, -1], [3, 7], [3, 6], [-1, -1], [-1, -1], [-1, -1], [-1, -1]],
[[-1, -1], [-1, -1], [2, 7], [2, 6], [-1, -1], [-1, -1], [-1, -1], [-1, -1]]
]
res = [['' for _ in range(8)] for _ in range(6)]
for i in range(6):
for j in range(8):
if 1 < i < 4 or 1 < j < 4:
res[replace[i][j][0]][replace[i][j][1]] = colors[i][j]
return res
運転
運転には4つほど速さに段階をつけました。それぞれの関数はcontrollerの引数が違うだけです。
''' 運転 '''
''' Drive '''
def start_slow_p():
# 安全運転
# Slow
global solution
solutionvar.set(controller(0.15, 0.15, 300, 1.2, solution))
solution = []
def start_medium_p():
# 通常運転
# Medium
global solution
solutionvar.set(controller(0.1, 0.1, 400, 1, solution))
solution = []
def start_fast_p():
# 速運転
# Fast
global solution
solutionvar.set(controller(0.095, 0.095, 550, 0.9, solution))
solution = []
def start_superfast_p():
# 爆速運転
# Super Fast
global solution
solutionvar.set(controller(0.1, 0.1, 600, 1, solution))
solution = []
まとめ
ここまで7つ、1週間かけて記事を連載しました。ここまで読んでくださりありがとうございました。特に解法探索の記事は誰かの役に立てるかなと思っています。なにか参考になったり、そして記事内のプログラムがあまり良くなかったりしたらコメントください!