ESP32を用いて,INA219の使用方法について解説していきたいと思います.
必要なもの
- お手元のパソコン
- INA219
- ESP32
- マイクロUSBコード×2
- マイクロUSB電源モジュール
- ジャンパワイヤ
以上の6つを揃えるところから始まります.
多分5000円以内に収まるのではないでしょうか.
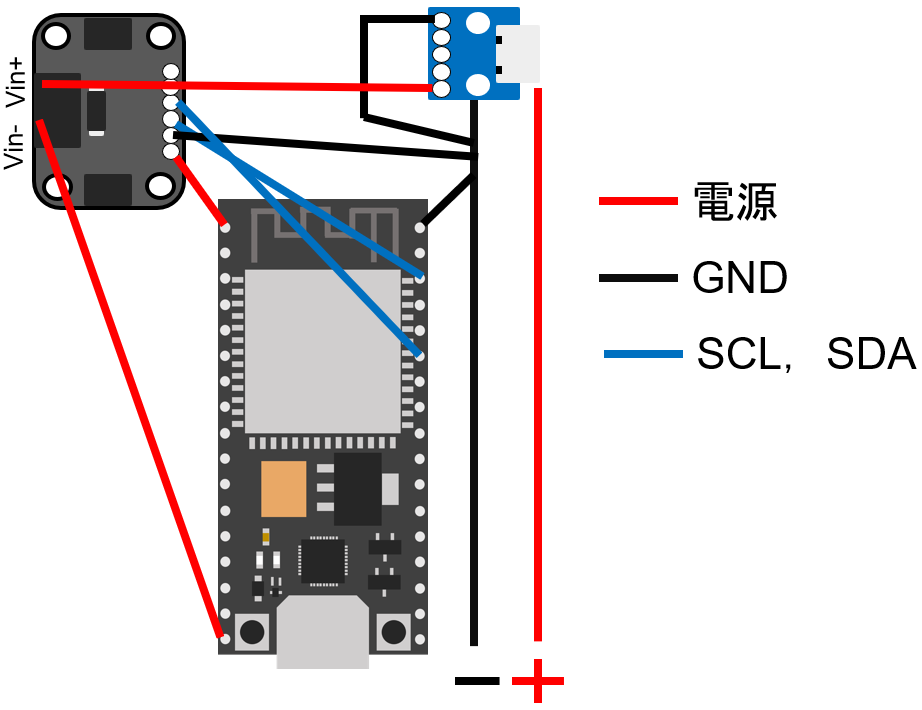
早速配線
配線図はこんな感じになります.
黒はGND 赤は電源 青はSCL,SDAになります.
プログラム
INA219MicroPythonプログラムをダウンロードします
以下がGitHubのページです.
https://github.com/chrisb2/pyb_ina219
そしたら中に
- ina219.py
- example.py
-
logging.py
の3つのファイルをダウンロードしてESP32にダウンロードしましょう.
乗っけときます.
ina219.py
"""MicroPython library for the INA219 sensor.
This library supports the INA219 sensor from Texas Instruments with
MicroPython using the I2C bus.
"""
import logging
import utime
from math import trunc
from micropython import const
class INA219:
"""Provides all the functionality to interact with the INA219 sensor."""
RANGE_16V = const(0) # Range 0-16 volts
RANGE_32V = const(1) # Range 0-32 volts
GAIN_1_40MV = const(0) # Maximum shunt voltage 40mV
GAIN_2_80MV = const(1) # Maximum shunt voltage 80mV
GAIN_4_160MV = const(2) # Maximum shunt voltage 160mV
GAIN_8_320MV = const(3) # Maximum shunt voltage 320mV
GAIN_AUTO = const(-1) # Determine gain automatically
ADC_9BIT = const(0) # 9-bit conversion time 84us.
ADC_10BIT = const(1) # 10-bit conversion time 148us.
ADC_11BIT = const(2) # 11-bit conversion time 2766us.
ADC_12BIT = const(3) # 12-bit conversion time 532us.
ADC_2SAMP = const(9) # 2 samples at 12-bit, conversion time 1.06ms.
ADC_4SAMP = const(10) # 4 samples at 12-bit, conversion time 2.13ms.
ADC_8SAMP = const(11) # 8 samples at 12-bit, conversion time 4.26ms.
ADC_16SAMP = const(12) # 16 samples at 12-bit,conversion time 8.51ms
ADC_32SAMP = const(13) # 32 samples at 12-bit, conversion time 17.02ms.
ADC_64SAMP = const(14) # 64 samples at 12-bit, conversion time 34.05ms.
ADC_128SAMP = const(15) # 128 samples at 12-bit, conversion time 68.10ms.
__ADC_CONVERSION = {
ADC_9BIT: "9-bit",
ADC_10BIT: "10-bit",
ADC_11BIT: "11-bit",
ADC_12BIT: "12-bit",
ADC_2SAMP: "12-bit, 2 samples",
ADC_4SAMP: "12-bit, 4 samples",
ADC_8SAMP: "12-bit, 8 samples",
ADC_16SAMP: "12-bit, 16 samples",
ADC_32SAMP: "12-bit, 32 samples",
ADC_64SAMP: "12-bit, 64 samples",
ADC_128SAMP: "12-bit, 128 samples"
}
__ADDRESS = 0x40
__REG_CONFIG = 0x00
__REG_SHUNTVOLTAGE = 0x01
__REG_BUSVOLTAGE = 0x02
__REG_POWER = 0x03
__REG_CURRENT = 0x04
__REG_CALIBRATION = 0x05
__RST = 15
__BRNG = 13
__PG1 = 12
__PG0 = 11
__BADC4 = 10
__BADC3 = 9
__BADC2 = 8
__BADC1 = 7
__SADC4 = 6
__SADC3 = 5
__SADC2 = 4
__SADC1 = 3
__MODE3 = 2
__MODE2 = 1
__MODE1 = 0
__OVF = 1
__CNVR = 2
__BUS_RANGE = [16, 32]
__GAIN_VOLTS = [0.04, 0.08, 0.16, 0.32]
__CONT_SH_BUS = 7
__AMP_ERR_MSG = ('Expected current %.3fA is greater '
'than max possible current %.3fA')
__RNG_ERR_MSG = ('Expected amps %.2fA, out of range, use a lower '
'value shunt resistor')
__VOLT_ERR_MSG = ('Invalid voltage range, must be one of: '
'RANGE_16V, RANGE_32V')
__LOG_FORMAT = '%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - INA219 %(message)s'
__LOG_MSG_1 = ('shunt ohms: %.3f, bus max volts: %d, '
'shunt volts max: %.2f%s, '
'bus ADC: %s, shunt ADC: %s')
__LOG_MSG_2 = ('calibrate called with: bus max volts: %dV, '
'max shunt volts: %.2fV%s')
__LOG_MSG_3 = ('Current overflow detected - '
'attempting to increase gain')
__SHUNT_MILLIVOLTS_LSB = 0.01 # 10uV
__BUS_MILLIVOLTS_LSB = 4 # 4mV
__CALIBRATION_FACTOR = 0.04096
# Max value supported value (65534 decimal) of the calibration register
# (D0 bit is always zero, p31 of spec)
__MAX_CALIBRATION_VALUE = 0xFFFE
# In the spec (p17) the current LSB factor for the minimum LSB is
# documented as 32767, but a larger value (100.1% of 32767) is used
# to guarantee that current overflow can always be detected.
__CURRENT_LSB_FACTOR = 32800
def __init__(self, shunt_ohms, i2c, max_expected_amps=None,
address=__ADDRESS, log_level=logging.ERROR):
"""Construct the class.
At a minimum pass in the resistance of the shunt resistor and I2C
interface to which the sensor is connected.
Arguments:
shunt_ohms -- value of shunt resistor in Ohms (mandatory).
i2c -- an instance of the I2C class from the *machine* module, either
I2C(1) or I2C(2) (mandatory).
max_expected_amps -- the maximum expected current in Amps (optional).
address -- the I2C address of the INA219, defaults to
*0x40* (optional).
log_level -- set to logging.DEBUG to see detailed calibration
calculations (optional).
"""
logging.basicConfig(level=log_level)
self._log = logging.getLogger("ina219")
self._i2c = i2c
self._address = address
self._shunt_ohms = shunt_ohms
self._max_expected_amps = max_expected_amps
self._min_device_current_lsb = self._calculate_min_current_lsb()
self._gain = None
self._auto_gain_enabled = False
def configure(self, voltage_range=RANGE_32V, gain=GAIN_AUTO,
bus_adc=ADC_12BIT, shunt_adc=ADC_12BIT):
"""Configure and calibrate how the INA219 will take measurements.
Arguments:
voltage_range -- The full scale voltage range, this is either 16V
or 32V represented by one of the following constants;
RANGE_16V, RANGE_32V (default).
gain -- The gain which controls the maximum range of the shunt
voltage represented by one of the following constants;
GAIN_1_40MV, GAIN_2_80MV, GAIN_4_160MV,
GAIN_8_320MV, GAIN_AUTO (default).
bus_adc -- The bus ADC resolution (9, 10, 11, or 12-bit) or
set the number of samples used when averaging results
represent by one of the following constants; ADC_9BIT,
ADC_10BIT, ADC_11BIT, ADC_12BIT (default),
ADC_2SAMP, ADC_4SAMP, ADC_8SAMP, ADC_16SAMP,
ADC_32SAMP, ADC_64SAMP, ADC_128SAMP
shunt_adc -- The shunt ADC resolution (9, 10, 11, or 12-bit) or
set the number of samples used when averaging results
represent by one of the following constants; ADC_9BIT,
ADC_10BIT, ADC_11BIT, ADC_12BIT (default),
ADC_2SAMP, ADC_4SAMP, ADC_8SAMP, ADC_16SAMP,
ADC_32SAMP, ADC_64SAMP, ADC_128SAMP
"""
self.__validate_voltage_range(voltage_range)
self._voltage_range = voltage_range
if self._max_expected_amps is not None:
if gain == self.GAIN_AUTO:
self._auto_gain_enabled = True
self._gain = self._determine_gain(self._max_expected_amps)
else:
self._gain = gain
else:
if gain != self.GAIN_AUTO:
self._gain = gain
else:
self._auto_gain_enabled = True
self._gain = self.GAIN_1_40MV
self._log.info('gain set to %.2fV', self.__GAIN_VOLTS[self._gain])
self._log.debug(
self.__LOG_MSG_1,
self._shunt_ohms, self.__BUS_RANGE[voltage_range],
self.__GAIN_VOLTS[self._gain],
self.__max_expected_amps_to_string(self._max_expected_amps),
self.__ADC_CONVERSION[bus_adc], self.__ADC_CONVERSION[shunt_adc])
self._calibrate(
self.__BUS_RANGE[voltage_range], self.__GAIN_VOLTS[self._gain],
self._max_expected_amps)
self._configure(voltage_range, self._gain, bus_adc, shunt_adc)
def voltage(self):
"""Return the bus voltage in volts."""
value = self._voltage_register()
return float(value) * self.__BUS_MILLIVOLTS_LSB / 1000
def supply_voltage(self):
"""Return the bus supply voltage in volts.
This is the sum of the bus voltage and shunt voltage. A
DeviceRangeError exception is thrown if current overflow occurs.
"""
return self.voltage() + (float(self.shunt_voltage()) / 1000)
def current(self):
"""Return the bus current in milliamps.
A DeviceRangeError exception is thrown if current overflow occurs.
"""
self._handle_current_overflow()
return self._current_register() * self._current_lsb * 1000
def power(self):
"""Return the bus power consumption in milliwatts.
A DeviceRangeError exception is thrown if current overflow occurs.
"""
self._handle_current_overflow()
return self._power_register() * self._power_lsb * 1000
def shunt_voltage(self):
"""Return the shunt voltage in millivolts.
A DeviceRangeError exception is thrown if current overflow occurs.
"""
self._handle_current_overflow()
return self._shunt_voltage_register() * self.__SHUNT_MILLIVOLTS_LSB
def sleep(self):
"""Put the INA219 into power down mode."""
configuration = self._read_configuration()
self._configuration_register(configuration & 0xFFF8)
def wake(self):
"""Wake the INA219 from power down mode."""
configuration = self._read_configuration()
self._configuration_register(configuration | 0x0007)
# 40us delay to recover from powerdown (p14 of spec)
utime.sleep_us(40)
def current_overflow(self):
"""Return true if the sensor has detect current overflow.
In this case the current and power values are invalid.
"""
return self._has_current_overflow()
def reset(self):
"""Reset the INA219 to its default configuration."""
self._configuration_register(1 << self.__RST)
def _handle_current_overflow(self):
if self._auto_gain_enabled:
while self._has_current_overflow():
self._increase_gain()
else:
if self._has_current_overflow():
raise DeviceRangeError(self.__GAIN_VOLTS[self._gain])
def _determine_gain(self, max_expected_amps):
shunt_v = max_expected_amps * self._shunt_ohms
if shunt_v > self.__GAIN_VOLTS[3]:
raise ValueError(self.__RNG_ERR_MSG % max_expected_amps)
gain = min(v for v in self.__GAIN_VOLTS if v > shunt_v)
return self.__GAIN_VOLTS.index(gain)
def _increase_gain(self):
self._log.info(self.__LOG_MSG_3)
gain = self._read_gain()
if gain < len(self.__GAIN_VOLTS) - 1:
gain = gain + 1
self._calibrate(self.__BUS_RANGE[self._voltage_range],
self.__GAIN_VOLTS[gain])
self._configure_gain(gain)
# 1ms delay required for new configuration to take effect,
# otherwise invalid current/power readings can occur.
utime.sleep_ms(1)
else:
self._log.info('Device limit reach, gain cannot be increased')
raise DeviceRangeError(self.__GAIN_VOLTS[gain], True)
def _configure(self, voltage_range, gain, bus_adc, shunt_adc):
configuration = (
voltage_range << self.__BRNG | gain << self.__PG0 |
bus_adc << self.__BADC1 | shunt_adc << self.__SADC1 |
self.__CONT_SH_BUS)
self._configuration_register(configuration)
def _calibrate(self, bus_volts_max, shunt_volts_max,
max_expected_amps=None):
self._log.info(self.__LOG_MSG_2,
bus_volts_max, shunt_volts_max,
self.__max_expected_amps_to_string(max_expected_amps))
max_possible_amps = shunt_volts_max / self._shunt_ohms
self._log.info("max possible current: %.3fA", max_possible_amps)
self._current_lsb = \
self._determine_current_lsb(max_expected_amps, max_possible_amps)
self._log.info("current LSB: %.3e A/bit", self._current_lsb)
self._power_lsb = self._current_lsb * 20
self._log.info("power LSB: %.3e W/bit", self._power_lsb)
max_current = self._current_lsb * 32767
self._log.info("max current before overflow: %.4fA", max_current)
max_shunt_voltage = max_current * self._shunt_ohms
self._log.info("max shunt voltage before overflow: %.4fmV",
max_shunt_voltage * 1000)
calibration = trunc(self.__CALIBRATION_FACTOR /
(self._current_lsb * self._shunt_ohms))
self._log.info("calibration: 0x%04x (%d)", calibration, calibration)
self._calibration_register(calibration)
def _determine_current_lsb(self, max_expected_amps, max_possible_amps):
if max_expected_amps is not None:
if max_expected_amps > round(max_possible_amps, 3):
raise ValueError(self.__AMP_ERR_MSG %
(max_expected_amps, max_possible_amps))
self._log.info("max expected current: %.3fA", max_expected_amps)
if max_expected_amps < max_possible_amps:
current_lsb = max_expected_amps / self.__CURRENT_LSB_FACTOR
else:
current_lsb = max_possible_amps / self.__CURRENT_LSB_FACTOR
else:
current_lsb = max_possible_amps / self.__CURRENT_LSB_FACTOR
if current_lsb < self._min_device_current_lsb:
current_lsb = self._min_device_current_lsb
return current_lsb
def _configuration_register(self, register_value):
self._log.debug("configuration: 0x%04x", register_value)
self.__write_register(self.__REG_CONFIG, register_value)
def _read_configuration(self):
return self.__read_register(self.__REG_CONFIG)
def _calculate_min_current_lsb(self):
return self.__CALIBRATION_FACTOR / \
(self._shunt_ohms * self.__MAX_CALIBRATION_VALUE)
def _read_gain(self):
configuration = self._read_configuration()
gain = (configuration & 0x1800) >> self.__PG0
self._log.info("gain is currently: %.2fV", self.__GAIN_VOLTS[gain])
return gain
def _configure_gain(self, gain):
configuration = self._read_configuration()
configuration = configuration & 0xE7FF
self._configuration_register(configuration | (gain << self.__PG0))
self._gain = gain
self._log.info("gain set to: %.2fV" % self.__GAIN_VOLTS[gain])
def _calibration_register(self, register_value):
self._log.debug("calibration: 0x%04x" % register_value)
self.__write_register(self.__REG_CALIBRATION, register_value)
def _has_current_overflow(self):
ovf = self._read_voltage_register() & self.__OVF
return (ovf == 1)
def _voltage_register(self):
register_value = self._read_voltage_register()
return register_value >> 3
def _read_voltage_register(self):
return self.__read_register(self.__REG_BUSVOLTAGE)
def _current_register(self):
return self.__read_register(self.__REG_CURRENT, True)
def _shunt_voltage_register(self):
return self.__read_register(self.__REG_SHUNTVOLTAGE, True)
def _power_register(self):
return self.__read_register(self.__REG_POWER)
def __validate_voltage_range(self, voltage_range):
if voltage_range > len(self.__BUS_RANGE) - 1:
raise ValueError(self.__VOLT_ERR_MSG)
def __write_register(self, register, register_value):
self.__log_register_operation("write", register, register_value)
register_bytes = self.__to_bytes(register_value)
self._i2c.writeto_mem(self._address, register, register_bytes)
def __to_bytes(self, register_value):
return bytearray([(register_value >> 8) & 0xFF, register_value & 0xFF])
def __read_register(self, register, negative_value_supported=False):
register_bytes = self._i2c.readfrom_mem(self._address, register, 2)
register_value = int.from_bytes(register_bytes, 'big')
if negative_value_supported:
# Two's compliment
if register_value > 32767:
register_value -= 65536
self.__log_register_operation("read", register, register_value)
return register_value
def __log_register_operation(self, msg, register, value):
# performance optimisation
if logging._level == logging.DEBUG:
binary = '{0:#018b}'.format(value)
self._log.debug("%s register 0x%02x: 0x%04x %s",
msg, register, value, binary)
def __max_expected_amps_to_string(self, max_expected_amps):
if max_expected_amps is None:
return ''
else:
return ', max expected amps: %.3fA' % max_expected_amps
class DeviceRangeError(Exception):
"""This exception is throw to prevent invalid readings.
Invalid readings occur When the current is greater than allowed given
calibration of the device.
"""
__DEV_RNG_ERR = ('Current out of range (overflow), '
'for gain %.2fV')
def __init__(self, gain_volts, device_max=False):
"""Construct the class."""
msg = self.__DEV_RNG_ERR % gain_volts
if device_max:
msg = msg + ', device limit reached'
super(DeviceRangeError, self).__init__(msg)
self.gain_volts = gain_volts
self.device_limit_reached = device_max
logging.py
import sys
CRITICAL = 50
ERROR = 40
WARNING = 30
INFO = 20
DEBUG = 10
NOTSET = 0
_level_dict = {
CRITICAL: "CRIT",
ERROR: "ERROR",
WARNING: "WARNING",
INFO: "INFO",
DEBUG: "DEBUG",
NOTSET: "NOTSET"
}
_stream = sys.stderr
class Logger:
level = NOTSET
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
def _level_str(self, level):
l = _level_dict.get(level)
if l is not None:
return l
return "LVL%s" % level
def setLevel(self, level):
self.level = level
def isEnabledFor(self, level):
return level >= (self.level or _level)
def log(self, level, msg, *args):
if level >= (self.level or _level):
_stream.write("%s:%s:" % (self._level_str(level), self.name))
if not args:
print(msg, file=_stream)
else:
print(msg % args, file=_stream)
def debug(self, msg, *args):
self.log(DEBUG, msg, *args)
def info(self, msg, *args):
self.log(INFO, msg, *args)
def warning(self, msg, *args):
self.log(WARNING, msg, *args)
def error(self, msg, *args):
self.log(ERROR, msg, *args)
def critical(self, msg, *args):
self.log(CRITICAL, msg, *args)
def exc(self, e, msg, *args):
self.log(ERROR, msg, *args)
sys.print_exception(e, _stream)
def exception(self, msg, *args):
self.exc(sys.exc_info()[1], msg, *args)
_level = INFO
_loggers = {}
def getLogger(name):
if name in _loggers:
return _loggers[name]
l = Logger(name)
_loggers[name] = l
return l
def info(msg, *args):
getLogger(None).info(msg, *args)
def debug(msg, *args):
getLogger(None).debug(msg, *args)
def basicConfig(level=INFO, filename=None, stream=None, format=None):
global _level, _stream
_level = level
if stream:
_stream = stream
if filename is not None:
print("logging.basicConfig: filename arg is not supported")
if format is not None:
print("logging.basicConfig: format arg is not supported")
example.py
from machine import I2C, Pin
from ina219 import INA219
from logging import INFO
I2C_INTERFACE_NO = 2
SHUNT_OHMS = 0.1 # Check value of shunt used with your INA219
i2c = I2C(-1, scl = Pin(22), sda = Pin(21))
ina = INA219(SHUNT_OHMS, i2c, log_level=INFO)
ina.configure()
print("Bus Voltage: %.3f V" % ina.voltage())
print("Current: %.3f mA" % ina.current())
print("Power: %.3f mW" % ina.power())
以上です.これらをESP32にいれてください.
example.pyを実行すれば,コードが実行された瞬間の電圧電流電力がプリントされると思います. 以下の画像が実行結果になります.
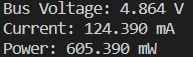
データを取り続けたい人はwhile文回したりしてみてください.
注意してほしいところがあります.
Bus VoltageとあるのですがUSBが刺さってるものによって値が変わります.なのでPowerもつられて値が変わっちゃいます.そこで電力が知りたい人は電流に×3.3してあげてくださいそしたら消費電力[mW]が出ると思います.
というのもINA219は3.3Vで動作してるからです.
おわりに
最後まで読んでくれたらありがとう,そうじゃない人もありがとう.
IoTデバイスには振り回されっぱなしです.
がんばろう