概要
EC2をWebサーバーとして利用する際に、EC2までの通信をHTTPSで暗号化したいケースがあると思います。
そんな時に便利なのがCertbotです。今回は、Certbotを使ってEC2のSSL化を試してみます。
Certbotとは
Let's Encryptを認証局とした無料かつ自動でSSL/TLSサーバー証明書を発行することができる無料のOSSツールです。
ACME (Automatic Certificate Management Environment)という証明書の管理を自動化するプロトコルを使い、Let's Encryptに対してSSL/TLSサーバー証明書の検証及び発行を実施します。
ACM (AWS Certificate Manager)ではできないのか
結論、できます。
ACMは各証明書のプロビジョニング及び管理するマネージドサービスです。
- Amazonの認証局 (Amazon Trust Services)から発行したパブリック証明書
- ACM Private Certificate Authority (プライベート認証局)から発行したプライベート証明書
- インポートしたサードパーティー製のパブリック/プライベート証明書
ACMで管理する証明書をプロビジョニングできるAWSサービスは公式サイトに記載されている通りです。
そのうちの一つにあるAWS Nitro EnclavesというEC2の機能を利用すれば、ACMで管理する証明書を使ってEC2への通信をHTTPSとすることが可能です。
ただし、利用可能なインスタンスタイプ及びOSに制限があります。
無料証明書ってどうなのか
以下の記事が非常にわかりやすいため掲載させていただきます。
実践
実際にCertbotを使って無料のSSL/TLSサーバー証明書を作成し、EC2にHTTPSで繋いで行きましょう。
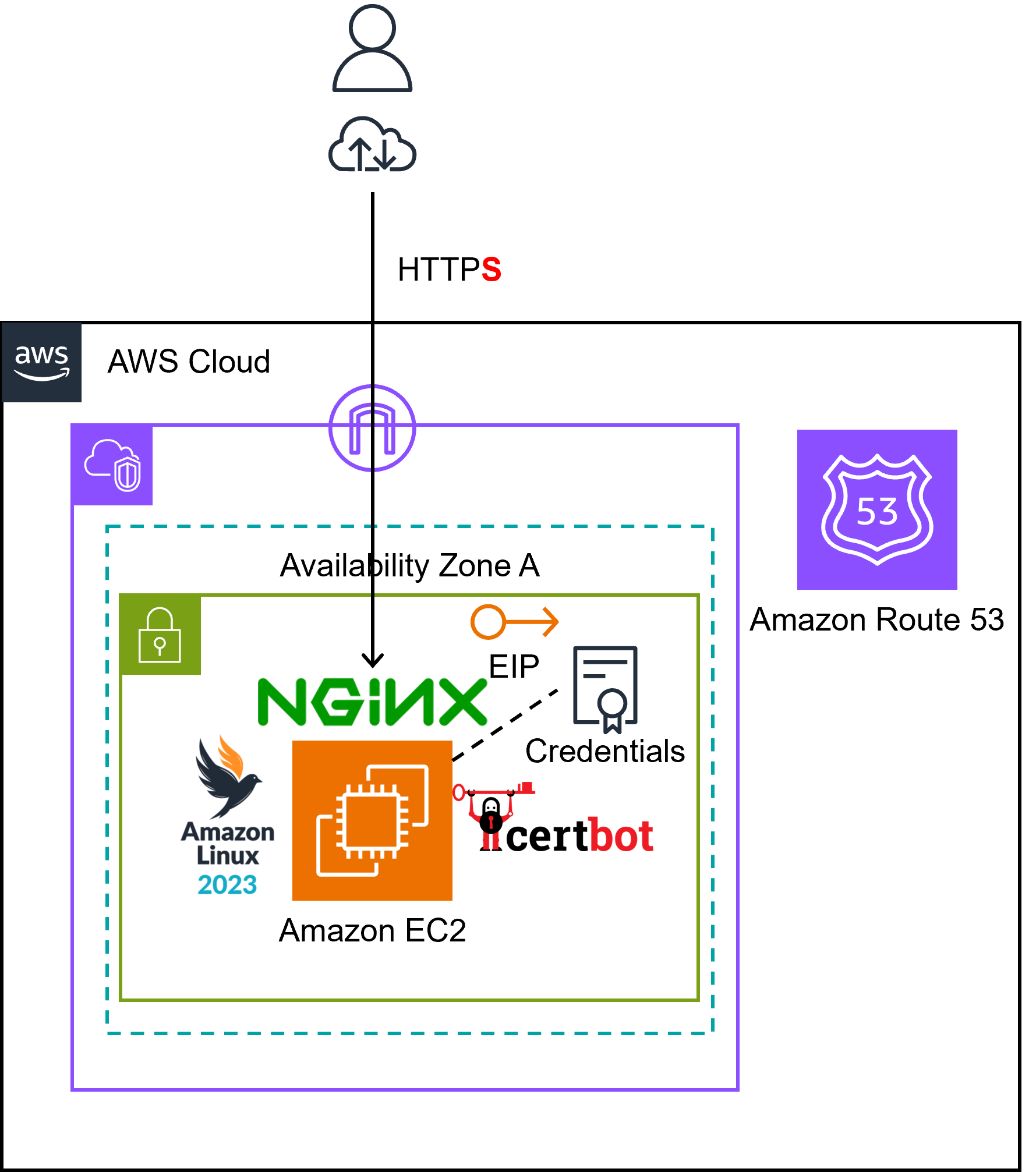
構成図は以下の通りです。詳細はGitHubを参照してみてください。
前提条件
- ドメイン取得済みで、EC2に対するAレコードが登録済みであること
- 以下作業は
rootユーザーで実施していきます
Nginxインストール
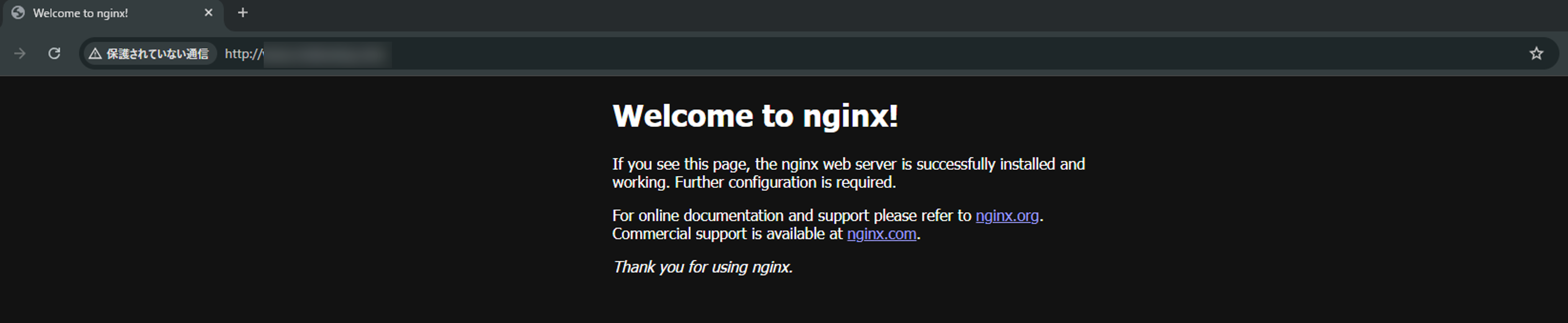
まずはNginxをインストールし、ブラウザからHTTPでアクセスできるかを確認していきます。
パッケージリスト更新
# dnf update
インストール
# dnf install nginx -y
Nginx起動&自動起動設定
# systemctl enable --now nginx
HTTPでブラウザからアクセス確認
Python仮想環境設定
Certbotのインストール方法はDockerなどもありますが、今回はpip (Pythonパッケージ管理ツール)を使った方法で実施していきます。
具体的には、venv (仮想環境ツール)を使ってPython仮想環境を作成し、その環境にCertbotをインストールします。そのための準備をしていきましょう。
パッケージインストール
- python3: Python
- augeas-libs: Apacheプラグイン
# dnf install python3 augeas-libs -y
仮想環境作成
# mkdir /opt/certbot
# python3 -m venv /opt/certbot
# /opt/certbot/bin/pip install --upgrade pip
Certbotインストール
Certbot&Nginx用パッケージインストール
# /opt/certbot/bin/pip install certbot certbot-nginx
シンボリックリンク作成
# ln -s /opt/certbot/bin/certbot /usr/bin/certbot
SSL/TLSサーバー証明書作成
nginx.confファイル修正
後述するコマンドを実行すると、Certbotが自動でnginx.confを修正してくれます。
ただその際に、ファイル内のserver_nameを確認するため、事前に修正します。
# For more information on configuration, see:
# * Official English Documentation: http://nginx.org/en/docs/
# * Official Russian Documentation: http://nginx.org/ru/docs/
user nginx;
worker_processes auto;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log notice;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
# Load dynamic modules. See /usr/share/doc/nginx/README.dynamic.
include /usr/share/nginx/modules/*.conf;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
types_hash_max_size 4096;
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
# Load modular configuration files from the /etc/nginx/conf.d directory.
# See http://nginx.org/en/docs/ngx_core_module.html#include
# for more information.
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
- server_name _;
+ server_name www.example.com; # 自身の登録するドメイン名に修正
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
# Load configuration files for the default server block.
include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
error_page 404 /404.html;
location = /404.html {
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
}
}
# Settings for a TLS enabled server.
#
# server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# listen [::]:443 ssl;
# http2 on;
# server_name _;
# root /usr/share/nginx/html;
#
# ssl_certificate "/etc/pki/nginx/server.crt";
# ssl_certificate_key "/etc/pki/nginx/private/server.key";
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 10m;
# ssl_ciphers PROFILE=SYSTEM;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
#
# # Load configuration files for the default server block.
# include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
#
# error_page 404 /404.html;
# location = /404.html {
# }
#
# error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
# location = /50x.html {
# }
# }
}
証明書作成&Nginx設定ファイル自動編集
# certbot --nginx
上記コマンドを実行すると、メールアドレスや登録するドメイン情報の入力が求められます。
nginx.confの確認
実際の変更点は以下の通りです。
# For more information on configuration, see:
# * Official English Documentation: http://nginx.org/en/docs/
# * Official Russian Documentation: http://nginx.org/ru/docs/
user nginx;
worker_processes auto;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log notice;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
# Load dynamic modules. See /usr/share/doc/nginx/README.dynamic.
include /usr/share/nginx/modules/*.conf;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
types_hash_max_size 4096;
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
# Load modular configuration files from the /etc/nginx/conf.d directory.
# See http://nginx.org/en/docs/ngx_core_module.html#include
# for more information.
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
server {
server_name www.example.com;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
or # Load configuration files for the default server block.
include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
error_page 404 /404.html;
location = /404.html {
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
}
+ listen [::]:443 ssl ipv6only=on; # managed by Certbot
+ listen 443 ssl; # managed by Certbot
+ ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/www.example.com/fullchain.pem; # managed by Certbot
+ ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/www.example.com/privkey.pem; # managed by Certbot
+ include /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-nginx.conf; # managed by Certbot
+ ssl_dhparam /etc/letsencrypt/ssl-dhparams.pem; # managed by Certbot
}
# Settings for a TLS enabled server.
#
# server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# listen [::]:443 ssl;
# http2 on;
# server_name _;
# root /usr/share/nginx/html;
#
# ssl_certificate "/etc/pki/nginx/server.crt";
# ssl_certificate_key "/etc/pki/nginx/private/server.key";
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 10m;
# ssl_ciphers PROFILE=SYSTEM;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
#
# # Load configuration files for the default server block.
# include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
#
# error_page 404 /404.html;
# location = /404.html {
# }
#
# error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
# location = /50x.html {
# }
# }
+ server {
+ if ($host = www.example.com) {
+ return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
+ } # managed by Certbot
+
+
+ listen 80;
+ listen [::]:80;
+ server_name www.example.com;
+ return 404; # managed by Certbot
+}}
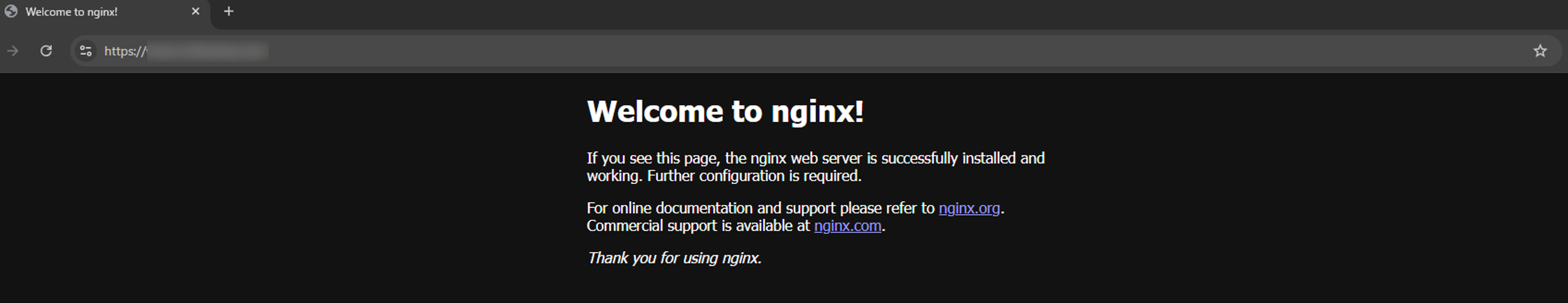
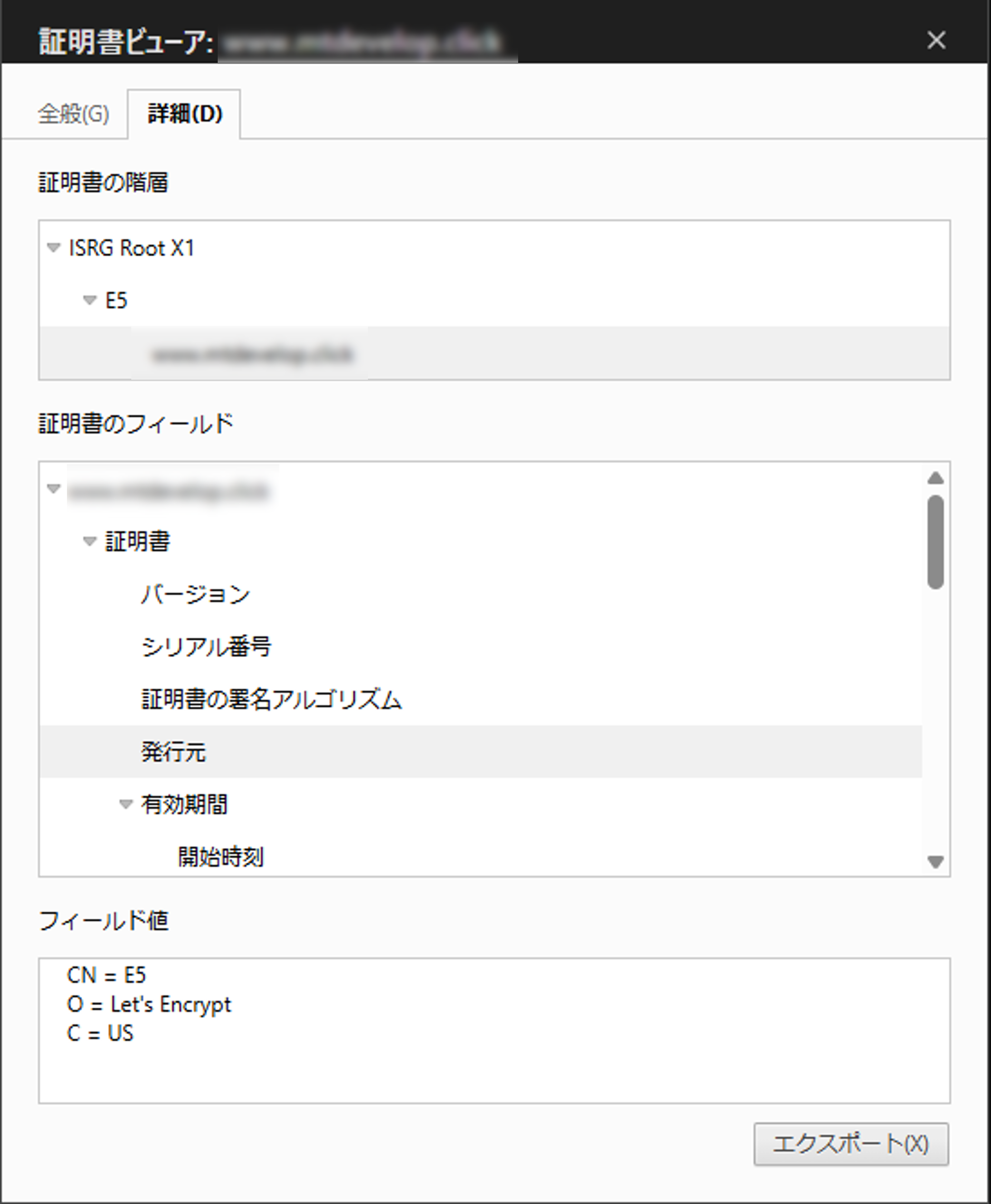
動作確認
証明書もLet's Encryptから発行されているのが確認できます。
自動更新設定(おまけ)
# echo "0 0,12 * * * root /opt/certbot/bin/python -c 'import random; import time; time.sleep(random.random() * 3600)' && sudo certbot renew -q" | sudo tee -a /etc/crontab > /dev/null
証明書失効(おまけ)
# /opt/certbot/bin/certbot revoke --cert-path /etc/letsencrypt/live/www.example.com/fullchain.pem
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Would you like to delete the certificate(s) you just revoked, along with all
earlier and later versions of the certificate?
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
(Y)es (recommended)/(N)o: Y
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
The following certificate(s) are selected for deletion:
* www.example.com
WARNING: Before continuing, ensure that the listed certificates are not being
used by any installed server software (e.g. Apache, nginx, mail servers).
Deleting a certificate that is still being used will cause the server software
to stop working. See https://certbot.org/deleting-certs for information on
deleting certificates safely.
Are you sure you want to delete the above certificate(s)?
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
(Y)es/(N)o: Y
Deleted all files relating to certificate www.example.com.
Congratulations! You have successfully revoked the certificate that was located at /etc/letsencrypt/live/www.example.com/fullchain.pem.
証明書削除(おまけ)
# /opt/certbot/bin/certbot delete --cert-name www.example.com
まとめ
今回はCertbotを使ったEC2のSSL化を実施してみました。
やってみると非常に簡単でした。
今回はLet's EncryptがCertbotへのドメイン認証方式としてHTTP-01 チャレンジを利用しているため、認証する際には80番ポートの解放が必要となります。自動更新設定を入れるとなると常時80番ポートの解放が必要となるため、本番環境での利用ではDNS-01 チャレンジ方式の採用を検討した方が良いかなと思います。
この記事が誰かの役に立てば幸いです。