要約
- ウィンドウ管理の煩雑さとメニューバーの混雑を解消するツールを紹介
- キーボード操作だけで効率的に作業できる環境を構築
- すべて無料または無料版で十分に使えるツールを厳選
はじめに
Macで作業していると、ウィンドウの配置に時間を取られたり、メニューバーがアイコンで溢れたり、どのウィンドウがアクティブなのかわからなくなったりしませんか?
特に、AI時代の今、ウィンドウを行き来する機会は多くなっていると思います。
この記事では、2025年に導入して本当に作業効率が上がったMac用ユーティリティツールを5つ紹介します。マウスに手を伸ばす回数が劇的に減り、無駄な操作が削減され、情報が整理された快適な作業環境を実現できました。
すべてのツールは無料または無料版で十分に使用できます。まずは気になったツールから試してみることをおすすめします。
対象読者
- Macでの作業効率を上げたい人
- ウィンドウ管理やメニューバーの煩雑さに悩んでいる人
- キーボード中心の操作環境を構築したい人
1. AeroSpace - タイル型ウィンドウマネージャー
概要
AeroSpaceは、i3ライクなタイル型ウィンドウマネージャーです。ウィンドウを手動で配置する手間と、複数のSpacesを管理する手間を一気に解消できます。
i3とは、Linux向けの軽量・高速なタイル型ウィンドウマネージャーです。ウィンドウを自動で格子状に配置し、キーボード操作を中心にレイアウト変更や移動・切り替えを行えるのが特徴です。
~/.aerospace.tomlに自分好みの設定を書くと、かなり快適に使えるはずです。
デフォルトの設定は公式サイトからコピペし、配置する必要があります。
解決できる課題
- ウィンドウを綺麗に並べる作業の手間
- マルチディスプレイでのウィンドウ管理の煩雑さ
- Spacesの切り替えと管理の面倒さ
おすすめの使い方
基本的に 1 ワークスペースに 1 アプリケーション
ワークスペースとは、作業スペースのことで、デフォルトでは1-9, A-Zまであります。大量に作業スペースを効率的に管理できるのが、既存のSpacesとの違いでもあります。
ワークスペースにてウィンドウを開くと、自動でワークスペースを埋めるようにウィンドウが広がります。
デフォルトの設定にはなぜか0が含まれていないので、設定ファイルに追加しておきましょう。使ってみるとわかりますが、ワークスペースはいくらあっても良いです。(個人の感想)
3つ以上のウィンドウの場合、アコーディオンを使う
AeroSpaceには2つの配置方法があります。
-
Tiles:
- 伝統的なタイルレイアウト
- ウィンドウ同士が均等に並び、画面を無駄なく使える
- コード+ブラウザの2分割や、資料+ノートの並行作業に向いています
-
Accordion:
- 現在フォーカス中のウィンドウに比重を置くレイアウト
- 他は折りたたむようにコンパクト化
- 3つ以上のウィンドウで「1つに集中、必要時だけ周辺をチラ見」するスタイルに最適
Alt + /でタイルに、Alt + ,でアコーディオンにできます。
Raycastと組み合わせる
Raycastのアプリランチャー機能と組み合わせると、以下のようなワークフローが実現できます:
-
Alt + TでTerminalを起動 -
Alt + Shift + 0でTerminalをワークスペース0に移動 - いつでも
Alt + 0でTerminalに移動
Finderなどはフロートにする
タイルにしたくないアプリはいくつかあります。例えば、Finderやシステム設定、スティッキーズなどが該当するでしょう。
それらはタイル(固定)にせず、フロート(浮いた状態)にすることが可能です。
設定に以下を追加します。
[[on-window-detected]]
if.app-id = 'com.apple.finder'
run = 'layout floating'
私の使用している設定
# Place a copy of this config to ~/.aerospace.toml
# After that, you can edit ~/.aerospace.toml to your liking
# Config version for compatibility and deprecations
# Fallback value (if you omit the key): config-version = 1
config-version = 2
# You can use it to add commands that run after AeroSpace startup.
# Available commands : https://nikitabobko.github.io/AeroSpace/commands
after-startup-command = [
'exec-and-forget borders active_color=0xffd08770 inactive_color=0xff494d64 width=12.0 hidpi=on'
]
# Start AeroSpace at login
start-at-login = true
# Normalizations. See: https://nikitabobko.github.io/AeroSpace/guide#normalization
enable-normalization-flatten-containers = true
enable-normalization-opposite-orientation-for-nested-containers = true
# See: https://nikitabobko.github.io/AeroSpace/guide#layouts
# The 'accordion-padding' specifies the size of accordion padding
# You can set 0 to disable the padding feature
accordion-padding = 30
# Possible values: tiles|accordion
default-root-container-layout = 'tiles'
# Possible values: horizontal|vertical|auto
# 'auto' means: wide monitor (anything wider than high) gets horizontal orientation,
# tall monitor (anything higher than wide) gets vertical orientation
default-root-container-orientation = 'auto'
# Mouse follows focus when focused monitor changes
# Drop it from your config, if you don't like this behavior
# See https://nikitabobko.github.io/AeroSpace/guide#on-focus-changed-callbacks
# See https://nikitabobko.github.io/AeroSpace/commands#move-mouse
# Fallback value (if you omit the key): on-focused-monitor-changed = []
on-focused-monitor-changed = ['move-mouse monitor-lazy-center']
# You can effectively turn off macOS "Hide application" (cmd-h) feature by toggling this flag
# Useful if you don't use this macOS feature, but accidentally hit cmd-h or cmd-alt-h key
# Also see: https://nikitabobko.github.io/AeroSpace/goodies#disable-hide-app
automatically-unhide-macos-hidden-apps = false
# List of workspaces that should stay alive even when they contain no windows,
# even when they are invisible.
# This config version is only available since 'config-version = 2'
# Fallback value (if you omit the key): persistent-workspaces = []
persistent-workspaces = ["1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "A", "B", "C",
"D", "E", "F", "G", "H", "I", "J", "K", "L", "M", "N", "O",
"P", "Q", "R", "S", "T", "U", "V", "W", "X", "Y", "Z"]
# A callback that runs every time binding mode changes
# See: https://nikitabobko.github.io/AeroSpace/guide#binding-modes
# See: https://nikitabobko.github.io/AeroSpace/commands#mode
on-mode-changed = []
# Possible values: (qwerty|dvorak|colemak)
# See https://nikitabobko.github.io/AeroSpace/guide#key-mapping
[key-mapping]
preset = 'qwerty'
# Gaps between windows (inner-*) and between monitor edges (outer-*).
# Possible values:
# - Constant: gaps.outer.top = 8
# - Per monitor: gaps.outer.top = [{ monitor.main = 16 }, { monitor."some-pattern" = 32 }, 24]
# In this example, 24 is a default value when there is no match.
# Monitor pattern is the same as for 'workspace-to-monitor-force-assignment'.
# See:
# https://nikitabobko.github.io/AeroSpace/guide#assign-workspaces-to-monitors
[gaps]
inner.horizontal = 10
inner.vertical = 10
outer.left = 10
outer.bottom = 10
outer.top = 10
outer.right = 10
# 'main' binding mode declaration
# See: https://nikitabobko.github.io/AeroSpace/guide#binding-modes
# 'main' binding mode must be always presented
# Fallback value (if you omit the key): mode.main.binding = {}
[mode.main.binding]
# All possible keys:
# - Letters. a, b, c, ..., z
# - Numbers. 0, 1, 2, ..., 9
# - Keypad numbers. keypad0, keypad1, keypad2, ..., keypad9
# - F-keys. f1, f2, ..., f20
# - Special keys. minus, equal, period, comma, slash, backslash, quote, semicolon,
# backtick, leftSquareBracket, rightSquareBracket, space, enter, esc,
# backspace, tab, pageUp, pageDown, home, end, forwardDelete,
# sectionSign (ISO keyboards only, european keyboards only)
# - Keypad special. keypadClear, keypadDecimalMark, keypadDivide, keypadEnter, keypadEqual,
# keypadMinus, keypadMultiply, keypadPlus
# - Arrows. left, down, up, right
# All possible modifiers: cmd, alt, ctrl, shift
# All possible commands: https://nikitabobko.github.io/AeroSpace/commands
# See: https://nikitabobko.github.io/AeroSpace/commands#exec-and-forget
# You can uncomment the following lines to open up terminal with alt + enter shortcut
# (like in i3)
# alt-enter = '''exec-and-forget osascript -e '
# tell application "Terminal"
# do script
# activate
# end tell'
# '''
# See: https://nikitabobko.github.io/AeroSpace/commands#layout
alt-slash = 'layout tiles horizontal vertical'
alt-comma = 'layout accordion horizontal vertical'
# See: https://nikitabobko.github.io/AeroSpace/commands#focus
alt-h = 'focus left'
alt-j = 'focus down'
alt-k = 'focus up'
alt-l = 'focus right'
# See: https://nikitabobko.github.io/AeroSpace/commands#move
alt-shift-h = 'move left'
alt-shift-j = 'move down'
alt-shift-k = 'move up'
alt-shift-l = 'move right'
# See: https://nikitabobko.github.io/AeroSpace/commands#resize
alt-minus = 'resize smart -50'
alt-semicolon = 'resize smart +50'
# See: https://nikitabobko.github.io/AeroSpace/commands#workspace
alt-1 = 'workspace 1'
alt-2 = 'workspace 2'
alt-3 = 'workspace 3'
alt-4 = 'workspace 4'
alt-5 = 'workspace 5'
alt-6 = 'workspace 6'
alt-7 = 'workspace 7'
alt-8 = 'workspace 8'
alt-9 = 'workspace 9'
alt-0 = 'workspace 0'
# See: https://nikitabobko.github.io/AeroSpace/commands#move-node-to-workspace
alt-shift-1 = 'move-node-to-workspace 1'
alt-shift-2 = 'move-node-to-workspace 2'
alt-shift-3 = 'move-node-to-workspace 3'
alt-shift-4 = 'move-node-to-workspace 4'
alt-shift-5 = 'move-node-to-workspace 5'
alt-shift-6 = 'move-node-to-workspace 6'
alt-shift-7 = 'move-node-to-workspace 7'
alt-shift-8 = 'move-node-to-workspace 8'
alt-shift-9 = 'move-node-to-workspace 9'
alt-shift-0 = 'move-node-to-workspace 0'
alt-shift-a = 'move-node-to-workspace A'
alt-shift-b = 'move-node-to-workspace B'
alt-shift-c = 'move-node-to-workspace C'
alt-shift-d = 'move-node-to-workspace D'
alt-shift-e = 'move-node-to-workspace E'
alt-shift-f = 'move-node-to-workspace F'
alt-shift-g = 'move-node-to-workspace G'
alt-shift-i = 'move-node-to-workspace I'
alt-shift-m = 'move-node-to-workspace M'
alt-shift-n = 'move-node-to-workspace N'
alt-shift-o = 'move-node-to-workspace O'
alt-shift-p = 'move-node-to-workspace P'
alt-shift-q = 'move-node-to-workspace Q'
alt-shift-r = 'move-node-to-workspace R'
alt-shift-s = 'move-node-to-workspace S'
alt-shift-t = 'move-node-to-workspace T'
alt-shift-u = 'move-node-to-workspace U'
alt-shift-v = 'move-node-to-workspace V'
alt-shift-w = 'move-node-to-workspace W'
alt-shift-x = 'move-node-to-workspace X'
alt-shift-y = 'move-node-to-workspace Y'
alt-shift-z = 'move-node-to-workspace Z'
# See: https://nikitabobko.github.io/AeroSpace/commands#workspace-back-and-forth
alt-tab = 'workspace-back-and-forth'
# See: https://nikitabobko.github.io/AeroSpace/commands#move-workspace-to-monitor
alt-shift-tab = 'move-workspace-to-monitor --wrap-around next'
# See: https://nikitabobko.github.io/AeroSpace/commands#mode
alt-shift-semicolon = 'mode service'
[workspace-to-monitor-force-assignment]
1 = 'main' # メインディスプレイ
2 = 'main'
3 = 'main'
4 = 'main'
5 = 'main'
6 = 'secondary' # サブディスプレイ(拡張側)
7 = 'secondary'
8 = 'secondary'
9 = 'secondary'
0 = 'secondary'
# 'service' binding mode declaration.
# See: https://nikitabobko.github.io/AeroSpace/guide#binding-modes
[mode.service.binding]
esc = ['reload-config', 'mode main']
r = ['flatten-workspace-tree', 'mode main'] # reset layout
f = ['layout floating tiling', 'mode main'] # Toggle between floating and tiling layout
backspace = ['close-all-windows-but-current', 'mode main']
# sticky is not yet supported https://github.com/nikitabobko/AeroSpace/issues/2
#s = ['layout sticky tiling', 'mode main']
alt-shift-h = ['join-with left', 'mode main']
alt-shift-j = ['join-with down', 'mode main']
alt-shift-k = ['join-with up', 'mode main']
alt-shift-l = ['join-with right', 'mode main']
# スティッキーズ
[[on-window-detected]]
if.app-id = 'com.apple.Stickies'
run = 'layout floating'
# システム設定
[[on-window-detected]]
if.app-id = 'com.apple.systempreferences'
run = 'layout floating'
# Finder
[[on-window-detected]]
if.app-id = 'com.apple.finder'
run = 'layout floating'
慣れるまで1〜2週間かかりますが、慣れてしまえば手放せなくなります。
参考
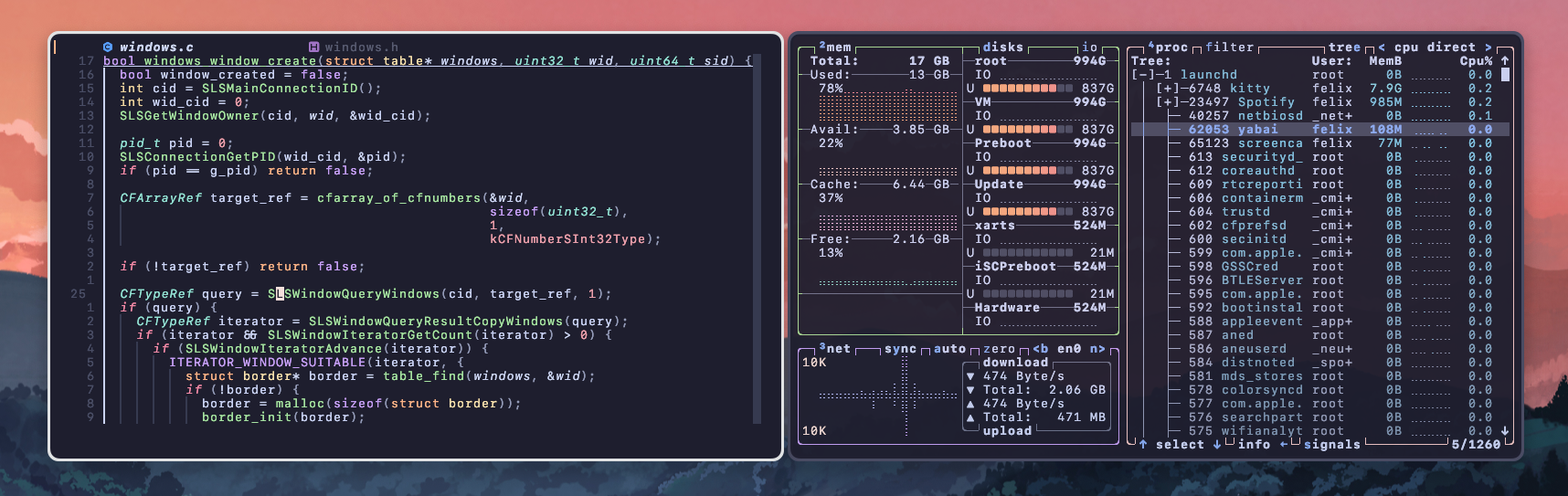
2. JankyBorders - アクティブウィンドウの可視化
概要
JankyBordersは、アクティブなウィンドウにボーダーを表示するシンプルなツールです。
解決できる課題
- アクティブなウィンドウがわかりづらい
- キーボード入力がどこに行くのか不明瞭
- 複数ウィンドウを開いているときの混乱
AeroSpaceとの相性
AeroSpaceでタイル型のレイアウトにすると、複数のウィンドウが並びます。そのときにどのウィンドウがアクティブなのか一目でわかるため、JankyBordersは必須のツールと言えます。
設定例
太めのボーダーがおすすめ
ボーダーは太くするほど視認性が上がります。合わせてAeroSpace側のギャップも大きくすることで、洗練された見た目になります。
# AeroSpaceの設定ファイルに追加
after-startup-command = [
'exec-and-forget borders active_color=0xffd08770 inactive_color=0xff494d64 width=12.0 hidpi=on'
]
active_colorとinactive_colorは好みの色に変更できます。上記はオレンジっぽい色です。
参考
3. Ice - メニューバー整理ツール
概要
Iceは、メニューバーのアイコンを隠したり表示したりできるツールです。
解決できる課題
- メニューバーがアイコンで溢れて煩雑
- 必要なときだけ表示したいアイコンがある
- 情報が視覚的に散らかっている
使い方
メニューに常に表示するアイコンと、メニューをクリックすると出てくるアイコンに分類できます。作業に集中したいときはすっきりとしたメニューバーにできます。
常に表示するアイコンを絞ることで、すっきりとしたメニューバーを実現できます。
実際のメニューバー
設定画面
やや不安定な部分もありますが、定期的にアップデートされており、改善が続いています。
参考
4. RunCat - システム負荷の可視化
概要
RunCatは、メニューバーで走る猫のアニメーションでCPU負荷を表示するツールです。
解決できる課題
- PCが重いときに原因がすぐにはわからない
- バックグラウンドで重い処理が走っているか不明
- システムモニターを開く手間
おすすめポイント
見た目がかわいい
機能的な面だけでなく、走る猫がかわいいという点も重要です。作業中にふと目に入ると癒されます。
猫以外にも、パロットやランナーなどのキャラクターを選択できます。
シンプルに負荷を確認できる
Activity Monitorやbtopなどを開かなくても、パッと見でCPU負荷が高いかどうかわかります。負荷が高いと猫の走る速度が速くなるため、直感的に理解できます。
特にアプリ開発では、ビルド処理でCPU負荷が急増しがちです。RunCatなら、メニューバーのアニメーション速度で「裏でビルドが走っているか」を即座に判断できます。
参考
5. BetterDisplay - 外部ディスプレイ制御
概要
BetterDisplayは、外部ディスプレイの輝度や音量、解像度などをソフトウェア側から制御できるツールです。MonitorControlの上位互換と言えます。
以前はMonitorControlを使っていましたが、今ではBetterDisplayに乗り換えて良かったなと感じています。
解決できる課題
- 外部ディスプレイの輝度調整が面倒
- モニターの物理ボタンを押す手間
- 解像度の切り替えが煩雑
DDC通信による制御
DDC(Display Data Channel)通信に対応しており、物理ボタンを触らずにソフトウェアから直接ディスプレイを制御できます。キーボードショートカットで輝度や音量を調整できるため、作業の流れを止めません。
実際に、輝度を調整するショートカットでサブモニターの明るさが変わるのは感動的でした。
注意点
安いハブを使用している場合
DDC通信は、使用しているUSB-Cハブやケーブルによってはサポートされていない場合があります。
安価なUSB-Cハブを使用している場合、DDC通信が正常に機能しない可能性があります。MacBook Proの場合、HDMIポートやThunderboltポートに直接接続すると動作する可能性が高いです。
無料版でも十分
有料版が用意されていますが、無料版でも基本的な機能は十分に使用できます。有料版ではより高度な機能が解放されますが、輝度・音量・解像度の調整だけであれば無料版で問題ありません。
参考
まとめ
この記事では、2025年に導入して作業効率が大きく向上した5つのツールを紹介しました:
- AeroSpace - タイル型ウィンドウマネージャーで配置の手間を削減
- JankyBorders - アクティブウィンドウを一目で識別
- Ice - メニューバーをすっきり整理
- RunCat - システム負荷を可愛く可視化
- BetterDisplay - 外部ディスプレイを快適に制御
これらのツールを組み合わせることで、マウスに手を伸ばす回数が減り、無駄な操作が削減され、情報が整理された快適な作業環境を実現できました。
特にAeroSpace + JankyBorders + Raycastの組み合わせは、慣れるまで時間はかかりますが、慣れてしまえば手放せなくなる強力なワークフローです。