はじめに
こんにちは、しゅんです。
この記事では、Appleがついに公開した新しい画像生成AI技術、STARFlowについて紹介します。記事執筆時(2025/12/02 3:25頃)、Appleは約1時間前にSTARFlowのモデルをHugging Faceで正式に公開しました。この技術の詳細と使い方を解説します。
まず、本編に入る前に、少しだけ私の個人的な考えを述べさせてください。Appleに対する批判が多い中で、AI分野、特に最近の LLM(生成AI) に関する技術の遅れが言われがちですが、私はそれには賛同できません。もちろんAppleのファンではありませんが、技術が進化している領域であれば、AIに遅れているという評価は不公平だと思っています。Appleは確実に多くのAI技術を活用しており、AIの進化に貢献しているのです。この個人的な意見をまず述べておきます。
では、長くなりましたが、本題に入ります。
そもそもSTARFlowとは?
論文
公式サイト
公式HuggingFace
公式 Github
もっと詳細を書いてる記事もあるので、ぜひみてみてください
STARFlow(Scalable Transformer Auto-Regressive Flow)は、Appleが開発した最先端の画像生成AI技術で、従来の画像生成手法である 拡散モデル(Diffusion Models) とは異なるアプローチを採用しています。STARFlowは、正規化フロー(Normalizing Flows)という手法を基盤にしており、これをTransformerアーキテクチャと組み合わせることで、高解像度かつ高品質な画像や動画の生成を実現しています。
STARFlowの技術的な特徴
-
可逆的な変換
STARFlowでは、従来の拡散モデルが使用する反復的なデノイジング(ノイズ除去)の代わりに、可逆的な関数を用いて生成プロセスを進めます。この可逆的な変換により、生成過程が数学的に追跡しやすく、予測可能な方法で進行します。これにより、計算リソースの効率的な使用が可能となり、より高速で安定した生成が可能になります。 -
Transformerアーキテクチャ
Transformerアーキテクチャは、自然言語処理や画像生成において高いパフォーマンスを発揮している技術です。STARFlowでは、このアーキテクチャを正規化フローと組み合わせ、複雑で高次元な生成タスクに対応しています。 -
高解像度の画像と動画生成
STARFlowは、テキストから高解像度の画像や動画を生成する能力を持っています。STARFlow-Vというモデルは、最大480pの解像度で、16fpsの動画を生成でき、動画生成タスクにも強力なパフォーマンスを発揮します。
何がすごい?
STARFlowがすごい理由は、技術的に革新性を持ち、従来の拡散モデルと比べて計算効率が優れていることです。具体的なポイントは以下の通りです:
-
正規化フローとTransformerの融合
STARFlowは、正規化フローを基盤にしており、これをTransformerアーキテクチャと組み合わせることで、生成プロセスが安定し、効率的に学習が進みます。これにより、従来の拡散モデルよりも迅速で効率的に高品質な生成を実現します。 -
計算効率と推論速度の向上
従来の拡散モデルは、ノイズ除去の過程を繰り返す必要があるため、計算リソースを大量に消費します。STARFlowでは、Deep-shallowアーキテクチャを採用しており、計算効率を大幅に向上させています。これにより、推論速度も速く、生成に必要な時間を短縮できます。 -
潜在空間での学習
STARFlowは、画像データを圧縮した潜在空間で学習を行い、その後高解像度の画像を生成します。この方法により、計算資源を効率よく使用し、情報損失を最小限に抑えつつ、高品質な画像や動画を生成することができます。 -
FIDスコアでの高評価
FIDスコア(Fréchet Inception Distance)は、生成された画像の品質を測るための指標です。STARFlowは、DALL-E 3やStable Diffusionといった最先端の拡散モデルと比較しても、非常に高いFIDスコアを記録しており、現代の画像生成技術の中でも非常に優れた性能を示しています。 -
動画生成能力
STARFlowは、テキストから高解像度の動画を生成する能力を持っています。STARFlow-Vは、最大480pの解像度で、最大16fpsの動画を生成でき、テキストから動画生成という新しい領域にも対応しています。
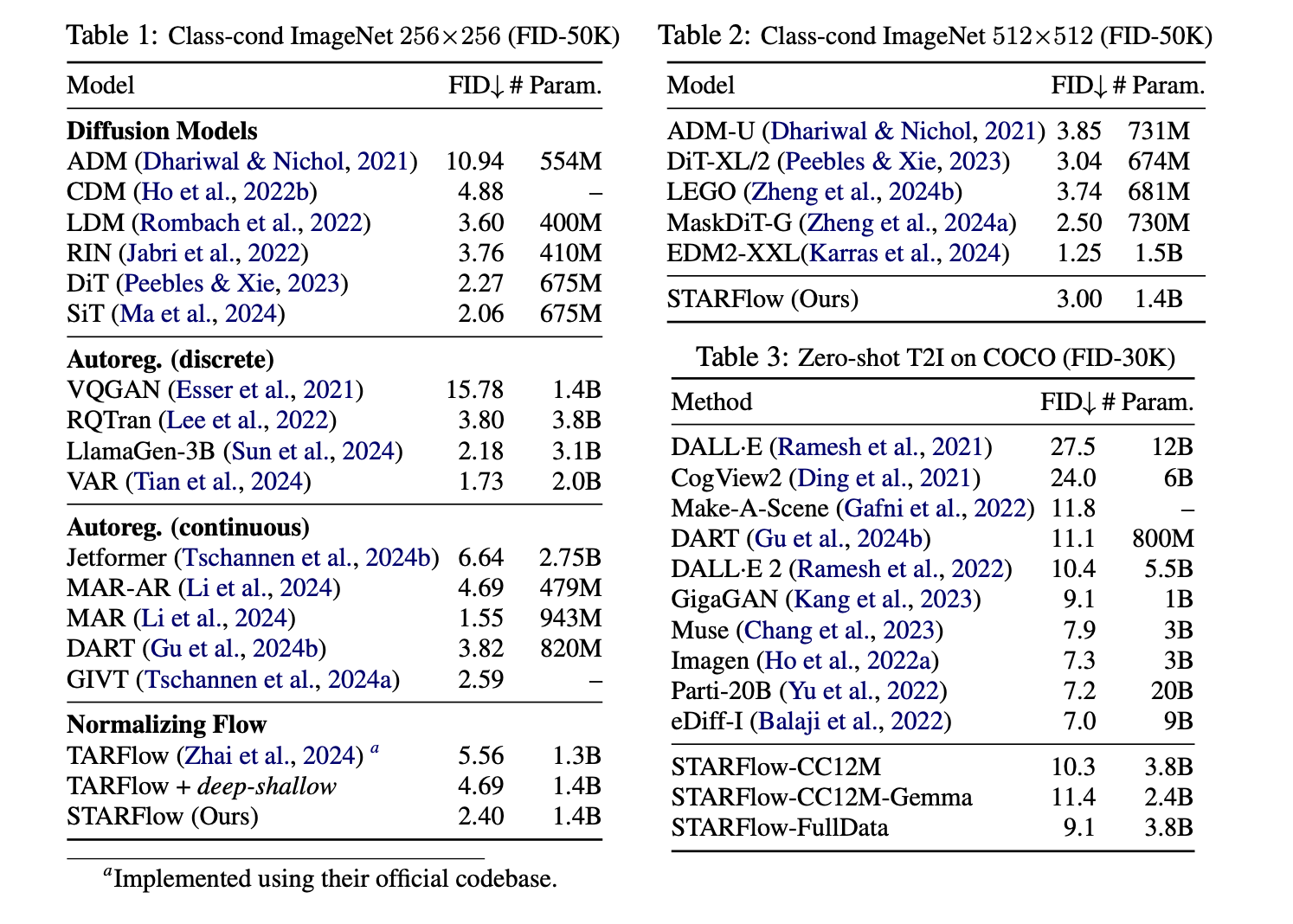
STARFlowのベンチマーク評価
STARFlowのFIDスコア(Fréchet Inception Distance)やパラメータ数に関する比較が示されています。
1. Class-cond ImageNet 256×256 (FID-50K)
- STARFlowのFIDスコアは2.40で、これは拡散モデルの中では優れたスコアです。特に、TARFlowやTARFlow + deep-shallow(それぞれ5.56、4.69)のスコアを大きく下回っています。このことは、STARFlowが正規化フローを用いて、拡散モデルよりも高効率で高品質な画像を生成できることを示唆しています。
2. Class-cond ImageNet 512×512 (FID-50K)
- STARFlowのFIDスコアは3.00であり、解像度が512×512に上がっても性能を落とすことなく、高品質な生成が可能であることが確認できます。DiT-XL/2(3.04)やLEGO(3.74)といった最先端モデルと同等のパフォーマンスを発揮しています。
3. Zero-shot T2I on COCO (FID-30K)
- STARFlowは、FIDスコア 9.1を記録しています。これは、GigaGAN(9.1)やImagen(7.3)に並ぶ優れた結果です。また、他の大規模なテキストから画像生成モデル(例えばDALL-E 2やCogView2)と比べて、同等またはそれ以上のパフォーマンスを示しています。
STARFlowの強みと弱み
強み
- 計算効率:拡散モデルに比べて、正規化フローを使用することで、生成プロセスが効率的で高速です。特に、推論速度が速い点は大きな利点です。
- 高品質な画像生成:FIDスコアが示すように、STARFlowは高解像度画像生成において優れたパフォーマンスを示し、特に低FIDスコアを維持しています。
- 動画生成能力:テキストからの画像生成だけでなく、動画生成にも対応し、特に動画生成では高解像度を保ちながら16fpsで長時間の動画を生成できます。
弱み
- 低解像度でのパフォーマンス:低解像度画像生成では、拡散モデルに比べてやや劣る場合があります。特に、非常に小さな画像やミニマルなタスクでは、もう少し最適化の余地があるかもしれません。
- 計算リソース:高解像度や長時間動画生成時には、依然として高い計算リソースが必要であり、推論速度の向上が求められます。
改善点
- 低解像度生成における改善:低解像度生成時における性能を強化し、より高品質な画像を生成できるよう最適化が進むことが期待されます。
- 推論速度の高速化:計算資源の節約と推論速度の改善に注力し、リソースの制限がある環境でもより効率的に利用できるようになるでしょう。
- さらに大規模なモデルに向けたスケーリング:現在のFIDスコアの優れた結果をさらに拡大し、より大規模なデータセットやタスクにも対応できるようになることが求められます。
今後の展望:
- オンデバイスAIへの応用が進むことで、AppleのiPhoneやMac上でも高品質な画像生成が可能になる未来が見込まれます。
- 実用的なアプリケーション(画像修復、指示ベースの画像編集)への応用が期待されます。STARFlowの可逆性を活かしたインタラクティブな画像編集が可能になるかもしれません。
環境構築
現在、Text-to-Video Generationは公開されていないため、今回はText-to-Image Generationの使用方法に関しての解説となります。動画生成のモデルstarflow-v_7B_t2v_caus_480p_v3.pthについては、Appleからのアップデートを待つ必要があります。
Issues3でstarflow-v_7B_t2v_caus_480p_v3.pth動画生成のモデルのことを質問投げてみたら、Appleの返事はまだアップしていないことが判明しました。
このモデルはまだアップロードされていません。更新します
公式は環境構築shのスクリプト→ conda とpipのrequest形式提供してます。
僕の記事を読んでる方ならわかると思いますが、Condaとjupyter 大嫌いなので、今回もvenv環境でやります。
# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/apple/ml-starflow
cd ml-starflow
# Set up conda environment (recommended)
bash scripts/setup_conda.sh
# Or install dependencies manually
pip install -r requirements.txt
ここでエラーは発生するはずです!
ERROR: Ignored the following versions that require a different python version: 1.6.2 Requires-Python >=3.7,<3.10; 1.6.3 Requires-Python >=3.7,<3.10; 1.7.0 Requires-Python >=3.7,<3.10; 1.7.1 Requires-Python >=3.7,<3.10; 1.7.2 Requires-Python >=3.7,<3.11; 1.7.3 Requires-Python >=3.7,<3.11; 1.8.0 Requires-Python >=3.8,<3.11; 1.8.0rc1 Requires-Python >=3.8,<3.11; 1.8.0rc2 Requires-Python >=3.8,<3.11; 1.8.0rc3 Requires-Python >=3.8,<3.11; 1.8.0rc4 Requires-Python >=3.8,<3.11; 1.8.1 Requires-Python >=3.8,<3.11
ERROR: Could not find a version that satisfies the requirement decord (from versions: none)
ERROR: No matching distribution found for decord
解決方法
- Mac の場合はpython 3.10 にすること。
- 元々の
decordをeva-decordに変更 - MPS ではなく CPU/CUDA で実行
- MPS で回すと黒画像になったり極端に遅かったため、MPS をデバイス候補から除外。
- CUDA があれば CUDA、なければ CPU を選ぶように sample.py を修正。
ここで遭遇したエラーは先ほど伝えてた通りに、基本はCUDAで動かすのが前提なので、色々とコードを更新して、色々検証して、mpsでは生成された画像は真っ黒になったり、演算が逆に遅くなったり、なのでCPUモードで回してます。一部修正したコードも載せます。
以下は修正したrequirements.txt
jupyter>=1.0.0
transformers
accelerate
torchinfo
einops
scipy
webdataset
sentencepiece
wandb[media]
torchmetrics[image]
simple_parsing
eva-decord
opencv-python
psutil
git+https://github.com/KeKsBoTer/torch-dwt
git+https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers.git
pyyaml
av==12.3.0
以下修正したコード
PR出したが、受け入れるかどうかはわからないが、一応Mac対応のコードです
sample.py デバイス判定を CUDA → CPU、MPS 分岐/キャッシュ処理を削除
sample.py
@@ -14,6 +14,7 @@ Usage:
"""
import argparse
+import contextlib
import copy
import pathlib
import time
@@ -48,13 +49,17 @@ DEFAULT_CAPTIONS = {
'template5': "A realistic selfie of a llama standing in front of a classic Ivy League building on the Princeton University campus. He is smiling gently, wearing his iconic wild hair and mustache, dressed in a wool sweater and collared shirt. The photo has a vintage, slightly sepia tone, with soft natural lighting and leafy trees in the background, capturing an academic and historical vibe.",
}
-
+def resolve_device() -> torch.device:
+ """Choose the best available device: CUDA -> CPU (explicitly disable MPS)."""
+ if torch.cuda.is_available():
+ return torch.device("cuda")
+ return torch.device("cpu")
def setup_model_and_components(args: argparse.Namespace) -> Tuple[torch.nn.Module, Optional[torch.nn.Module], tuple]:
"""Initialize and load the model, VAE, and text encoder."""
dist = utils.Distributed()
- device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
+ device = resolve_device()
# Set random seed
utils.set_random_seed(args.seed + dist.rank)
@@ -81,7 +86,9 @@ def setup_model_and_components(args: argparse.Namespace) -> Tuple[torch.nn.Modul
print(f"Loading checkpoint from local path: {args.checkpoint_path}")
state_dict = torch.load(args.checkpoint_path, map_location='cpu')
model.load_state_dict(state_dict, strict=False)
- del state_dict; torch.cuda.empty_cache()
+ del state_dict
+ if device.type == "cuda":
+ torch.cuda.empty_cache()
# Set model to eval mode and disable gradients
for p in model.parameters():
@@ -190,6 +197,9 @@ def main(args: argparse.Namespace) -> None:
trainer_dict = vars(trainer_args)
trainer_dict.update(vars(args))
args = argparse.Namespace(**trainer_dict)
+ device = resolve_device()
+ if device.type != "cuda":
+ args.fsdp = 0 # CPU/MPS fallback
# Handle target length configuration for video
if args.target_length is not None:
@@ -205,7 +215,8 @@ def main(args: argparse.Namespace) -> None:
args.context_length = args.local_attn_window - 1
# Override some settings for sampling
- args.fsdp = 1 # sampling using FSDP if available.
+ if device.type == "cuda":
+ args.fsdp = 1 # sampling using FSDP if available.
if args.use_pretrained_lm is not None:
args.text = args.use_pretrained_lm
@@ -223,19 +234,24 @@ def main(args: argparse.Namespace) -> None:
# Prepare captions and sampling parameters
fixed_y, fixed_idxs, num_samples, caption_name = prepare_captions(args, dist)
- print(f'Sampling {num_samples} from {args.caption} on {dist.world_size} GPU(s)')
+ print(f'Sampling {num_samples} from {args.caption} on {dist.world_size} device(s) [{device.type}]')
get_noise = get_noise_shape(args, vae)
sampling_kwargs = build_sampling_kwargs(args, caption_name)
noise_std = args.target_noise_std if args.target_noise_std else args.noise_std
# Start sampling
- print(f'Starting sampling with global batch size {args.sample_batch_size}x{dist.world_size} GPUs')
- torch.cuda.synchronize()
+ print(f'Starting sampling with global batch size {args.sample_batch_size}x{dist.world_size} devices')
+ if device.type == "cuda":
+ torch.cuda.synchronize()
start_time = time.time()
with torch.no_grad():
- with torch.autocast(device_type='cuda', dtype=torch.float32):
+ if device.type == "cuda":
+ autocast_ctx = torch.autocast(device_type='cuda', dtype=torch.float32)
+ else:
+ autocast_ctx = contextlib.nullcontext()
+ with autocast_ctx:
for i in tqdm.tqdm(range(int(np.ceil(num_samples / (args.sample_batch_size * dist.world_size))))):
# Determine aspect ratio and image shape
x_aspect = args.aspect_ratio if args.mix_aspect else None
@@ -290,7 +306,9 @@ def main(args: argparse.Namespace) -> None:
# Generate samples
samples = model(noise, y, reverse=True, kv_caches=kv_caches, **sampling_kwargs)
- del kv_caches; torch.cuda.empty_cache() # free up memory
+ del kv_caches
+ if device.type == "cuda":
+ torch.cuda.empty_cache() # free up memory
# Apply denoising if enabled
samples = process_denoising(
@@ -330,7 +348,8 @@ def main(args: argparse.Namespace) -> None:
)
# Print timing statistics
- torch.cuda.synchronize()
+ if device.type == "cuda":
+ torch.cuda.synchronize()
elapsed_time = time.time() - start_time
print(f'{model_name} cfg {args.cfg:.2f}, bsz={args.sample_batch_size}x{dist.world_size}, '
f'time={elapsed_time:.2f}s, speed={num_samples / elapsed_time:.2f} images/s')
dataset.py(multiprocessing Manager を遅延初期化、macOS の spawn で落ちないように Lock 取得を安全化)
dataset.py
@@
-# Initialize multiprocessing manager
-manager = torch.multiprocessing.Manager()
+# Lazy multiprocessing manager; creating at import breaks spawn on macOS
+manager = None
+
+
+def get_mp_manager():
+ """Create or return a global multiprocessing Manager."""
+ global manager
+ if manager is None:
+ manager = torch.multiprocessing.Manager()
+ return manager
@@
class OnlineImageTarDataset(ImageTarDataset):
max_retry_n = 20
max_read = 4096
- tar_keys_lock = manager.Lock() if manager is not None else None
def __init__(self, dataset_tsv, image_size, batch_size=None, **kwargs):
super().__init__(dataset_tsv, image_size, **kwargs)
+
+ mgr = get_mp_manager()
+ self.tar_keys_lock = mgr.Lock() if mgr is not None else None
@@
for key in self.tar_lists.keys():
repeat = int(self.weights.get(key, 1))
self.reset_tar_keys.extend([key] * repeat)
- self.tar_keys = manager.list(self.reset_tar_keys) if manager is not None else list(self.reset_tar_keys)
+ self.tar_keys = mgr.list(self.reset_tar_keys) if mgr is not None else list(self.reset_tar_keys)
@@
def _get_next_key(self):
- with self.tar_keys_lock:
+ lock = self.tar_keys_lock
+ if lock:
+ with lock:
+ if not self.tar_keys or len(self.tar_keys) == 0:
+ xprint(f'[WARN] all dataset exhausted... this should not happen usually')
+ self.tar_keys.extend(list(self.reset_tar_keys)) # reset
+ random.shuffle(self.tar_keys)
+ return self.tar_keys.pop(0) # remove and return the first key
+ else:
if not self.tar_keys or len(self.tar_keys) == 0:
xprint(f'[WARN] all dataset exhausted... this should not happen usually')
self.tar_keys.extend(list(self.reset_tar_keys)) # reset
random.shuffle(self.tar_keys)
- return self.tar_keys.pop(0) # remove and return the first key
+ return self.tar_keys.pop(0)
@@
# shuffle the image list
random.shuffle(self.tar_lists[key]) # shuffle the list
- with self.tar_keys_lock:
- self.tar_keys.append(key) # return the key to the list so other workers can use it
+ if self.tar_keys_lock:
+ with self.tar_keys_lock:
+ self.tar_keys.append(key) # return the key to the list so other workers can use it
+ else:
+ self.tar_keys.append(key)
utils/inference.py(デバイスに応じた cache clear / to(device) に修正、MPS/CPU 両対応)
####utils/inference.py
- torch.cuda.empty_cache()
+ # Track the original device (CUDA/MPS/CPU) and clear cache when supported
+ device = samples.device
+ if torch.cuda.is_available():
+ torch.cuda.empty_cache()
+ elif torch.backends.mps.is_available():
+ torch.mps.empty_cache()
@@
- x_all = torch.clone(samples[j * db : (j + 1) * db]).detach().cuda()
+ x_all = torch.clone(samples[j * db : (j + 1) * db]).detach().to(device)
@@
- torch.cuda.empty_cache()
+ if torch.cuda.is_available():
+ torch.cuda.empty_cache()
+ elif torch.backends.mps.is_available():
+ torch.mps.empty_cache()
@@
- return torch.cat(denoised_samples, dim=0).cuda()
+ return torch.cat(denoised_samples, dim=0).to(device)
utils/training.py(CPU では backend を gloo にし、CUDA なしでも落ちないよう DDP/FSDP を抑止)
- if os.environ.get('MASTER_PORT'): # When running with torchrun
+ use_cuda = torch.cuda.is_available()
+ if os.environ.get('MASTER_PORT'): # When running with torchrun
@@
- torch.distributed.init_process_group(
- backend='nccl',
+ backend = 'nccl' if use_cuda else 'gloo'
+ torch.distributed.init_process_group(
+ backend=backend,
@@
- torch.cuda.set_device(self.local_rank)
+ if use_cuda:
+ torch.cuda.set_device(self.local_rank)
@@
def parallelize_model(args, model: nn.Module, dist: Distributed, device='cuda', block_names=['AttentionBlock']) -> nn.Module:
+ device_type = device.type if hasattr(device, "type") else str(device)
+
+ # FSDP/DP only make sense on CUDA
+ if (not torch.cuda.is_available()) or (device_type != 'cuda'):
+ args.fsdp = 0
+
+ requires_grad_exists = any(p.requires_grad for p in model.parameters())
@@
- if dist.distributed:
+ if dist.distributed and requires_grad_exists and device_type == 'cuda':
print(f"Using DDP")
- model_ddp = torch.nn.parallel.DistributedDataParallel(model, device_ids=[dist.local_rank])
+ ddp_kwargs = {"device_ids": [dist.local_rank]} if device_type == 'cuda' else {"device_ids": None}
+ model_ddp = torch.nn.parallel.DistributedDataParallel(model, **ddp_kwargs)
@@
- torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed)
+ torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed)
transformer_flow.py(torch.distributed 未初期化時の all_reduce 呼び出しをガード)
def jacobi(self,
z: torch.Tensor,
y: torch.Tensor | None = None,
guidance: float = 0,
rope=None,
kv_cache=None,
verbose=False,
jacobi_block_size: int = 32,
jacobi_max_iter: int = 32,
jacobi_th: float = 0.001,
context_length: int = None,
**unused_kwargs) -> torch.Tensor:
assert self.use_sos, "Jacobi iteration requires SOS token to be used"
assert self.pos_embed is None, "Jacobi iteration does not support positional embedding"
# Ensure sampling tensors are in float32 for numerical stability
original_dtype = z.dtype
z = z.float()
freqs_cis = self.get_freqs_cis(z, y, rope) if rope is not None else None
if guidance > 0:
z = torch.cat([z, z], 0)
# kv cache
reuse_kv_cache = kv_cache.prefix_cache is not None and kv_cache.kv_index[0] > 0
kv_cache = self.initialize_kv_cache(kv_cache, z, freqs_cis, reuse_kv_cache)
video_length = z.size(1) if z.dim() == 5 else 1
# permute the input
z = self.permutation(z)
# prepare input
x_full = torch.cat([self.get_sos_embed(z), z.clone()], dim=1)
if reuse_kv_cache:
x_full[:, 1: kv_cache.prefix_cache.size(1) + 1] = kv_cache.prefix_cache # fill the prefix cache
# conditioning
if self.txt_dim > 0:
if not reuse_kv_cache:
self.reverse_step_condition(y, kv_cache, freqs_cis=freqs_cis)
txt_size = y.size(1) if self.txt_dim > 0 else 0
video_frame_size = z.size(1) // video_length
start_idx = 0
if reuse_kv_cache:
start_idx = kv_cache.kv_index[0] - txt_size # start from the last cached index
prog_bar = tqdm.tqdm(total=z.size(1), disable=not verbose, desc='Block-wise Jacobi Iteration', leave=False)
prog_bar.update(start_idx)
local_attn_window = self.local_attn_window * video_frame_size if self.local_attn_window is not None else None
target_frame_size = z.size(1) if local_attn_window is None else min(z.size(1), local_attn_window)
context_size = None if local_attn_window is None else context_length * video_frame_size
while target_frame_size <= z.size(1):
while start_idx < target_frame_size:
chunk_size = jacobi_block_size if start_idx <= video_frame_size else jacobi_block_size * 4
local_done = torch.zeros((), dtype=torch.bool, device=x_full.device)
for i in tqdm.tqdm(range(jacobi_max_iter), disable=True, desc='Jacobi Iteration', leave=False):
if start_idx + chunk_size >= target_frame_size:
chunk_size = target_frame_size - start_idx
if i == 0 and start_idx > video_frame_size: # optional to use past frame to initialize the current frame
x = x_full[:, start_idx - video_frame_size: start_idx + chunk_size - video_frame_size]
else:
x = x_full[:, start_idx: start_idx + chunk_size]
# main forward - convert to model dtype for neural network computation
if hasattr(self.proj_in, 'weight'):
target_dtype = self.proj_in.weight.dtype
x = x.to(target_dtype)
x = self.get_proj_in(x)
for it, block in enumerate(self.attn_blocks):
_kv_cache = partial(kv_cache, it) if kv_cache is not None else None
x = block(x, None, freqs_cis=freqs_cis, kv_cache=_kv_cache)[0]
if self.use_final_norm:
x = self.final_norm(x)
x = self.get_proj_out(x)
xa, xb = x.chunk(2, dim=-1)
# Convert back to float32 for sampling computations
xa, xb = xa.float(), xb.float()
if not self.use_softplus:
xa = xa.exp()
else:
xa = F.softplus(xa + INV_SOFTPLUS_1)
if guidance > 0:
xb, xa = self.guidance(xa, xb, guidance, 1.0, 'ab')
# compute the Jacobi Iteration - all in float32
new_x = xb + xa * z[:, start_idx: start_idx+chunk_size]
diff = ((new_x - x_full[:, start_idx+1: start_idx+1+chunk_size]) ** 2).mean() / (new_x ** 2).mean()
x_full[:, start_idx+1: start_idx+1+chunk_size] = new_x
if diff < jacobi_th or i == jacobi_max_iter - 1: # do not clean the cache on the last iteration
local_done.fill_(1)
global_done = local_done.clone()
# Single-process runs (e.g., MPS) might not initialize torch.distributed
if torch.distributed.is_available() and torch.distributed.is_initialized():
torch.distributed.all_reduce(global_done, op=torch.distributed.ReduceOp.MIN)
if int(global_done.item()) == 1:
break
kv_cache.backward_in_time(chunk_size)
start_idx += chunk_size
prog_bar.update(chunk_size)
if target_frame_size >= z.size(1):
break
target_frame_size += local_attn_window - context_size if local_attn_window is not None else video_frame_size
target_frame_size = min(target_frame_size, z.size(1))
# re-encode the context with attention blocks
print(f're-encoding the context {start_idx+1-context_size}:{start_idx+1}')
kv_cache.reset_kv_index()
if self.txt_dim > 0:
self.reverse_step_condition(y, kv_cache, freqs_cis=freqs_cis)
x_context = x_full[:, start_idx+1-context_size: start_idx+1]
x_context_in, x_context =(x_context)
x_context = self.get_proj_in(x_context)
for it, block in enumerate(self.attn_blocks):
_kv_cache = partial(kv_cache, it) if kv_cache is not None else None
x_context = block(x_context, None, freqs_cis=freqs_cis, kv_cache=_kv_cache)[0]
x = x_full[:, 1:]
if guidance > 0:
x = x.chunk(2, dim=0)[0] # remove SOS token
x = self.permutation(x, inverse=True)
# Convert back to original dtype if needed
return x.to(original_dtype)
scripts/test_sample_image.sh(デフォルト batch を 16 に変更)
これはパソコンの性能によって自分で変えてください。
-bz=8
+bz=16
Text-to-Image Generation の実行方法と結果
画像生成を行うには、以下のコマンドを実行し、プロンプトを入力します:
bash scripts/test_sample_image_mps.sh "a film still of a cat playing piano"
生成された画像の保存先
生成された画像は自動で次のフォルダに保存されます:
/ml-starflow/logs/starflow_3B_t2i_256x256/
公式プロンプトを使った結果
- プロンプト: "a film still of a cat playing piano"
試したプロンプト 1
- プロンプト: "A girl with backlighting, her silhouette against the sunset, bright halo effect"
試したプロンプト 2
- プロンプト: "A anime girl with backlighting, her silhouette against the sunset, bright halo effect"
試したプロンプト 3
何これ。。。普通に怖い😱
- プロンプト: "A mysterious and ethereal figure with translucent wings, glowing eyes, and hair that flows like liquid silver"
まとめ
生成された画像は、期待していたものとは少し違いましたが、それでも非常に面白い結果でした。今後、生成AI技術がどのように進化していくのか、非常に楽しみです!
STARFlowは、計算効率、生成品質、そして安定性を兼ね備えた新世代の画像生成技術です。正規化フローとTransformerアーキテクチャの融合により、従来の拡散モデルに対抗する強力なツールとして登場しました。特に、FIDスコアや動画生成能力において、現行の最先端技術と比較して遜色のないパフォーマンスを示しており、今後のさらなる進化が非常に楽しみです。
一日試行錯誤を重ねた結果、上手くいった部分もあり、次は動画生成にも挑戦してみたいと思っています(Appleさん待ち) 最後この投稿時 モデルがHugging Face 100位ランキングインしたそうです!
最後まで読んでいただき、ありがとうございました!