前回はNEATの概念をご紹介し、populationを用意する段階まで進みました。
今回は用意したpopulationを種に分ける操作を行います。
種に分ける(②)
次のコードを用意します。
compatibility_threshold = 3.0
initial_connection = 'full'
compatibility_disjoint_coefficient = 1.0
class Species(object):
def __init__(self, key, generation):
self.key = key
self.created = generation
self.last_improved = generation
self.representative = None
self.members = {}
self.fitness = None
self.adjusted_fitness = None
self.fitness_history = []
def update(self, representative, members):
self.representative = representative
self.members = members
def get_fitnesses(self):
return [m.fitness for m in self.members.values()]
class DefaultSpeciesSet(object):
def __init__(self):
self.indexer = count(1)
self.species = {}
self.genome_to_species = {}
@staticmethod
def distance(me, other):
node_distance = 0.0
if me.nodes or other.nodes:
disjoint_nodes = 0
for k2 in other.nodes:
if k2 not in me.nodes:
disjoint_nodes += 1
for k1, n1 in me.nodes.items():
n2 = other.nodes.get(k1)
if n2 is None:
disjoint_nodes += 1
else:
node_distance += n1.distance(n2)
max_nodes = max(len(me.nodes), len(other.nodes))
node_distance = (node_distance +
(compatibility_disjoint_coefficient *
disjoint_nodes)) / max_nodes
connection_distance = 0.0
if me.connections or other.connections:
disjoint_connections = 0
for k2 in other.connections:
if k2 not in me.connections:
disjoint_connections += 1
for k1, c1 in me.connections.items():
c2 = other.connections.get(k1)
if c2 is None:
disjoint_connections += 1
else:
connection_distance += c1.distance(c2)
max_conn = max(len(me.connections), len(other.connections))
connection_distance = (connection_distance +
(compatibility_disjoint_coefficient *
disjoint_connections)) / max_conn
distance = node_distance + connection_distance
return distance
def speciate(self, population, generation):
unspeciated = set(population)
new_representatives = {}
new_members = {}
for sid, s in self.species.items():
candidates = []
for gid in unspeciated:
g = population[gid]
d = self.distance(s.representative, g)
candidates.append((d, g))
ignored_rdist, new_rep = min(candidates, key=lambda x: x[0])
new_rid = new_rep.key
new_representatives[sid] = new_rid
new_members[sid] = [new_rid]
unspeciated.remove(new_rid)
while unspeciated:
gid = unspeciated.pop()
g = population[gid]
candidates = []
for sid, rid in new_representatives.items():
rep = population[rid]
d = self.distance(rep, g)
if d < compatibility_threshold:
candidates.append((d, sid))
if candidates:
ignored_sdist, sid = min(candidates, key=lambda x: x[0])
new_members[sid].append(gid)
else:
sid = next(self.indexer)
new_representatives[sid] = gid
new_members[sid] = [gid]
self.genome_to_species = {}
for sid, rid in new_representatives.items():
s = self.species.get(sid)
if s is None:
s = Species(sid, generation)
self.species[sid] = s
members = new_members[sid]
for gid in members:
self.genome_to_species[gid] = sid
member_dict = dict((gid, population[gid]) for gid in members)
s.update(population[rid], member_dict)
def get_species_id(self, individual_id):
return self.genome_to_species[individual_id]
これで種の管理をするSpeciesクラスと種に分けるメソッドspeciateを含むDefaultSpeciesSetを定義することができました。
そして次のコードで種に分ける操作をします。
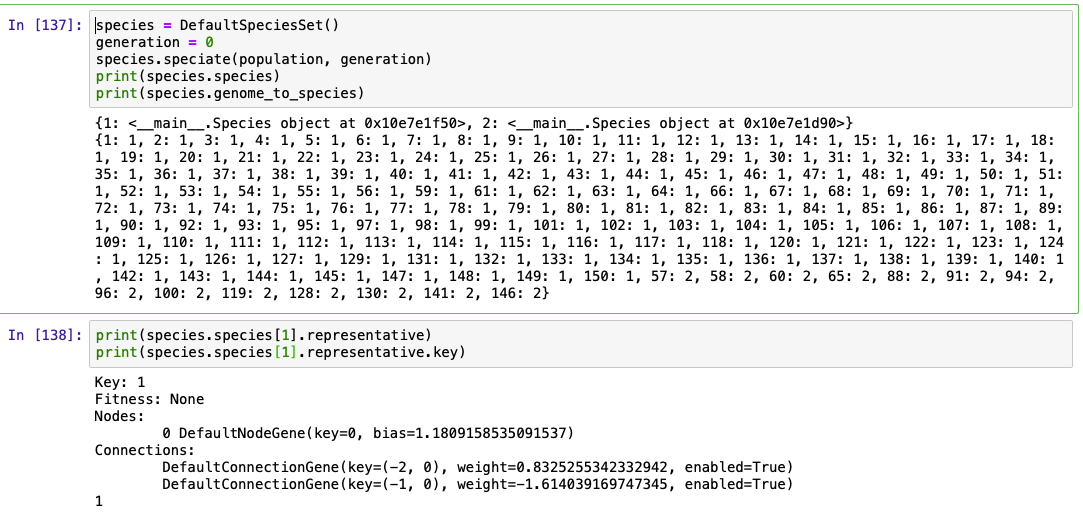
species = DefaultSpeciesSet()
generation = 0
species.speciate(population, generation)
print(species.species)
print(species.genome_to_species)
print(species.species[1].representative)
print(species.species[1].representative.key)
print(species.species)をみると、辞書型が表示されており、そのkeyが一つしかないことから、一種類の種ができたことがわかります。また、print(species.genome_to_species)より、150体あるpopulationのどのネットワークも1という種に分類されている様子がわかります。
さらに、print(species.species[1].representative)より種の代表(representative)がpopulationのKey=1のネットワークであることもわかります。
representativeは各世代の中のそれぞれの種に一つあり、その種を代表するネットワークとして種を分ける際に基準のネットワークとなります。
ここで、種を分ける方法について説明します。
speciate
種に分ける際は、ネットワーク同士の距離(distance)がある水準より大きいか小さいかを計算します。
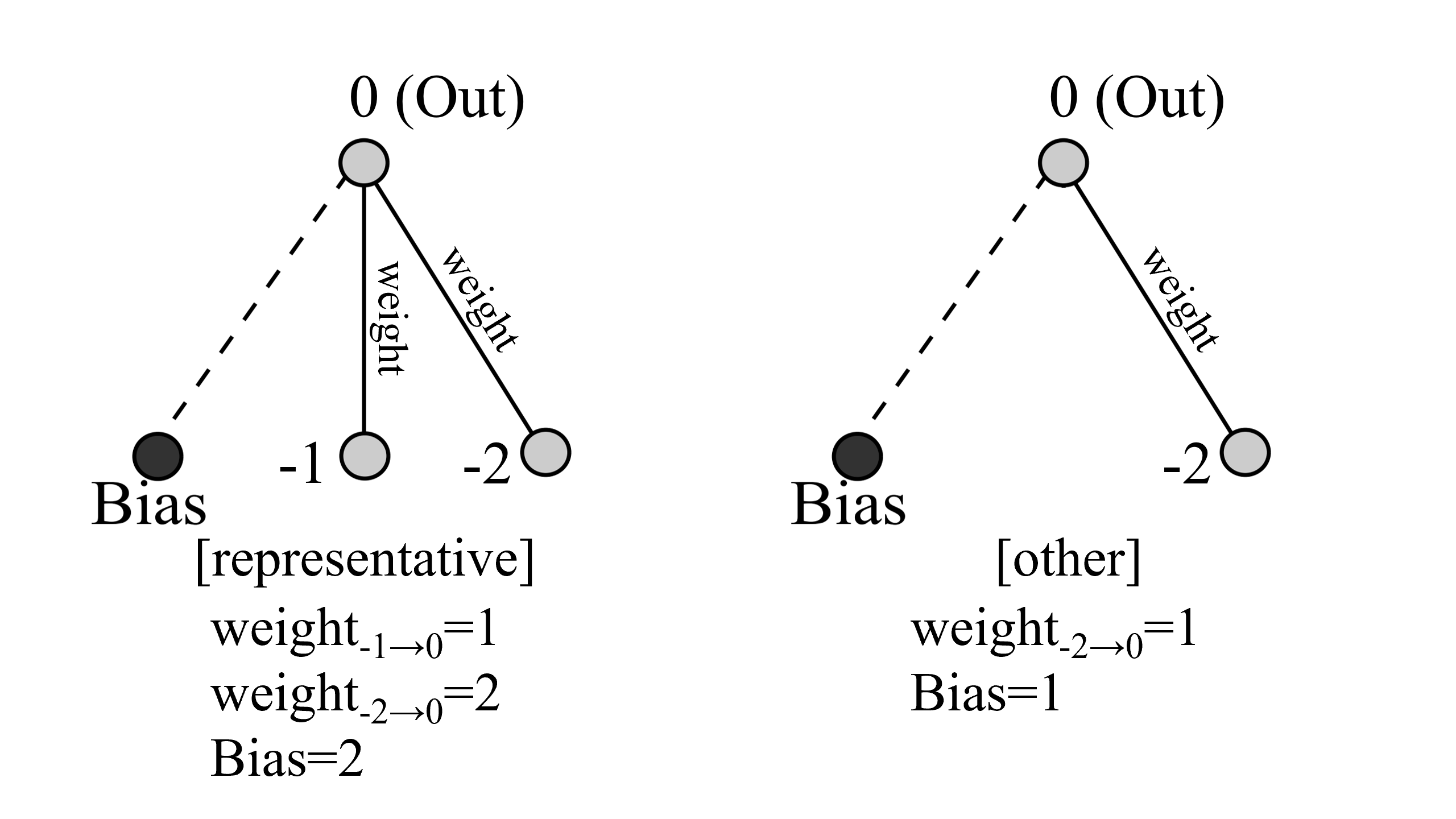
例として次の簡易的な二つのネットワークのdistanceを測ります。
左がrepresentativeで右が比較する対象となるotherです。それぞれNodesとConnectionsがあり、weightやBiasも値が与えられています。
コードに従って説明すると、distanceはnode_distanceとconnection_distanceの和で表すことができます。
node_distance
まず、Inputを除くNodesの差を見ます、この例ではどちらも0Nodesしかなく、違いはありません。
disjoint_nodes=0
次に共通のNodesに関してそのBiasの差を計算します。
node_distance=(Bias(rep)-Bias(other))×compatibility_weight_coefficient
=(2-1)×0.5=0.5
また、max_nodesを計算します。
max_nodesはrepresentative、またはotherのうちより多い方のNodes数です。今回はどちらも1なので、
max_nodes=1
となります(BiasはNodesとして含めません)。
最終的に求めるnode_distanceは
node_distance=(node_distance+compatibility_disjoint_coefficient×disjoint_nodes)/max_nodes
より、
node_distance=(0.5+1.0×0)/1=0.5
connection_distance
まず、Connectionsの差を見ます、この例ではrepresentativeが2本あり、otherは1本なので、違いは+1として考えます。
disjoint_connections=1
次に共通のConnectionsに関してそのweightの差を計算します。
connection_distance=(weight(rep)-weight(other))×compatibility_weight_coefficient
=(2-1)×0.5=0.5
また、max_connを計算します。
max_connはrepresentative、またはotherのうちより多い方のConnections数です。今回はrepresentativeの2本を採用して、
max_nodes=2
となります。
最終的に求めるconnection_distanceは
connection_distance=(connection_distance+compatibility_disjoint_coefficient×disjoint_connections)/max_conn
より、
connection_distance=(0.5+1.0×1)/2=0.75
つまりdistanceは
distance=node_distance+connection_distance=0.5+0.75=1.25
となります。このような計算を行った上でdistanceがcompatibility_threshold(今回は3.0)を超えれば新たな種が生まれます。
generation=0のときは、populationの最初のネットワーク(Key=1)をrepresentativeとして他のネットワークとの距離(distance)を測ります。generation=1以降は一つ前のrepresentativeと最も近いネットワークをその世代のrepresentativeとし、そのネットワークをそれ以外のネットワークと比べてdistanceを測ります。
次回はネットワークの成績を計算します。