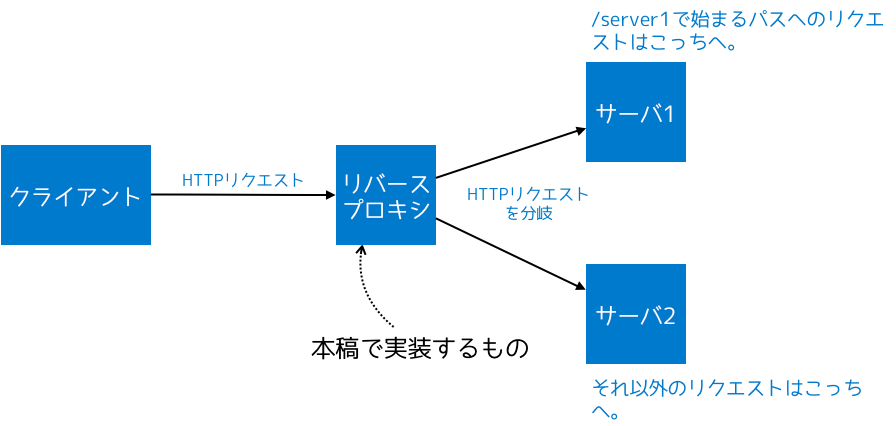
本稿では、node-http-proxyを使い、TypeScriptでサーバを振り分けるリバースプロキシを作る方法を紹介する。
node-http-proxyの基本的な使い方は、TypeScript: node-http-proxyを用いリクエスト/レスポンスを書き換えるリバースプロキシを作る方法で説明しているので、合わせてご参照いただきたい。
本稿のゴール
HTTPリクエストのパスに応じて、HTTPリクエストをサーバ1とサーバ2に振り分けるリバースプロキシをTypeScriptで書けるようになる。
リクエストを振り分けるリバースプロキシを実装する
ここでは、HTTPリクエストのパスに応じて、HTTPリクエストをサーバ1とサーバ2に振り分けるリバースプロキシの実装例を示す。
import http, {IncomingMessage, ServerResponse} from 'http'
import httpProxy from 'http-proxy'
// HTTPサーバ1
http.createServer((req: IncomingMessage, res: ServerResponse): void => {
res.write('HTTP Server 1')
res.end()
}).listen(9001)
// HTTPサーバ2
http.createServer((req: IncomingMessage, res: ServerResponse): void => {
res.write('HTTP Server 2')
res.end()
}).listen(9002)
// プロキシサーバ
const proxy = httpProxy.createProxyServer()
http.createServer((req: IncomingMessage, res: ServerResponse): void => {
// パスに応じて送信先を変える処理
const target = req.url && req.url.startsWith('/server1')
? 'http://127.0.0.1:9001'
: 'http://127.0.0.1:9002'
proxy.web(req, res, {target})
}).listen(8000)
ここでのポイントとしては、リクエストに応じたロジックを書く上で、次のイディオムがあるということ。
const proxy = httpProxy.createProxyServer()
http.createServer((req: IncomingMessage, res: ServerResponse): void => {
//
// リクエストに応じたロジックを書く場所
//
proxy.web(req, res, options)
}).listen(proxyPortNumber)
最初に示した実装例のプロキシサーバを動かしてみる。
次のリクエストを送ると、
GET /server1/foo/bar HTTP/1.1
Host: localhost:8000
リクエストはサーバ1に振り分けられ、次のレスポンスが返ってくる:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
connection: close
date: Tue, 24 Sep 2019 08:51:38 GMT
transfer-encoding: chunked
HTTP Server 1
今度は、サーバ2に振り分けられるリクエストを投げてみる:
GET /foo/bar HTTP/1.1
Host: localhost:8000
期待通りサーバ2からレスポンスが返ってくる:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
connection: close
date: Tue, 24 Sep 2019 09:07:24 GMT
transfer-encoding: chunked
HTTP Server 2