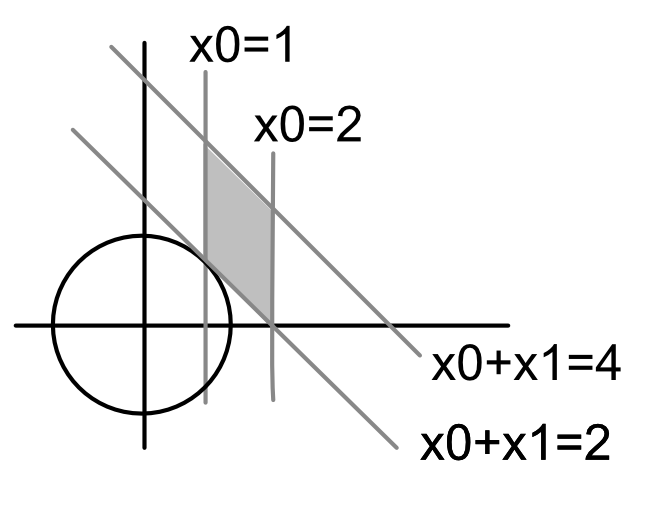環境
この記事は以下の環境で動いています。
| 項目 | 値 |
|---|---|
| CPU | Core i5-8250U |
| Ubuntu | 18.04 |
| ROS | Melodic |
インストールについてはROS講座02 インストールを参照してください。
またこの記事のプログラムはgithubにアップロードされています。ROS講座11 gitリポジトリを参照してください。
概要
ロボット系のアルゴリズムの中には最適化計算を行うものが多くあります。python等では簡単にこのような計算ができるcvxpyなどの便利なライブラリがありますが、c++で使えるものとして最適化計算ツールのipoptと自動微分ツールのcppadを紹介します。
install
sudo apt install -y ros-melodic-ifopt
sudo apt install -y cppad
最適化計算とは
最適化計算とは以下で定式化される数列Xに対して、それの値からの制約(L<D(X)<U)の中で最小のf(X)を求める計算です。
min f(X)\\
(X=(x_0,x_1,x_2...)^T)\\
L<D(X)<U
最小を求めるfのことをコスト関数、Dを制約関数といいます。
今回は例として以下のような計算を行います。
min f(X)=x_0^2+x_1^2\\
1<x_0<2\\
2<x_0+x_1<4\\
今回は2変数の単純な例なので以下のように図示してみます。答えは(x0,x1)=(1,1)とわかります。
最適化計算のサンプル1
ヤコビアン
ipoptというライブラリを使用します。このライブラリではコスト関数、制約関数の値とそのヤコビアンを入力する必要があります。
ヤコビアンは関数のそれぞれの変数に対する偏微分のベクトルを指します
今回のコスト関数$f=x_0^2+x_1^2$に対してヤコビアンは
j =(df/dx_0, df/dx_1) = (2x_0, 2x_1)
となります。
また制約関数$D=(x_0+x_1)$に対して
j = (dD/dx_0, dD/dx_1) = (1, 1)
となります。
コード
# include <ifopt/problem.h>
# include <ifopt/ipopt_solver.h>
# include <ifopt/constraint_set.h>
# include <ifopt/variable_set.h>
# include <ifopt/cost_term.h>
# include <cmath>
# include <iostream>
// Define Variables
class TestVariables : public ifopt::VariableSet
{
public:
TestVariables() : VariableSet(2, "var_set1")
{
x0_ = 0.0;
x1_ = 0.0;
}
void SetVariables(const VectorXd& x) override
{
x0_ = x(0);
x1_ = x(1);
};
VectorXd GetValues() const override
{
return Eigen::Vector2d(x0_, x1_);
};
VecBound GetBounds() const override
{
VecBound bounds(GetRows());
bounds.at(0) = ifopt::Bounds(1.0, 2.0);
bounds.at(1) = ifopt::NoBound;
return bounds;
}
private:
double x0_, x1_;
};
// Define Constraint
class TestConstraint : public ifopt::ConstraintSet
{
public:
TestConstraint() : ConstraintSet(1, "constraint1")
{
}
VectorXd GetValues() const override
{
VectorXd g(GetRows());
Eigen::Vector2d x = GetVariables()->GetComponent("var_set1")->GetValues();
g(0) = x(0) + x(1); // Calculate Constraint
return g;
};
VecBound GetBounds() const override
{
VecBound b(GetRows());
b.at(0) = ifopt::Bounds(2.0, 4.0); // bound of g(0)
return b;
}
void FillJacobianBlock(std::string var_set, Jacobian& jac_block) const override
{
if (var_set == "var_set1")
{
Eigen::Vector2d x = GetVariables()->GetComponent("var_set1")->GetValues();
jac_block.coeffRef(0, 0) = 1.0; // d(g(0))/d(x(0))
jac_block.coeffRef(0, 1) = 1.0; // d(g(0))/d(x(1))
}
}
};
// Define Cost
class TestCost : public ifopt::CostTerm
{
public:
TestCost() : CostTerm("cost_term1")
{
}
double GetCost() const override
{
Eigen::Vector2d x = GetVariables()->GetComponent("var_set1")->GetValues();
return std::pow(x(0), 2) + std::pow(x(1), 2); // calcurate cost
};
void FillJacobianBlock(std::string var_set, Jacobian& jac) const override
{
if (var_set == "var_set1")
{
Eigen::Vector2d x = GetVariables()->GetComponent("var_set1")->GetValues();
jac.coeffRef(0, 0) = 2.0 * x(0); // d(c)/d(x(0))
jac.coeffRef(0, 1) = 2.0 * x(1); // d(c)/d(x(1))
}
}
};
int main()
{
// Define problem
ifopt::Problem nlp;
nlp.AddVariableSet(std::make_shared<TestVariables>());
nlp.AddConstraintSet(std::make_shared<TestConstraint>());
nlp.AddCostSet(std::make_shared<TestCost>());
// Initialize solver
ifopt::IpoptSolver ipopt;
ipopt.SetOption("linear_solver", "mumps");
ipopt.SetOption("jacobian_approximation", "exact");
ipopt.SetOption("print_level", 0); // supress log
ipopt.Solve(nlp);
std::cout << nlp.GetOptVariables()->GetValues().transpose() << std::endl;
}
- 最適化計算をするためには変数クラス、制約クラス、コストクラスの3つのモデルに対するクラスが必要です。
- 変数クラスは
ifopt::VariableSetを継承するクラスでコンストラクターでは各変数の初期値を決めます。またGetBounds()メソッドで各変数の上下限を定めることが出来ます。もちろん上下限なしにもできます。 - 制約クラスは
ifopt::ConstraintSetを継承するクラスです。制約はx<yのような形ではなくx-y<0の様に必ず値として評価できる形で記述します。GetValues()メソッドではその制約を評価する値を、GetBounds()ではその値の制約をifopt::Bounds(2.0, 4.0)の様に記述します。=1などの場合はifopt::Bounds(1.0, 1.0)と記述します。FillJacobianBlock()では計算用にヤコビアンを入れます。制約はもちろん複数入れることが出来ます。 - コストクラスは
ifopt::CostTermを継承するクラスです。GetValues()とFillJacobianBlock()メソッドを実装します。
実行
実行すると以下のような表示が出ます。解析解(1,1)とほぼあった値が出ます。
******************************************************************************
This program contains Ipopt, a library for large-scale nonlinear optimization.
Ipopt is released as open source code under the Eclipse Public License (EPL).
For more information visit http://projects.coin-or.org/Ipopt
******************************************************************************
1.00286 0.997138
自動微分のサンプル
上記のようにすれば最適化計算をすれば計算ができますが、正しくヤコビアンを入れないと間違った答が出ます。ヤコビアンの取得を自動化する
ために自動微分ライブラリであるCppAdを使ってみます。
コード
# include <cppad/cppad.hpp>
# include <iostream>
int main()
{
std::vector<CppAD::AD<double>> ax(2);
CppAD::Independent(ax);
std::vector<CppAD::AD<double>> ay(1);
ay[0] = 2 * CppAD::pow(ax[0], 3) + CppAD::pow(ax[1], 2);
CppAD::ADFun<double> f(ax, ay);
std::vector<double> x(2);
x[0] = 2;
x[1] = 3;
std::vector<double> fw0 = f.Forward(0, x);
std::cout << fw0[0] << "=f(" << x[0] << "," << x[1] << ")" << std::endl;
std::vector<double> jac = f.Jacobian(x);
std::cout << jac[0] << "=dy/dx0(" << x[0] << "," << x[1] << ")" << std::endl;
std::cout << jac[1] << "=dy/dx1(" << x[0] << "," << x[1] << ")" << std::endl;
}
- 今回対象とする関数は$2x_0^3+x_1^2$です。一応手でヤコビアンを計算すると$(\frac{dy}{dx_0}, \frac{dy}{dx_1}) = (6x_0^2, 2x_1)$となります。
-
f.Forward(0, x)では$x=(x_0,x_1)=(2,3)$に対してこの関数の元の値(=25)が取得できます。 -
f.Jacobian(x)では$x=(x_0,x_1)=(2,3)$にたいしてこの関数のヤコビアンの値($(\frac{dy}{dx_0}, \frac{dy}{dx_1}) = (24, 4)$)が取得できます。
実行結果
25=f(2,3)
24=dy/dx0(2,3)
6=dy/dx1(2,3)
最適化計算のサンプル2
ではCppAdを使って上記のサンプルを書き直します。
# include <ifopt/problem.h>
# include <ifopt/ipopt_solver.h>
# include <ifopt/constraint_set.h>
# include <ifopt/variable_set.h>
# include <ifopt/cost_term.h>
# include <cppad/cppad.hpp>
# include <cmath>
# include <iostream>
// Define Variables
class TestVariables : public ifopt::VariableSet
{
public:
TestVariables() : VariableSet(2, "var_set1")
{
x0_ = 0.0;
x1_ = 0.0;
}
void SetVariables(const VectorXd& x) override
{
x0_ = x(0);
x1_ = x(1);
};
VectorXd GetValues() const override
{
return Eigen::Vector2d(x0_, x1_);
};
VecBound GetBounds() const override
{
VecBound bounds(GetRows());
bounds.at(0) = ifopt::Bounds(1.0, 2.0);
bounds.at(1) = ifopt::NoBound;
return bounds;
}
private:
double x0_, x1_;
};
// Define Constraint
class TestConstraint : public ifopt::ConstraintSet
{
public:
TestConstraint() : ConstraintSet(1, "constraint1")
{
}
VectorXd GetValues() const override
{
Eigen::Vector2d x = GetVariables()->GetComponent("var_set1")->GetValues();
std::vector<double> tx(2);
tx[0] = x(0);
tx[1] = x(1);
std::vector<double> fw = getAdFun().Forward(0, tx);
VectorXd g(GetRows());
g(0) = fw[0];
return g;
};
VecBound GetBounds() const override
{
VecBound b(GetRows());
b.at(0) = ifopt::Bounds(2.0, 4.0); // bound of g(0)
return b;
}
void FillJacobianBlock(std::string var_set, Jacobian& jac_block) const override
{
if (var_set == "var_set1")
{
Eigen::Vector2d x = GetVariables()->GetComponent("var_set1")->GetValues();
std::vector<double> tx(2);
tx[0] = x(0);
tx[1] = x(1);
std::vector<double> ad_jac = getAdFun().Jacobian(tx);
jac_block.coeffRef(0, 0) = ad_jac[0]; // d(c)/d(x(0))
jac_block.coeffRef(0, 1) = ad_jac[1]; // d(c)/d(x(1))
}
}
private:
CppAD::ADFun<double> getAdFun(void) const {
std::vector<CppAD::AD<double>> ax(2);
CppAD::Independent(ax);
std::vector<CppAD::AD<double>> ay(1);
ay[0] = ax[0] + ax[1];
CppAD::ADFun<double> f(ax, ay);
return f;
}
};
// Define Cost
class TestCost : public ifopt::CostTerm
{
public:
TestCost() : CostTerm("cost_term1")
{
}
double GetCost() const override
{
Eigen::Vector2d x = GetVariables()->GetComponent("var_set1")->GetValues();
std::vector<double> tx(2);
tx[0] = x(0);
tx[1] = x(1);
std::vector<double> fw0;
fw0 = getAdFun().Forward(0, tx);
return fw0[0];
};
void FillJacobianBlock(std::string var_set, Jacobian& jac) const override
{
if (var_set == "var_set1")
{
Eigen::Vector2d x = GetVariables()->GetComponent("var_set1")->GetValues();
std::vector<double> tx(2);
tx[0] = x(0);
tx[1] = x(1);
std::vector<double> ad_jac = getAdFun().Jacobian(tx);
jac.coeffRef(0, 0) = ad_jac[0]; // d(c)/d(x(0))
jac.coeffRef(0, 1) = ad_jac[1]; // d(c)/d(x(1))
}
}
private:
CppAD::ADFun<double> getAdFun(void) const {
std::vector<CppAD::AD<double>> ax(2);
CppAD::Independent(ax);
std::vector<CppAD::AD<double>> ay(1);
ay[0] = CppAD::pow(ax[0], 2) + CppAD::pow(ax[1], 2);
CppAD::ADFun<double> f(ax, ay);
return f;
}
};
int main()
{
// Define problem
ifopt::Problem nlp;
nlp.AddVariableSet(std::make_shared<TestVariables>());
nlp.AddConstraintSet(std::make_shared<TestConstraint>());
nlp.AddCostSet(std::make_shared<TestCost>());
// Initialize solver
ifopt::IpoptSolver ipopt;
ipopt.SetOption("linear_solver", "mumps");
ipopt.SetOption("jacobian_approximation", "exact");
ipopt.SetOption("print_level", 0); // supress log
ipopt.SetOption("sb", "yes"); // supress startup message
ipopt.Solve(nlp);
std::cout << nlp.GetOptVariables()->GetValues().transpose() << std::endl;
}
-
ipopt.SetOption("sb", "yes")とすると最適化計算時のスタートアップメッセージが出なくなります
実行
1.00286 0.997138