この記事は VR法人HIKKY Advent Calendar 2024 の 17 日目の記事です。
終盤に差し掛かってきたかと思いますが、後半もまだまだ有益な情報があるかと思うのでぜひご覧いただければと思います。
はじめに
Webフロントエンドチームで なんでもできるエンジニアになろうと日々もがいている伊藤です。
本記事は 規約を設けて実装の標準化を図ったがうまくいかなかった経験から出した一つの解決案として記事を書いています。
この案が最適解かどうかはわからないので、認識の上読んでいただければと思います。
また私がNuxt3での実装経験が長いので今回はプレーンなNuxt3プロジェクト(これ)に調整を行うケースで記事を書いています。
その規約本当に必要?
みなさん、コーディング規約を都度更新していくことに疲弊していませんか?
私はそこまで長いこと運用していないのでまだ大丈夫なのですが、これがずっと続くと管理が出来なくなるとすでに思い始めています。
それで着目したのがESLintとStylelint(Linter)です。
ESLintとStylelintにはカスタム定義を追加し、独自のチェック&エラー出力をすることができます。
なので、コーディング規約にあるけどカスタム定義でエラーが出せるような内容は全部Linterでエラーを出しちゃえ!というのが、私の出した結論です。
そうすることで規約の記述を少なくしつつ、エラーが出るので実装者は直さないといけないという流れにできればと考えました。
最終的なゴール
以下の規約があると仮定して実際にカスタム定義を実装しようと思います。
componentはファイル先頭に決められたコメントを設定する
ファイル先頭に以下のようなコメントをしない場合エラーとします。
<!--
@name AtomsButton
@description コンポーネントの説明
-->
- name
- ファイル検索などで引っ掛かるようにします
※タグと同じ記載にしないとエラーにします
- ファイル検索などで引っ掛かるようにします
- description
- コンポーネントがどんな目的で使われるかの説明を記載します
useStateはcomposableファイルでのみ利用可能とする
composableファイル以外でのuseStateの利用を禁止します。
禁止にする理由は個人的にデータの取り回しが面倒になるケースがあり使いたくないためです。
使う場合はcomposableファイルでのみ使うようにと考えています。
composableファイルでuseStateを使う場合「NOTE:」コメントをつける
基本的にはuseStateの利用を禁止したいのですが、ログイン情報などページを横断して使う必要がある情報に対してのみ使えるようにします。
利用する際は 何故(何に)利用するのかを示すために「NOTE:」のコメントを残さないとエラーにするようにします。
各vueファイルのstyleで詳細度が低いルート位置のstyleをエラーとする
以下のようなcomponent構成でstyle実装をした場合に、ローカル実行ではデザインが崩れないけどビルドした成果物だとデザインが崩れるという事案があったため実装時点で防ぐためのルールです。
// parent component
<template>
<ChildComponent class="child" />
</template>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
.child {
color: #FF0000;
}
</style>
// child component
<template>
<p class="text">テキスト</p>
</template>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
.text {
color: #0075c2;
}
</style>
上記のような実装を行うとローカル実行ではテキストが 赤になり、ビルドした成果物ではテキストが青になるようなケースが発生したためLinterを用いてエラーとなるようにします。
以上4つをカスタムルールとして作ろうと思います。
実装
環境構築
まずはプレーンな環境を準備してESLintとStylelintを適用しましょう。
パッケージ管理ツールはお好きなものを使ってください。
1.プロジェクトの作成
npx nuxi init custom-linter
2.必要なライブラリをインストール
cssはscssで実装するのでsassのライブラリもインストールしています。
cd custom-linter
npm install --save-dev eslint @nuxt/eslint stylelint @nuxtjs/stylelint-module sass-embedded postcss-html stylelint-config-recommended stylelint-config-recommended-scss specificity
3.Nuxt側の型情報生成
Nuxt系の型情報が欠落しているため生成処理を実行します。
npx nuxt prepare
4.configファイルの作成
ESLintとStylelint用の設定ファイルを作成します。
// eslint.config.mjs
// @ts-check
import withNuxt from './.nuxt/eslint.config.mjs'
export default withNuxt(
// Your custom configs here
)
// .stylelintrc.cjs
module.exports = {
customSyntax: "postcss-html",
extends: [
"stylelint-config-recommended",
"stylelint-config-recommended-scss",
],
rules: {},
};
5.nuxt.config.tsでLinterを適用
// https://nuxt.com/docs/api/configuration/nuxt-config
export default defineNuxtConfig({
compatibilityDate: 'xxxx-xx-xx',
devtools: { enabled: true },
+ modules: [
+ '@nuxt/eslint',
+ '@nuxtjs/stylelint-module',
+ ],
})
6.package.jsonでlintのチェックをするscriptを追加
"scripts": {
...
+ "lint:eslint": "eslint --cache --cache-strategy content .",
+ "lint:style": "stylelint \"**/*.{css,scss,sass,vue}\" --ignore-path .gitignore --cache --cache-strategy content"
...
},
以上で環境構築は終了です。
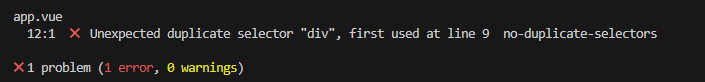
試しにapp.vueにエラーが出るコードを実装してからscriptを実行してエラーを確認してみましょう。
// app.vue
<template>
<div>
<NuxtRouteAnnouncer />
<NuxtWelcome />
</div>
<img />
</template>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
div {
color: red;
}
div {
color: red;
}
</style>
画像のようなエラーが出れば問題なく設定が出来ている状態となります。

カスタム定義の実装
ここからが本題のカスタム定義の実装となります。
以下のようなディレクトリ構成になるように実装をしますが、必ずこの構成でなくても動くので各プロジェクトに沿った構成で実装していただければと思います。
project-root/
├── linter/
│ ├── eslint/ # 以降「eslintフォルダとします」
│ │ └── いろんなカスタム定義.js
│ ├── stylelint/ # 以降「stylelintフォルダとします」
│ │ └── いろんなカスタム定義.js
├── package.json
└── その他
slintのカスタム定義の実装
基本的には公式のドキュメントに沿った設定をします。
実装する内容としてはざっくり以下のようなものとなっています。
- meta:ルールのメタ情報を定義、エラーメッセージなどもここで定義します
- create:スコープに対してカスタム処理を追加しエラーを表示するか、どこに表示するかなどを制御します
※ここでごにょごにょして独自のルールを実装します。
それでは実際にカスタム定義の実装をしていこうと思います。
「componentはファイル先頭に決められたコメントを設定する」定義の実装
eslintフォルダにカスタム定義用のファイルを新規で作成し以下のコードの反映をしてください。
※ここでは「require-component-header-comment.js」とします。
// require-component-header-comment.js
import path from 'path'
/**
* @type {import('eslint').Rule.RuleModule}
*/
export const requireComponentHeaderComment = {
meta: {
type: 'problem',
docs: {
description:
'ファイルの先頭に @name と @description を含むコメントブロックがあるかどうかチェックするルール',
recommended: false,
},
schema: [],
messages: {
missingComment:
'ファイルの先頭に @name と @description を含むコメントブロックが必要です。',
missingName: 'ファイルの先頭のコメントブロックに @name タグが必要です。',
missingDescription:
'ファイルの先頭のコメントブロックに @description タグが必要です。',
missingNameCamelCase:
'@nameタグはcomponent以下のディレクトリ階層+ファイル名をキャメルケースでつなげ拡張子を削除したテキストを指定してください。(例:AtomsBaseInput)',
},
},
create: function (context) {
return {
Program: function (node) {
const sourceCode = context.sourceCode
const text = sourceCode.text
// ファイルの先頭にあるコメントブロックを抽出
const firstCommentMatch = text.match(/^<!--([\s\S]*?)-->/)
// 最初のコメントが空、またはタグがない場合にエラーを出力
if (!firstCommentMatch || !firstCommentMatch[1].trim()) {
context.report({
node,
messageId: 'missingComment',
loc: {
start: { line: 1, column: 0 },
end: { line: 1, column: 0 },
},
})
return
}
// コメントブロック内のテキスト
const commentText = firstCommentMatch[1]
// @name と @description の存在確認
const hasName = /@name\s+\S+/.test(commentText)
const hasDescription = /@description\s+\S+/.test(commentText)
// @name がない場合にエラーを報告
if (!hasName) {
context.report({
node,
messageId: 'missingName',
loc: {
start: { line: 1, column: 0 },
end: { line: 1, column: 0 },
},
})
}
// @description がない場合にエラーを報告
if (!hasDescription) {
context.report({
node,
messageId: 'missingDescription',
loc: {
start: { line: 1, column: 0 },
end: { line: 1, column: 0 },
},
})
}
// ファイルのパスから適切な @name の内容を生成
const filePath = context.physicalFilename
const projectRoot = process.cwd()
const relativePath = path.relative(projectRoot, filePath)
const ext = path.extname(filePath)
const parts = relativePath
.replace(ext, '')
.replace(/-/g, '\\')
.replace(/.*components/g, '')
.split(path.sep)
const camelCaseText = parts
.map((part) => part.charAt(0).toUpperCase() + part.slice(1))
.join('')
if (hasName && !commentText.includes(`@name ${camelCaseText}`)) {
context.report({
node,
messageId: 'missingNameCamelCase',
loc: {
start: { line: 1, column: 0 },
end: { line: 1, column: 0 },
},
})
}
},
}
},
}
上記の実装は以下のようなことを行っています。
※metaの部分の説明は割愛
- ソースコードを取得し、ファイルの先頭にある
<!-- -->のコメントブロックを取得
※getAllComments関数があるのですが、<!-- -->のコメントブロックを拾えないので正規表現で取得するようにしています。 - 取得したコメントブロックが空もしくはコメントブロックがファイルの先頭に無い場合はエラーとします。
- その後、コメントブロック内のテキストが期待されたものになっているかチェックを行うようにしています。
「useStateはcomposableファイルでのみ利用可能とする」定義の実装
続いてuseState利用を制限する定義となります。
同じくeslintフォルダにカスタム定義用のファイルを新規で作成し以下のコードの反映をしてください。
※ここでは「no-use-state.js」とします。
// no-use-state.js
/**
* @type {import('eslint').Rule.RuleModule}
*/
export const noUseState = {
meta: {
type: 'problem',
docs: {
description: 'useStateを使う場合、jsdocを必須とするルール',
recommended: false,
},
schema: [], // ルールにオプションがない場合は空の配列
messages: {
useStateError:
'useStateの使用は禁止されています。 composable+provide/inject を使用してください。',
},
},
create: function (context) {
return {
ImportDeclaration: function (node) {
// "useState" がインポートされているかをチェック
if (
node.specifiers.some(
(specifier) =>
specifier.imported && specifier.imported.name === 'useState',
)
) {
context.report({
node,
messageId: 'useStateError',
})
}
},
CallExpression: function (node) {
// "useState" が関数として呼び出されているかをチェック
if (node.callee.name === 'useState') {
context.report({
node,
messageId: 'useStateError',
})
}
},
}
},
}
上記の実装は以下のようなことを行っています。
※metaの部分の説明は割愛
- ImportDeclarationではimport層でuseStateをimportしていないかチェックしています
- CallExpressionではuseStateを関数として実行していないかチェックしています
Nuxt3ではauto-importが有効なのでimportを行わなくても利用できることからチェックするようにしています。
「composableファイルでuseStateを使う場合「NOTE:」コメントをつける」定義の実装
先ほどと同様でこちらもuseStateのルールになります。
基本的に利用は禁止としますが、それでも使うケースがあるのでその場合は「NOTE:」でコメントを残さないとエラーとします。
同じくeslintフォルダにカスタム定義用のファイルを新規で作成し以下のコードの反映をしてください。
※ここでは「use-state-with-note-comment.js」とします。
// use-state-with-note-comment.js
/**
* @type {import('eslint').Rule.RuleModule}
*/
export const useStateWithNoteComment = {
meta: {
type: 'problem',
docs: {
description: 'useStateを使う場合、Note: コメントを必須とするルール',
recommended: false,
},
schema: [], // ルールにオプションがない場合は空の配列
messages: {
missingNote:
'useStateを使用する場合は NOTE: コメントを記述してください。',
},
},
create: function (context) {
return {
CallExpression: function (node) {
if (node.callee.name === 'useState') {
// 全てのコメントの中から対象のuseStateの前のコメントを取得
const commentList = context.sourceCode.getAllComments()
const nodeLine = node.loc?.start.line ?? 0
const comment = commentList.find(
(comment) => (comment.loc?.end.line ?? 0) === nodeLine - 1,
)
if (!comment || !comment.value.includes('NOTE:')) {
context.report({
node,
messageId: 'missingNote',
})
}
}
},
}
},
}
上記の実装は以下のようなことを行っています。
※metaの部分の説明は割愛
- 対象ファイルからすべてのコメントを取得
- 対象のuseStateを呼び出している一つ上のコメントを取得し「NOTE:」コメントかチェック
これでeslintのカスタム定義の実装は終わりになります。
動作確認は最後に行うので次はstylelintのカスタム定義の実装を行います。
stylelintのカスタム定義の実装
基本的には公式のドキュメントに沿った設定をします。
実装する内容としてはざっくり以下のようなものとなっています。
- stylelintのライブラリに必要なmoduleは大体詰まっているのでこれを利用して定義などを作成する
- createPlugin関数を実行し、第二引数にエラーチェック用の処理を実装する
※この関数の戻り値にその他必要な情報を付与したりする
それでは実際にカスタム定義の実装をしていこうと思います。
「各vueファイルのstyleで詳細度が低いルート位置のstyleをエラーとする」定義の実装
stylelintフォルダに定義用のファイルを作成し以下のコードの実装をしてください。
※ここでは「component-class-specificity-rule.js」とします。
import path from 'path'
import stylelint from 'stylelint'
import * as specificity from 'specificity'
const {
createPlugin,
utils: { ruleMessages }
} = stylelint;
// 関数: ファイルパスから期待するクラス名を生成
function generateExpectedClassName(filePath) {
const projectRoot = process.cwd() // 現在の作業ディレクトリを取得
const relativePath = path.relative(projectRoot, filePath)
// 相対パスをディレクトリ名で分割し、最後の要素(ファイル名)を含むようにクラス名を生成
const parts = relativePath.split(path.sep)
const fileName = path.basename(parts.pop(), path.extname(filePath))
parts.push(fileName)
// すべてのパス部分をハイフンで連結し、無効な文字を削除
return `.${parts.join('-').replace(/.*components-/g, '')}`
}
const ruleName = 'custom/component-class-specificity'
const messages = ruleMessages(ruleName, {
rejected: () => 'ルートで指定するセレクタは詳細度を [0, 1, 1] 以上にしてください',
})
const meta = {}
/**
* @type {import('stylelint').Rule}
*/
const ruleFunction = (primaryOption) => {
return (root, result) => {
const validOptions = stylelint.utils.validateOptions(result, ruleName, {
actual: primaryOption,
})
if (!validOptions) {
return
}
// ファイルパスを取得して期待するクラス名を生成
const filePath = result.opts.from
const expectedClassName = generateExpectedClassName(filePath).replace(/.*components/g, '')
// すべてのルールを走査
root.walkRules((rule) => {
// ルートセレクタの場合のみチェック
if (rule.parent && rule.parent.type !== 'root') {
return // 入れ子のセレクタはスキップ
}
// specificity パッケージを使用して詳細度を計算
const specificityResults = specificity.calculate(rule.selector)
// 計算結果が存在し、適切な詳細度データが含まれているかをチェック
if (!specificityResults) {
return // 結果が無効な場合はスキップ
}
const score =
specificityResults.A * 100 +
specificityResults.B * 10 +
specificityResults.C
// 詳細度が [0, 1, 0] 以下で、期待されるクラス名ではない場合にエラーを出力
if (score <= 10 && rule.selector !== expectedClassName) {
stylelint.utils.report({
message: messages.rejected,
node: rule,
result,
ruleName,
})
}
})
}
};
ruleFunction.ruleName = ruleName;
ruleFunction.messages = messages;
ruleFunction.meta = meta;
export default createPlugin(ruleName, ruleFunction);
上記の実装は以下のようなことを行っています。
※metaの部分の説明は割愛
- 対象ファイルから生成されるルートクラスを許容するためのクラス名を生成
※components/test/hoge-componentなら「test-hoge-component」となる - すべてのセレクタを次の条件でチェックし引っ掛かる場合はエラーとする
- ルートセレクタ以外の場合はチェックしない
※入れ子のセレクタは詳細度が必ず「0, 1, 1」以上になるため - 1.で生成したクラスの場合はチェックしない
- 対象のセレクタの詳細度を計算し「0, 1, 0」以下の場合エラー
- ルートセレクタ以外の場合はチェックしない
stylelintのカスタム定義はこれのみとなっています。
全てのカスタム定義の実装が終わったので実際に適用してエラーを見てみましょう
カスタム定義の適用
実装したカスタム定義を適用し、linterのエラーとしてチェックするようにします。
環境構築時に作成した「eslint.config.mjs」と「.stylelintrc.cjs」に修正を行います。
// eslint.config.mjs
// @ts-check
import withNuxt from './.nuxt/eslint.config.mjs'
+ import { requireComponentHeaderComment } from './linter/eslint/require-component-header-comment.js'
+ import { noUseState } from './linter/eslint/no-use-state.js'
+ import { useStateWithNoteComment } from './linter/eslint/use-state-with-note-comment.js'
export default withNuxt(
// Your custom configs here
+ {
+ plugins: {
+ 'custom-rules': { // カスタム定義をルールとして設定
+ rules: {
+ 'require-component-header-comment': requireComponentHeaderComment,
+ 'no-use-state': noUseState,
+ 'use-state-with-note-comment': useStateWithNoteComment,
+ }
+ }
+ },
+ rules: {
+ 'custom-rules/no-use-state': 'error', // すべてのファイルでno-use-stateのルールを適用
+ },
+ },
+ {
+ files: ['**/components/**/*.vue'],
+ rules: {
+ 'custom-rules/require-component-header-comment': 'error', // ファイルの先頭にコメントブロックが必要
+ },
+ },
+ {
+ files: ['**/composables/**/*.ts'],
+ rules: {
+ 'custom-rules/no-use-state': 'off', // composable内でのuseStateの使用を許容
+ 'custom-rules/use-state-with-note-comment': 'error', // useStateを使う場合、// Note: コメントを必須とする
+ },
+ },
)
// .stylelintrc.cjs
module.exports = {
customSyntax: "postcss-html",
extends: [
"stylelint-config-recommended",
"stylelint-config-recommended-scss",
],
+ plugins: [
+ './linter/stylelint/component-class-specificity-rule.js' // カスタム定義を読み込み
+ ],
rules: {},
+ overrides: [
+ {
+ files: ['**/components/**/*.vue', '**/pages/**/*.vue'], // linterを適用するファイル
+ rules: {
+ 'custom/component-class-specificity': true, // 読み込んだカスタム定義を適用
+ },
+ },
+ ],
};
これで設定は終了です。
試しに「components/test/hoge-huga-component.vue」と「composables/useTest.ts」を実装し実際にエラーが起きるかscriptを実行してみようと思います。
// components/test/hoge-huga-component.vue
<!--
@name この名前だとエラーが出るはず
@description test
-->
<template>
<div class="test">test</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
const aaa = useState() // useStateは禁止なのでエラーが出るはず
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
.test { // ファイル名から定められるクラスではないのでエラーになるはず
color: red;
.hoge {
color: blue; // ここは入れ子の構造なのでエラーにならないはず
}
}
</style>
// composables/useTest.ts
export const useTest = () => {
const state = useState() // NOTE:のコメントが無いからエラーになるはず
return {
state
}
}
実際にscriptを実行してみたところ以下の通りエラーが発生しました。
※このようなエラーが出ればカスタム定義がうまく動いている状態です。
npm run lint:eslint
custom-linter\components\test\hoge-huga-component.vue
1:1 error @nameタグはcomponent以下のディレクトリ階層+ファイル名をキャメルケースでつなげ拡張子を削除したテキストを指定してください。(例:AtomsBaseInput) custom-rules/require-component-header-comment
10:13 error useStateの使用は禁止されています。 composable+provide/inject を使用してください。 custom-rules/no-use-state
custom-linter\composables\useTest.ts
2:18 error useStateを使用する場合は NOTE: コメントを記述してください。 custom-rules/use-state-with-note-comment
npm run lint:style
components/test/hoge-huga-component.vue
14:2 ✖ ルートで指定するセレクタは詳細度を [0, 1, 0] 以上にしてください custom/component-class-specificity
終わり
これでESlint / Stylelintを使ったカスタム定義の作成の仕方について終わりとなります。
この記事で作成したコードを確認したい場合は以下で見れるようにしています。
個人的には他にももっといろんなことができると思っているので色々なカスタム定義を作ってみようと考えています。
今後ドキュメント化したいけどLinterに任せられそうなものがあったらこんなのがあったなぁ程度に覚えていただければ嬉しいです
以上、読んでいただきありがとうございました!!