はじめに
ディープラーニングの学習経過の画像をjupyter上でリアルタイムに表示できるものがないかと探していたところ、Bokehというライブラリがあったので試してみました。
学習内容
Chainer を使って1層のDeconvolution 2D(簡単なフィルタみたいなもの)を学習させてみました。Deconvolutionについては以前にこちらで紹介したことなど参考にしてください。
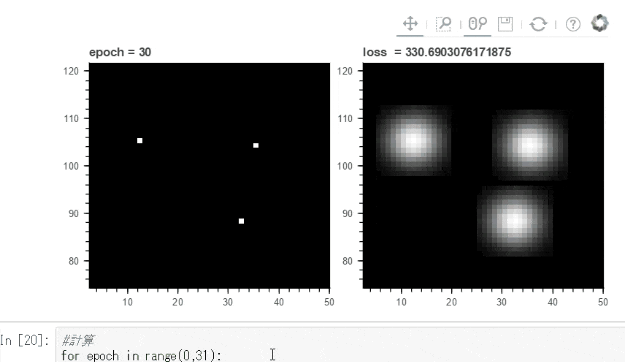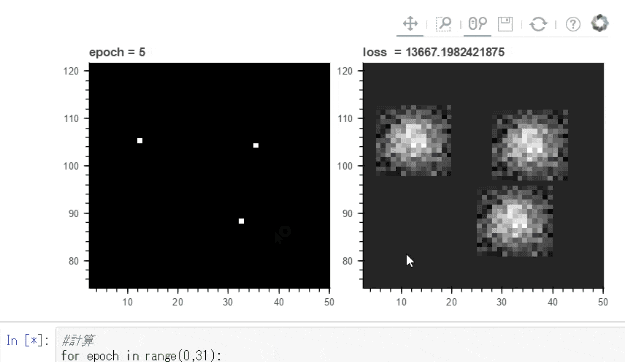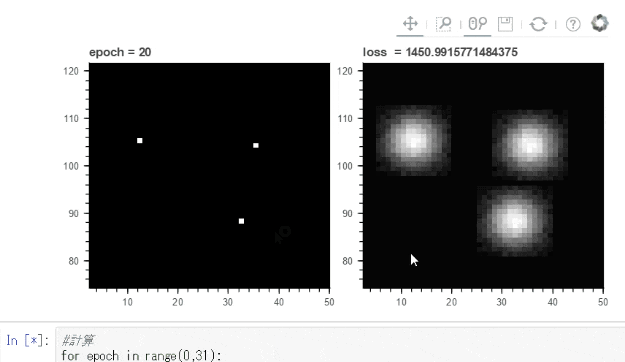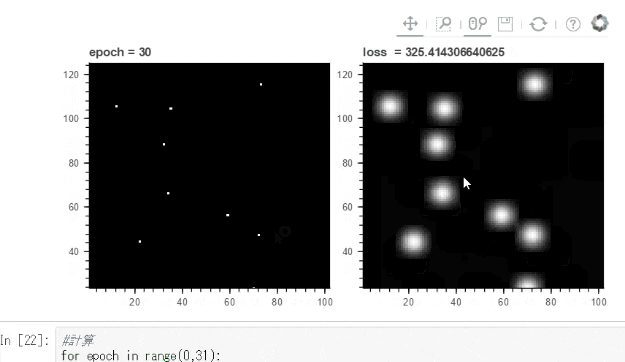
下のgifでは点 ⇒ 球状の模様に変化させるように学習させています。
Bokehでは画像をマウスホイールで拡大縮小などできるので学習の確認には便利です。
ソース
以前のChainerではnumpyを一度Variableに変換する必要がありましたが、Ver 1.17の現在では自動でVariableに変換してくれるようです。
Bokehのjupyter上での表示についてはこちらなど参考にしています。
import chainer.links as L
import chainer.functions as F
from chainer import Variable, optimizers
import numpy as np
import math
import time
# 1つの球状の模様を作成(ガウスですが)
def make_one_core():
max_xy=15
sig=5.0
sig2=sig*sig
c_xy=7
core=np.zeros((max_xy, max_xy), dtype= np.float32)
for px in range(0, max_xy):
for py in range(0, max_xy):
r2=(px-c_xy)*(px-c_xy)+(py-c_xy)*(py-c_xy)
core[py][px]=math.exp(-r2/sig2)*1
return core.reshape((1, 1, core.shape[0], core.shape[1]))
# 点と球状のimageを作成
def get_image(N=1, img_w=128, img_h=128):
#ランダムに0.1%の点を作る
img_p = np.random.randint(0, 10000, size = N*img_w*img_h)
img_p[img_p < 9990]=0
img_p[img_p >= 9990]=255
img_p = img_p.reshape((N,1,img_h, img_w)).astype(np.float32)
decon_core = L.Deconvolution2D(1, 1, 15, stride=1, pad=7)
#Wに球状の模様をあてる
decon_core.W.data = make_one_core()
#点⇒球に変換
img_core = decon_core(img_p)#Variableに変換なしでもOK
return img_p, img_core.data
# 初期描画
from bokeh.plotting import figure
from bokeh.io import push_notebook, show, output_notebook
from bokeh.layouts import gridplot
output_notebook()
palette_256 = ['#%02x%02x%02x' %(i,i,i) for i in range(256)] #256段階で白黒表示用
img_p, img_core = get_image()#点と球状のimageを取得
img_h = img_p.shape[2]
img_w = img_p.shape[3]
plt1 = figure(title = 'epoch = --', x_range=[0, img_w], y_range=[0, img_h])
rend1 = plt1.image(image=[img_p[0][0]],x=[0], y=[0], dw=[img_w], dh=[img_h], palette=palette_256)
plt2 = figure(title = 'loss = 0', x_range=plt1.x_range, y_range=plt1.y_range)
rend2 = plt2.image(image=[img_core[0][0]],x=[0], y=[0], dw=[img_w], dh=[img_h], palette=palette_256)
plts = gridplot([[plt1,plt2]], plot_width=300, plot_height=300)
handle = show(plts, notebook_handle=True)
# モデル・オプティマイザ設定
model = L.Deconvolution2D(1, 1, 15, stride=1, pad=7)#1層のDeconvolution
optimizer = optimizers.SGD(lr=0.001)#大きいと発散する
optimizer.setup(model)
# 計算
for epoch in range(0,31):
#1層のDeconvolutionを通してロスを計算しアップデート
model.cleargrads()
img_y = model(img_p)
loss = F.mean_squared_error(img_y, img_core)
loss.backward()
optimizer.update()
#画像・ロスデータをセット
rend1.data_source.data['image'] = [img_p[0][0]]
rend2.data_source.data['image'] = [img_y.data[0][0]]
plt1.title.text='epoch = '+str(epoch)
plt2.title.text='loss = '+str(loss.data)
push_notebook(handle = handle)#表示をアップデート
time.sleep(0.5)