どうも、オリィ研究所(http://orylab.com/) の ryo_grid こと神林です。
今回はOpen AI Gymで遊んでみたので、それについて書いてみます。
Open AI Gym (https://gym.openai.com) とは
AI開発者が自分のAIを動かすことのできるシミュレータを提供してくれる環境です。
Python向けにはライブラリを提供しています。
AI GymによりAI開発者やAI研究者はAIの学習ロジックの研究開発に専念でき、その可視化やシミュレーションを行う手間が省けます。また、同じシミュレーションを複数のユーザが競い合って解いているので、参加者全体でのアルゴリズムの性能向上が期待されます。
主なターゲットは強化学習によって構築されるAIです。Deep Q-Learning Network(DQN)を代表とする深層強化学習と呼ばれる手法が少し前から話題ですが、それらも強化学習の一種なので、動かすことが可能です。
最近話題になった、Google(Alphabet)傘下のDeepMindが公開したDeepMind Labと似たようなもので、AI Gymの方が古株です。
グーグルのDeepMind、AI訓練プラットフォームをオープンソース化
http://japan.zdnet.com/article/35093248/
試してみよう
必要なライブラリをインストールします。
pip install gym
他には、動画の生成に必要なffmpegが要求されるので、apt-getやhomebrewでよろしく入れておいて下さい。
下は公式のサンプルコードで、
import gym
env = gym.make('CartPole-v0')
env.monitor.start('./cartpole-experiment')
for i_episode in range(20):
observation = env.reset()
for t in range(100):
env.render()
action = env.action_space.sample()
observation, reward, done, info = env.step(action)
if done:
print("Episode finished after {} timesteps".format(t+1))
break
env.monitor.close()
gym.upload('./cartpole-experiment', api_key='YOUR_API_KEY')
これを動かすと、動画やら統計データがアップロードされて、下のようなページができます。
なお、API_KEYはGithubアカウントでAI gymにログインすると入手できます。
倒立振り子のシミュレータです。何も考えずにランダムにアクション(0:左移動, 1:右移動)を行っています。
アクションとはなんぞや?という方は下のリンク先などで強化学習について調べてみてください。
ゼロからDeepまで学ぶ強化学習
http://qiita.com/icoxfog417/items/242439ecd1a477ece312
gymのstepメソッドは環境情報、報酬、エピソードが終了条件に達したか、なんか参考の情報(よくわからない)の4つを返してきます。前の2つは強化学習を回すうえでの中心となる情報で、これを利用することでAIの強化学習が可能です。
DQNで倒立振り子
やってみました。
# coding: utf-8
import numpy as np
import time
import chainer
from chainer import cuda, Function, gradient_check, Variable, optimizers, serializers, utils
from chainer import Link, Chain, ChainList
import chainer.functions as F
import chainer.links as L
import gym
np.random.seed(7)
# 過去何コマを見るか
STATE_NUM = 4
# DQN内部で使われるニューラルネット
class Q(Chain):
def __init__(self,state_num=STATE_NUM):
super(Q,self).__init__(
l1=L.Linear(state_num, 16), # stateがインプット
l2=L.Linear(16, 32),
l3=L.Linear(32, 64),
l4=L.Linear(64, 256),
l5=L.Linear(256, 2), # 出力2チャネル(Qvalue)がアウトプット
)
def __call__(self,x,t):
return F.mean_squared_error(self.predict(x,train=True),t)
def predict(self,x,train=False):
h1 = F.leaky_relu(self.l1(x))
h2 = F.leaky_relu(self.l2(h1))
h3 = F.leaky_relu(self.l3(h2))
h4 = F.leaky_relu(self.l4(h3))
y = F.leaky_relu(self.l5(h4))
return y
# DQNアルゴリズムにしたがって動作するエージェント
class DQNAgent():
def __init__(self, epsilon=0.99):
self.model = Q()
self.optimizer = optimizers.Adam()
self.optimizer.setup(self.model)
self.epsilon = epsilon # ランダムアクションを選ぶ確率
self.actions=[0,1] # 行動の選択肢
self.experienceMemory = [] # 経験メモリ
self.memSize = 300*100 # 経験メモリのサイズ(300サンプリングx100エピソード)
self.experienceMemory_local=[] # 経験メモリ(エピソードローカル)
self.memPos = 0 #メモリのインデックス
self.batch_num = 32 # 学習に使うバッチサイズ
self.gamma = 0.9 # 割引率
self.loss=0
self.total_reward_award=np.ones(100)*-1000 #100エピソード
def get_action_value(self, seq):
# seq後の行動価値を返す
x = Variable(np.hstack([seq]).astype(np.float32).reshape((1,-1)))
return self.model.predict(x).data[0]
def get_greedy_action(self, seq):
action_index = np.argmax(self.get_action_value(seq))
return self.actions[action_index]
def reduce_epsilon(self):
self.epsilon-=1.0/100000
def get_epsilon(self):
return self.epsilon
def get_action(self,seq,train):
'''
アクションを返す。
'''
action=0
if train==True and np.random.random()<self.epsilon:
# random
action = np.random.choice(self.actions)
else:
# greedy
action= self.get_greedy_action(seq)
return action
def experience_local(self,old_seq, action, reward, new_seq):
#エピソードローカルな記憶
self.experienceMemory_local.append( np.hstack([old_seq,action,reward,new_seq]) )
def experience_global(self,total_reward):
#グローバルな記憶
#ベスト100に入る経験を取り込む
if np.min(self.total_reward_award)<total_reward:
i=np.argmin(self.total_reward_award)
self.total_reward_award[i]=total_reward
# GOOD EXPERIENCE REPLAY
for x in self.experienceMemory_local:
self.experience( x )
#一定確率で優秀でないものも取り込む
if np.random.random()<0.01:
# # NORMAL EXPERIENCE REPLAY
for x in self.experienceMemory_local:
self.experience( x )
self.experienceMemory_local=[]
def experience(self,x):
if len(self.experienceMemory)>self.memSize:
self.experienceMemory[int(self.memPos%self.memSize)]=x
self.memPos+=1
else:
self.experienceMemory.append( x )
def update_model(self,old_seq, action, reward, new_seq):
'''
モデルを更新する
'''
# 経験メモリにたまってない場合は更新しない
if len(self.experienceMemory)<self.batch_num:
return
# 経験メモリからバッチを作成
memsize=len(self.experienceMemory)
batch_index = list(np.random.randint(0,memsize,(self.batch_num)))
batch =np.array( [self.experienceMemory[i] for i in batch_index ])
x = Variable(batch[:,0:STATE_NUM].reshape( (self.batch_num,-1)).astype(np.float32))
targets=self.model.predict(x).data.copy()
for i in range(self.batch_num):
#[ seq..., action, reward, seq_new]
a = batch[i,STATE_NUM]
r = batch[i, STATE_NUM+1]
ai=int((a+1)/2) #±1 をindex(0,1)に。
new_seq= batch[i,(STATE_NUM+2):(STATE_NUM*2+2)]
targets[i,ai]=( r+ self.gamma * np.max(self.get_action_value(new_seq)))
t = Variable(np.array(targets).reshape((self.batch_num,-1)).astype(np.float32))
# ネットの更新
self.model.zerograds()
loss=self.model(x ,t)
self.loss = loss.data
loss.backward()
self.optimizer.update()
class pendulumEnvironment():
'''
振り子環境。
'''
def __init__(self):
self.env = gym.make('CartPole-v0')
self.env.monitor.start('./cartpole-experiment')
def reset(self):
self.env.reset()
def step(self, action):
return self.env.step(action)
def monitor_close(self):
self.env.monitor.close()
# シミュレータ。
class simulator:
def __init__(self, environment, agent):
self.agent = agent
self.env = environment
self.num_seq=STATE_NUM
self.reset_seq()
self.learning_rate=1.0
self.highscore=0
self.log=[]
def reset_seq(self):
self.seq=np.zeros(self.num_seq)
def push_seq(self, state):
self.seq[1:self.num_seq]=self.seq[0:self.num_seq-1]
self.seq[0]=state
def run(self, train=True):
self.env.reset()
self.reset_seq()
total_reward=0
for i in range(300):
# 現在のstateからなるシーケンスを保存
old_seq = self.seq.copy()
# エージェントの行動を決める
action = self.agent.get_action(old_seq,train)
# 環境に行動を入力する
observation, reward, done, info = self.env.step(action)
total_reward +=reward
# 結果を観測してstateとシーケンスを更新する
state = observation[2]
self.push_seq(state)
new_seq = self.seq.copy()
# エピソードローカルなメモリに記憶する
self.agent.experience_local(old_seq, action, reward, new_seq)
if done:
print("Episode finished after {} timesteps".format(i+1))
break
# エピソードローカルなメモリ内容をグローバルなメモリに移す
self.agent.experience_global(total_reward)
if train:
# 学習用メモリを使ってモデルを更新する
self.agent.update_model(old_seq, action, reward, new_seq)
self.agent.reduce_epsilon()
return total_reward
if __name__ == '__main__':
agent=DQNAgent()
env=pendulumEnvironment()
sim=simulator(env,agent)
best_reword = 0
for i in range(300000):
total_reword = sim.run(train=True)
if best_reword < total_reword:
best_reword = total_reword
print(str(i) + " " + str(total_reword) + " " + str(best_reword))
env.reset()
if best_reword > 195:
break
env.monitor_close()
gym.upload('./cartpole-experiment', api_key='YOUR_API_KEY')
結果はこちら。
https://gym.openai.com/evaluations/eval_zmiiqkPRgK10SOqMev3A#reproducibility
実装にあたっては、多くの部分を以下の記事のコードを流用させていただいています。
ありがとうございます。
倒立振子で学ぶ DQN (Deep Q Network)
http://qiita.com/ashitani/items/bb393e24c20e83e54577
2足歩行ロボでDQN
アクションは(-1,0,1)を値に取る4次元配列なので注意。
# coding: utf-8
import numpy as np
import time
import chainer
from chainer import cuda, Function, gradient_check, Variable, optimizers, serializers, utils
from chainer import Link, Chain, ChainList
import chainer.functions as F
import chainer.links as L
import gym
np.random.seed(7)
STATE_NUM = 24
# DQN内部で使われるニューラルネット
class Q(Chain):
def __init__(self,state_num=STATE_NUM):
super(Q,self).__init__(
l1=L.Linear(state_num, 16), # stateがインプット
l2=L.Linear(16, 32),
l3=L.Linear(32, 64),
l4=L.Linear(64, 256),
l5=L.Linear(256, 3*3*3*3), # 出力2チャネル(Qvalue)がアウトプット
)
def __call__(self,x,t):
return F.mean_squared_error(self.predict(x,train=True),t)
def predict(self,x,train=False):
h1 = F.leaky_relu(self.l1(x))
h2 = F.leaky_relu(self.l2(h1))
h3 = F.leaky_relu(self.l3(h2))
h4 = F.leaky_relu(self.l4(h3))
y = F.leaky_relu(self.l5(h4))
return y
# DQNアルゴリズムにしたがって動作するエージェント
class DQNAgent():
def __init__(self, epsilon=0.99):
self.model = Q()
self.optimizer = optimizers.Adam()
self.optimizer.setup(self.model)
self.epsilon = epsilon # ランダムアクションを選ぶ確率
self.actions=[-1,0,1] # 行動の選択肢
self.experienceMemory = [] # 経験メモリ
self.memSize = 300*100 # 経験メモリのサイズ(300サンプリングx100エピソード)
self.experienceMemory_local=[] # 経験メモリ(エピソードローカル)
self.memPos = 0 #メモリのインデックス
self.batch_num = 32 # 学習に使うバッチサイズ
self.gamma = 0.9 # 割引率
self.loss=0
self.total_reward_award=np.ones(100)*-1000 #100エピソード
def index_to_list(self, index):
ret_arr = []
a = int(index / 27) - 1
rest = index - 27*int(index / 27)
ret_arr.append(a)
a = int(rest / 9) - 1
rest = rest - 9*int(rest / 9)
ret_arr.append(a)
a = int(rest / 3) - 1
rest = rest - 3*int(rest / 3)
ret_arr.append(a)
ret_arr.append(rest -1)
return ret_arr
def list_to_index(self, lst):
ret = 0
ret += (lst[0] + 1)*27
ret += (lst[1] + 1)*9
ret += (lst[2] + 1)*3
ret += (lst[3] + 1)
return ret
def get_action_value(self, seq):
# seq後の行動価値を返す
x = Variable(np.hstack([seq]).astype(np.float32).reshape((1,-1)))
return self.model.predict(x).data[0]
def get_greedy_action(self, seq):
action_index = np.argmax(self.get_action_value(seq))
return self.index_to_list(action_index)
def reduce_epsilon(self):
self.epsilon-=1.0/10000
def get_epsilon(self):
return self.epsilon
def get_action(self,seq,train):
'''
seq (env, old_env)に対して
アクションを返す。
'''
action=[]
if train==True and np.random.random()<self.epsilon:
# random
action.append(np.random.choice(self.actions))
action.append(np.random.choice(self.actions))
action.append(np.random.choice(self.actions))
action.append(np.random.choice(self.actions))
else:
# greedy
action= self.get_greedy_action(seq)
return action
def experience_local(self,old_seq, action, reward, new_seq):
#エピソードローカルな記憶
self.experienceMemory_local.append( np.hstack([old_seq,action,reward,new_seq]) )
def experience_global(self,total_reward):
#グローバルな記憶
#ベスト100に入る経験を取り込む
if np.min(self.total_reward_award)<total_reward:
i=np.argmin(self.total_reward_award)
self.total_reward_award[i]=total_reward
# GOOD EXPERIENCE REPLAY
for x in self.experienceMemory_local:
self.experience( x )
#一定確率で優秀でないものも取り込む
if np.random.random()<0.01:
# # NORMAL EXPERIENCE REPLAY
for x in self.experienceMemory_local:
self.experience( x )
self.experienceMemory_local=[]
def experience(self,x):
if len(self.experienceMemory)>self.memSize:
self.experienceMemory[int(self.memPos%self.memSize)]=x
self.memPos+=1
else:
self.experienceMemory.append( x )
def update_model(self,old_seq, action, reward, new_seq):
'''
モデルを更新する
'''
# 経験メモリにたまってない場合は更新しない
if len(self.experienceMemory)<self.batch_num:
return
# 経験メモリからバッチを作成
memsize=len(self.experienceMemory)
batch_index = list(np.random.randint(0,memsize,(self.batch_num)))
batch =np.array( [self.experienceMemory[i] for i in batch_index ])
x = Variable(batch[:,0:STATE_NUM].reshape( (self.batch_num,-1)).astype(np.float32))
targets=self.model.predict(x).data.copy()
for i in range(self.batch_num):
#[ seq..., action, reward, seq_new]
a = batch[i,STATE_NUM]
r = batch[i, STATE_NUM+1]
ai=a
new_seq= batch[i,(STATE_NUM+2):(STATE_NUM*2+2)]
targets[i,ai]=( r+ self.gamma * np.max(self.get_action_value(new_seq)))
t = Variable(np.array(targets).reshape((self.batch_num,-1)).astype(np.float32))
# ネットの更新
self.model.zerograds()
loss=self.model(x ,t)
self.loss = loss.data
loss.backward()
self.optimizer.update()
class walkerEnvironment():
def __init__(self):
self.env = gym.make('BipedalWalkerHardcore-v2')
self.env.monitor.start('./walker-experiment')
def reset(self):
self.env.reset()
def step(self, action):
return self.env.step(action)
def monitor_close(self):
self.env.monitor.close()
# シミュレータ。
class simulator:
def __init__(self, environment, agent):
self.agent = agent
self.env = environment
self.num_seq=STATE_NUM
self.reset_seq()
self.learning_rate=1.0
self.highscore=0
self.log=[]
def reset_seq(self):
self.seq=np.zeros(self.num_seq)
def push_seq(self, state):
self.seq = state
def run(self, train=True):
self.env.reset()
self.reset_seq()
total_reward=0
for i in range(100000):
# 現在のstateからなるシーケンスを保存
old_seq = self.seq.copy()
# エージェントの行動を決める
action = self.agent.get_action(old_seq,train)
# 環境に行動を入力する
observation, reward, done, info = self.env.step(action)
total_reward +=reward
# 結果を観測してstateとシーケンスを更新する
state = observation
self.push_seq(state)
new_seq = self.seq.copy()
# エピソードローカルなメモリに記憶する
action_idx = self.agent.list_to_index(action)
self.agent.experience_local(old_seq, action_idx, reward, new_seq)
if done:
print("Episode finished after {} timesteps".format(i+1))
break
# エピソードローカルなメモリ内容をグローバルなメモリに移す
self.agent.experience_global(total_reward)
if train:
# 学習用メモリを使ってモデルを更新する
action_idx = self.agent.list_to_index(action)
self.agent.update_model(old_seq, action_idx, reward, new_seq)
self.agent.reduce_epsilon()
return total_reward
if __name__ == '__main__':
agent=DQNAgent()
env=walkerEnvironment()
sim=simulator(env,agent)
best_reword = -200
for i in range(10000):
total_reword = sim.run(train=True)
if best_reword < total_reword:
best_reword = total_reword
print(str(i) + " " + str(total_reword) + " " + str(best_reword))
env.reset()
if best_reword > 200:
break
env.monitor_close()
gym.upload('./walker-experiment', api_key='YOUR_API_KEY')
結果はこちら。
https://gym.openai.com/evaluations/eval_qaM0iTJSST2DDd5Br0HE6A#reproducibility
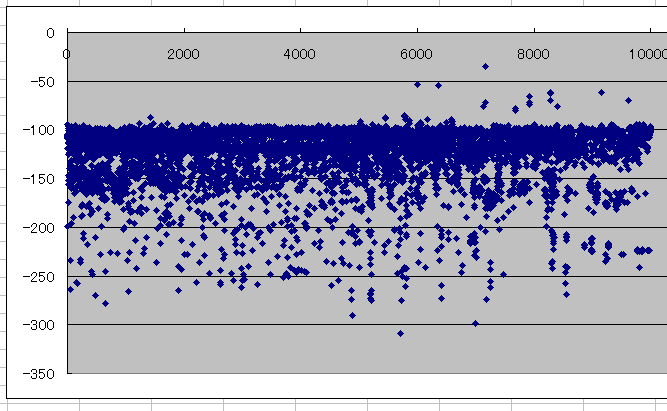
生まれたての小鹿にしかなりませんでしたが、
10000エピソード学習する過程で得られた award (報酬) の推移を見ると、終盤に良いスコアを記録している様子が見て取れる。
ただ、全体的には下がっているようにも見えて不思議。
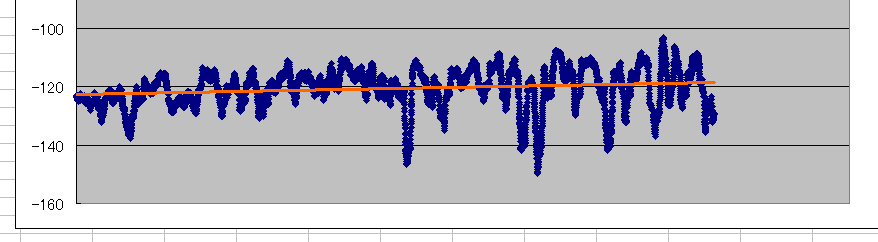
そこで、100エピソードで移動平均をとると、まあちゃんと学習してるっぽいことが読み取れる。
よかったよかった。
なお、上記のAIは環境の情報のセマンティックスを意識することなく動作しています。
どうも、良くできたAIというのはセマンティクスを意識しなくても良いのだ、と偉い人か良くわからない人が言っているのをネットで見ました。ので、それに従っています(Gym側は環境の各情報のセマンティクスを教えてくれないので意識しようがないという話もある)。
ちなみに、よくできた学習アルゴリズムだとこんな感じで歩きます。
https://gym.openai.com/evaluations/eval_Gxwojs5T5a8jayWaVwFA
現場からは以上です。
(12/19追記)
二足歩行ロボ、転がってたコードを真似したら、それなりに歩くようにでけた!
https://gym.openai.com/evaluations/eval_wzmU0dtQCeoz2dWyhsD5Q
Neuroevolutionと呼ばれる技術の中の一手法であるNEAT(NeuroEvolution of Augmenting Topologies)というやつを使っている。
ざっくり言うと遺伝的アルゴリズムでニューラルネットワークの結合?の最適化をしたりする手法みたいです。
(1/10追記)
再チャレンジについて書きました
http://qiita.com/ryo_grid/items/af60750659d1d7ffeef9