こんにちは。
株式会社クラスアクト インフラストラクチャ事業部の大塚です。
この記事ではプライベートコンテナレジストリであるHarborをRook-Cephを使ってKubernetesクラスタ上にデプロイしていきたいと思います。HarborデプロイにはHelmを使います。
Rook-Cephの構築は以下をご覧ください。
Helmの構築は以下をご覧ください。
用語
Harbor
以下のサイトが簡潔で分かりやすいです。
コンテナレジストリと言って真っ先に思いつくのがdocker hubかと思いますが、あれはpublicネットワーク上にあるので、いくら外部非公開にできるとは言え、本番環境用のコンテナイメージをアップロードしておくのは少々怖いですよね。
そこでHarborの出番というわけです。これはprivateなネットワークに構築するため、攻撃されない限りは外部の人間から見られることはありません。
RBD
多分"RADOS Block Device"の略。
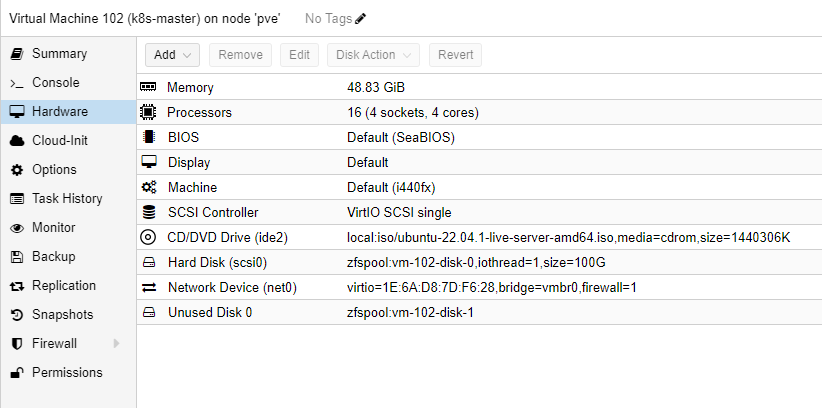
Cephの提供するサービスの1つである【CephFS】が仮想的なファイルシステムを提供するのに対して、【RBD】は仮想的なブロックデバイスを提供します。ブロックデバイスと聞くと難しく聞こえますが、HDDとかSSDとかのイメージを持っておけばいいような気がします。VMをよく立ち上げている人であれば、以下の画像でいうHard Diskの部分なんだよな~と認識すれば。。。!
公式サイトは以下です。
ブロックデバイス
ブロックデバイスとは、データを固定サイズのブロック単位で管理するデータストレージの手法のことです。ブロックデバイスを使用することで、データの読み書きを効率的に行うことができます。ハードディスクドライブやSSD(ソリッドステートドライブ)などがブロックデバイスの代表例です。
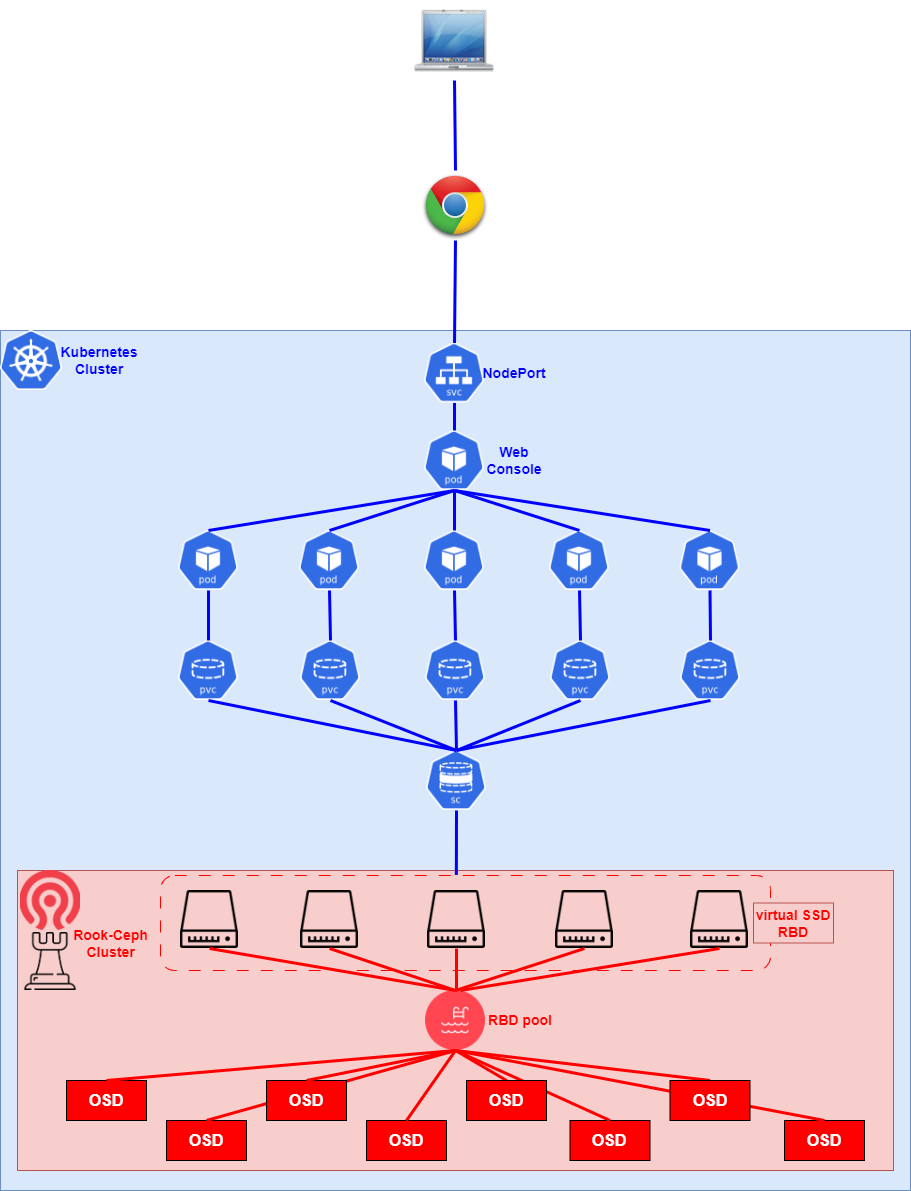
構築イメージ
以下がざっくりとしたイメージとなります。HelmでHarborをデプロイする前に、Rook-Ceph上にRBD用のpoolとそこに紐づいてくるStorageClassをデプロイします。その後、Helm上のHarborからvalues.yamlを生成してconfigをいじり、ストレージが必要となるPod(redisとかRegistry、PostgreSQLとか)に対してどのSCを使うかを指定させます。また、HarborのdashboardにはNodePortを使うように併せてconfigをいじります。Helmを使ってHarborをデプロイする際、values.yamlを指定してデプロイします。
クラスタノードのHW詳細
ちょっとぐちゃぐちゃですが、正直ここまでDiskはいらないはずです。
HardDisk3の部分は丸っとなくしても全く問題ないと思いますし、HardDisk2に対してもここまでいらないと思います。
Rook-Cephはこの表のDisk2と3を使ってクラスタを構成しています。
| hostname | IP Address | CPU | Memory | HardDisk1 | HardDisk2 | HardDisk3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k8s-master | 192.168.2.30/24 | 4 sockets 4 cores | 48.83GiB | 100G | - | - |
| k8s-worker01 | 192.168.2.31/24 | 2 sockets 4 cores | 29.30GiB | 60G | 50G | 50G |
| k8s-worker02 | 192.168.2.32/24 | 2 sockets 4 cores | 29.30GiB | 60G | 50G | 50G |
| k8s-worker03 | 192.168.2.33/24 | 2 sockets 4 cores | 29.30GiB | 60G | 50G | 50G |
| k8s-ceph01 | 192.168.2.37/24 | 2 sockets 4 cores | 19.53GiB | 50G | 50G | 50G |
| k8s-ceph02 | 192.168.2.38/24 | 2 sockets 4 cores | 19.53GiB | 50G | 50G | 50G |
| k8s-ceph03 | 192.168.2.39/24 | 2 sockets 4 cores | 19.53GiB | 50G | 50G | 50G |
参考にした手順
構築
RBDのpoolとStorageClassをデプロイする
Rook-Cephを最初の方で提示した手順をもとに作成していると、rook/deploy/examples/というようなディレクトリがサーバ上に存在するはずなので、その下にあるcsi/rbd/まで移動します。
すると配下にstorageclass.yamlという名前のファイルがあるはずです。
root@k8s-master:~# cd rook/deploy/examples/csi/rbd/
root@k8s-master:~/rook/deploy/examples/csi/rbd# ls -ltr storageclass.yaml
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 3475 Jun 24 06:20 storageclass.yaml
このファイルの中身はデフォルトで以下のようになっています。
CephBlockPoolというデータを格納するpool(CephFSでいうdata poolとかmetadata poolの類と思われる)とSCを定義していることがわかります。
apiVersion: ceph.rook.io/v1
kind: CephBlockPool
metadata:
name: replicapool
namespace: rook-ceph # namespace:cluster
spec:
failureDomain: host
replicated:
size: 3
# Disallow setting pool with replica 1, this could lead to data loss without recovery.
# Make sure you're *ABSOLUTELY CERTAIN* that is what you want
requireSafeReplicaSize: true
# gives a hint (%) to Ceph in terms of expected consumption of the total cluster capacity of a given pool
# for more info: https://docs.ceph.com/docs/master/rados/operations/placement-groups/#specifying-expected-pool-size
#targetSizeRatio: .5
---
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: rook-ceph-block
# Change "rook-ceph" provisioner prefix to match the operator namespace if needed
provisioner: rook-ceph.rbd.csi.ceph.com
parameters:
# clusterID is the namespace where the rook cluster is running
# If you change this namespace, also change the namespace below where the secret namespaces are defined
clusterID: rook-ceph # namespace:cluster
# If you want to use erasure coded pool with RBD, you need to create
# two pools. one erasure coded and one replicated.
# You need to specify the replicated pool here in the `pool` parameter, it is
# used for the metadata of the images.
# The erasure coded pool must be set as the `dataPool` parameter below.
#dataPool: ec-data-pool
pool: replicapool
# (optional) mapOptions is a comma-separated list of map options.
# For krbd options refer
# https://docs.ceph.com/docs/master/man/8/rbd/#kernel-rbd-krbd-options
# For nbd options refer
# https://docs.ceph.com/docs/master/man/8/rbd-nbd/#options
# mapOptions: lock_on_read,queue_depth=1024
# (optional) unmapOptions is a comma-separated list of unmap options.
# For krbd options refer
# https://docs.ceph.com/docs/master/man/8/rbd/#kernel-rbd-krbd-options
# For nbd options refer
# https://docs.ceph.com/docs/master/man/8/rbd-nbd/#options
# unmapOptions: force
# RBD image format. Defaults to "2".
imageFormat: "2"
# RBD image features. Available for imageFormat: "2". CSI RBD currently supports only `layering` feature.
imageFeatures: layering
# The secrets contain Ceph admin credentials. These are generated automatically by the operator
# in the same namespace as the cluster.
csi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-name: rook-csi-rbd-provisioner
csi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-namespace: rook-ceph # namespace:cluster
csi.storage.k8s.io/controller-expand-secret-name: rook-csi-rbd-provisioner
csi.storage.k8s.io/controller-expand-secret-namespace: rook-ceph # namespace:cluster
csi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-name: rook-csi-rbd-node
csi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-namespace: rook-ceph # namespace:cluster
# Specify the filesystem type of the volume. If not specified, csi-provisioner
# will set default as `ext4`. Note that `xfs` is not recommended due to potential deadlock
# in hyperconverged settings where the volume is mounted on the same node as the osds.
csi.storage.k8s.io/fstype: ext4
# uncomment the following to use rbd-nbd as mounter on supported nodes
# **IMPORTANT**: CephCSI v3.4.0 onwards a volume healer functionality is added to reattach
# the PVC to application pod if nodeplugin pod restart.
# Its still in Alpha support. Therefore, this option is not recommended for production use.
#mounter: rbd-nbd
allowVolumeExpansion: true
reclaimPolicy: Delete
特に変更をかけずにデプロイをしていきます。
デプロイされていることも併せて確認しておきましょう。
root@k8s-master:~/rook/deploy/examples/csi/rbd# kubectl apply -f storageclass.yaml
cephblockpool.ceph.rook.io/replicapool created
storageclass.storage.k8s.io/rook-ceph-block created
root@k8s-master:~/rook/deploy/examples/csi/rbd# kubectl get CephBlockPool -n rook-ceph
NAME PHASE
replicapool Ready
root@k8s-master:~/yaml/harbor# kubectl get pv,pvc,sc -A
NAMESPACE NAME PROVISIONER RECLAIMPOLICY VOLUMEBINDINGMODE ALLOWVOLUMEEXPANSION AGE
storageclass.storage.k8s.io/rook-ceph-block rook-ceph.rbd.csi.ceph.com Delete Immediate true 14m
Ceph管理コンソールでもPoolsタブでデプロイを確認することができます。

Harborのvalues.yamlの生成とconfig設定
HelmにHarborをインストールしていきます。
root@k8s-master:~/yaml# helm repo add harbor https://helm.goharbor.io
"harbor" has been added to your repositories
root@k8s-master:~/yaml# helm repo list
NAME URL
bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami
metallb https://metallb.github.io/metallb
harbor https://helm.goharbor.io
root@k8s-master:~/yaml# helm repo update
Hang tight while we grab the latest from your chart repositories...
...Successfully got an update from the "metallb" chart repository
...Successfully got an update from the "harbor" chart repository
...Successfully got an update from the "bitnami" chart repository
Update Complete. ?Happy Helming!?
helm pullに--uintarオプションを付与するとカレントディレクトリにharborというディレクトリができます。
ここに移動するとvalues.yamlがあるはずなのでこれをいじっていきます。
またいじる前にkubectl get nodes -o jsonpath="{.items[0].status.addresses[0].address}"を実行してIPアドレスを控えます。
root@k8s-master:~/yaml# helm pull harbor/harbor --untar
root@k8s-master:~/yaml# ls -ltr
total 24
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jul 1 14:03 metal-lb
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jul 1 17:03 wp
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jul 1 18:07 prometheus
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jul 1 18:12 ingress
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jul 2 06:41 rook-ceph
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Jul 2 07:15 harbor
root@k8s-master:~/yaml# cd harbor/
root@k8s-master:~/yaml/harbor# ls -ltr
total 248
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 33874 Jul 2 07:15 values.yaml
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 567 Jul 2 07:15 Chart.yaml
drwxr-xr-x 15 root root 4096 Jul 2 07:15 templates
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 192242 Jul 2 07:15 README.md
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 11357 Jul 2 07:15 LICENSE
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jul 2 07:15 conf
root@k8s-master:~/yaml/harbor# kubectl get nodes -o jsonpath="{.items[0].status.addresses[0].address}"
192.168.2.37
valusesのバックアップを取得し、編集します。今回は以下のように編集しております。
typeのところにnodePorを記載し、nodePortでアクセスするようにしています。
HelmでHarborをデプロイする際、DB podとか諸々デプロイされるのですが、そのデータの格納先をRBDとしています。
root@k8s-master:~/yaml/harbor# cp -p values.yaml values.yaml.org
root@k8s-master:~/yaml/harbor# vi values.yaml
root@k8s-master:~/yaml/harbor# diff values.yaml values.yaml.org
4c4
< type: nodePort
---
> type: ingress
23c23
< commonName: "192.168.2.37"
---
> commonName: ""
127c127
< externalURL: https://192.168.2.37:30003
---
> externalURL: https://core.harbor.domain
212c212
< storageClass: "rook-ceph-block"
---
> storageClass: ""
220c220
< storageClass: "rook-ceph-block"
---
> storageClass: ""
229c229
< storageClass: "rook-ceph-block"
---
> storageClass: ""
238c238
< storageClass: "rook-ceph-block"
---
> storageClass: ""
245c245
< storageClass: "rook-ceph-block"
---
> storageClass: ""
Harborのデプロイ
Helmを使いHarborをデプロイしていきます。nsは事前に作成しておいてください。
Helm実行時、-fでvalues.yamlを指定できます。
root@k8s-master:~/yaml/harbor# kubectl create ns harbor
namespace/harbor created
root@k8s-master:~/yaml/harbor# helm install harbor -n harbor -f values.yaml harbor/harbor
NAME: harbor
LAST DEPLOYED: Sat Jul 8 22:59:07 2023
NAMESPACE: harbor
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
Please wait for several minutes for Harbor deployment to complete.
Then you should be able to visit the Harbor portal at https://core.harbor.domain
For more details, please visit https://github.com/goharbor/harbor
root@k8s-master:~/yaml/harbor# helm ls -n harbor
AME NAMESPACE REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART APP VERSION
harbor harbor 1 2023-07-08 22:59:07.474125967 +0000 UTC deployed harbor-1.12.2 2.8.2
うまく定義ができていればpv,pvcが作成されます。
root@k8s-master:~/yaml/harbor# kubectl get pv,pvc,sc -A
NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS REASON AGE
persistentvolume/pvc-3e6fe087-bea7-4263-bae9-7fe7414f0b86 5Gi RWO Delete Bound harbor/harbor-registry rook-ceph-block 41s
persistentvolume/pvc-44503116-a371-4d60-a538-edfae95d057e 1Gi RWO Delete Bound harbor/data-harbor-redis-0 rook-ceph-block 41s
persistentvolume/pvc-659c5329-8d12-4328-86bf-b47f113345da 1Gi RWO Delete Bound harbor/harbor-jobservice rook-ceph-block 41s
persistentvolume/pvc-a6ad099a-34ce-407b-8df0-91d4f2f68f6c 1Gi RWO Delete Bound harbor/database-data-harbor-database-0 rook-ceph-block 41s
persistentvolume/pvc-a74769a2-97b9-4e8d-9b3a-b1bf769efd34 5Gi RWO Delete Bound harbor/data-harbor-trivy-0 rook-ceph-block 41s
NAMESPACE NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
harbor persistentvolumeclaim/data-harbor-redis-0 Bound pvc-44503116-a371-4d60-a538-edfae95d057e 1Gi RWO rook-ceph-block 42s
harbor persistentvolumeclaim/data-harbor-trivy-0 Bound pvc-a74769a2-97b9-4e8d-9b3a-b1bf769efd34 5Gi RWO rook-ceph-block 42s
harbor persistentvolumeclaim/database-data-harbor-database-0 Bound pvc-a6ad099a-34ce-407b-8df0-91d4f2f68f6c 1Gi RWO rook-ceph-block 42s
harbor persistentvolumeclaim/harbor-jobservice Bound pvc-659c5329-8d12-4328-86bf-b47f113345da 1Gi RWO rook-ceph-block 42s
harbor persistentvolumeclaim/harbor-registry Bound pvc-3e6fe087-bea7-4263-bae9-7fe7414f0b86 5Gi RWO rook-ceph-block 42s
NAMESPACE NAME PROVISIONER RECLAIMPOLICY VOLUMEBINDINGMODE ALLOWVOLUMEEXPANSION AGE
storageclass.storage.k8s.io/rook-ceph-block rook-ceph.rbd.csi.ceph.com Delete Immediate true 20m
podも以下のようにデプロイされます。
jobserviceのpodが作成に一番時間がかかるイメージがあります。またCrashLoopBackoffがデプロイ直後に発生するかもです。
root@k8s-master:~/yaml/harbor# kubectl get pod -n harbor
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
harbor-core-56d48cdfcf-5cmfh 0/1 Running 0 77s
harbor-database-0 1/1 Running 0 77s
harbor-jobservice-f74b96f5f-v5bpg 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 77s
harbor-nginx-765998b9c5-jmm2k 1/1 Running 0 77s
harbor-notary-server-6f6c766dbb-qnmpm 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 77s
harbor-notary-signer-55cd9c9d65-p6swq 0/1 CrashLoopBackOff 1 (13s ago) 77s
harbor-portal-7d54d7bc96-4jlt7 1/1 Running 0 77s
harbor-redis-0 1/1 Running 0 77s
harbor-registry-86cc6cc8c7-sg6pv 2/2 Running 0 77s
harbor-trivy-0 1/1 Running 0 77s
root@k8s-master:~/yaml/harbor# kubectl get pod -n harbor
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
harbor-core-56d48cdfcf-5cmfh 1/1 Running 0 3m19s
harbor-database-0 1/1 Running 0 3m19s
harbor-jobservice-f74b96f5f-v5bpg 1/1 Running 0 3m19s
harbor-nginx-765998b9c5-jmm2k 1/1 Running 0 3m19s
harbor-notary-server-6f6c766dbb-qnmpm 1/1 Running 0 3m19s
harbor-notary-signer-55cd9c9d65-p6swq 1/1 Running 2 (2m15s ago) 3m19s
harbor-portal-7d54d7bc96-4jlt7 1/1 Running 0 3m19s
harbor-redis-0 1/1 Running 0 3m19s
harbor-registry-86cc6cc8c7-sg6pv 2/2 Running 0 3m19s
harbor-trivy-0 1/1 Running 0 3m19s
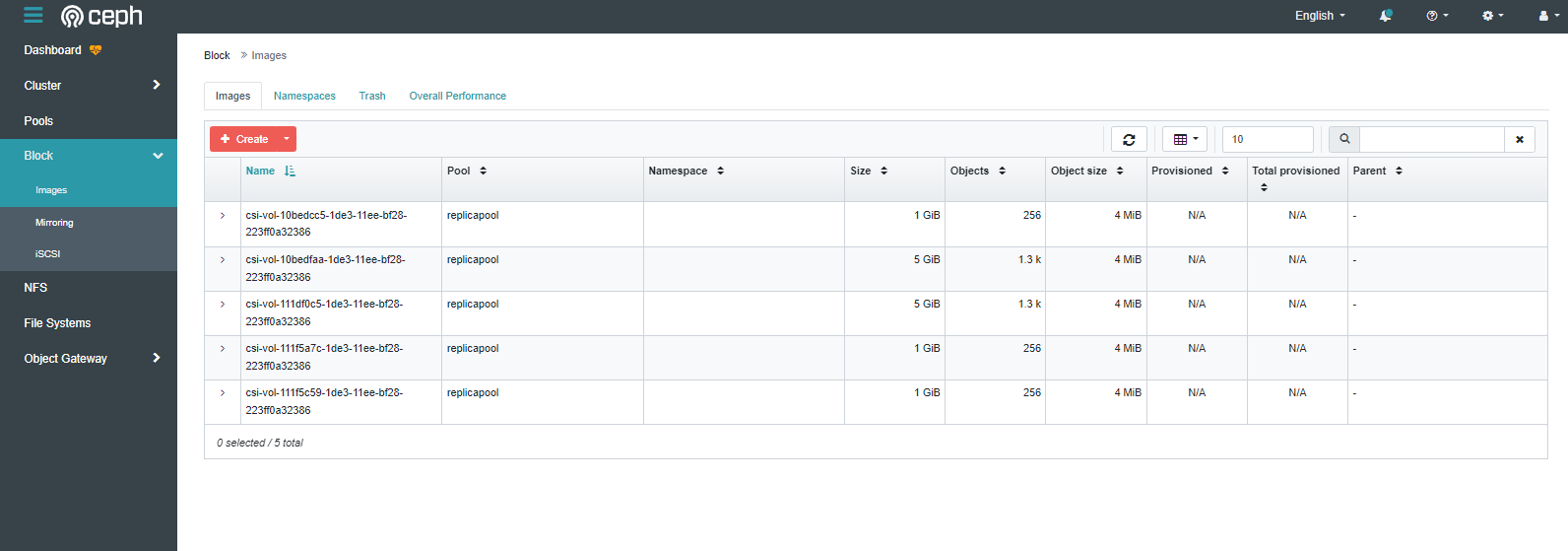
ここまで作成すると、Cephの管理コンソールにRBDが出力されます。
このタイミングでRBDが作成されたということですね。
HarborのWebコンソールにログインする。
HarborのWebコンソールにアクセスします。
私と同様であればhttps://"クラスタノードのIPいずれか":30003でアクセスできるはずです。
ユーザとパスワードはadminとHarbor12345になります。
※パスワードはvaluesに書いています。
【オマケ】values.yaml
不要かと思いますが、values.yamlをすべて吐き出しておきましたので、適宜ご覧いただければと思います。
expose:
# Set how to expose the service. Set the type as "ingress", "clusterIP", "nodePort" or "loadBalancer"
# and fill the information in the corresponding section
type: nodePort
tls:
# Enable TLS or not.
# Delete the "ssl-redirect" annotations in "expose.ingress.annotations" when TLS is disabled and "expose.type" is "ingress"
# Note: if the "expose.type" is "ingress" and TLS is disabled,
# the port must be included in the command when pulling/pushing images.
# Refer to https://github.com/goharbor/harbor/issues/5291 for details.
enabled: true
# The source of the tls certificate. Set as "auto", "secret"
# or "none" and fill the information in the corresponding section
# 1) auto: generate the tls certificate automatically
# 2) secret: read the tls certificate from the specified secret.
# The tls certificate can be generated manually or by cert manager
# 3) none: configure no tls certificate for the ingress. If the default
# tls certificate is configured in the ingress controller, choose this option
certSource: auto
auto:
# The common name used to generate the certificate, it's necessary
# when the type isn't "ingress"
commonName: "192.168.2.37"
secret:
# The name of secret which contains keys named:
# "tls.crt" - the certificate
# "tls.key" - the private key
secretName: ""
# The name of secret which contains keys named:
# "tls.crt" - the certificate
# "tls.key" - the private key
# Only needed when the "expose.type" is "ingress".
notarySecretName: ""
ingress:
hosts:
core: core.harbor.domain
notary: notary.harbor.domain
# set to the type of ingress controller if it has specific requirements.
# leave as `default` for most ingress controllers.
# set to `gce` if using the GCE ingress controller
# set to `ncp` if using the NCP (NSX-T Container Plugin) ingress controller
# set to `alb` if using the ALB ingress controller
# set to `f5-bigip` if using the F5 BIG-IP ingress controller
controller: default
## Allow .Capabilities.KubeVersion.Version to be overridden while creating ingress
kubeVersionOverride: ""
className: ""
annotations:
# note different ingress controllers may require a different ssl-redirect annotation
# for Envoy, use ingress.kubernetes.io/force-ssl-redirect: "true" and remove the nginx lines below
ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "true"
ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-body-size: "0"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "true"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-body-size: "0"
notary:
# notary ingress-specific annotations
annotations: {}
# notary ingress-specific labels
labels: {}
harbor:
# harbor ingress-specific annotations
annotations: {}
# harbor ingress-specific labels
labels: {}
clusterIP:
# The name of ClusterIP service
name: harbor
# Annotations on the ClusterIP service
annotations: {}
ports:
# The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTP
httpPort: 80
# The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTPS
httpsPort: 443
# The service port Notary listens on. Only needed when notary.enabled
# is set to true
notaryPort: 4443
nodePort:
# The name of NodePort service
name: harbor
ports:
http:
# The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTP
port: 80
# The node port Harbor listens on when serving HTTP
nodePort: 30002
https:
# The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTPS
port: 443
# The node port Harbor listens on when serving HTTPS
nodePort: 30003
# Only needed when notary.enabled is set to true
notary:
# The service port Notary listens on
port: 4443
# The node port Notary listens on
nodePort: 30004
loadBalancer:
# The name of LoadBalancer service
name: harbor
# Set the IP if the LoadBalancer supports assigning IP
IP: ""
ports:
# The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTP
httpPort: 80
# The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTPS
httpsPort: 443
# The service port Notary listens on. Only needed when notary.enabled
# is set to true
notaryPort: 4443
annotations: {}
sourceRanges: []
# The external URL for Harbor core service. It is used to
# 1) populate the docker/helm commands showed on portal
# 2) populate the token service URL returned to docker/notary client
#
# Format: protocol://domain[:port]. Usually:
# 1) if "expose.type" is "ingress", the "domain" should be
# the value of "expose.ingress.hosts.core"
# 2) if "expose.type" is "clusterIP", the "domain" should be
# the value of "expose.clusterIP.name"
# 3) if "expose.type" is "nodePort", the "domain" should be
# the IP address of k8s node
#
# If Harbor is deployed behind the proxy, set it as the URL of proxy
externalURL: https://192.168.2.37:30003
# The internal TLS used for harbor components secure communicating. In order to enable https
# in each components tls cert files need to provided in advance.
internalTLS:
# If internal TLS enabled
enabled: false
# There are three ways to provide tls
# 1) "auto" will generate cert automatically
# 2) "manual" need provide cert file manually in following value
# 3) "secret" internal certificates from secret
certSource: "auto"
# The content of trust ca, only available when `certSource` is "manual"
trustCa: ""
# core related cert configuration
core:
# secret name for core's tls certs
secretName: ""
# Content of core's TLS cert file, only available when `certSource` is "manual"
crt: ""
# Content of core's TLS key file, only available when `certSource` is "manual"
key: ""
# jobservice related cert configuration
jobservice:
# secret name for jobservice's tls certs
secretName: ""
# Content of jobservice's TLS key file, only available when `certSource` is "manual"
crt: ""
# Content of jobservice's TLS key file, only available when `certSource` is "manual"
key: ""
# registry related cert configuration
registry:
# secret name for registry's tls certs
secretName: ""
# Content of registry's TLS key file, only available when `certSource` is "manual"
crt: ""
# Content of registry's TLS key file, only available when `certSource` is "manual"
key: ""
# portal related cert configuration
portal:
# secret name for portal's tls certs
secretName: ""
# Content of portal's TLS key file, only available when `certSource` is "manual"
crt: ""
# Content of portal's TLS key file, only available when `certSource` is "manual"
key: ""
# trivy related cert configuration
trivy:
# secret name for trivy's tls certs
secretName: ""
# Content of trivy's TLS key file, only available when `certSource` is "manual"
crt: ""
# Content of trivy's TLS key file, only available when `certSource` is "manual"
key: ""
ipFamily:
# ipv6Enabled set to true if ipv6 is enabled in cluster, currently it affected the nginx related component
ipv6:
enabled: true
# ipv4Enabled set to true if ipv4 is enabled in cluster, currently it affected the nginx related component
ipv4:
enabled: true
# The persistence is enabled by default and a default StorageClass
# is needed in the k8s cluster to provision volumes dynamically.
# Specify another StorageClass in the "storageClass" or set "existingClaim"
# if you already have existing persistent volumes to use
#
# For storing images and charts, you can also use "azure", "gcs", "s3",
# "swift" or "oss". Set it in the "imageChartStorage" section
persistence:
enabled: true
# Setting it to "keep" to avoid removing PVCs during a helm delete
# operation. Leaving it empty will delete PVCs after the chart deleted
# (this does not apply for PVCs that are created for internal database
# and redis components, i.e. they are never deleted automatically)
resourcePolicy: "keep"
persistentVolumeClaim:
registry:
# Use the existing PVC which must be created manually before bound,
# and specify the "subPath" if the PVC is shared with other components
existingClaim: ""
# Specify the "storageClass" used to provision the volume. Or the default
# StorageClass will be used (the default).
# Set it to "-" to disable dynamic provisioning
storageClass: "rook-ceph-block"
subPath: ""
accessMode: ReadWriteOnce
size: 5Gi
annotations: {}
jobservice:
jobLog:
existingClaim: ""
storageClass: "rook-ceph-block"
subPath: ""
accessMode: ReadWriteOnce
size: 1Gi
annotations: {}
# If external database is used, the following settings for database will
# be ignored
database:
existingClaim: ""
storageClass: "rook-ceph-block"
subPath: ""
accessMode: ReadWriteOnce
size: 1Gi
annotations: {}
# If external Redis is used, the following settings for Redis will
# be ignored
redis:
existingClaim: ""
storageClass: "rook-ceph-block"
subPath: ""
accessMode: ReadWriteOnce
size: 1Gi
annotations: {}
trivy:
existingClaim: ""
storageClass: "rook-ceph-block"
subPath: ""
accessMode: ReadWriteOnce
size: 5Gi
annotations: {}
# Define which storage backend is used for registry to store
# images and charts. Refer to
# https://github.com/docker/distribution/blob/master/docs/configuration.md#storage
# for the detail.
imageChartStorage:
# Specify whether to disable `redirect` for images and chart storage, for
# backends which not supported it (such as using minio for `s3` storage type), please disable
# it. To disable redirects, simply set `disableredirect` to `true` instead.
# Refer to
# https://github.com/docker/distribution/blob/master/docs/configuration.md#redirect
# for the detail.
disableredirect: false
# Specify the "caBundleSecretName" if the storage service uses a self-signed certificate.
# The secret must contain keys named "ca.crt" which will be injected into the trust store
# of registry's containers.
# caBundleSecretName:
# Specify the type of storage: "filesystem", "azure", "gcs", "s3", "swift",
# "oss" and fill the information needed in the corresponding section. The type
# must be "filesystem" if you want to use persistent volumes for registry
type: filesystem
filesystem:
rootdirectory: /storage
#maxthreads: 100
azure:
accountname: accountname
accountkey: base64encodedaccountkey
container: containername
#realm: core.windows.net
# To use existing secret, the key must be AZURE_STORAGE_ACCESS_KEY
existingSecret: ""
gcs:
bucket: bucketname
# The base64 encoded json file which contains the key
encodedkey: base64-encoded-json-key-file
#rootdirectory: /gcs/object/name/prefix
#chunksize: "5242880"
# To use existing secret, the key must be gcs-key.json
existingSecret: ""
useWorkloadIdentity: false
s3:
# Set an existing secret for S3 accesskey and secretkey
# keys in the secret should be REGISTRY_STORAGE_S3_ACCESSKEY and REGISTRY_STORAGE_S3_SECRETKEY for registry
#existingSecret: ""
region: us-west-1
bucket: bucketname
#accesskey: awsaccesskey
#secretkey: awssecretkey
#regionendpoint: http://myobjects.local
#encrypt: false
#keyid: mykeyid
#secure: true
#skipverify: false
#v4auth: true
#chunksize: "5242880"
#rootdirectory: /s3/object/name/prefix
#storageclass: STANDARD
#multipartcopychunksize: "33554432"
#multipartcopymaxconcurrency: 100
#multipartcopythresholdsize: "33554432"
swift:
authurl: https://storage.myprovider.com/v3/auth
username: username
password: password
container: containername
#region: fr
#tenant: tenantname
#tenantid: tenantid
#domain: domainname
#domainid: domainid
#trustid: trustid
#insecureskipverify: false
#chunksize: 5M
#prefix:
#secretkey: secretkey
#accesskey: accesskey
#authversion: 3
#endpointtype: public
#tempurlcontainerkey: false
#tempurlmethods:
oss:
accesskeyid: accesskeyid
accesskeysecret: accesskeysecret
region: regionname
bucket: bucketname
#endpoint: endpoint
#internal: false
#encrypt: false
#secure: true
#chunksize: 10M
#rootdirectory: rootdirectory
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
# Use this set to assign a list of default pullSecrets
imagePullSecrets:
# - name: docker-registry-secret
# - name: internal-registry-secret
# The update strategy for deployments with persistent volumes(jobservice, registry): "RollingUpdate" or "Recreate"
# Set it as "Recreate" when "RWM" for volumes isn't supported
updateStrategy:
type: RollingUpdate
# debug, info, warning, error or fatal
logLevel: info
# The initial password of Harbor admin. Change it from portal after launching Harbor
# or give an existing secret for it
# key in secret is given via (default to HARBOR_ADMIN_PASSWORD)
# existingSecretAdminPassword:
existingSecretAdminPasswordKey: HARBOR_ADMIN_PASSWORD
harborAdminPassword: "Harbor12345"
# The name of the secret which contains key named "ca.crt". Setting this enables the
# download link on portal to download the CA certificate when the certificate isn't
# generated automatically
caSecretName: ""
# The secret key used for encryption. Must be a string of 16 chars.
secretKey: "not-a-secure-key"
# If using existingSecretSecretKey, the key must be secretKey
existingSecretSecretKey: ""
# The proxy settings for updating trivy vulnerabilities from the Internet and replicating
# artifacts from/to the registries that cannot be reached directly
proxy:
httpProxy:
httpsProxy:
noProxy: 127.0.0.1,localhost,.local,.internal
components:
- core
- jobservice
- trivy
# Run the migration job via helm hook
enableMigrateHelmHook: false
# The custom ca bundle secret, the secret must contain key named "ca.crt"
# which will be injected into the trust store for core, jobservice, registry, trivy components
# caBundleSecretName: ""
## UAA Authentication Options
# If you're using UAA for authentication behind a self-signed
# certificate you will need to provide the CA Cert.
# Set uaaSecretName below to provide a pre-created secret that
# contains a base64 encoded CA Certificate named `ca.crt`.
# uaaSecretName:
# If service exposed via "ingress", the Nginx will not be used
nginx:
image:
repository: goharbor/nginx-photon
tag: v2.8.2
# set the service account to be used, default if left empty
serviceAccountName: ""
# mount the service account token
automountServiceAccountToken: false
replicas: 1
revisionHistoryLimit: 10
# resources:
# requests:
# memory: 256Mi
# cpu: 100m
nodeSelector: {}
tolerations: []
affinity: {}
## Additional deployment annotations
podAnnotations: {}
## The priority class to run the pod as
priorityClassName:
portal:
image:
repository: goharbor/harbor-portal
tag: v2.8.2
# set the service account to be used, default if left empty
serviceAccountName: ""
# mount the service account token
automountServiceAccountToken: false
replicas: 1
revisionHistoryLimit: 10
# resources:
# requests:
# memory: 256Mi
# cpu: 100m
nodeSelector: {}
tolerations: []
affinity: {}
## Additional deployment annotations
podAnnotations: {}
## The priority class to run the pod as
priorityClassName:
core:
image:
repository: goharbor/harbor-core
tag: v2.8.2
# set the service account to be used, default if left empty
serviceAccountName: ""
# mount the service account token
automountServiceAccountToken: false
replicas: 1
revisionHistoryLimit: 10
## Startup probe values
startupProbe:
enabled: true
initialDelaySeconds: 10
# resources:
# requests:
# memory: 256Mi
# cpu: 100m
nodeSelector: {}
tolerations: []
affinity: {}
## Additional deployment annotations
podAnnotations: {}
## Additional service annotations
serviceAnnotations: {}
# Secret is used when core server communicates with other components.
# If a secret key is not specified, Helm will generate one.
# Must be a string of 16 chars.
secret: ""
# Fill the name of a kubernetes secret if you want to use your own
# TLS certificate and private key for token encryption/decryption.
# The secret must contain keys named:
# "tls.key" - the private key
# "tls.crt" - the certificate
secretName: ""
# If not specifying a preexisting secret, a secret can be created from tokenKey and tokenCert and used instead.
# If none of secretName, tokenKey, and tokenCert are specified, an ephemeral key and certificate will be autogenerated.
# tokenKey and tokenCert must BOTH be set or BOTH unset.
# The tokenKey value is formatted as a multiline string containing a PEM-encoded RSA key, indented one more than tokenKey on the following line.
tokenKey: |
# If tokenKey is set, the value of tokenCert must be set as a PEM-encoded certificate signed by tokenKey, and supplied as a multiline string, indented one more than tokenCert on the following line.
tokenCert: |
# The XSRF key. Will be generated automatically if it isn't specified
xsrfKey: ""
## The priority class to run the pod as
priorityClassName:
# The time duration for async update artifact pull_time and repository
# pull_count, the unit is second. Will be 10 seconds if it isn't set.
# eg. artifactPullAsyncFlushDuration: 10
artifactPullAsyncFlushDuration:
gdpr:
deleteUser: false
jobservice:
image:
repository: goharbor/harbor-jobservice
tag: v2.8.2
replicas: 1
revisionHistoryLimit: 10
# set the service account to be used, default if left empty
serviceAccountName: ""
# mount the service account token
automountServiceAccountToken: false
maxJobWorkers: 10
# The logger for jobs: "file", "database" or "stdout"
jobLoggers:
- file
# - database
# - stdout
# The jobLogger sweeper duration (ignored if `jobLogger` is `stdout`)
loggerSweeperDuration: 14 #days
notification:
webhook_job_max_retry: 3
webhook_job_http_client_timeout: 3 # in seconds
reaper:
# the max time to wait for a task to finish, if unfinished after max_update_hours, the task will be mark as error, but the task will continue to run, default value is 24
max_update_hours: 24
# the max time for execution in running state without new task created
max_dangling_hours: 168
# resources:
# requests:
# memory: 256Mi
# cpu: 100m
nodeSelector: {}
tolerations: []
affinity: {}
## Additional deployment annotations
podAnnotations: {}
# Secret is used when job service communicates with other components.
# If a secret key is not specified, Helm will generate one.
# Must be a string of 16 chars.
secret: ""
## The priority class to run the pod as
priorityClassName:
registry:
# set the service account to be used, default if left empty
serviceAccountName: ""
# mount the service account token
automountServiceAccountToken: false
registry:
image:
repository: goharbor/registry-photon
tag: v2.8.2
# resources:
# requests:
# memory: 256Mi
# cpu: 100m
controller:
image:
repository: goharbor/harbor-registryctl
tag: v2.8.2
# resources:
# requests:
# memory: 256Mi
# cpu: 100m
replicas: 1
revisionHistoryLimit: 10
nodeSelector: {}
tolerations: []
affinity: {}
## Additional deployment annotations
podAnnotations: {}
## The priority class to run the pod as
priorityClassName:
# Secret is used to secure the upload state from client
# and registry storage backend.
# See: https://github.com/docker/distribution/blob/master/docs/configuration.md#http
# If a secret key is not specified, Helm will generate one.
# Must be a string of 16 chars.
secret: ""
# If true, the registry returns relative URLs in Location headers. The client is responsible for resolving the correct URL.
relativeurls: false
credentials:
username: "harbor_registry_user"
password: "harbor_registry_password"
# If using existingSecret, the key must be REGISTRY_PASSWD and REGISTRY_HTPASSWD
existingSecret: ""
# Login and password in htpasswd string format. Excludes `registry.credentials.username` and `registry.credentials.password`. May come in handy when integrating with tools like argocd or flux. This allows the same line to be generated each time the template is rendered, instead of the `htpasswd` function from helm, which generates different lines each time because of the salt.
# htpasswdString: $apr1$XLefHzeG$Xl4.s00sMSCCcMyJljSZb0 # example string
middleware:
enabled: false
type: cloudFront
cloudFront:
baseurl: example.cloudfront.net
keypairid: KEYPAIRID
duration: 3000s
ipfilteredby: none
# The secret key that should be present is CLOUDFRONT_KEY_DATA, which should be the encoded private key
# that allows access to CloudFront
privateKeySecret: "my-secret"
# enable purge _upload directories
upload_purging:
enabled: true
# remove files in _upload directories which exist for a period of time, default is one week.
age: 168h
# the interval of the purge operations
interval: 24h
dryrun: false
trivy:
# enabled the flag to enable Trivy scanner
enabled: true
image:
# repository the repository for Trivy adapter image
repository: goharbor/trivy-adapter-photon
# tag the tag for Trivy adapter image
tag: v2.8.2
# set the service account to be used, default if left empty
serviceAccountName: ""
# mount the service account token
automountServiceAccountToken: false
# replicas the number of Pod replicas
replicas: 1
# debugMode the flag to enable Trivy debug mode with more verbose scanning log
debugMode: false
# vulnType a comma-separated list of vulnerability types. Possible values are `os` and `library`.
vulnType: "os,library"
# severity a comma-separated list of severities to be checked
severity: "UNKNOWN,LOW,MEDIUM,HIGH,CRITICAL"
# ignoreUnfixed the flag to display only fixed vulnerabilities
ignoreUnfixed: false
# insecure the flag to skip verifying registry certificate
insecure: false
# gitHubToken the GitHub access token to download Trivy DB
#
# Trivy DB contains vulnerability information from NVD, Red Hat, and many other upstream vulnerability databases.
# It is downloaded by Trivy from the GitHub release page https://github.com/aquasecurity/trivy-db/releases and cached
# in the local file system (`/home/scanner/.cache/trivy/db/trivy.db`). In addition, the database contains the update
# timestamp so Trivy can detect whether it should download a newer version from the Internet or use the cached one.
# Currently, the database is updated every 12 hours and published as a new release to GitHub.
#
# Anonymous downloads from GitHub are subject to the limit of 60 requests per hour. Normally such rate limit is enough
# for production operations. If, for any reason, it's not enough, you could increase the rate limit to 5000
# requests per hour by specifying the GitHub access token. For more details on GitHub rate limiting please consult
# https://developer.github.com/v3/#rate-limiting
#
# You can create a GitHub token by following the instructions in
# https://help.github.com/en/github/authenticating-to-github/creating-a-personal-access-token-for-the-command-line
gitHubToken: ""
# skipUpdate the flag to disable Trivy DB downloads from GitHub
#
# You might want to set the value of this flag to `true` in test or CI/CD environments to avoid GitHub rate limiting issues.
# If the value is set to `true` you have to manually download the `trivy.db` file and mount it in the
# `/home/scanner/.cache/trivy/db/trivy.db` path.
skipUpdate: false
# The offlineScan option prevents Trivy from sending API requests to identify dependencies.
#
# Scanning JAR files and pom.xml may require Internet access for better detection, but this option tries to avoid it.
# For example, the offline mode will not try to resolve transitive dependencies in pom.xml when the dependency doesn't
# exist in the local repositories. It means a number of detected vulnerabilities might be fewer in offline mode.
# It would work if all the dependencies are in local.
# This option doesn’t affect DB download. You need to specify skipUpdate as well as offlineScan in an air-gapped environment.
offlineScan: false
# Comma-separated list of what security issues to detect. Possible values are `vuln`, `config` and `secret`. Defaults to `vuln`.
securityCheck: "vuln"
# The duration to wait for scan completion
timeout: 5m0s
resources:
requests:
cpu: 200m
memory: 512Mi
limits:
cpu: 1
memory: 1Gi
nodeSelector: {}
tolerations: []
affinity: {}
## Additional deployment annotations
podAnnotations: {}
## The priority class to run the pod as
priorityClassName:
notary:
enabled: true
server:
# set the service account to be used, default if left empty
serviceAccountName: ""
# mount the service account token
automountServiceAccountToken: false
image:
repository: goharbor/notary-server-photon
tag: v2.8.2
replicas: 1
# resources:
# requests:
# memory: 256Mi
# cpu: 100m
nodeSelector: {}
tolerations: []
affinity: {}
## Additional deployment annotations
podAnnotations: {}
## The priority class to run the pod as
priorityClassName:
## Additional service annotations
serviceAnnotations: {}
signer:
# set the service account to be used, default if left empty
serviceAccountName: ""
# mount the service account token
automountServiceAccountToken: false
image:
repository: goharbor/notary-signer-photon
tag: v2.8.2
replicas: 1
# resources:
# requests:
# memory: 256Mi
# cpu: 100m
nodeSelector: {}
tolerations: []
affinity: {}
## Additional deployment annotations
podAnnotations: {}
## The priority class to run the pod as
priorityClassName:
# Fill the name of a kubernetes secret if you want to use your own
# TLS certificate authority, certificate and private key for notary
# communications.
# The secret must contain keys named ca.crt, tls.crt and tls.key that
# contain the CA, certificate and private key.
# They will be generated if not set.
secretName: ""
database:
# if external database is used, set "type" to "external"
# and fill the connection information in "external" section
type: internal
internal:
# set the service account to be used, default if left empty
serviceAccountName: ""
# mount the service account token
automountServiceAccountToken: false
image:
repository: goharbor/harbor-db
tag: v2.8.2
# The initial superuser password for internal database
password: "changeit"
# The size limit for Shared memory, pgSQL use it for shared_buffer
# More details see:
# https://github.com/goharbor/harbor/issues/15034
shmSizeLimit: 512Mi
# resources:
# requests:
# memory: 256Mi
# cpu: 100m
# The timeout used in livenessProbe; 1 to 5 seconds
livenessProbe:
timeoutSeconds: 1
# The timeout used in readinessProbe; 1 to 5 seconds
readinessProbe:
timeoutSeconds: 1
nodeSelector: {}
tolerations: []
affinity: {}
## The priority class to run the pod as
priorityClassName:
initContainer:
migrator: {}
# resources:
# requests:
# memory: 128Mi
# cpu: 100m
permissions: {}
# resources:
# requests:
# memory: 128Mi
# cpu: 100m
external:
host: "192.168.0.1"
port: "5432"
username: "user"
password: "password"
coreDatabase: "registry"
notaryServerDatabase: "notary_server"
notarySignerDatabase: "notary_signer"
# if using existing secret, the key must be "password"
existingSecret: ""
# "disable" - No SSL
# "require" - Always SSL (skip verification)
# "verify-ca" - Always SSL (verify that the certificate presented by the
# server was signed by a trusted CA)
# "verify-full" - Always SSL (verify that the certification presented by the
# server was signed by a trusted CA and the server host name matches the one
# in the certificate)
sslmode: "disable"
# The maximum number of connections in the idle connection pool per pod (core+exporter).
# If it <=0, no idle connections are retained.
maxIdleConns: 100
# The maximum number of open connections to the database per pod (core+exporter).
# If it <= 0, then there is no limit on the number of open connections.
# Note: the default number of connections is 1024 for postgre of harbor.
maxOpenConns: 900
## Additional deployment annotations
podAnnotations: {}
redis:
# if external Redis is used, set "type" to "external"
# and fill the connection information in "external" section
type: internal
internal:
# set the service account to be used, default if left empty
serviceAccountName: ""
# mount the service account token
automountServiceAccountToken: false
image:
repository: goharbor/redis-photon
tag: v2.8.2
# resources:
# requests:
# memory: 256Mi
# cpu: 100m
nodeSelector: {}
tolerations: []
affinity: {}
## The priority class to run the pod as
priorityClassName:
external:
# support redis, redis+sentinel
# addr for redis: <host_redis>:<port_redis>
# addr for redis+sentinel: <host_sentinel1>:<port_sentinel1>,<host_sentinel2>:<port_sentinel2>,<host_sentinel3>:<port_sentinel3>
addr: "192.168.0.2:6379"
# The name of the set of Redis instances to monitor, it must be set to support redis+sentinel
sentinelMasterSet: ""
# The "coreDatabaseIndex" must be "0" as the library Harbor
# used doesn't support configuring it
coreDatabaseIndex: "0"
jobserviceDatabaseIndex: "1"
registryDatabaseIndex: "2"
trivyAdapterIndex: "5"
# username field can be an empty string and it will be authenticated against the default user
username: ""
password: ""
# If using existingSecret, the key must be REDIS_PASSWORD
existingSecret: ""
## Additional deployment annotations
podAnnotations: {}
exporter:
replicas: 1
revisionHistoryLimit: 10
# resources:
# requests:
# memory: 256Mi
# cpu: 100m
podAnnotations: {}
serviceAccountName: ""
# mount the service account token
automountServiceAccountToken: false
image:
repository: goharbor/harbor-exporter
tag: v2.8.2
nodeSelector: {}
tolerations: []
affinity: {}
cacheDuration: 23
cacheCleanInterval: 14400
## The priority class to run the pod as
priorityClassName:
metrics:
enabled: false
core:
path: /metrics
port: 8001
registry:
path: /metrics
port: 8001
jobservice:
path: /metrics
port: 8001
exporter:
path: /metrics
port: 8001
## Create prometheus serviceMonitor to scrape harbor metrics.
## This requires the monitoring.coreos.com/v1 CRD. Please see
## https://github.com/prometheus-operator/prometheus-operator/blob/master/Documentation/user-guides/getting-started.md
##
serviceMonitor:
enabled: false
additionalLabels: {}
# Scrape interval. If not set, the Prometheus default scrape interval is used.
interval: ""
# Metric relabel configs to apply to samples before ingestion.
metricRelabelings:
[]
# - action: keep
# regex: 'kube_(daemonset|deployment|pod|namespace|node|statefulset).+'
# sourceLabels: [__name__]
# Relabel configs to apply to samples before ingestion.
relabelings:
[]
# - sourceLabels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_node_name]
# separator: ;
# regex: ^(.*)$
# targetLabel: nodename
# replacement: $1
# action: replace
trace:
enabled: false
# trace provider: jaeger or otel
# jaeger should be 1.26+
provider: jaeger
# set sample_rate to 1 if you wanna sampling 100% of trace data; set 0.5 if you wanna sampling 50% of trace data, and so forth
sample_rate: 1
# namespace used to differentiate different harbor services
# namespace:
# attributes is a key value dict contains user defined attributes used to initialize trace provider
# attributes:
# application: harbor
jaeger:
# jaeger supports two modes:
# collector mode(uncomment endpoint and uncomment username, password if needed)
# agent mode(uncomment agent_host and agent_port)
endpoint: http://hostname:14268/api/traces
# username:
# password:
# agent_host: hostname
# export trace data by jaeger.thrift in compact mode
# agent_port: 6831
otel:
endpoint: hostname:4318
url_path: /v1/traces
compression: false
insecure: true
# timeout is in seconds
timeout: 10
# cache layer configurations
# if this feature enabled, harbor will cache the resource
# `project/project_metadata/repository/artifact/manifest` in the redis
# which help to improve the performance of high concurrent pulling manifest.
cache:
# default is not enabled.
enabled: false
# default keep cache for one day.
expireHours: 24