『ライブラリーを使わずにPythonでニューラルネットワークを構築してみる』 (以下、元記事)の内容をchainerで実行してみる。
元記事は非常にわかりやすく丁寧に書かれているため是非一読をおすすめする。
インストール
必要なパッケージをpipでインストールするだけ
$ pip3 install numpy scipy scikit-learn chainer
実行
IPython Notebook上で実行した
gistにも上げました
https://gist.github.com/maueki/ae4ce4de7c689c2b6a2df9fd7a9a0c31
インポート
import numpy as np
import sklearn.datasets
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import chainer
from chainer import cuda, Function, gradient_check, Variable, optimizers, serializers, utils
from chainer import Link, Chain, ChainList
import chainer.functions as F
import chainer.links as L
%matplotlib inline
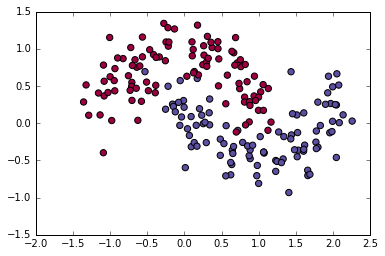
データ生成
元記事と全く同じ
np.random.seed(0)
X,y=sklearn.datasets.make_moons(200,noise=0.20)
plt.scatter(X[:,0], X[:,1], s=40, c=y, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral)
Chain作成
n_units = 3
class Model(Chain):
def __init__(self):
super(Model, self).__init__(
l1=L.Linear(2, n_units),
l2=L.Linear(n_units, 2),
)
def __call__(self, x):
h1 = F.tanh(self.l1(x))
y = self.l2(h1)
return y
Chainクラスを継承しコンストラクタでネットワークを記述、__call__メソッドにforward関数を記述する
Classifier Chain 作成
softmax関数を使った損失関数の定義等はClassifierクラスが隠蔽してくれるので自作する必要はない
model = L.Classifier(Model())
optimizer 作成
学習、モデルの更新はoptimizerが行ってくれる。今回は元記事とは異なるがアルゴリズムとしてAdamを選択(SDGでは満足いく結果にならなかった)
optimizer = optimizers.Adam()
optimizer.setup(model)
学習
x = Variable(X.astype(np.float32))
t = Variable(y.astype(np.int32))
for _ in range(20000):
optimizer.update(model, x, t)
chainerでは入力値等をVariableにして与える。この時入力値はfloat32, 出力値はint32にしないとエラーとなるため型変換をしていることに注意。
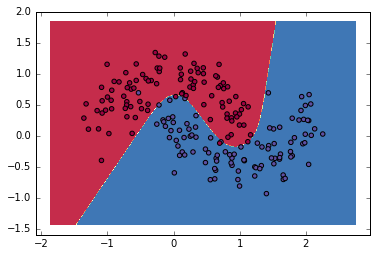
結果表示
def predict(model, x_data):
x = Variable(x_data.astype(np.float32))
y = model.predictor(x)
return np.argmax(y.data, axis=1)
plot_decision_boundary(lambda x: predict(model, x))
元記事に近い結果が得られた
# https://gist.github.com/dennybritz/ff8e7c2954dd47a4ce5f
def plot_decision_boundary(pred_func):
# Set min and max values and give it some padding
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - .5, X[:, 0].max() + .5
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - .5, X[:, 1].max() + .5
h = 0.01
# Generate a grid of points with distance h between them
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h), np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
# Predict the function value for the whole gid
Z = pred_func(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
# Plot the contour and training examples
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral)
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral)