はじめに
以下の記事を参考に、A*アルゴリズムをRubyで実装してみました。スタートからゴールまでの最短経路の探索と、探索した経路の可視化を実装しました。
よくわかるA*(A-star)アルゴリズム (Unity2Dのサンプルコードつき)
A*アルゴリズムとは
参考記事より引用いたします。
A*アルゴリズムとは、探索アルゴリズムの一種です。経路をノードで表現して、スタートノード(開始地点)からゴールノード(目標地点)までの経路を計算し、この経路が最短であることを保証するアルゴリズムとなります。そしてスタートからゴールまでの間に障害物があってもちゃんと迂回してくれます。
製作したRubyコード
今回の実装では、以下の2つのクラスを作成しました。
- A_star_fieldクラス:経路を探索するフィールドを表すクラスです。
- A_star_nodeクラス:フィールドを構成するノードを表すクラスです。
以下、それぞれのクラスについて、コードを紹介します。
A_star_fieldクラス
コード
require './a_star_node.rb'
require 'cairo'
class A_star_field
def initialize(x_length,y_length)
@field = Array.new(x_length).map{Array.new(y_length).map{A_star_node.new}}
@field.each_with_index do |x_line,x|
x_line.each_with_index do |node,y|
node.set_xy_coordinate x,y
end
end
@start_node
@goal_node
end
def set_impassable_nodes(node_places)
node_places.each do |x,y|
@field[x][y].impassable
end
end
def set_start_node(x,y)
@start_node = @field[x][y]
end
def set_goal_node(x,y)
@goal_node = @field[x][y]
end
def get_surrounding_node(x,y)
node_array = []
(x-1..x+1).each do |i|
(y-1..y+1).each do |j|
next if i == x and j == y
next if i < 0 or 5 <= i # フィールドの範囲内のノードだけ取り出す
next if j < 0 or 5 <= j # フィールドの範囲内のノードだけ取り出す
node_array << @field[i][j]
end
end
node_array
end
def get_minimum_score_node(opened_nodes)
minimum_score_node = opened_nodes[1]
opened_nodes.each do |node|
next unless node.passable
minimum_score_node = node if node.score < minimum_score_node.score
end
minimum_score_node
end
def find_route
@start_node.open
@start_node.calc_estimated_cost(@goal_node.x,@goal_node.y)
@start_node.calc_score
reference_node = @start_node # スタートノードの設定
opened_nodes = [] # オープンされているノード
until reference_node == @goal_node
# p reference_node
surrounding_nodes = get_surrounding_node reference_node.x,reference_node.y
surrounding_nodes.each do |node|
next unless node.open # オープンに失敗したら、次のノードを評価する
node.calc_actual_cost reference_node.actual_cost
node.calc_estimated_cost(@goal_node.x,@goal_node.y)
node.calc_score
node.set_parent_node reference_node
opened_nodes << node # オープンされているノードに追加
end
reference_node.close
reference_node = get_minimum_score_node(opened_nodes)
opened_nodes.delete(reference_node)
end
end
def show_route_to_goal_node
node = @goal_node
until node.nil?
puts "(#{node.x},#{node.y})"
node = node.parent_node
end
end
def output_picture
format = Cairo::FORMAT_ARGB32
width = @field.length * 50 + 50 # 両端に25の余白。四角は50四方
height = @field[0].length * 50 + 50 # 両端に25の余白。四角は50四方
surface = Cairo::ImageSurface.new(format, width, height)
context = Cairo::Context.new(surface)
# 背景
context.set_source_rgb(1, 1, 1) # 白
context.rectangle(0, 0, width, height)
context.fill
# ノードのマス目を作成
rect_width = 50
context.set_source_rgb(0,0,0) # 黒
@field.each_with_index do |x_line,x|
x_line.each_with_index do |node,y|
x_start = 25+x*rect_width
y_start = 25+y*rect_width
context.rectangle(x_start, y_start, rect_width, rect_width)
if node.passable
context.stroke
else
context.fill
end
end
end
# ゴールノードが設定されていない場合、または
# 経路が作成されていない場合(スタートノードが設定されていない場合含む)、return
return if @goal_node.nil?
return if @goal_node.parent_node.nil?
# 経路の線を引く
context.set_source_rgb(1,0,0)
first_node = @goal_node
second_node = @goal_node.parent_node
until second_node.nil?
context.move_to(50*(first_node.x+1), 50*(first_node.y+1))
context.line_to(50*(second_node.x+1), 50*(second_node.y+1))
context.stroke
# draw_line(50*(first_node.x+1), 50*(first_node.y+1), 50*(second_node.x+1), 50*(second_node.y+1))
first_node = second_node
second_node = second_node.parent_node
end
context.set_source_rgb(0,0,0)
context.font_size = 20
# スタートノードに"S"を表示
context.move_to(50*(@start_node.x+1), 50*(@start_node.y+1))
context.show_text("S")
# ゴールノードに"G"を表示
context.move_to(50+@goal_node.x*50, 50*(@goal_node.y+1))
context.show_text("G")
surface.write_to_png("field.png")
end
end
インスタンス変数
| インスタンス変数名 | 内容 |
|---|---|
| @field | A_star_nodeクラスの二次元配列。二次元のフィールドを表している。 |
| @start_node | スタートノード。@fieldの中のノードの1つが代入される。 |
| @goal_node | ゴールノード。@fieldの中のノードの1つが代入される。 |
メソッド
| メソッド名 | 内容 |
|---|---|
| initialize | 初期化メソッド。引数として、フィールドのx方向及びy方向の大きさを渡す。引数の値に従って、@fieldに格納する配列を作成する。 |
| set_impassable_nodes | フィールドのノードの中で、通過できないノードを設定する。引数には、座標の配列を渡す。 |
| set_start_node | スタートノードを設定する。 |
| set_goal_node | ゴールノードを設定する。 |
| get_surrounding_node | 引数で指定した座標の周囲にあるノードを返す。 |
| get_minimum_score_node | 引数で渡されたノードの中で、スコアが最小であるノードを返す。 |
| find_route | 経路の探索を行うメソッド。 |
| show_route_to_goal_node | ゴールノードまでの経路をテキストベースで出力する。 |
| output_picture | 可視化メソッド。フィールド及び探索経路を、画像として出力する。詳細は後述。 |
可視化処理
参考記事の内容に加えて、フィールドと探索経路を可視化する処理を実装しました。今回は、cairoを用いて、画像として出力を行います。可視化処理を担うoutput_pictureメソッドにて、以下の処理を行っています。
- cairoのsurfaceに、フィールドを描画する。各ノードを、四角で描画する。
- 通行可能なノードは白抜きの四角(□)
- 通行可能でないノードは黒塗りの四角(■)
- cairoのsurfaceに、探索経路を描画する。ゴールノードから親ノードを辿っていき、直線を描画する。
- 画像として出力する。
A_star_nodeクラス
コード
class A_star_node
def initialize
@passable = true # trueなら、ノードを通行可能
@moving_cost = 1
@status = "none"
@x
@y
@actual_cost = 0 # 実コスト
@estimated_cost = 0# 推定コスト
@score = 0 # スコア
@parent_node = nil
end
attr_reader :x, :y, :actual_cost, :score, :passable, :parent_node
def open
if(@passable and @status == "none")
@status = "open"
true
else false
end
end
def close
@status = "close"
end
def impassable
@passable = false
end
def set_xy_coordinate(x,y)
@x = x
@y = y
end
def calc_actual_cost(cost)
@actual_cost = cost + @moving_cost
end
def calc_estimated_cost(goal_x,goal_y)
dx = goal_x - @x
dx *= -1 if dx < 0
dy = goal_y - @y
dy *= -1 if dy < 0
@estimated_cost = (dx > dy ? dx : dy)
end
def calc_score
@score = @actual_cost + @estimated_cost
end
def set_parent_node(node)
@parent_node = node
end
end
インスタンス変数
| インスタンス変数名 | 内容 |
|---|---|
| passable | ノードが通過可能かを示すフラグ。trueなら通過可能 |
| moving_cost | ノードの移動コスト |
| status | ノードの状態。none,open,closeの3状態のいずれか |
| x | ノードのx座標 |
| y | ノードのy座標 |
| actual_cost | スタートノードからの移動の実コスト |
| estimated_cost | ゴールノードまでの移動の推定コスト |
| score | 実コストと推定コストの和 |
| parent_node | 親ノード(このノードに移動する前のノード)へのポインタ |
実行結果
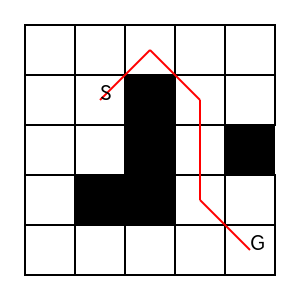
参考記事にて登場しているフィールドを対象に、経路探索を行いました。可視化結果を以下に示します。
通行可能でないノードを迂回し、スタートノードからゴールノードまでの経路が探索できていることが分かります。