Splunk と python の関係を見ると以下の2つがあるかと思います。
- Splunk のサーチコマンド内で、python プログラムを実行する場合
- Pythonコードから、splunkに問い合わせてサーチ結果を取り出す場合
1)については、カスタムサーチコマンドとして Splunk上で作成したpythonを実行できます。すでに他の方の記事もあるので、今回は 2) の pythonから、splunk内のデータをサーチ文を投げて、その結果を取り込んでみたいと思います。また今回はその後のコーディングが簡単になるように pandas の DataFrame形式で取り込むところまで jupyter notebookを使ってやってみます。
これで pythonから、Splunkデータを扱いやすくなります。
ちなみに今回のコードは、こちらのblog を参考にしました。
https://www.splunk.com/blog/2019/03/18/leveraging-external-data-science-stacks-with-splunk-today.html
全体の流れ
- jupyter notebook を利用し、splunk サーバに接続
- サーチの実行
- dataframe にデータを変換
1) jupyter notebook を利用し、splunk サーバに接続
まずは、ローカルPC上で jupyter notebookを起動してください。(あるいは、google のcolaboratoryでも大丈夫です)
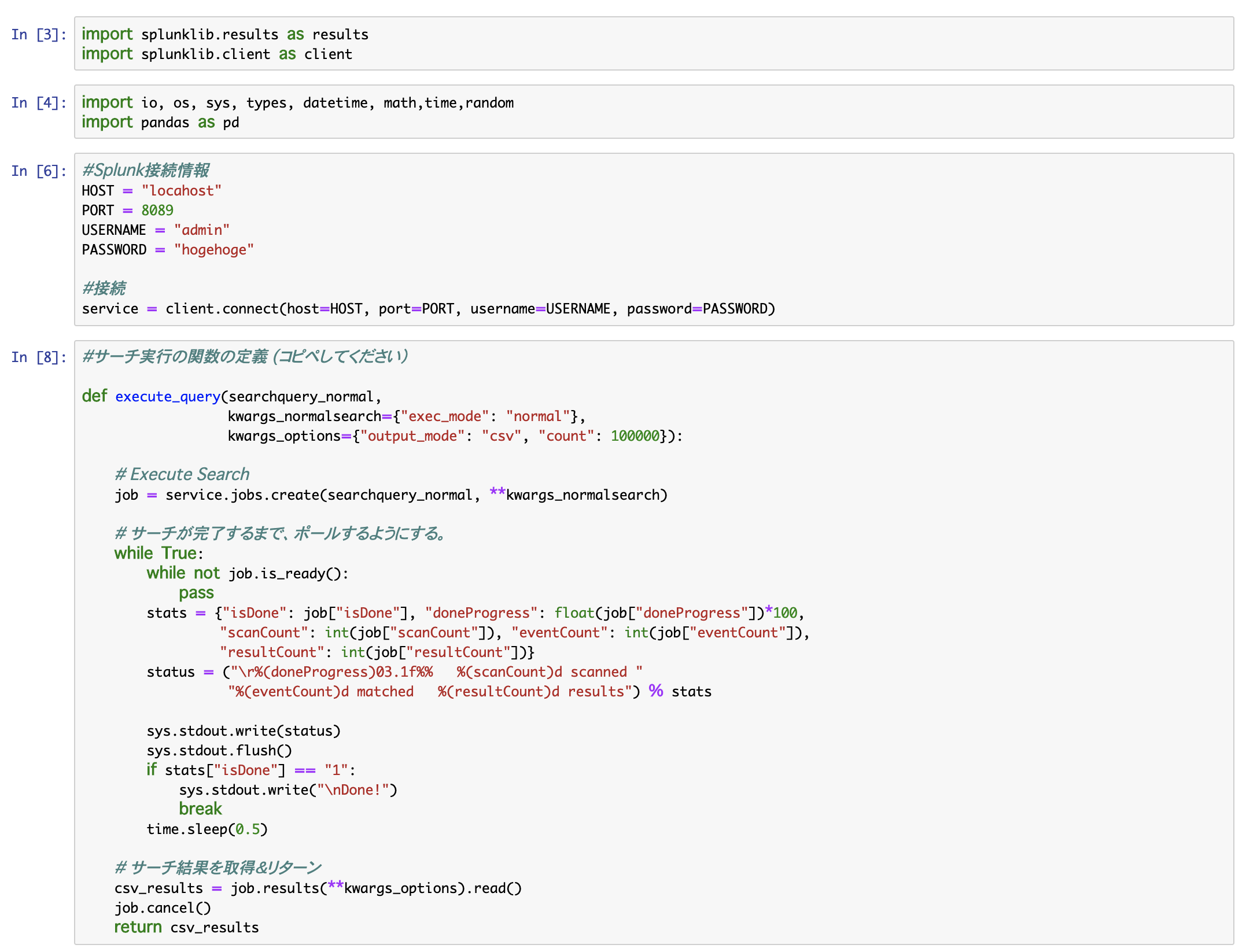
まず splunk-sdk をインストールし、モジュールをインポートします。
!pip install splunk-sdk
import splunklib.results as results
import splunklib.client as client
他に import するモジュールは適当に。 (ioと pandasは、今回必須)
import io, os, sys, types, datetime, math,time,random
import pandas as pd
次に spluk サーバーに接続します。
#Splunk接続情報
HOST = "localhost"
PORT = 8089
USERNAME = "admin"
PASSWORD = "hogehoge"
#接続
service = client.connect(host=HOST, port=PORT, username=USERNAME, password=PASSWORD)
##2) サーチの実行
まずは、サーチ実行のための関数を作成します。
ここは、あまり深く考えずコピペして利用ください。中身はサーチが完了するまで待ったり、完了の表示をしたり、カウント数を表示したりしてくれます。
#サーチ実行の関数の定義 (コピペしてください)
def execute_query(searchquery_normal,
kwargs_normalsearch={"exec_mode": "normal"},
kwargs_options={"output_mode": "csv", "count": 100000}):
# Execute Search
job = service.jobs.create(searchquery_normal, **kwargs_normalsearch)
# サーチが完了するまで、ポールするようにする。
while True:
while not job.is_ready():
pass
stats = {"isDone": job["isDone"], "doneProgress": float(job["doneProgress"])*100,
"scanCount": int(job["scanCount"]), "eventCount": int(job["eventCount"]),
"resultCount": int(job["resultCount"])}
status = ("\r%(doneProgress)03.1f%% %(scanCount)d scanned "
"%(eventCount)d matched %(resultCount)d results") % stats
sys.stdout.write(status)
sys.stdout.flush()
if stats["isDone"] == "1":
sys.stdout.write("\nDone!")
break
time.sleep(0.5)
# サーチ結果を取得&リターン
csv_results = job.results(**kwargs_options).read()
job.cancel()
return csv_results
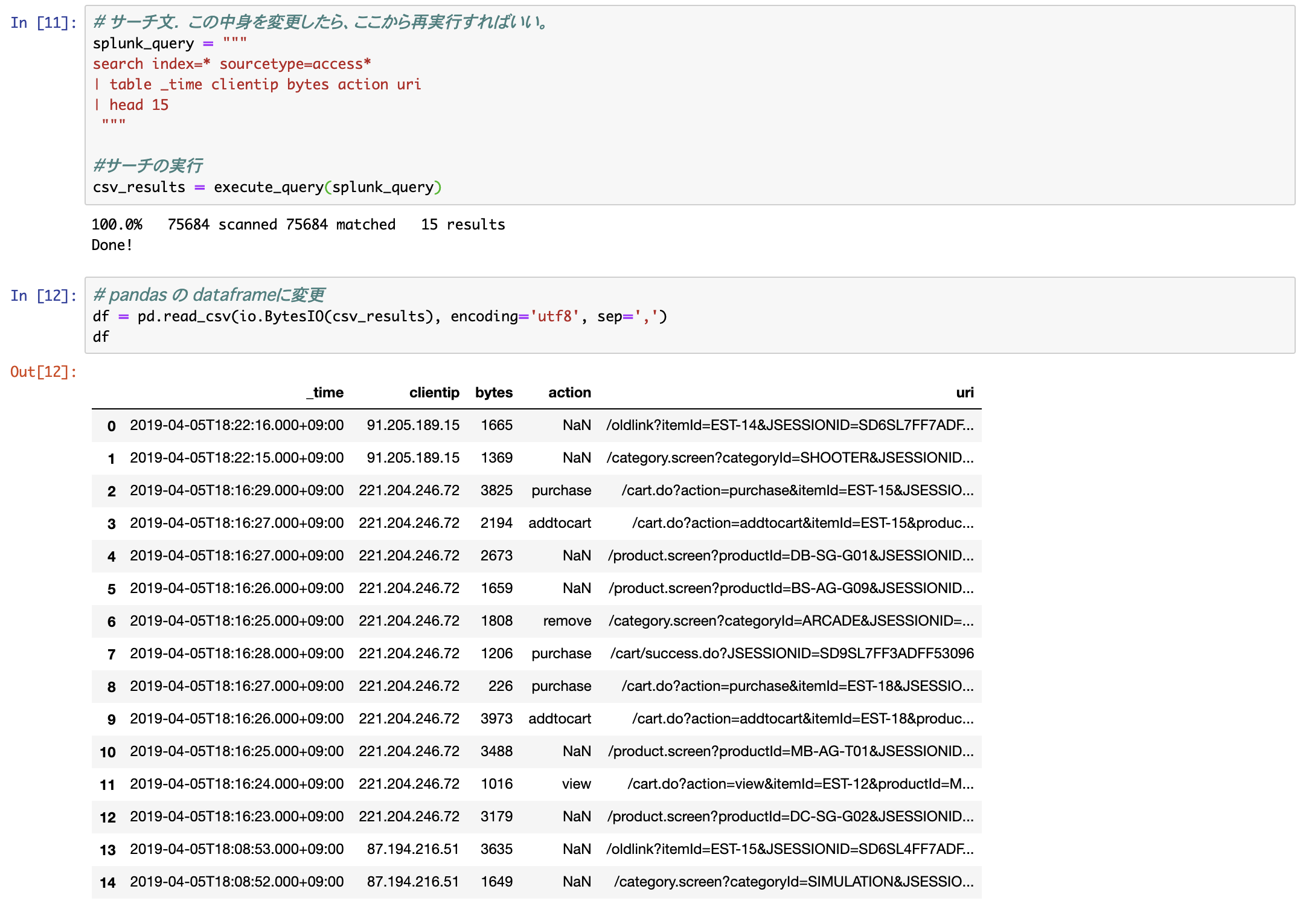
実際のサーチ文を記述し、実行。
jupyter notebook (or colaboratory) のいいところは、このサーチ文の箇所を変更し、途中からなんども実行し、結果をすぐに確認できるところですね。
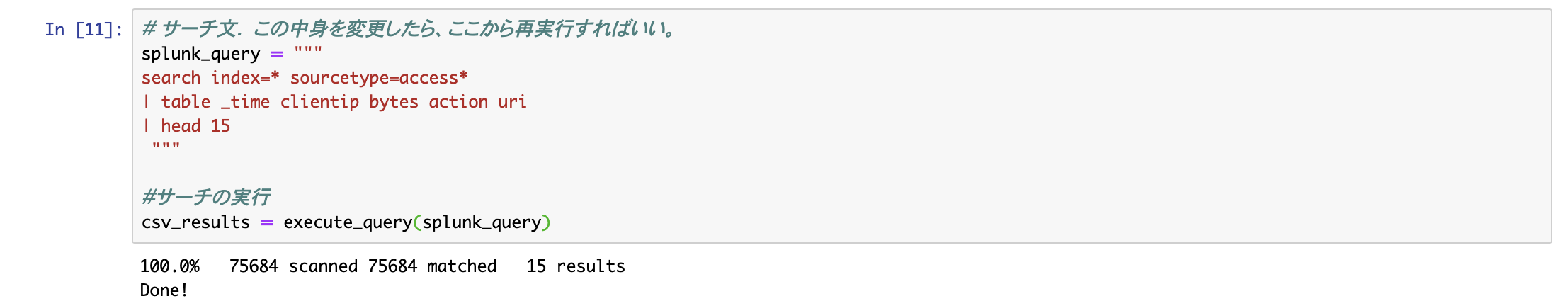
# サーチ文. この中身を変更したら、ここから再実行すればいい。
splunk_query = """
search index=* sourcetype=access*
| table _time clientip bytes action uri
| head 15
"""
#サーチの実行
csv_results = execute_query(splunk_query)
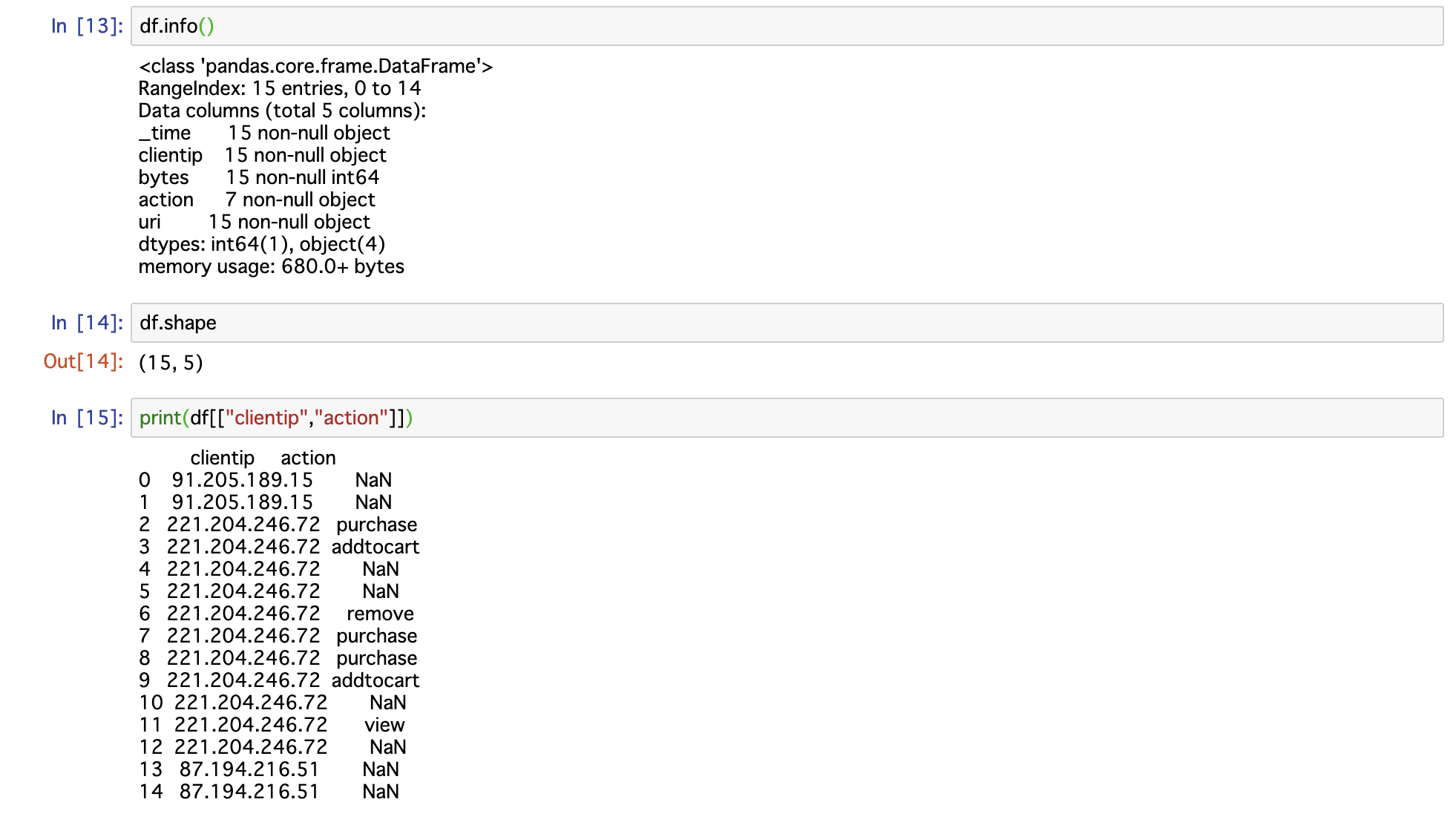
3) 最後に、取得したサーチ結果を、pythonで扱いやすくするため pandasのdataframeに変換
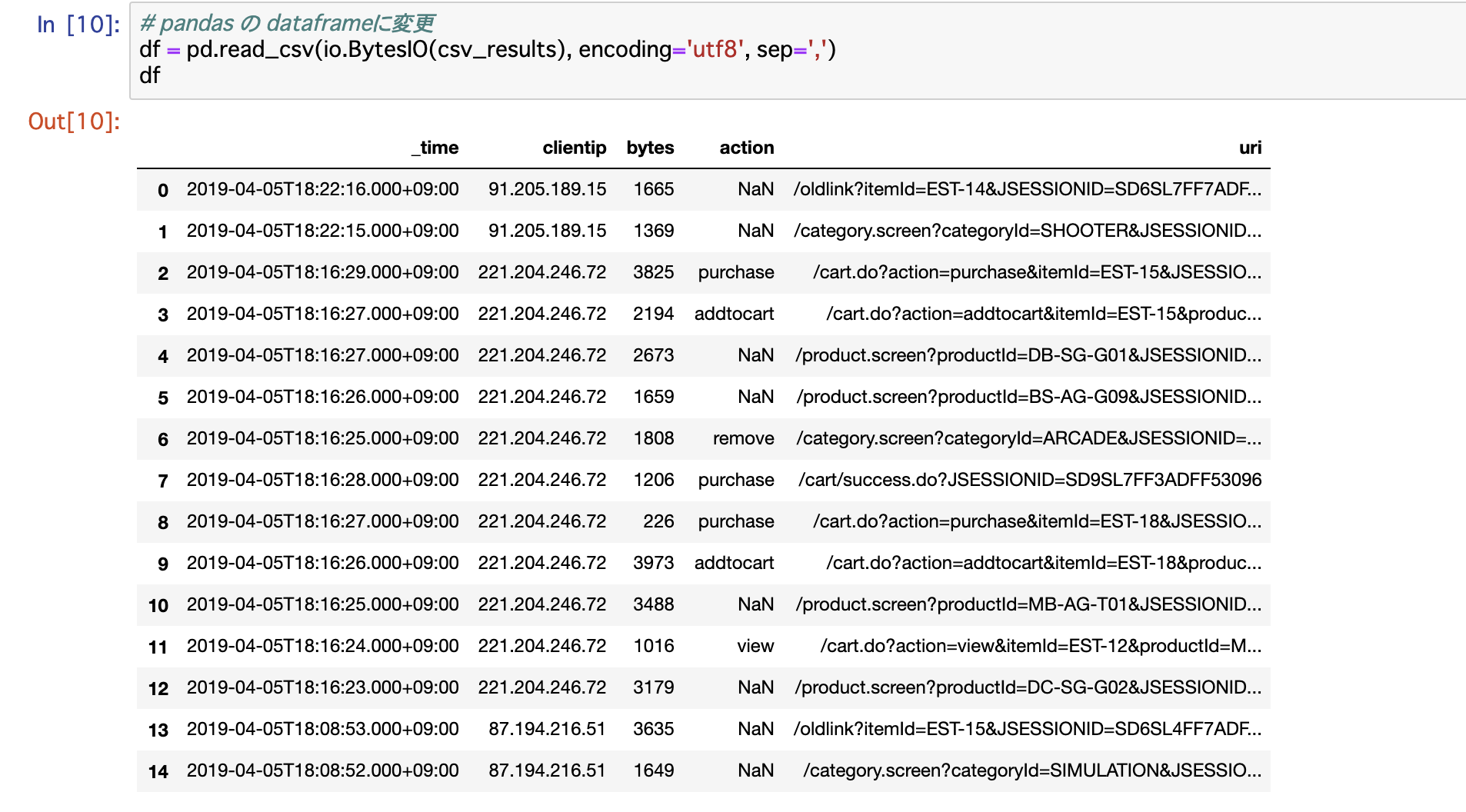
このまま、取得データをみると、まさにログデータのようになっている。(今回はcsv形式で指定している)

そこで DataFrame 形式に変換
df = pd.read_csv(io.BytesIO(csv_results), encoding='utf8', sep=',')
これで、pythonで処理しやすくなりますね。
まとめ
##最後に、今回実行したものをまとめて書いておきます。
!pip install splunk-sdk # 一度インストールしたら、2度目は不要
import splunklib.client as client
import splunklib.results as results
import io, os, sys, types, datetime, math,time,random
import pandas as pd
#Splunk接続情報
HOST = "localhost"
PORT = 8089
USERNAME = "admin"
PASSWORD = "hogehoge"
#接続
service = client.connect(host=HOST, port=PORT, username=USERNAME, password=PASSWORD)
#サーチ実行のメソッドの定義
def execute_query(searchquery_normal,
kwargs_normalsearch={"exec_mode": "normal"},
kwargs_options={"output_mode": "csv", "count": 100000}):
# Execute Search
job = service.jobs.create(searchquery_normal, **kwargs_normalsearch)
# サーチが完了するまで、ポールしたり、カウント数を表示したり
while True:
while not job.is_ready():
pass
stats = {"isDone": job["isDone"], "doneProgress": float(job["doneProgress"])*100,
"scanCount": int(job["scanCount"]), "eventCount": int(job["eventCount"]),
"resultCount": int(job["resultCount"])}
status = ("\r%(doneProgress)03.1f%% %(scanCount)d scanned "
"%(eventCount)d matched %(resultCount)d results") % stats
sys.stdout.write(status)
sys.stdout.flush()
if stats["isDone"] == "1":
sys.stdout.write("\nDone!")
break
time.sleep(0.5)
# サーチ結果を取得&リターン
csv_results = job.results(**kwargs_options).read()
job.cancel()
return csv_results
# サーチ文. この中身を変更したら、ここから再実行すればいい。
splunk_query = """
search index=* sourcetype=access*
| table _time clientip bytes action uri
| head 15
"""
#サーチの実行
csv_results = execute_query(splunk_query)
# pandas の dataframeに変更
df = pd.read_csv(io.BytesIO(csv_results), encoding='utf8', sep=',')