Flutterレイアウトシリーズのその他の記事
- Stackの使い方
- FlutterレイアウトのOverlayの使用
- FlutterレイアウトのFlex、Row、Column、Wrap、Stack
- FlutterレイアウトのExpanded、Flexible、Spacer
- FlutterのBoxConstraintsを理解する
Flutterのレイアウトウェジェットって、複数子を持つ親と一人子しか持たない親ウェジェットがあります。複数個子ウェジェットを持つ親について、Flex、Row、Column、Wrap、Stackがあり、その説明は前の記事に詳しく記載しました。この記事は一人子を持つレイアウトウェジェットを理解するため書いたものです。
※本記事は下記のZenn本にまとめました。
https://zenn.dev/cxj/books/07def04506182d
ConstrainedBox
BoxConstraintsの属性を持つウェジェットが多数ありますが、代表的なウェジェットは下記のConstrainedBoxです。属性はBoxConstraintsのみです。
/// Creates a widget that imposes additional constraints on its child.
///
/// The [constraints] argument must not be null.
ConstrainedBox({
Key? key,
required this.constraints,
Widget? child,
}) : assert(constraints != null),
assert(constraints.debugAssertIsValid()),
super(key: key, child: child);
上記はConstrainedBoxのコンストラクターです。属性のBoxConstraintsにて、ボックス制約を子に渡されます。BoxConstraintsをどうやって破れるかについて、前に記事に記載しましたので、リンクにてご確認ください。
下記のソースにて、属性のalignmentを用いて、厳しめ(tight)制約と緩め(loose)制約を切り替えて子ウェジェット受けた制約の影響を確認しましょう。
final BoxConstraints addToChild = const BoxConstraints(
maxWidth: 100,
maxHeight: 280,
minWidth: 50,
minHeight: 25,
);
return Scaffold(
body: Center(
child: Container(
//alignment: Alignment.topLeft,
margin: const EdgeInsets.all(5),
width: 250,
height: 150,
color: Colors.red,
child: LayoutBuilder(
builder: (_, constraints) {
print("ConstrainedBox 親から受けた制約: ${constraints}");
print("ConstrainedBox 自ら設けている制約: ${addToChild}");
return ConstrainedBox(
constraints: addToChild,
child: LayoutBuilder(
builder: (_, realConstraints) {
print("ConstrainedBox 機能している制約: ${realConstraints}");
return const ColoredBox(
color: Colors.blue,
);
},
),
);
},
),
),
),
);
緩め
alignment: Alignment.topLeftの属性を設定してあって、画面は下記のように表示されている
flutter: ConstrainedBox 親から受けた制約: BoxConstraints(0.0<=w<=250.0, 0.0<=h<=150.0)
flutter: ConstrainedBox 自ら設けている制約: BoxConstraints(50.0<=w<=100.0, 25.0<=h<=280.0)
flutter: ConstrainedBox 機能している制約: BoxConstraints(50.0<=w<=100.0, 25.0<=h<=150.0)
上記の結果から分かること:
緩めの場合、機能している制約は親と自ら設けている制約の交差であることはわかった。
A:BoxConstraints(0.0<=w<=250.0, 0.0<=h<=150.0)
B:BoxConstraints(50.0<=w<=100.0, 25.0<=h<=280.0)
C:BoxConstraints(50.0<=w<=100.0, 25.0<=h<=150.0)
すなわち、A∩B=C
厳しめ
alignment: Alignment.topLeftの属性を設定してなく、画面は下記のように表示されている

flutter: ConstrainedBox 親から受けた制約: BoxConstraints(w=250.0, h=150.0)
flutter: ConstrainedBox 自ら設けている制約: BoxConstraints(50.0<=w<=100.0, 25.0<=h<=280.0)
flutter: ConstrainedBox 機能している制約: BoxConstraints(w=250.0, h=150.0)
上記の結果から分かること:
厳しめの場合、
自ら設けていた制約BoxConstraints(50.0<=w<=100.0, 25.0<=h<=280.0)が機能してなく、親から継承した制約を機能している。
まとめ
- 制約が厳しめの場合、定義していた制約は機能してなく、親から継承した制約を機能する
- 制約が緩めの場合、機能している制約は親から継承した制約と自ら定義した制約の交差が機能している
SizedBox
/// See also:
///
/// * [ConstrainedBox], a more generic version of this class that takes
/// arbitrary [BoxConstraints] instead of an explicit width and height.
...
class SizedBox extends SingleChildRenderObjectWidget {
/// Creates a fixed size box. The [width] and [height] parameters can be null
/// to indicate that the size of the box should not be constrained in
/// the corresponding dimension.
ConstrainedBoxと同じく、SizedBoxはSingleChildRenderObjectWidgetを継承し、高さと幅を定義できるボックスです。
下記のソースでconstraintsを確認しましょう
return Scaffold(
body: Center(
child: Container(
//alignment: Alignment.topLeft,
margin: const EdgeInsets.all(5),
width: 250,
height: 150,
color: Colors.red,
child: LayoutBuilder(
builder: (_, constraints) {
print("ConstrainedBox 親から受けた制約: ${constraints}");
return SizedBox(
height: 25,
width: 100,
child: LayoutBuilder(
builder: (_, realConstraints) {
print("ConstrainedBox 機能している制約: ${realConstraints}");
return const ColoredBox(
color: Colors.blue,
);
},
),
);
},
),
),
),
);
結果:
- 厳しめ
flutter: ConstrainedBox 親から受けた制約: BoxConstraints(w=250.0, h=150.0)
flutter: ConstrainedBox 自ら設けている制約: w=100.0, h=25.0
flutter: ConstrainedBox 機能している制約: BoxConstraints(w=250.0, h=150.0)
- 緩め
flutter: ConstrainedBox 親から受けた制約: BoxConstraints(0.0<=w<=250.0, 0.0<=h<=150.0)
flutter: ConstrainedBox 自ら設けている制約: w=100.0, h=25.0
flutter: ConstrainedBox 機能している制約: BoxConstraints(w=100.0, h=25.0)
結論
ConstrainedBoxと同じです。
- 制約が厳しめの場合、定義していた制約は機能してなく、親から継承した制約を機能する
- 制約が緩めの場合、機能している制約は親から継承した制約と自ら定義した制約の交差が機能している
LimitedBox
下記はLimitedBoxのコンストラクター、ボックスの最大高さと幅のみ制限できることはわかります。
class LimitedBox extends SingleChildRenderObjectWidget {
/// Creates a box that limits its size only when it's unconstrained.
///
/// The [maxWidth] and [maxHeight] arguments must not be null and must not be
/// negative.
const LimitedBox({
Key? key,
this.maxWidth = double.infinity,
this.maxHeight = double.infinity,
Widget? child,
}) : assert(maxWidth != null && maxWidth >= 0.0),
assert(maxHeight != null && maxHeight >= 0.0),
super(key: key, child: child);
下記のソースでconstraintsを確認しましょう
final double maxWidth = 25;
final double maxHeight = 150;
return Scaffold(
body: Center(
child: Container(
//alignment: Alignment.topLeft,
margin: const EdgeInsets.all(5),
width: 250,
height: 150,
color: Colors.red,
child: LayoutBuilder(
builder: (_, constraints) {
print("ConstrainedBox 親から受けた制約: ${constraints}");
print("ConstrainedBox 自ら設けている制約: width:${maxWidth} height:${maxHeight}");
return LimitedBox(
maxHeight: 25,
maxWidth: 100,
child: LayoutBuilder(
builder: (_, realConstraints) {
print("ConstrainedBox 機能している制約: ${realConstraints}");
return const ColoredBox(
color: Colors.blue,
);
},
),
);
},
),
),
),
);
結果:
- 厳しめ
flutter: ConstrainedBox 親から受けた制約: BoxConstraints(w=250.0, h=150.0)
flutter: ConstrainedBox 自ら設けている制約: width:25.0 height:150.0
flutter: ConstrainedBox 機能している制約: BoxConstraints(w=250.0, h=150.0)
- 緩め
flutter: ConstrainedBox 親から受けた制約: BoxConstraints(0.0<=w<=250.0, 0.0<=h<=150.0)
flutter: ConstrainedBox 自ら設けている制約: width:25.0 height:150.0
flutter: ConstrainedBox 機能している制約: BoxConstraints(0.0<=w<=250.0, 0.0<=h<=150.0)
上記の例から、自ら設定しているconstraints制約は機能していないことはわかります。
LimitedBoxのソースコードに下記のコメントがあります。すなわち、親の制約がない時、LimitedBoxの最大値制限はできます。
/// A box that limits its size only when it's unconstrained.
///
/// If this widget's maximum width is unconstrained then its child's width is
/// limited to [maxWidth]. Similarly, if this widget's maximum height is
/// unconstrained then its child's height is limited to [maxHeight].
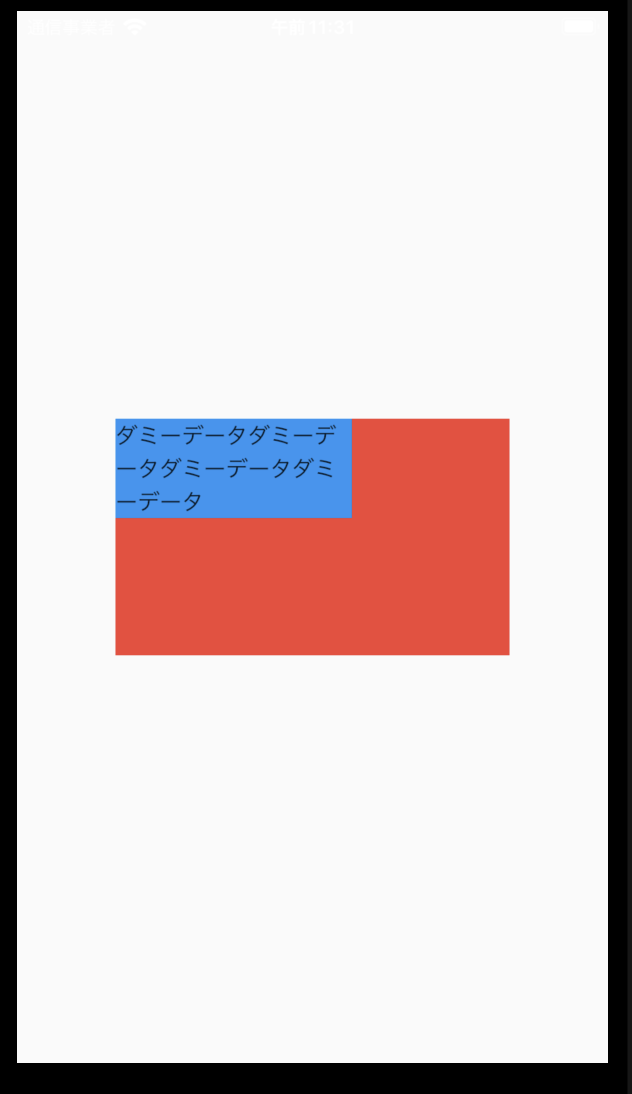
下記の例で最大幅を150に設定してみましょう。
final double maxWidth = 150;
final double maxHeight = 250;
return Scaffold(
body: Center(
child: Container(
alignment: Alignment.topLeft,
margin: const EdgeInsets.all(5),
width: 250,
height: 150,
color: Colors.red,
child: Row(
children: [
LayoutBuilder(
builder: (_, constraints) {
print("ConstrainedBox 親から受けた制約: ${constraints}");
print("ConstrainedBox 自ら設けている制約: width:${maxWidth} height:${maxHeight}");
return LimitedBox(
maxHeight: maxWidth,
maxWidth: maxWidth,
child: LayoutBuilder(
builder: (_, realConstraints) {
print("ConstrainedBox 機能している制約: ${realConstraints}");
return const ColoredBox(
color: Colors.blue,
child: Text("ダミーデータダミーデータダミーデータダミーデータ"),
);
},
),
);
},
),
],
),
),
),
);
Align
コンストラクター
/// Creates an alignment widget.
///
/// The alignment defaults to [Alignment.center].
const Align({
Key? key,
this.alignment = Alignment.center,
this.widthFactor,
this.heightFactor,
Widget? child,
}) : assert(alignment != null),
assert(widthFactor == null || widthFactor >= 0.0),
assert(heightFactor == null || heightFactor >= 0.0),
super(key: key, child: child);
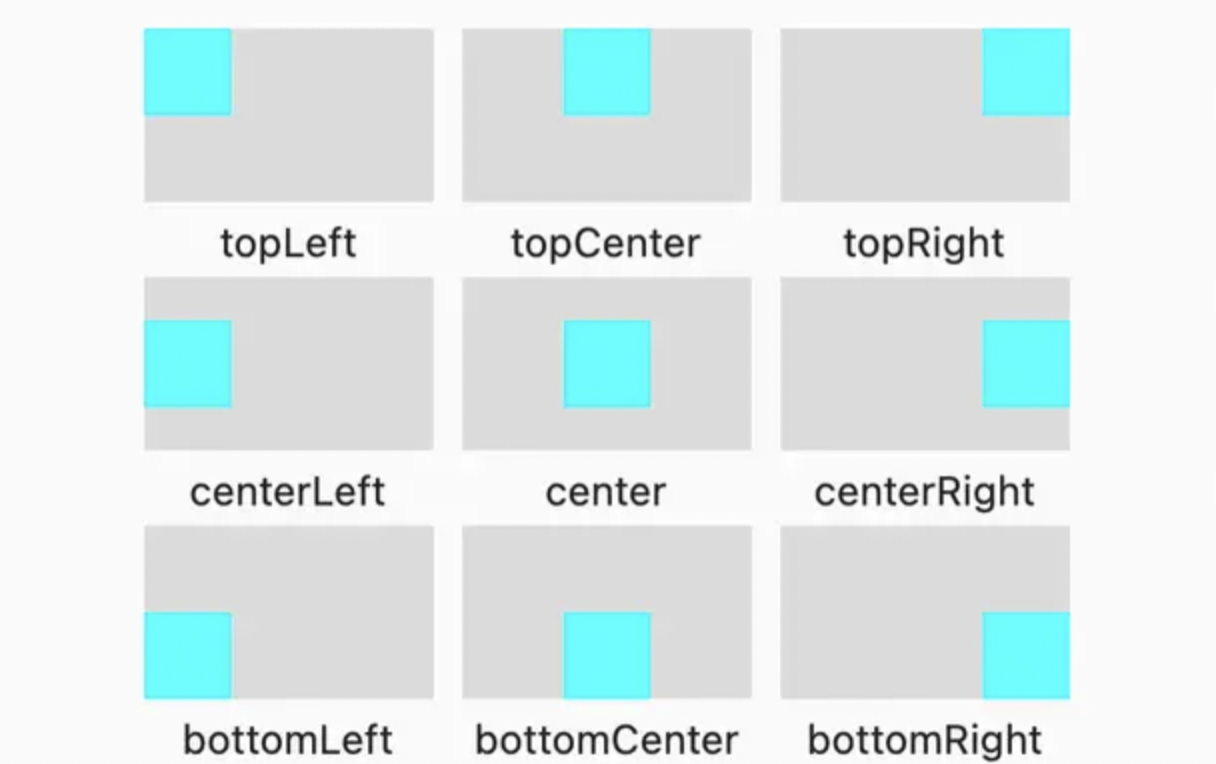
alignment
Alignmentには、下記のstatic変数が用意されている
/// The top left corner.
static const Alignment topLeft = Alignment(-1.0, -1.0);
/// The center point along the top edge.
static const Alignment topCenter = Alignment(0.0, -1.0);
/// The top right corner.
static const Alignment topRight = Alignment(1.0, -1.0);
/// The center point along the left edge.
static const Alignment centerLeft = Alignment(-1.0, 0.0);
/// The center point, both horizontally and vertically.
static const Alignment center = Alignment(0.0, 0.0);
/// The center point along the right edge.
static const Alignment centerRight = Alignment(1.0, 0.0);
/// The bottom left corner.
static const Alignment bottomLeft = Alignment(-1.0, 1.0);
/// The center point along the bottom edge.
static const Alignment bottomCenter = Alignment(0.0, 1.0);
/// The bottom right corner.
static const Alignment bottomRight = Alignment(1.0, 1.0);
widthFactorとheightFactor
widthFactorとheightFactorは名前の通り、高さと幅サイズの係数(倍数)
Alignウェジェットのソースには、下記の記述があります。
/// This widget will be as big as possible if its dimensions are constrained and
/// [widthFactor] and [heightFactor] are null. If a dimension is unconstrained
/// and the corresponding size factor is null then the widget will match its
/// child's size in that dimension. If a size factor is non-null then the
/// corresponding dimension of this widget will be the product of the child's
/// dimension and the size factor. For example if widthFactor is 2.0 then
/// the width of this widget will always be twice its child's width.
[widthFactor]と[heightFactor]がnullではなく、サイズ制限がない場合、このウィジェットの幅・高さは常に子の幅のwidthFactor/heightFactorの倍になる。たとえば、widthFactorが2.0の場合、このウィジェットの幅は常に子の幅の2倍になります。
下記のソースでどういう動作するかを確認しましょう。
Containerにはサイズ設定がなくAlignのwidthFactorとheightFactorの設定値によって、親のサイズが子の何倍にするかを制限できます。
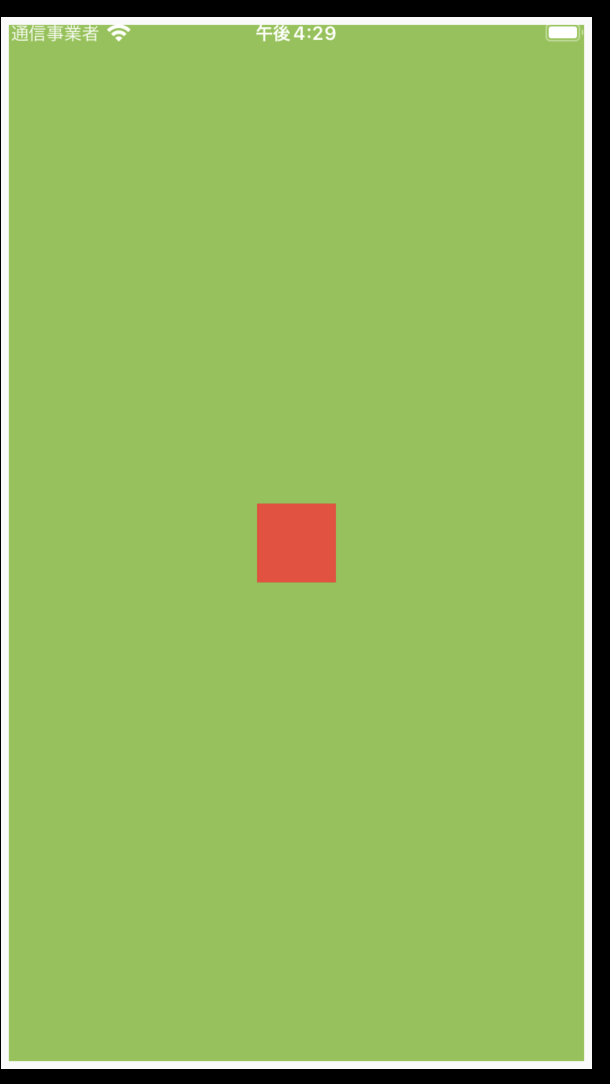
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
body: Center(
child: Container(
margin: const EdgeInsets.all(5),
//alignment: Alignment.topLeft,
color: Colors.lightGreen,
child: const Align(
//widthFactor: 2,
heightFactor: 1.5,
alignment: Alignment.center,
child: SizedBox(
width: 50,
height: 50,
child: ColoredBox(
color: Colors.red,
),
),
),
),
),
);
}
heightFactorの設定値
| なし | 1.5 | 3 |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
OverflowBox
コンストラクター
/// Creates a widget that lets its child overflow itself.
const OverflowBox({
Key? key,
this.alignment = Alignment.center,
this.minWidth,
this.maxWidth,
this.minHeight,
this.maxHeight,
Widget? child,
}) : super(key: key, child: child);
ほとんどのウェジェットは親からの制約に影響与えられてしまうが、OverflowBoxは親からの制約受けられない。
constraints制約
下記の例から見ると、親から継承した制約は(50.0<=w<=100.0, 25.0<=h<=280.0),ColoredBoxのサイズは継承したサイズの最小値になっている(50*25)
const Test111({Key? key}) : super(key: key);
final double maxWidth = 100;
final double maxHeight = 280;
final double minWidth = 50;
final double minHeight = 25;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
body: Center(
child: Container(
//alignment: Alignment.topLeft,
width: 250,
height: 150,
color: Colors.grey.withAlpha(33),
child: LayoutBuilder(
builder: (_, constraints) {
print("OverflowBox 親から受けた制約: ${constraints}");
print("OverflowBox(${minWidth}<=w<=${maxWidth}, ${minHeight}<=h<=${maxHeight})");
return Center(
child: OverflowBox(
// alignment: Alignment.center,
maxHeight: maxHeight,
maxWidth: maxWidth,
minWidth: minWidth,
minHeight: minHeight,
child: LayoutBuilder(
builder: (_, constraints) {
print("OverflowBox 機能している制約: ${constraints}");
return const ColoredBox(
color: Colors.blue,
);
},
),
),
);
},
),
),
),
);
}
結果:
flutter: OverflowBox 親から受けた制約: BoxConstraints(w=250.0, h=150.0)
flutter: OverflowBox(50.0<=w<=100.0, 25.0<=h<=280.0)
flutter: OverflowBox 機能している制約: BoxConstraints(50.0<=w<=100.0, 25.0<=h<=280.0)
特徴
OverflowBoxの特徴は親のサイズを超えることできることである。
上記のソースで親の高さは150だが、サイズを300にし、ColoredBoxをSizedBoxにラッパーすると、下記の図のようになる、親のサイズを超えるは可能だが、OverflowBoxの最大サイズには超えない。300サイズにしたが、親の150サイズを超えたが、OverflowBoxの最大サイズ280を超えられない。
return const SizedBox(
height: 300,
child: ColoredBox(
color: Colors.blue,
),
);
まとめ
- OverflowBoxは指定の最大最小サイズに制限されるが、親の制限サイズを無視できる
- サイズの最大最小値はOverflowBox制限している
- alignmentで位置の調整できる
SizedOverflowBox
コンストラクター
/// Creates a widget of a given size that lets its child overflow.
///
/// The [size] argument must not be null.
const SizedOverflowBox({
Key? key,
required this.size,
this.alignment = Alignment.center,
Widget? child,
}) : assert(size != null),
assert(alignment != null),
super(key: key, child: child);
特徴
下記のソースでSizedOverflowBoxの動作を確認しましょう。
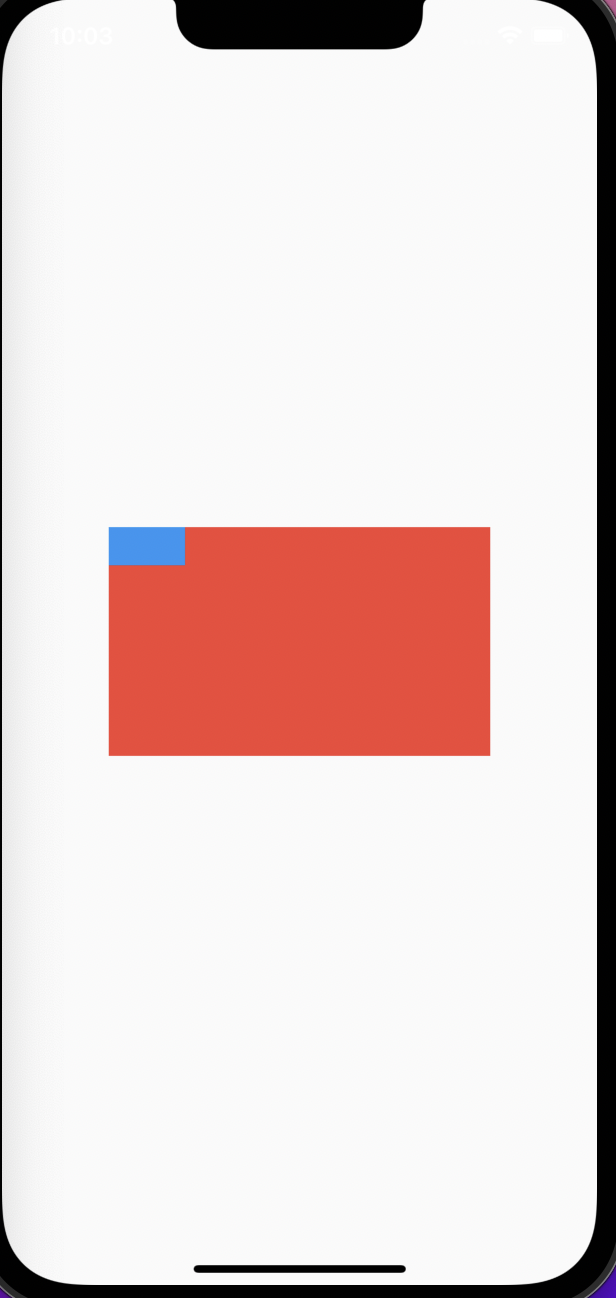
SizedOverflowBoxの属性であるSize()がSizedOverflowBoxのSize範囲を定義しており、SizedBoxが幅30の赤い四角形を描画しています。Dev Toolで確認すると、SizedOverflowBoxの範囲は一目瞭然です。

return Scaffold(
body: Center(
child: Container(
alignment: Alignment.topLeft,
width: 250,
height: 150,
color: Colors.lightGreen,
child: LayoutBuilder(
builder: (_, constraints) {
print("OverflowBox 親から受けた制約: ${constraints}");
return Center(
child: SizedOverflowBox(
alignment: Alignment.topLeft,
size: const Size(150, 150),
child: LayoutBuilder(
builder: (_, constraints) {
print("OverflowBox 機能している制約: ${constraints}");
return const SizedBox(
height: 30,
width: 30,
child: ColoredBox(
color: Colors.red,
),
);
},
),
),
);
},
),
),
),
);
まとめ
- Size経由で、親の制約で定義したサイズ範囲内でサイズを定義する。上記の例だと、Size(x,y)は親のサイズ250*150を超えられない。
- alignmentはSizedOverflowBoxのサイズ範囲内位置を調整する
FractionallySizedBox
コンストラクター
/// Creates a widget that sizes its child to a fraction of the total available space.
///
/// If non-null, the [widthFactor] and [heightFactor] arguments must be
/// non-negative.
const FractionallySizedBox({
Key? key,
this.alignment = Alignment.center,
this.widthFactor,
this.heightFactor,
Widget? child,
}) : assert(alignment != null),
assert(widthFactor == null || widthFactor >= 0.0),
assert(heightFactor == null || heightFactor >= 0.0),
super(key: key, child: child);
特徴
heightFactorとwidthFactorがnullの場合、親の制約は変更されずに子に渡されます。null以外の場合、子には制約が与えられます。入力幅の制約にこの係数を掛けたもの。サイズは親を超えることは可能です。但し、位置調整は親を基づく調整します。
下記のソースで動作を確認しましょう。
return Scaffold(
body: Center(
child: Container(
alignment: Alignment.topLeft,
width: 250,
height: 150,
color: Colors.lightGreen,
child: LayoutBuilder(
builder: (_, constraints) {
return Center(
child: FractionallySizedBox(
widthFactor: 0.5,
heightFactor: 0.5,
alignment: Alignment.topLeft,
child: LayoutBuilder(
builder: (_, constraints) {
return const ColoredBox(
color: Colors.red,
);
},
),
),
);
},
),
),
),
);
| widthFactor: 0.5 | widthFactor: 2.5 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
AspectRatio
コンストラクター
/// Creates a widget with a specific aspect ratio.
///
/// The [aspectRatio] argument must be a finite number greater than zero.
const AspectRatio({
Key? key,
required this.aspectRatio,
Widget? child,
}) : assert(aspectRatio != null),
assert(aspectRatio > 0.0),
// can't test isFinite because that's not a constant expression
super(key: key, child: child);
属性は1つのみです。高さと幅の比率を表すものです。
FittedBox
コンストラクター
/// Creates a widget that scales and positions its child within itself according to [fit].
///
/// The [fit] and [alignment] arguments must not be null.
const FittedBox({
Key? key,
this.fit = BoxFit.contain,
this.alignment = Alignment.center,
this.clipBehavior = Clip.none,
Widget? child,
}) : assert(fit != null),
assert(alignment != null),
assert(clipBehavior != null),
super(key: key, child: child);
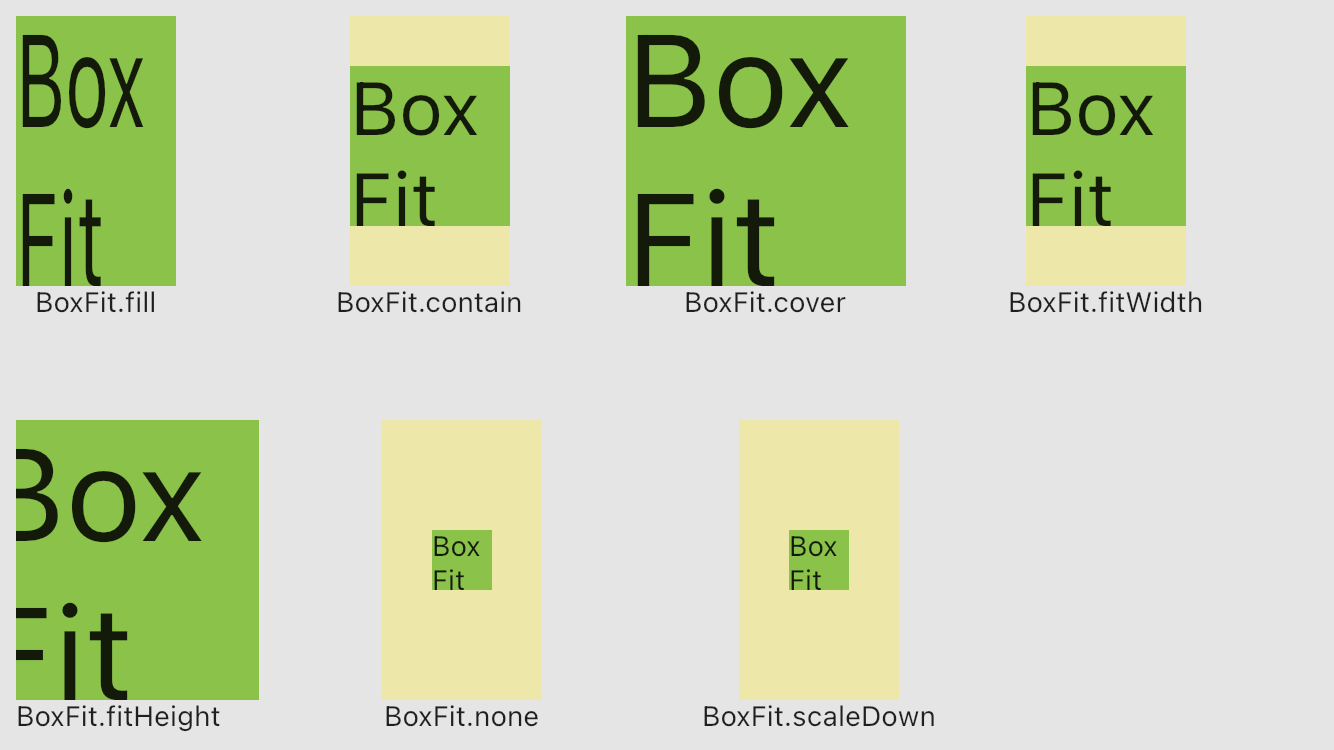
各BoxFitの属性にる、子のサイズを親のサイズを超えた場合のUI表現は下記の通りです。
| BoxFit | 説明 |
|---|---|
| BoxFit.fill | 親に塡充する |
| BoxFit.contain | 自身のサイズ比率を確保した上で、親領域でサイズを拡大する |
| BoxFit.cover | 自身のサイズ比率を確保した上で、親領域をラップする |
| BoxFit.fitWidth | 幅が親領域を満たし、比率を確保した上で高さをスケーリングする |
| BoxFit.fitHeight | 高さが親領域を満たし、比率を確保した上で幅をスケーリングする |
| BoxFit.none | 何もしない |
| BoxFit.scaleDown | 自身のサイズ比率を確保した上で、もし子が親より大きい場合、子をスケーリングして親の領域中にあることを確保する |