Reference
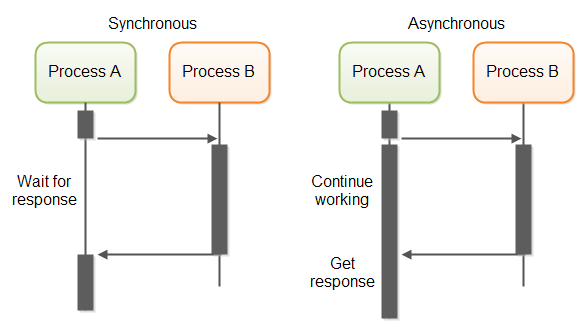
Synchrounous and asynchrounous requests
A process need to wait for another process got finished and then does something else in synchrounous model; in contract, asynchrounous one does not. ( It will describe with sync and async below.)
Sample for async functions
function first(){
// Simulate a code delay
setTimeout( function(){
console.log(1);
}, 500 );
}
function second(){
console.log(2);
}
first();
second();
// 2
// 1
Non-blocking environment
- how to handle the result of each async processes below??
- how does our system know the async process is done??
To handle async processes
Method 1: Callback function // ES4 standard
function first(subject, callback) {
console.log(subject + " 1");
callback();
}
function second(){
console.log('Call 2');
}
first('Hello', second);
// Hello 1
// Call 2
Real example 1: XMLHttpRequest ES5 standard
const oReq = new XMLHttpRequest();
// Handle async responses
oReq.addEventListener("load", function () {
console.log('show: '+this.responseText);
});
oReq.upload.addEventListener("progress", function(){
console.log('updateProgress');
});
// Async request
oReq.open("GET", "http://www.example.org/example.txt");
oReq.send();
Method 2: Promise ES6 standard
An object to wrap and unwrap objects and functions asynchronously
// Wrap async function using Promise
function timeoutPromise(interval) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(function(){
console.log("processing");
resolve('processed');
}, interval);
});
};
// Use then(), catch() to unwrap Promise when calling
timeoutPromise(1000).then(function(result) {
console.log(result); // processing, processed
console.log('done'); // done
});
// Unwrap Promise sequentially
Promise.all([timeoutPromise(1000), timeoutPromise(1000)]).then(function(values) {
console.log(values);
});
// processing, processing, ['processed','processed']
Real example 2a: jQuery
// Async request
$.get('http://www.example.org/example.json', function(response){
console.log(JSON.stringify(response));
});
Real example 2b: Fetch HTML5 standard
// Async request
fetch('http://www.example.org/example.json')
.then((response) => {
return response.json();
})
.then((jsonContent) => { // extract json
console.log(jsonContent);
});
Method 3: async/await ES7 candidate
For unwrap Promise object easily
function timeoutPromise(interval) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(function(){
console.log("processing");
resolve();
}, interval);
});
};
// Unwrap Promise sequentially
async function timeTest() {
await timeoutPromise(3000);
await timeoutPromise(3000);
console.log('done');
}
timeTest(); // processing, processing, done
Summary
Because sending requests asynchrounously is hard for developers to handle their responses. Using these new methods could be easier to take asynchrounous functions sequentially like accessing synchrounous functions.
Please be aware that Promise.all() does not guarantee all requests in a sequence but for the resolved result; besides, if a process got failed, Promise.all() would only get error catch
// Summary
var p1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(`processing one`);
return resolve('one')
},4000);
});
var p2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(`processing two`);
return resolve('two')
},3000);
});
var p3 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(`processing three`);
return resolve('three')
},2000);
});
var p4 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(`processing four`);
return resolve('four')
},1000);
});
// error
var p5 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
reject(new Error('reject'));
});
// execute
Promise.all([p1, p2, p3, p4])
.then(values => {
console.log(values); // [ 'one', 'two', 'three', 'four' ]
})
.catch(error => {
console.error(error.message) // if run with p5
});
//processing four
//processing three
//processing two
//processing one
Reference