(この記事は一連の解説記事の一つになります)
注意事項
ここまで連続記事という体をとって、特記のない事項についてはそれまでと同じとしてきましたが、今回の記事から環境を変えたので特に注意してください。
環境
**Minecraft Forgeのバージョンを上げました。**開発中のバージョンであり未整備な部分が多かったためです。また、更新後も同様に開発中のバージョンであり、日々更新版が出ているのでご注意ください。
| version | |
|---|---|
| OS | Winsows 10 Home |
| Oracle JDK | 8u212 |
| Minecraft | 1.16.1 |
| Minecraft Forge | 1.16.1 (32.0.108) -> 1.16.1 (33.0.22) |
| InteliJ IDEA | 2020.1.3 (CE) |
各ブロック・アイテムの追加
ブロックの追加を参考に原木・葉・苗ブロックを追加します。
package jp.koteko.liveinwater.block;
import jp.koteko.liveinwater.LiveInWater;
import jp.koteko.liveinwater.block.trees.WaterTree;
import net.minecraft.block.*;
import net.minecraft.block.material.Material;
import net.minecraft.block.material.MaterialColor;
import net.minecraft.client.renderer.RenderType;
import net.minecraft.client.renderer.RenderTypeLookup;
import net.minecraft.world.FoliageColors;
import net.minecraft.world.biome.BiomeColors;
import net.minecraftforge.client.event.ColorHandlerEvent;
import net.minecraftforge.event.RegistryEvent;
import net.minecraftforge.eventbus.api.SubscribeEvent;
import net.minecraftforge.fml.common.Mod;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@Mod.EventBusSubscriber(modid = LiveInWater.MOD_ID, bus = Mod.EventBusSubscriber.Bus.MOD)
public class Blocks {
public static List<Block> blockList = new ArrayList<Block>();
public static Block WATERTREE_ROOT_BLOCK = register("watertree_root_block", new Block(AbstractBlock.Properties.create(Material.WOOD).hardnessAndResistance(2.5F).sound(SoundType.WOOD)));
public static Block WATERTREE_LOG = register("watertree_log", new RotatedPillarBlock(AbstractBlock.Properties.create(Material.WOOD, MaterialColor.WOOD).hardnessAndResistance(2.0F).sound(SoundType.WOOD)));
public static Block WATERTREE_LEAVES = register("watertree_leaves", new LeavesBlock(AbstractBlock.Properties.create(Material.LEAVES).hardnessAndResistance(0.2F).tickRandomly().sound(SoundType.PLANT).notSolid()));
public static Block WATERTREE_SAPLING = register("watertree_sapling", new SaplingBlock(new WaterTree(), AbstractBlock.Properties.create(Material.PLANTS).doesNotBlockMovement().tickRandomly().zeroHardnessAndResistance().sound(SoundType.PLANT)));
private static Block register(String key, Block blockIn){
blockList.add(blockIn);
return blockIn.setRegistryName(LiveInWater.MOD_ID, key);
}
@SubscribeEvent
public static void registerBlocks(RegistryEvent.Register<Block> event) {
for (Block block : blockList) {
event.getRegistry().register(block);
if (block instanceof SaplingBlock) {
RenderTypeLookup.setRenderLayer(block, RenderType.getCutout());
}
}
}
@SubscribeEvent
public static void registerBlockColors(ColorHandlerEvent.Block event) {
event.getBlockColors().register((p_210229_0_, p_210229_1_, p_210229_2_, p_210229_3_) -> {
return p_210229_1_ != null && p_210229_2_ != null ? BiomeColors.getFoliageColor(p_210229_1_, p_210229_2_) : FoliageColors.getDefault();
}, WATERTREE_LEAVES);
}
}
原木はRotatedPillarBlock、葉はLeavesBlock、苗はSaplingBlockクラスで作ります。細かな設定はBlockに共通するもの(たとえば.hardnessAndResistance()で硬さや耐性を設定)なので適宜変更してください。上述のものはそれぞれに標準的な値(のはず)です。
SaplingBlockのコンストラクタに渡す第一引数は、苗が生成する木のインスタンスになります。まだ定義していませんが後述します。
また、ブロック登録部分に記述が追加されています。これは苗ブロックのテクスチャ表示を正しく行うためにレンダータイプの設定を行っています。これを行わないと透過されるべき部分が黒塗り状態になってしまいました。参考
最後に、葉ブロックの色をバイオームカラーに応じて変更するよう設定しています。1.14.4のときの記述をそのまま持ってきたので深く中は見てません。BlockColorsクラスを観察するともっといろいろ分かると思います。バイオームカラーについては参考ページを参照してください。これを設定しない場合、全バイオームでテクスチャの色がそのまま使われるので、省略可能です。
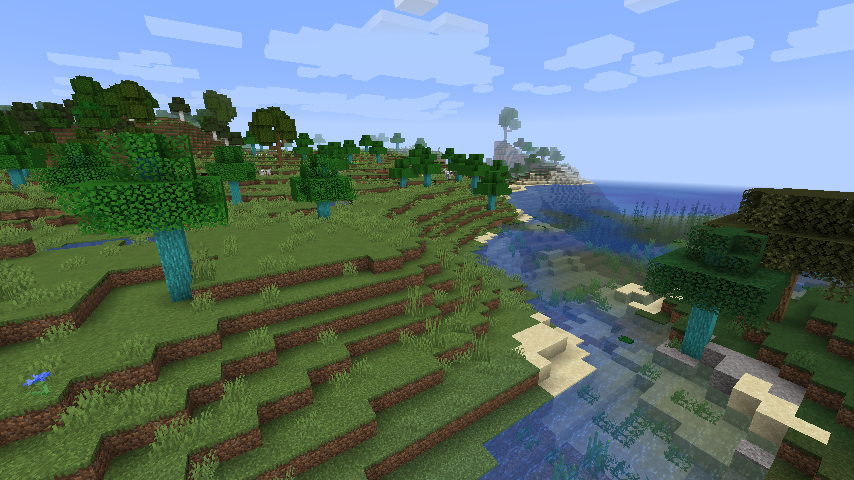
バイオームに応じて葉の色が変わる様子(記事末尾の自然生成まで実装後の様子なのでこの時点ではワールドに木は生成されません)
package jp.koteko.liveinwater.item;
import jp.koteko.liveinwater.LiveInWater;
import jp.koteko.liveinwater.block.Blocks;
import net.minecraft.block.Block;
import net.minecraft.item.BlockItem;
import net.minecraft.item.Item;
import net.minecraft.item.ItemGroup;
import net.minecraftforge.event.RegistryEvent;
import net.minecraftforge.eventbus.api.SubscribeEvent;
import net.minecraftforge.fml.common.Mod;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@Mod.EventBusSubscriber(modid = LiveInWater.MOD_ID, bus = Mod.EventBusSubscriber.Bus.MOD)
public class Items {
public static List<Item> itemList = new ArrayList<Item>();
public static final Item WATERTREE_ROOT = register("watertree_root", new Item((new Item.Properties()).group(LiwItemGroup.DEFAULT)));
public static final Item WATERTREE_ROOT_BLOCK = register("watertree_root_block", Blocks.WATERTREE_ROOT_BLOCK, LiwItemGroup.DEFAULT);
public static final Item WATERTREE_LOG = register("watertree_log", Blocks.WATERTREE_LOG, LiwItemGroup.DEFAULT);
public static final Item WATERTREE_LEAVES = register("watertree_leaves", Blocks.WATERTREE_LEAVES, LiwItemGroup.DEFAULT);
public static final Item WATERTREE_SAPLING = register("watertree_sapling", Blocks.WATERTREE_SAPLING, LiwItemGroup.DEFAULT);
private static Item register(String key, Item itemIn) {
itemList.add(itemIn);
return itemIn.setRegistryName(LiveInWater.MOD_ID, key);
}
private static Item register(String key, Block blockIn, ItemGroup itemGroupIn) {
return register(key, new BlockItem(blockIn, (new Item.Properties()).group(itemGroupIn)));
}
@SubscribeEvent
public static void registerItems(RegistryEvent.Register<Item> event) {
for (Item item : itemList) {
event.getRegistry().register(item);
}
}
}
BlockItemを宣言・登録します。アイテムの追加も参照してください。
resourcesの設定をします。
\src\main\resources
├ assets
│ └ example_mod
│ ├ blockstates
│ │ ├ watertree_leaves.json
│ │ ├ watertree_log.json
│ │ └ watertree_sapling.json
│ ├ lang
│ │ └ en_us.json
│ │ └ ja_jp.json
│ ├ models
│ │ ├ block
│ │ │ ├ watertree_leaves.json
│ │ │ ├ watertree_log.json
│ │ │ └ watertree_sapling.json
│ │ └ item
│ │ ├ example_leaves.json
│ │ ├ example_log.json
│ │ └ example_sapling.json
│ └ textures
│ ├ block
│ │ ├ watertree_leaves.json
│ │ ├ watertree_log.json
│ │ └ watertree_sapling.json
│ └ item
│ └ watertree_sapling.json
└ data
└ liveinwater
└ loot_tables
└ blocks
├ example_leaves.json
├ example_log.json
└ example_sapling.json
{
"variants": {
"": { "model": "liveinwater:block/watertree_leaves" }
}
}
{
"variants": {
"axis=y": { "model": "liveinwater:block/watertree_log" },
"axis=z": { "model": "liveinwater:block/watertree_log", "x": 90 },
"axis=x": { "model": "liveinwater:block/watertree_log", "x": 90, "y": 90 }
}
}
設置方向によってモデルを回転させます。
{
"variants": {
"": { "model": "liveinwater:block/watertree_sapling" }
}
}
{
"item.liveinwater.watertree_log": "WaterTree Log",
"item.liveinwater.watertree_leaves": "WaterTree Leaves",
"item.liveinwater.watertree_sapling": "WaterTree Sapling",
"block.liveinwater.watertree_log": "WaterTree Log",
"block.liveinwater.watertree_leaves": "WaterTree Leaves",
"block.liveinwater.watertree_sapling": "WaterTree Sapling"
}
{
"item.liveinwater.watertree_log": "ウォーターツリーの原木",
"item.liveinwater.watertree_leaves": "ウォーターツリーの葉",
"item.liveinwater.watertree_sapling": "ウォーターツリーの苗",
"block.liveinwater.watertree_log": "ウォーターツリーの原木",
"block.liveinwater.watertree_leaves": "ウォーターツリーの葉",
"block.liveinwater.watertree_sapling": "ウォーターツリーの苗"
}
{
"parent": "block/leaves",
"textures": {
"all": "liveinwater:block/watertree_leaves"
}
}
{
"parent": "block/cube_column",
"textures": {
"end": "liveinwater:block/watertree_log_top",
"side": "liveinwater:block/watertree_log"
}
}
parentにblock/cube_columnを指定し、立方体型で上下面と側面で区別したテクスチャを適用します。それぞれのテクスチャファイルへのパスを指定しましょう。
{
"parent": "block/cross",
"textures": {
"cross": "liveinwater:block/watertree_sapling"
}
}
{
"parent": "liveinwater:block/watertree_leaves"
}
{
"parent": "liveinwater:block/watertree_log"
}
{
"parent": "item/generated",
"textures": {
"layer0": "liveinwater:item/watertree_sapling"
}
}
{
"type": "minecraft:block",
"pools": [
{
"rolls": 1,
"entries": [
{
"type": "minecraft:alternatives",
"children": [
{
"type": "minecraft:item",
"conditions": [
{
"condition": "minecraft:alternative",
"terms": [
{
"condition": "minecraft:match_tool",
"predicate": {
"item": "minecraft:shears"
}
},
{
"condition": "minecraft:match_tool",
"predicate": {
"enchantments": [
{
"enchantment": "minecraft:silk_touch",
"levels": {
"min": 1
}
}
]
}
}
]
}
],
"name": "liveinwater:watertree_leaves"
},
{
"type": "minecraft:item",
"conditions": [
{
"condition": "minecraft:survives_explosion"
},
{
"condition": "minecraft:table_bonus",
"enchantment": "minecraft:fortune",
"chances": [
0.05,
0.0625,
0.083333336,
0.1
]
}
],
"name": "liveinwater:watertree_sapling"
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
詳しくは参考ページを参照のこと。
{
"type": "minecraft:block",
"pools": [
{
"rolls": 1,
"entries": [
{
"type": "minecraft:item",
"name": "liveinwater:watertree_log"
}
]
}
]
}
{
"type": "minecraft:block",
"pools": [
{
"rolls": 1,
"entries": [
{
"type": "minecraft:item",
"name": "liveinwater:watertree_sapling"
}
]
}
]
}
タグへの追加
追加した原木ブロックをminecraft:logsのタグに追加します。(他の部分でも活用されているかもしれませんが)これは葉ブロックの消滅判定に用いられるので、これを行わないと生成した木の葉ブロックがすぐに消滅を開始してしまいます。
\src\main\resources
├ assets
└ data
├ liveinwater
└ minecraft
└ tags
└ blocks
└ logs.json
自分のプロジェクトフォルダ内に\src\main\resources\data\minecraft\tags\blocksフォルダを作り、そこにlogs.jsonを配置します。この名前は必ず同じにしてください。
{
"replace": false,
"values": [
"liveinwater:watertree_log"
]
}
replaceにfalseを与えることにより、同名のminecraft:logsにこのファイルでの記述が統合されます。valuesの中でブロックを指定しましょう。
同様に葉ブロックもminecraft:leavesのタグに追加します。これは苗から木が成長する際に葉ブロックを障害物判定しないために必要です(leavesのタグにない場合木が生成される際に上書きされない)。
\src\main\resources
├ assets
└ data
├ liveinwater
└ minecraft
└ tags
└ blocks
├ leaves.json
└ logs.json
{
"replace": false,
"values": [
"liveinwater:watertree_leaves"
]
}
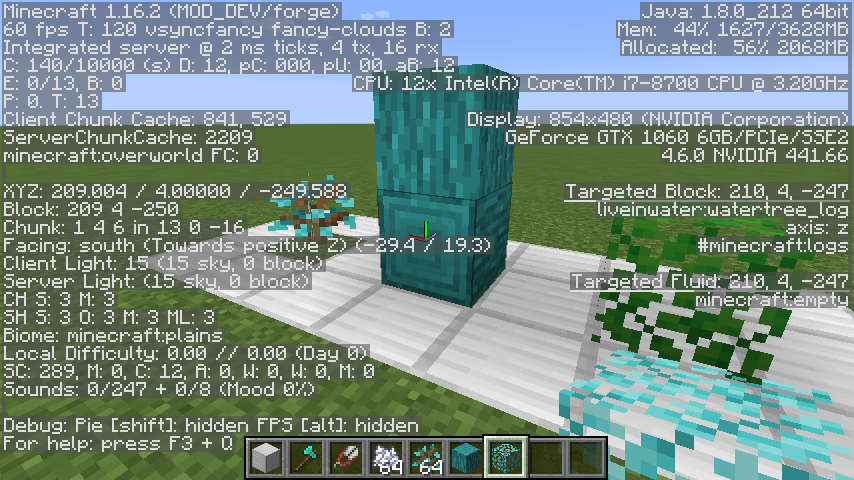
ゲーム内でF3を押してデバッグ表示をしブロックにカーソルを合わせた際に、画面右中央あたりにタグ(例えば#mineraft:logs)の表示が出ていることを確認します。
TreeFeatureクラスとTreeクラスの追加
これらは違いを言葉で説明するのが難しいですが、ともに木を管理するクラスです。Treeクラスは木自体を管理するクラスで、この後で追加する苗に関連して必要になります。一方で、TreeFeatureクラスは木の生成に関することを管理しており、Treeクラスから該当するTreeFeatureを取得することもできます。
\src\main\java\jp\koteko\liveinwater\
├ block
│ └ trees
│ └ WaterTree.java
├ item
├ world
│ └ gen
│ └ feature
│ └ WaterTreeFeature.java
└ LiveInWater.java
package jp.koteko.liveinwater.block.trees;
import jp.koteko.liveinwater.world.gen.TreeGenerator;
import net.minecraft.block.trees.Tree;
import net.minecraft.world.gen.feature.BaseTreeFeatureConfig;
import net.minecraft.world.gen.feature.ConfiguredFeature;
import javax.annotation.Nullable;
import java.util.Random;
public class WaterTree extends Tree {
@Nullable
protected ConfiguredFeature<BaseTreeFeatureConfig, ?> getTreeFeature(Random randomIn, boolean p_225546_2_) {
return TreeGenerator.WATERTREE.setConfiguration();
}
}
Tree抽象クラスをextendsしてクラスを定義します。抽象メソッドgetTreeFeatureを、後述するWaterTreeFeatureにコンフィグを与えた状態のBaseTreeFeatureConfigクラスのインスタンスを返すように定義しましょう(TreeGeneratorについては後の項で示します)。乱数を受け取るようになっていますが、これは木が確率で巨大種に成長する場合などに用いるので、必要であれば乱数に応じて返す値を変えましょう。
package jp.koteko.liveinwater.world.gen.feature;
import com.google.common.collect.ImmutableList;
import com.mojang.serialization.Codec;
import jp.koteko.liveinwater.block.Blocks;
import net.minecraft.world.gen.blockstateprovider.SimpleBlockStateProvider;
import net.minecraft.world.gen.feature.*;
import net.minecraft.world.gen.foliageplacer.BlobFoliagePlacer;
import net.minecraft.world.gen.placement.AtSurfaceWithExtraConfig;
import net.minecraft.world.gen.placement.Placement;
import net.minecraft.world.gen.treedecorator.BeehiveTreeDecorator;
import net.minecraft.world.gen.trunkplacer.StraightTrunkPlacer;
public class WaterTreeFeature extends TreeFeature {
public WaterTreeFeature(Codec<BaseTreeFeatureConfig> codec) {
super(codec);
}
public ConfiguredFeature<?, ?> configure() {
return this.setConfiguration().withPlacement(Placement.field_242902_f.configure(new AtSurfaceWithExtraConfig(10, 0.1F, 1)).func_242728_a());
}
public ConfiguredFeature<BaseTreeFeatureConfig, ?> setConfiguration() {
return this.withConfiguration(
new BaseTreeFeatureConfig.Builder(
new SimpleBlockStateProvider(Blocks.WATERTREE_LOG.getDefaultState()),
new SimpleBlockStateProvider(Blocks.WATERTREE_LEAVES.getDefaultState()),
new BlobFoliagePlacer(FeatureSpread.func_242252_a(2), FeatureSpread.func_242252_a(0), 3),
new StraightTrunkPlacer(5, 2, 0),
new TwoLayerFeature(1, 0, 1)
).func_236700_a_().func_236703_a_(ImmutableList.of(new BeehiveTreeDecorator(0.002F))).build());
}
}
TreeFeatureクラスをextendsしてクラスを定義します。
他のクラスからFeatureを用いる際のgenericsによる制限(<BaseTreeFeatureConfig, ?>の部分)に対応するため、2つのメソッドを定義します。
まず下のsetConfiguration()では、この木がどのような形を持つかということを設定しています(withConfiguration())。
コンフィグにはビルダーが用意されており、引数は順に、幹となるブロックのプロバイダ、葉となるブロックのプロバイダ、葉の配置形状、幹の配置形状、(用途不明な引数AbstractFeatureSizeType)、です。名前が分かりづらいですが、func_236700_a_()はignore_vinesをtrueにする関数、func_236703_a_()は引数(今回の例では0.002の確率でハチの巣を生成するもの)をデコレーターとして与える関数、としてそれぞれビルダーに定義されています。最後にbuild()を呼ぶことでBaseTreeFeatureConfigを作成し、withConfiguration()の引数に渡します。
次にconfigure()では、setConfiguration()したFeatureにさらに配置場所の設定を与えます(withPlacement())。
Placementには沢山の種類が用いられており、また複数を重ねて使うようなこともされることがわかっています。そのため好みの配置を作るにはPlacementの中身を深く観察する必要があるでしょう。今回は私が確認し一例のみを示しました。例えば、Placement.field_242902_fで抽選回数を決定し、func_242728_a()が最終的にSquarePlacementを適用してgetPosisionsのメソッドでチャンク内のランダム座標のリストを返す、といった風なふるまいをしているようです。この辺りのことはもう少し深く理解したら別記事にまとめるかもしれません。
木の生成
最後に、実装した木をワールド生成時に自動で生成されるようにしましょう。
\src\main\java\jp\koteko\liveinwater\
├ block
├ item
├ world
│ └ gen
│ ├ feture
│ └ TreeGenerator.java
└ LiveInWater.java
package jp.koteko.liveinwater.world.gen;
import com.google.common.collect.Lists;
import jp.koteko.liveinwater.world.gen.feature.WaterTreeFeature;
import net.minecraft.util.RegistryKey;
import net.minecraft.util.registry.Registry;
import net.minecraft.util.registry.WorldGenRegistries;
import net.minecraft.world.biome.Biome;
import net.minecraft.world.biome.BiomeGenerationSettings;
import net.minecraft.world.gen.GenerationStage;
import net.minecraft.world.gen.feature.BaseTreeFeatureConfig;
import net.minecraft.world.gen.feature.ConfiguredFeature;
import net.minecraftforge.fml.common.ObfuscationReflectionHelper;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
public class TreeGenerator {
public static WaterTreeFeature WATERTREE;
public static ConfiguredFeature<?, ?> CONFIGURED_WATERTREE;
public static void init() {
WATERTREE = Registry.register(Registry.FEATURE, "liveinwater:watertree", new WaterTreeFeature(BaseTreeFeatureConfig.field_236676_a_));
CONFIGURED_WATERTREE = Registry.register(WorldGenRegistries.field_243653_e, "liveinwater:watertree", WATERTREE.configure());
}
public static void setup() {
addTreeToOverworld(CONFIGURED_WATERTREE);
}
private static void addTreeToOverworld(ConfiguredFeature<?, ?> featureIn){
for(Map.Entry<RegistryKey<Biome>, Biome> biome : WorldGenRegistries.field_243657_i.func_239659_c_()) {
if(!biome.getValue().getCategory().equals(Biome.Category.NETHER) && !biome.getValue().getCategory().equals(Biome.Category.THEEND)) {
addFeatureToBiome(biome.getValue(), GenerationStage.Decoration.VEGETAL_DECORATION, featureIn);
}
}
}
public static void addFeatureToBiome(Biome biome, GenerationStage.Decoration decoration, ConfiguredFeature<?, ?> configuredFeature) {
List<List<Supplier<ConfiguredFeature<?, ?>>>> biomeFeatures = new ArrayList<>(biome.func_242440_e().func_242498_c());
while (biomeFeatures.size() <= decoration.ordinal()) {
biomeFeatures.add(Lists.newArrayList());
}
List<Supplier<ConfiguredFeature<?, ?>>> features = new ArrayList<>(biomeFeatures.get(decoration.ordinal()));
features.add(() -> configuredFeature);
biomeFeatures.set(decoration.ordinal(), features);
ObfuscationReflectionHelper.setPrivateValue(BiomeGenerationSettings.class, biome.func_242440_e(), biomeFeatures, "field_242484_f");
}
}
全部を理解するのは難しい部分なので、必要に応じて変える部分を判断してください(実際私もそうしたので)。1.16.1版では、以前のような方法でBiomeにFeatureを登録することができなくなっていました。そのため参考になるコードを探し、BluePower様のコードを参考にさせていただきました。
最下部のaddFeatureToBiomeを定義することによって、今までと似たような方法でBiomeにFeatureを登録することを可能にしています。簡単に説明すると、BiomeGenerationSettingsクラスのメンバ変数field_242484_fがFeatureのリストを持っているようなので、上書きして追加するという作業をしているようです。
addFeatureToBiomeが定義されたら、あとは以前の方法に近い形で実装ができます。OverworldのBiomeに登録を行うaddTreeToOverworldメソッドを定義し、setupメソッド内で呼び出すようにしました。また、各Featureらはあらかじめ宣言し、initメソッドで登録を行うようにします。この時、上記のようにFeatureの登録とConfiguredFeatureの登録をそれぞれ行っておかないと上手くいかないようです(かなり詰まったけれど完全には理解できませんでした)。
最後に、今定義したTreeGenerator.init()``TreeGenerator.setup()をメインファイル内で呼びます。
package jp.koteko.liveinwater;
import jp.koteko.liveinwater.world.gen.TreeGenerator;
import net.minecraftforge.common.MinecraftForge;
import net.minecraftforge.eventbus.api.SubscribeEvent;
import net.minecraftforge.fml.common.Mod;
import net.minecraftforge.fml.event.lifecycle.FMLClientSetupEvent;
import net.minecraftforge.fml.event.lifecycle.FMLCommonSetupEvent;
import net.minecraftforge.fml.event.lifecycle.InterModEnqueueEvent;
import net.minecraftforge.fml.event.lifecycle.InterModProcessEvent;
import net.minecraftforge.fml.event.server.FMLServerStartingEvent;
import net.minecraftforge.fml.javafmlmod.FMLJavaModLoadingContext;
import org.apache.logging.log4j.LogManager;
import org.apache.logging.log4j.Logger;
@Mod(LiveInWater.MOD_ID)
public class LiveInWater
{
public static final String MOD_ID = "liveinwater";
private static final Logger LOGGER = LogManager.getLogger();
public LiveInWater() {
FMLJavaModLoadingContext.get().getModEventBus().addListener(this::setup);
FMLJavaModLoadingContext.get().getModEventBus().addListener(this::enqueueIMC);
FMLJavaModLoadingContext.get().getModEventBus().addListener(this::processIMC);
FMLJavaModLoadingContext.get().getModEventBus().addListener(this::doClientStuff);
TreeGenerator.init();
MinecraftForge.EVENT_BUS.register(this);
}
private void setup(final FMLCommonSetupEvent event)
{
LOGGER.info("SETUP START");
TreeGenerator.setup();
LOGGER.info("SETUP END");
}
private void doClientStuff(final FMLClientSetupEvent event) {
// do something that can only be done on the client
}
private void enqueueIMC(final InterModEnqueueEvent event)
{
// some example code to dispatch IMC to another mod
}
private void processIMC(final InterModProcessEvent event)
{
// some example code to receive and process InterModComms from other mods
}
@SubscribeEvent
public void onServerStarting(FMLServerStartingEvent event) {
LOGGER.info("server starting");
}
}
ゲームを起動して新たにワールドを生成します。
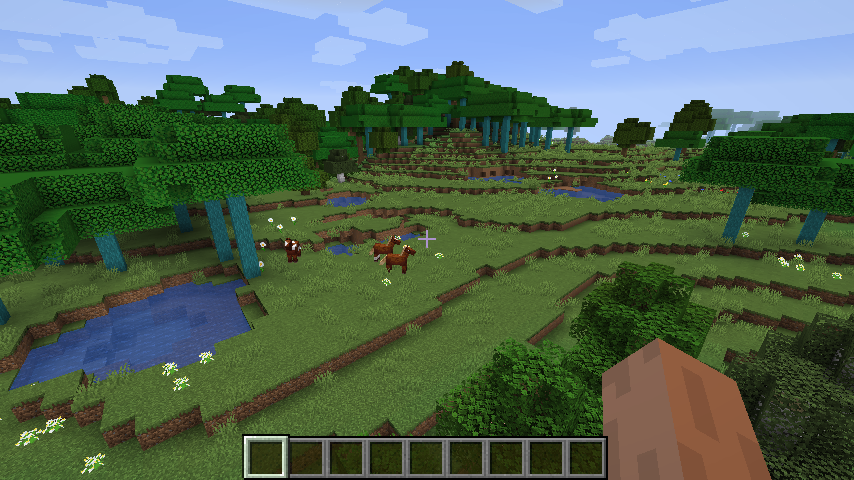
木が生成されている様子(PlacementやConfigを変化させた場合)
参考
[Java]MinecraftのModを作成しよう 1.14.4【9. 木の追加と生成】 - Qiita
BluePower/BPWorldGen.java at master · Qmunity/BluePower · GitHub
1.14.3 Tags help - Modder Support - Forge Forums
バイオーム - Minecraft Wiki
ルートテーブル - Minecraft Wiki
[SOLVED] [1.15.2] A texture issue with cross models? - Modder Support - Forge Forums
Forge 1.16.1 32.0.108 での実装記録
Forgeのバージョンアップ前で取り敢えず動くレベルにまで実装した例を参考までに記録しておきます。
折り畳み
\src\main\java\jp\koteko\liveinwater\
├ block
├ item
├ world
│ └ gen
│ ├ feature
│ │ └ WaterTreeFeature.java
│ └ TreeGenerator.java
└ LiveInWater.java
package jp.koteko.liveinwater.world.gen.feature;
import com.mojang.serialization.Codec;
import net.minecraft.world.gen.feature.BaseTreeFeatureConfig;
import net.minecraft.world.gen.feature.TreeFeature;
public class WaterTreeFeature extends TreeFeature {
public WaterTreeFeature(Codec<BaseTreeFeatureConfig> codec) {
super(codec);
}
}
実際まだ親クラスと何ら変わらないのでこれは今の時点では無意味です。1.14の頃と異なり、Codecというインターフェースが導入されているようです。なんとなく眺めてみた感じでは、色んなクラスのオブジェクトを汎用的に扱うためのもののようです。
package jp.koteko.liveinwater.world.gen;
import com.google.common.collect.ImmutableList;
import jp.koteko.liveinwater.world.gen.feature.WaterTreeFeature;
import net.minecraft.block.Blocks;
import net.minecraft.world.biome.Biome;
import net.minecraft.world.gen.GenerationStage;
import net.minecraft.world.gen.blockstateprovider.SimpleBlockStateProvider;
import net.minecraft.world.gen.feature.BaseTreeFeatureConfig;
import net.minecraft.world.gen.feature.ConfiguredFeature;
import net.minecraft.world.gen.feature.TwoLayerFeature;
import net.minecraft.world.gen.foliageplacer.BlobFoliagePlacer;
import net.minecraft.world.gen.placement.AtSurfaceWithExtraConfig;
import net.minecraft.world.gen.placement.Placement;
import net.minecraft.world.gen.treedecorator.BeehiveTreeDecorator;
import net.minecraft.world.gen.trunkplacer.StraightTrunkPlacer;
import net.minecraftforge.registries.ForgeRegistries;
import java.util.OptionalInt;
public class TreeGenerator {
public static void setup() {
addTreeToOverworld(
new WaterTreeFeature(BaseTreeFeatureConfig.field_236676_a_)
.withConfiguration(
(new BaseTreeFeatureConfig.Builder(
new SimpleBlockStateProvider(Blocks.ACACIA_WOOD.getDefaultState()),
new SimpleBlockStateProvider(Blocks.BLUE_WOOL.getDefaultState()),
new BlobFoliagePlacer(2, 0, 0, 0, 3),
new StraightTrunkPlacer(5, 2, 0),
new TwoLayerFeature(0, 0, 0, OptionalInt.of(4)))
).func_236700_a_().func_236703_a_(ImmutableList.of(new BeehiveTreeDecorator(0.002F))).build())
.withPlacement(Placement.COUNT_EXTRA_HEIGHTMAP.configure(new AtSurfaceWithExtraConfig(10, 0.1F, 1)))
);
}
private static void addTreeToOverworld(ConfiguredFeature<?, ?> featureIn) {
for(Biome biome : ForgeRegistries.BIOMES) {
if (!biome.getCategory().equals(Biome.Category.NETHER) && !biome.getCategory().equals(Biome.Category.THEEND)) {
biome.addFeature(GenerationStage.Decoration.VEGETAL_DECORATION, featureIn);
}
}
}
}
基本的に1.14の時と同じでBiome#addFeatureによって生成したいバイオームに木のFeatureを追加することで生成させます。名前が分かりづらい状態のものが多く、またFeatureやConfiguredFeatureの扱いが変わったらしく、Biome#createDecoratedFeatureも見当たらなくなっていました。バニラのコードを観察して書いたのが上記のコードです。
ConfiguredFeature(new WaterTreeFeature())に対して、withConfiguration()とwithPlacement()でコンフィグ(この場合では木の構成ブロックや形状)とプレースメント(自然生成時の抽選される場所)を設定します。
コンフィグはビルダーが用意されていたので、これを用います。順に、幹となるブロック(のプロバイダ)、葉となるブロック(のプロバイダ)、葉の配置形状、幹の配置形状、最小サイズのタイプ(詳細不明)です。プロバイダは特別なことをしない限りSimpleBlockStateProviderクラスのインスタンスを渡せばよいでしょう。ブロックの種類だけ適宜変更します。葉と幹の配置形状については、バニラでもいくつかの種類が用いられているので適したものを用います。FoliagePlacer,AbstractTrunkPlacerのサブクラスを観察しましょう。引数で高さ等を指定します。ビルダー第5引数についてはminimum_sizeという名前で管理されるAbstractFeatureSizeTypeクラスのオブジェクトのようですが、どのようにはたらくか不明だったため、他のコードに合わせておきます。ビルダーに対してbuild()を呼ぶことでコンフィグのインスタンスを返します。func_236700_a_()はツタの生成をしない指定、func_236703_a_()はこのように引数を渡すことでハチの巣を生成するよう指定しています。
プレースメントは適当な種類(Placementクラスを参照)を選択し、configure()で設定します。