久しぶり?にニッチ向け記事。
導入
OpenAI社やGoogle社などの高性能なプロプライエタリLLMが注目を集める一方で、オープンソースのLLMも目覚ましい進化を遂げてきていると感じています。
特に、AIエージェントの普及が加速する中で、外部APIの利用コストが将来的に上昇する可能性を考えると、自社や個人でコントロールできるローカルLLMの重要性はますます高まっていくのではないでしょうか。
というわけで、最近はあまり記事にしていなかったのですが、改めてオープンウェイトで公開されているLLMをセルフホストする知見を高めたいと思い、今回はExLlamaV3という推論エンジンを用いて、LLMエンドポイントをDatabricks Model Serving上でサーブし、LangChainを通じて利用してみます。
実装はDatabricks on AWS上で行いました。
ノートブックにはGPUクラスタ(A10G)を利用しています。DBRは17.1MLです。
今回やること
ExLlamaV3を推論エンジンとしたLLM APIエンドポイントをDatabricks上でサーブします。
エンドポイントは以下の機能を持たせます。
- EXL3量子化フォーマットのモデルサーブ(今回はEXL3変換済みのQwen 4Bを利用します)
- Responses API対応(部分的)
- 構造化出力対応
- Tool Calling対応
- ストリーミング出力対応
- Reasoning Model対応(今回は使いませんが)
ExLlamaV3とは
リポジトリはこちら。
ExLlamaV3は、最新のコンシューマーGPUでローカルLLMを実行するための推論ライブラリです。主な特徴は以下の通りです。
- QTIPに基づく新しい EXL3 量子化フォーマット
- コンシューマーハードウェア設定向けの柔軟なテンソル並列およびエキスパート並列推論
- TabbyAPI を介して提供されるOpenAI互換サーバー
- Continuous/Dynamicバッチ処理
- Hugging Face Transformersプラグイン
- Hugging Faceモデルのサポート
- 投機的デコーディングの対応
- 2〜8ビットキャッシュ量子化
- マルチモーダルサポート
ExLlamaV3の公式かつ推奨されるバックエンドサーバーはTabbyAPIです。これは、ローカルまたはリモート推論のためのOpenAI互換APIを提供し、Hugging Faceモデルのダウンロード、埋め込みモデルのサポート、Hugging Face Jinja2チャットテンプレートのサポートなどの拡張機能も備えています。
ありていに言えばTransformersやLlama.cppのようなオープンウェイトのLLMを用いた推論エンジンの一種です。QTIPという量子化技術に基づいたフォーマットEXL3形式をサポートしており、従来の量子化と比べて低ビットレートでも精度を維持しやすいのが特徴です。
(ik_llama.cppというLlama.cppのフォークも同種の量子化をサポートしているらしいですが、未検証)
この分野のデファクトはvLLMであったりLlama.cpp/Ollamaが有名ですが、個人的にExLlamaも割と使いやすいと思っています。(ミドルレベルまで挙動をコントロールできるので)
実際のところ、vLLMなどのオンラインサーバを使えばもっと簡単に実装できるのですが、なるべくVRAM消費を抑えて(コストを抑えて)サーブする実験をしたかったので、今回はExLlamaV3を採用しています。
ExLlamaV3は比較的新しいパッケージであり、まだ十分に習熟しているとは言い難いと思います。
また、大規模な開発体制があるわけでもないため、本番利用を検討する際は注意ください。
サーブする
準備
まずはDatabricks上にノートブックを作成し、必要なパッケージをインストールします。
ポイントはFlash AttentionとExLlamaV3のビルド済みパッケージをインストールすることです。
%pip install -U tokenizers>=0.22.0 transformers==4.56.1 mlflow>=3.3.2 databricks-agents
# flash attension
%pip install https://github.com/Dao-AILab/flash-attention/releases/download/v2.8.3/flash_attn-2.8.3+cu12torch2.7cxx11abiTRUE-cp312-cp312-linux_x86_64.whl
# exllamav3
%pip install https://github.com/turboderp-org/exllamav3/releases/download/v0.0.6/exllamav3-0.0.6+cu128.torch2.7.0-cp312-cp312-linux_x86_64.whl
%restart_python
MLflow カスタムResponsesAgentの定義
Databricks Model ServingにサーブするモデルをMLflow ResponsesAgentとして定義します。
かなり長いので折り畳み。
exllamav3_agent.py
%%writefile exllamav3_agent.py
from typing import Any, Callable, Generator, Optional
import os
import json
import uuid
import argparse
import torch
import gc
import re
import pydantic
import mlflow
from mlflow.pyfunc import ResponsesAgent
from mlflow.types.responses import (
ResponsesAgentRequest,
ResponsesAgentResponse,
ResponsesAgentStreamEvent,
)
from mlflow.types.responses_helpers import Tool, ReasoningParams
from mlflow.exceptions import MlflowException
import exllamav3
from exllamav3 import model_init, ComboSampler, Job, FormatronFilter
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
from formatron.schemas import json_schema
from formatron.integrations.transformers import create_formatter_logits_processor_list
from formatron.formatter import FormatterBuilder
# 定数
TOOL_CALL_SCHEMA = {
"$id": "https://example.com/function_calling.json",
"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/draft-07/schema#",
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"function": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"name": {"type": "string"},
"arguments": {"type": "object"},
},
"required": ["name", "arguments"],
},
},
"required": ["function"],
},
}
DEFAULT_TEMPERATURE = 0.0
DEFAULT_TOP_P = 0.95
DEFAULT_MAX_OUTPUT_TOKENS = 4000
def convert_to_chat_completion_format(message: dict[str, Any]) -> list[dict[str, Any]]:
"""ResponsesAgentの出力をChatCompletions互換のメッセージリストに変換します。
Args:
message (dict[str, Any]): メッセージの辞書。
Returns:
list[dict[str, Any]]: 変換されたメッセージのリスト。
"""
msg_type = message.get("type", None)
if msg_type == "function_call":
return [
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": None,
"tool_calls": [
{
"id": message["call_id"],
"type": "function",
"function": {
"arguments": message["arguments"],
"name": message["name"],
},
}
],
}
]
if msg_type == "message" and isinstance(message["content"], list):
return [
{"role": message["role"], "content": content["text"]}
for content in message["content"]
]
if msg_type == "function_call_output":
return [
{
"role": "tool",
"content": message["output"],
"tool_call_id": message["call_id"],
}
]
# Generic message handling
compatible_keys = ["role", "content", "name", "tool_calls", "tool_call_id"]
if not message.get("content") and message.get("tool_calls"):
message["content"] = "tool call"
filtered = {k: v for k, v in message.items() if k in compatible_keys}
return [filtered] if filtered else []
class ModelTagConfig(pydantic.BaseModel):
tool_start_tag: str = "<tool_call>"
reasoning_start_tag: str = "<think>"
reasoning_end_tag: str = "</think>"
eos_tags: list[str] = []
class ModelLoader:
"""モデルの読み込みを担当するクラス"""
@staticmethod
def load_model(model_path: str) -> tuple[exllamav3.Generator, AutoTokenizer]:
"""指定されたパスからモデルを読み込みます。
Args:
model_path (str): モデルのパス。
Returns:
tuple[exllamav3.Generator, AutoTokenizer]: 読み込まれたモデルとトークナイザー。
"""
# GPUキャッシュクリア
gc.collect()
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
# 環境変数からの初期化引数作成
tp = ["-tp"] if os.environ.get("EXLLAMAV3_TP") == "1" else []
cache_size = os.environ.get("EXLLAMAV3_CACHE_SIZE", [])
if cache_size:
cache_size = ["--cache_size", cache_size]
cache_quant = os.environ.get("EXLLAMAV3_CACHE_QUANT", [])
if cache_quant:
cache_quant = ["--cache_quant", cache_quant]
# モデル初期化
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
model_init.add_args(parser, cache=True)
args = parser.parse_args(
args=["-m", model_path, "--verbose"] + tp + cache_size + cache_quant
)
# モデル読み込み
model, config, cache, tokenizer = model_init.init(args)
generator = exllamav3.Generator(model=model, cache=cache, tokenizer=tokenizer)
hf_tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(args.model_dir)
return generator, hf_tokenizer
class FilterBuilder:
"""フィルターの作成を担当するクラス"""
@staticmethod
def _parse_text_schema(text: Any) -> Optional[dict]:
"""テキストスキーマをパースします。
Args:
text (Any): テキストまたはスキーマ。
Returns:
Optional[dict]: パースされたスキーマ。
"""
if not text:
return None
if isinstance(text, str):
try:
return json.loads(text)
except Exception as e:
raise MlflowException.invalid_parameter_value(
f"Invalid JSON in text parameter: {e}"
)
elif isinstance(text, dict):
return text
else:
raise MlflowException.invalid_parameter_value(
"Text parameter must be string or dict"
)
@staticmethod
def create_structured_output_filters(text: Any, tokenizer) -> list:
"""構造化出力用のフィルターを作成します。
Args:
text (Any): テキストまたはスキーマ。
tokenizer: トークナイザー。
Returns:
list: 作成されたフィルターのリスト。
"""
text_schema = FilterBuilder._parse_text_schema(text)
if not text_schema:
return None
format_info = text_schema.get("format")
if not format_info or format_info.get("type") != "json_schema":
raise MlflowException.invalid_parameter_value(
"Invalid text format: expected json_schema type"
)
schema = format_info.get("schema")
if not schema:
raise MlflowException.invalid_parameter_value(
"Missing schema in text format"
)
# スキーマ準備
template = {
"$id": "https://example.com/person.json",
"$schema": "https://json-schema.org/draft/2020-12/schema",
}
schema = json_schema.create_schema(template | schema)
# フィルター作成
f = FormatterBuilder()
f.append_line(f"{f.json(schema, capture_name='json')}")
filters = [
FormatronFilter(tokenizer, eos_after_completed=True, formatter_builder=f)
]
# 先頭の{を強制
f = FormatterBuilder()
f.append_line("{")
filters.append(FormatronFilter(tokenizer, formatter_builder=f))
return filters
@staticmethod
def create_tool_call_filters(tokenizer) -> list:
"""ツール呼び出し用のフィルターを作成します。
Args:
tokenizer: トークナイザー。
Returns:
list: 作成されたフィルターのリスト。
"""
schema = json_schema.create_schema(TOOL_CALL_SCHEMA)
f = FormatterBuilder()
f.append_line(f"{f.json(schema, capture_name='json')}")
filters = [
FormatronFilter(tokenizer, eos_after_completed=True, formatter_builder=f)
]
# 先頭の[{を強制
f = FormatterBuilder()
f.append_line("[{")
filters.append(FormatronFilter(tokenizer, formatter_builder=f))
return filters
class ExLlamaV3Agent(ResponsesAgent):
"""メインのエージェントクラス"""
def __init__(
self,
generator: exllamav3.Generator = None,
hf_tokenizer: AutoTokenizer = None,
model_tag_config: ModelTagConfig = ModelTagConfig(),
auto_unload: bool = True,
):
"""エージェントを初期化します。
Args:
generator (exllamav3.Generator, optional): モデルのジェネレーター。
hf_tokenizer (AutoTokenizer, optional): トークナイザー。
model_tag_config (ModelTagConfig, optional): ツール呼び出しの設定。
auto_unload (bool): インスタンス破棄時にモデルをアンロードするかどうか。
"""
self.generator = generator
self.hf_tokenizer = hf_tokenizer
self.model_tag_config = model_tag_config
self.auto_unload = auto_unload
def __del__(self):
if self.auto_unload and self.generator and self.generator.model:
self.generator.model.unload()
def load_context(self, context):
"""コンテキストからモデルを読み込みます。
Args:
context: モデルのコンテキスト。
"""
model_path = context.artifacts["model_path"]
self.generator, self.hf_tokenizer = ModelLoader.load_model(model_path)
model_tag_config = context.model_config.get("model_tag_config")
if model_tag_config:
self.model_tag_config = ModelTagConfig(**model_tag_config)
def prep_msgs_for_llm(self, messages: list[dict[str, Any]]) -> list[dict[str, Any]]:
"""LLM用にメッセージを前処理します。
Args:
messages (list[dict[str, Any]]): メッセージのリスト。
Returns:
list[dict[str, Any]]: 前処理されたメッセージのリスト。
"""
chat_msgs = []
for msg in messages:
chat_msgs.extend(convert_to_chat_completion_format(msg))
return chat_msgs
def _create_sampler_and_token_ids(
self, messages: list[dict[str, Any]], **kwargs
) -> tuple[ComboSampler, list, bool]:
"""サンプラーとトークンのIDリストを作成します。
Args:
messages (list[dict[str, Any]]): メッセージのリスト。
**kwargs: その他の引数。
Returns:
tuple[ComboSampler, list, bool]: サンプラーとトークンIDのリスト、Reasoningモードかどうかの判定
"""
temperature = kwargs.get("temperature") or DEFAULT_TEMPERATURE
top_p = kwargs.get("top_p") or DEFAULT_TOP_P
tools = kwargs.get("tools")
sampler = ComboSampler(temperature=temperature, top_p=top_p)
formatted_messages = self.hf_tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True,
add_bos=True,
tools=tools,
)
# Reasoning Modeかどうかの判定
is_reasoning = False
if (
self.model_tag_config.reasoning_start_tag
and self.model_tag_config.reasoning_end_tag
):
is_reasoning = formatted_messages.rstrip().endswith(
self.model_tag_config.reasoning_start_tag
)
ids = self.generator.tokenizer.encode(
formatted_messages, add_bos=False, encode_special_tokens=True
)
return sampler, ids, is_reasoning
def _is_tool_call_triggered(self, result: dict) -> bool:
"""ツール呼び出しがトリガーされたかをチェックします。
Args:
result (dict): 結果の辞書。
Returns:
bool: ツール呼び出しがトリガーされたかどうか。
"""
return (
result["eos_reason"] == "stop_string"
and result["eos_triggering_string"] == self.model_tag_config.tool_start_tag
)
def _parse_reasoning_message(self, text_output: str) -> tuple[str, str]:
"""Reasoningモードのメッセージをパースします。"""
if (
not self.model_tag_config.reasoning_start_tag
or not self.model_tag_config.reasoning_end_tag
):
return "", text_output
# reasoning_start_tagとreasoning_end_tagで囲まれた部分とそうでない部分を分離
reasoning_start = self.model_tag_config.reasoning_start_tag
reasoning_end = self.model_tag_config.reasoning_end_tag
reasoning_parts = []
non_reasoning_parts = []
pattern = re.compile(
re.escape(reasoning_start) + r"(.*?)" + re.escape(reasoning_end),
re.DOTALL,
)
last_end = 0
for m in pattern.finditer(text_output):
# reasoningタグ外の部分
if m.start() > last_end:
non_reasoning_parts.append(text_output[last_end : m.start()])
# reasoningタグ内の部分
reasoning_parts.append(m.group(1))
last_end = m.end()
# reasoningタグの後ろに残った部分
if last_end < len(text_output):
non_reasoning_parts.append(text_output[last_end:])
return "".join(reasoning_parts).strip(), "".join(non_reasoning_parts).strip()
def create_reasoning_item(self, text: str, id: str) -> dict[str, Any]:
"""resoning itemスキーマに準拠した辞書を作成するヘルパーメソッド。
Args:
text (str): 出力するテキスト。
id (str): 出力アイテムのID。
"""
return {
"id": id,
"summary": [
{
"text": text,
"type": "summary_text",
}
],
"type": "reasoning",
}
@torch.inference_mode()
def call_llm(
self, id: str, messages: list[dict[str, Any]], **kwargs
) -> Generator[ResponsesAgentStreamEvent, None, None]:
"""LLMを呼び出してテキストを生成します。
Args:
id (str): メッセージID。
messages (list[dict[str, Any]]): メッセージのリスト。
**kwargs: その他の引数。
Yields:
Generator[ResponsesAgentStreamEvent, None, None]: ストリームイベント。
"""
max_output_tokens = kwargs.get("max_output_tokens") or DEFAULT_MAX_OUTPUT_TOKENS
text = kwargs.get("text")
# samplerとtoken idsの取得
sampler, ids, is_reasoning = self._create_sampler_and_token_ids(
messages, **kwargs
)
# 構造化出力のフィルター作成
filters = FilterBuilder.create_structured_output_filters(
text, self.generator.tokenizer
)
if filters:
is_reasoning = False # フィルターが有効な場合、Reasoningモードを無効にする
# ジョブ作成・実行
job = Job(
ids,
max_new_tokens=max_output_tokens,
stop_conditions=[
self.generator.tokenizer.eos_token_id,
self.model_tag_config.tool_start_tag,
]
+ self.model_tag_config.eos_tags,
sampler=sampler,
filters=filters,
)
self.generator.enqueue(job)
# 生成処理
text_output = ""
# Reasoningモードの開始処理
if is_reasoning:
text_output = self.model_tag_config.reasoning_start_tag
yield ResponsesAgentStreamEvent(
**self.create_text_delta(
delta=self.model_tag_config.reasoning_start_tag, item_id=id
)
)
while self.generator.num_remaining_jobs():
for r in self.generator.iterate():
chunk = r.get("text", "")
text_output += chunk
if r["eos"]:
# Reasoning Modeの場合、推論部と回答部を切り分けて返す
if is_reasoning:
reasoning_text, non_reasoning_text = (
self._parse_reasoning_message(text_output)
)
yield ResponsesAgentStreamEvent(
type="response.output_item.done",
item=self.create_reasoning_item(reasoning_text, id=id),
)
yield ResponsesAgentStreamEvent(
type="response.output_item.done",
item=self.create_text_output_item(
text=non_reasoning_text, id=id
),
)
# ツール呼び出し(Reasoningの内容を反映)
if self._is_tool_call_triggered(r):
yield from self.generate_tool_call_response(
id,
messages
+ [
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": reasoning_text,
}
],
**kwargs,
)
else:
# 非Reasoning Modeの場合
yield ResponsesAgentStreamEvent(
type="response.output_item.done",
item=self.create_text_output_item(text=text_output, id=id),
)
# ツール呼び出し
if self._is_tool_call_triggered(r):
yield from self.generate_tool_call_response(
id, messages, **kwargs
)
else:
yield ResponsesAgentStreamEvent(
**self.create_text_delta(delta=chunk, item_id=id),
)
@torch.inference_mode()
def generate_tool_call_response(
self, id: str, messages: list[dict[str, Any]], **kwargs
) -> Generator[ResponsesAgentStreamEvent, None, None]:
"""ツール呼び出しを生成します。
Args:
id (str): メッセージID。
messages (list[dict[str, Any]]): メッセージのリスト。
**kwargs: その他の引数。
Yields:
Generator[ResponsesAgentStreamEvent, None, None]: ストリームイベント。
"""
max_output_tokens = kwargs.get("max_output_tokens", DEFAULT_MAX_OUTPUT_TOKENS)
sampler, ids, _ = self._create_sampler_and_token_ids(messages, **kwargs)
filters = FilterBuilder.create_tool_call_filters(self.generator.tokenizer)
# ジョブ作成・実行
job = Job(
ids,
max_new_tokens=max_output_tokens,
stop_conditions=[self.generator.tokenizer.eos_token_id]
+ self.model_tag_config.eos_tags,
sampler=sampler,
filters=filters,
)
self.generator.enqueue(job)
# ツール呼び出し生成処理
text = ""
while self.generator.num_remaining_jobs():
for r in self.generator.iterate():
chunk = r.get("text", "")
text += chunk
if r["eos"]:
try:
tool_calls = json.loads(text)
for tool_call in tool_calls:
call_id = f"call-{uuid.uuid4()}"
yield ResponsesAgentStreamEvent(
type="response.output_item.done",
item=self.create_function_call_item(
id=id,
call_id=call_id,
name=tool_call["function"]["name"],
arguments=json.dumps(
tool_call["function"]["arguments"]
),
),
)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error processing tool call: {e}")
raise e
def predict(self, request: ResponsesAgentRequest) -> ResponsesAgentResponse:
"""予測を実行します。
Args:
request (ResponsesAgentRequest): リクエストオブジェクト。
Returns:
ResponsesAgentResponse: 予測結果のレスポンス。
"""
outputs = [
event.item
for event in self.predict_stream(request)
if event.type == "response.output_item.done"
]
return ResponsesAgentResponse(output=outputs, **request.model_dump())
def predict_stream(
self, request: ResponsesAgentRequest
) -> Generator[ResponsesAgentStreamEvent, None, None]:
"""ストリーミング予測を実行します。
Args:
request (ResponsesAgentRequest): リクエストオブジェクト。
Yields:
Generator[ResponsesAgentStreamEvent, None, None]: ストリームイベント。
"""
self.generator.clear_queue()
id = f"msg-{uuid.uuid4()}"
messages = self.prep_msgs_for_llm([i.model_dump() for i in request.input])
yield from self.call_llm(id, messages, **request.model_dump())
AGENT = ExLlamaV3Agent()
mlflow.models.set_model(AGENT)
モデルのロギング
今回はHuggingfaceで公開されている以下のモデルを利用します。
(量子化前のオリジナルはQwen3-4B-Instruct-2507です)
一度セッションをリスタート。
%restart_python
通常はMLflowにモデルをロギングする処理に進むのですが、MLflow 3.3.2ではまだResponsesAgentそのままだとTool Callingに対応した入力スキーマが設定されていません。
そのため、入力スキーマを修正する処理を入れます。
from mlflow.types.responses import ResponsesAgentRequest
from mlflow.types.type_hints import _infer_schema_from_type_hint
from mlflow.types.schema import Schema
from mlflow.types.chat import BaseModel
import json
from typing import Any
from pprint import pprint
import mlflow.types.responses
# Toolのスキーマを修正する
class Tool(BaseModel):
name: str
parameters: dict[str, Any]
strict: bool | None = None
type: str = "function"
description: str | None = None
tool_prop = _infer_schema_from_type_hint(Tool).to_dict()[0]["properties"]
properties = _infer_schema_from_type_hint(ResponsesAgentRequest).to_dict()[0][
"properties"
]
formatted_properties = [{**prop, "name": name} for name, prop in properties.items()]
for e in formatted_properties:
if e.get("name") == "tools":
e["items"]["properties"].update(tool_prop)
# パッチあて
mlflow.types.responses.RESPONSES_AGENT_INPUT_SCHEMA = Schema.from_json(
json.dumps(formatted_properties)
)
from mlflow.types.responses import RESPONSES_AGENT_INPUT_SCHEMA
RESPONSES_AGENT_INPUT_SCHEMA
['context': {conversation_id: string (optional), user_id: string (optional)} (optional), 'custom_inputs': Map(str -> Any) (optional), 'input': Array(Any) (required), 'max_output_tokens': long (optional), 'metadata': Map(str -> DataType.string) (optional), 'parallel_tool_calls': boolean (optional), 'reasoning': {effort: string (optional), generate_summary: string (optional)} (optional), 'store': boolean (optional), 'stream': boolean (optional), 'temperature': double (optional), 'text': Any (optional), 'tool_choice': Any (optional), 'tools': Array({description: string (optional), name: string (required), parameters: Map(str -> Any) (required), strict: boolean (optional), type: string (required)}) (optional), 'top_p': double (optional), 'truncation': string (optional), 'user': string (optional)]
最後にモデルをロギングします。
import mlflow
import os
mlflow.set_registry_uri("databricks-uc")
model_path = "<huggingfaceからダウンロードしたEXL3フォーマットモデルのパス>"
extra_pip_requirements = [
"torch==2.7.0 --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu124",
"tokenizers>=0.22.0",
"transformers==4.56.1",
# flash attension
"https://github.com/Dao-AILab/flash-attention/releases/download/v2.8.3/flash_attn-2.8.3+cu12torch2.7cxx11abiTRUE-cp312-cp312-linux_x86_64.whl",
# exllamav3
"https://github.com/turboderp-org/exllamav3/releases/download/v0.0.6/exllamav3-0.0.6+cu128.torch2.7.0-cp312-cp312-linux_x86_64.whl",
]
pip_requirements = mlflow.pyfunc.get_default_pip_requirements() + extra_pip_requirements
artifacts = {
"model_path": model_path,
}
model_config = {
"model_tag_config": {
"tool_start_tag": "<tool_call>",
"reasoning_start_tag": "<think>",
"reasoning_end_tag": "</think>"
}
}
input_example = {
"input": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "9.9と9.11、どちらの数字が大きい?",
}
],
}
with mlflow.start_run() as run:
logged_model = mlflow.pyfunc.log_model(
name="exllamav3_model",
python_model="exllamav3_agent.py",
artifacts=artifacts,
model_config=model_config,
input_example=input_example,
pip_requirements=pip_requirements,
await_registration_for=3000,
)
モデルのサーブ
Databricks Model Servingを使ってAPIエンドポイントをサーブします。
まずは先ほどロギングしたモデルをUnity Catalogに登録します。
mlflow.set_registry_uri("databricks-uc")
registered_model_name = "<UnityCatalogのパス(catalog.schema.model_name)>"
# register the model to UC
uc_registered_model_info = mlflow.register_model(
model_uri=logged_model.model_uri,
name=registered_model_name,
await_registration_for=3000,
)
エンドポイントを作成します。
少しトリッキーですが、まずdatabricks.agentsパッケージを用いてエージェントとしてデプロイします。
from databricks import agents
endpoint_name = "llm_qwen3_4b_inst_exl3"
result = agents.deploy(
model_name=registered_model_name,
model_version="1",
scale_to_zero=True,
endpoint_name=endpoint_name,
)
print(result)
処理実行後、「サービング」メニューに移動し、該当のエンドポイントの更新をキャンセルします。
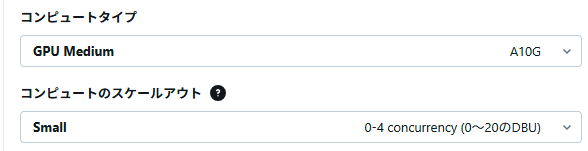
その後、編集からコンピュートタイプをGPU Mediumに変更します。(ExLlamaV3はCPU推論ができないため)
変更後、デプロイ処理が再開され、正常に処理が進めば数十分ほどでデプロイされます。
使ってみる
エンドポイントのデプロイが完了したら、LangChainを使って動作試験してみます。
別のノットブックを作成し、LangChain等のパッケージをインストール。
(α版ですが、langchain 1.0をインストールしました)
%pip install --pre -U langchain langchain_openai mlflow openai
%restart_python
ChatOpenAIクラスを利用してエンドポイントに接続するクライアントを作成します。
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
import mlflow
mlflow.langchain.autolog()
creds = mlflow.utils.databricks_utils.get_databricks_host_creds()
llm = ChatOpenAI(
model="llm_qwen3_4b_inst_exl3",
api_key=creds.token,
base_url=creds.host + "/serving-endpoints",
use_responses_api=True,
max_tokens=2000,
temperature=0.0,
)
単純な実行
llm.invoke("Hello")
AIMessage(content=[{'type': 'text', 'text': 'Hello! How can I assist you today? 😊', 'annotations': [], 'id': 'msg-e9a5e2c3-1b96-4580-b200-4d6a60e62cd7'}], additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={'id': '342cc860-54d2-4228-85af-dc2586c81297', 'object': 'response', 'model_provider': 'openai', 'model_name': None}, id='342cc860-54d2-4228-85af-dc2586c81297')
まずは実行できました。
構造化出力&Tool Calling
構造化出力を試します。
まずはTool Callingを使った構造化出力です。
適当な構造定義をPydanticで作成します。
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
class ResponseFormatter(BaseModel):
"""Always use this tool to structure your response to the user."""
answer: str = Field(description="The answer to the user's question")
followup_question: str = Field(description="A followup question the user could ask")
定義した構造を使ってクエリを実行。
model_with_tools = llm.bind_tools([ResponseFormatter])
result = model_with_tools.invoke("日本で一番高い山は?")
result.tool_calls[0]["args"]
{'answer': '日本で一番高い山は富士山です。標高は3,776メートルです。',
'followup_question': '富士山の地形や歴史について知りたいですか?'}
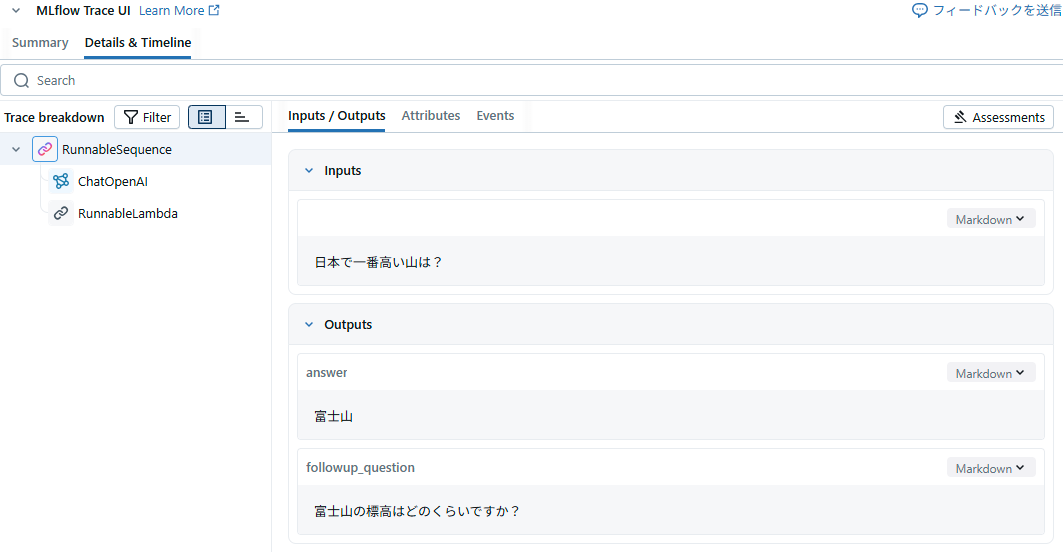
構造化されたデータで取得できました。
次はToolCallingではなく、直接の構造化出力も試します。
model_with_structure = llm.with_structured_output(ResponseFormatter)
model_with_structure.invoke("日本で一番高い山は?")
ResponseFormatter(answer='富士山', followup_question='富士山の標高はどのくらいですか?')
問題なく出力できました。
また、MLflow Tracingとしても記録されます。
エージェントでの利用
エージェントからもLLMのエンドポイントとして利用してみます。
from langchain.agents import create_agent
from pprint import pprint
def get_weather(city: str) -> str:
"""指定した都市の天気を取得します。"""
return f"It's always sunny in {city}!"
# エージェントの作成
agent = create_agent(
model=llm,
tools=[get_weather],
prompt="You are a helpful assistant",
)
response = agent.invoke(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "東京の天気を教えて"}]}
)
pprint(response)
{'messages': [HumanMessage(content='東京の天気を教えて', additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={}, id='87329a72-e4ae-47f7-8ece-6662438e293b'),
AIMessage(content=[{'type': 'text', 'text': '', 'annotations': [], 'id': 'msg-ae5b0cdb-7bef-43f2-9ff3-70aad37eb2f3'}, {'arguments': '{"city": "\\u6771\\u4eac"}', 'call_id': 'call-1fa0bc45-a377-4d26-be7d-d83311696f01', 'name': 'get_weather', 'type': 'function_call', 'id': 'msg-ae5b0cdb-7bef-43f2-9ff3-70aad37eb2f3'}], additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={'id': '45b4428a-3f05-4a69-abad-350ff24c8a7b', 'object': 'response', 'model_provider': 'openai', 'model_name': None}, id='45b4428a-3f05-4a69-abad-350ff24c8a7b', tool_calls=[{'name': 'get_weather', 'args': {'city': '東京'}, 'id': 'call-1fa0bc45-a377-4d26-be7d-d83311696f01', 'type': 'tool_call'}]),
ToolMessage(content="It's always sunny in 東京!", name='get_weather', id='ed1b01d7-f6d3-40cf-960f-7cfcd8e85b31', tool_call_id='call-1fa0bc45-a377-4d26-be7d-d83311696f01'),
AIMessage(content=[{'type': 'text', 'text': '東京はいつも晴れています!', 'annotations': [], 'id': 'msg-2ed5c9b9-5842-4826-af03-5e1b3a80c656'}], additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={'id': '8fb63ce3-c3f7-49ea-b1f9-66e4b6a82758', 'object': 'response', 'model_provider': 'openai', 'model_name': None}, id='8fb63ce3-c3f7-49ea-b1f9-66e4b6a82758')]}
問題なく実行できました。
その他
もちろんLangChainを使わずにOpenAIのクライアントをそのまま利用することもできます。
from openai import OpenAI
import mlflow
mlflow.openai.autolog()
creds = mlflow.utils.databricks_utils.get_databricks_host_creds()
client = OpenAI(api_key=creds.token, base_url=creds.host + "/serving-endpoints")
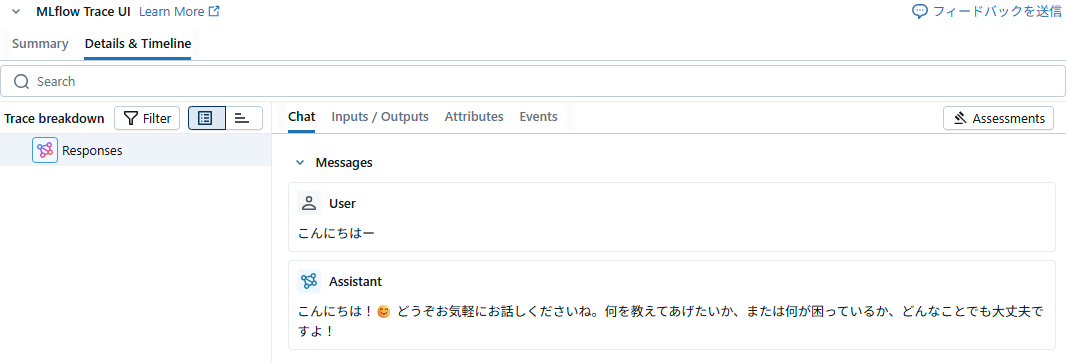
response = client.responses.create(
model="llm_qwen3_4b_inst_exl3",
input=[
{"role": "user", "content": "こんにちはー"}
],
)
print(response.output_text)
おわりに
ExLlamaV3を推論エンジンとしたLLMエンドポイントをDatabricks Model Serving上でデプロイしました。
不完全ではありますが、主要なResponses APIのインターフェースを備えさせています。
ちなみに、現状Qwenモデルでしかまともにテストしていませんので、他のモデルだと動かない可能性があります。試す際はご注意を。
エージェントはトークンを大量に消費するので、単純なものであればこういったエンドポイントを利用することでコストを圧縮できる可能性があります。
(現状はプロプライエタリなAPIやDatabricksの基盤モデルを利用したほうがトータルコストは優位だと思いますが)
オープンウェイトモデルの活用は様々な可能性を秘めているなと改めて感じました。
しかし、久しぶりにオープンウェイトモデルを触ったのですが、ResponsesAPIの仕様含めていい勉強になりました。
この分野もかなり面白いですね。