はじめに
Databricks AppsはDatabricksプラットフォーム上でデータアプリケーションやAIアプリケーションを構築できる仕組です。
対応しているフレームワークにはPythonだとStreamlitやGradioがあるのですが、 「そういやChainlitはApps上で使えるんだっけ?」 と疑問に思ったので試してみました。
今回の検証はDatabricks Free Edition上で行っています。サクッとした検証にはとても便利です。
Chainlitとは
チャット形式のアプリケーションをPythonで容易に作成できるフレームワークです。
Streamlit等と比べてチャットアプリに特化しています。
*2025年5月からコミュニティ管理に切り替わったのですね。しばらく利用していなかったので知りませんでした。。。
結論:使えるの?
動きました。
Databricks公式でのサポートが謡われているわけではありませんので、ご注意ください。
動作確認してみる
Databricks Free EditionからDatabricks Apps上でアプリを作成します。
テンプレートを使わずにカスタムアプリを作成します。
今回アプリ名は「chainlit-chatbot」にしました。(名前は任意です)
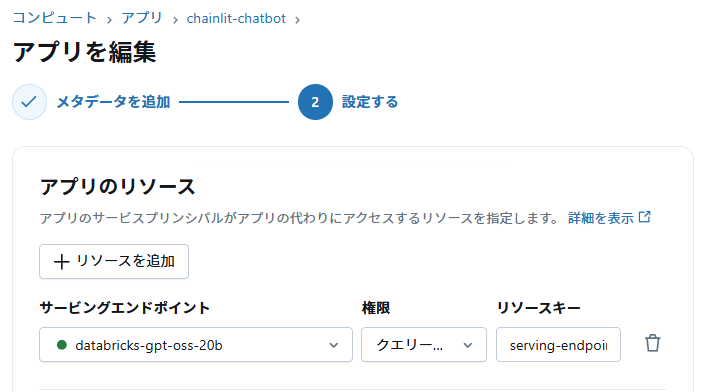
チャット用に、アプリのリソースとしてサービングエンドポイントを設定します。
今回は「databricks-gpt-oss-20b」をチャット用のLLMとして利用することにしました。
次にデプロイに必要なファイルを準備します。
まずrequirements.txt。Chainlitなどの依存関係を設定しておきます。
databricks-sdkはopenaiクライアントを利用可能なように最新化します。
mlflow>=3.4.0
python-dotenv==1.1.1
chainlit==2.8.2
databricks-sdk[openai]==0.67.0
次にapp.yaml。
ここでchainlitの起動コマンドを設定します。
command: [
"chainlit",
"run",
"app.py",
]
env:
- name: "SERVING_ENDPOINT"
valueFrom: "serving-endpoint"
念のため、.envファイル。
開発時に利用します。
SERVING_ENDPOINT="databricks-gpt-oss-20b"
最後に処理を記述したPythonファイルであるapp.pyを用意します。
今回はOpenAIクライアントを使ってDatabricksのサービングエンドポイントを利用する単純なチャットアプリを作成しました。
import chainlit as cl
import os
from databricks.sdk import WorkspaceClient
from dotenv import load_dotenv
# サービングエンドポイント設定の取得
serving_endpoint = os.getenv("SERVING_ENDPOINT")
if serving_endpoint is None:
load_dotenv(verbose=True)
serving_endpoint = os.getenv("SERVING_ENDPOINT")
assert serving_endpoint, (
"Unable to determine serving endpoint to use for chatbot app. If developing locally, "
"set the SERVING_ENDPOINT environment variable to the name of your serving endpoint. If "
"deploying to a Databricks app, include a serving endpoint resource named "
"'serving_endpoint' with CAN_QUERY permissions, as described in "
"https://docs.databricks.com/aws/en/generative-ai/agent-framework/chat-app#deploy-the-databricks-app"
)
@cl.on_chat_start
async def start():
cl.user_session.set("message_history", [])
@cl.on_message
async def main(message: cl.Message):
""" 応答作成 """
w = WorkspaceClient()
client = w.serving_endpoints.get_open_ai_client()
message_history = cl.user_session.get("message_history")
input_message = {"role": "user", "content": message.content}
input_messages = (message_history + [input_message])[-5:] # 直近5個までの履歴を使用
ai_response = ""
# gpt-oss-20BはThinkingステップがあるので、その対応
async with cl.Step(name="Thinking...", type="reasoning") as thinking_step:
final_message = cl.Message(content="")
final_message.author = serving_endpoint
await final_message.send()
streaming_response = client.chat.completions.create(model=serving_endpoint, messages=input_messages, stream=True)
for chunk in streaming_response:
delta = chunk.choices[0].delta
if isinstance(delta.content, list):
dict_output = delta.content[0]
if "type" in dict_output and dict_output["type"] == "reasoning":
await thinking_step.stream_token(dict_output["summary"][0]["text"])
elif isinstance(delta.content, str) and delta.content:
await final_message.stream_token(delta.content)
ai_response += delta.content
await final_message.update()
if ai_response:
message_history.append(input_message)
message_history.append({"role":"assistant", "content":ai_response})
cl.user_session.set("message_history", message_history)
これらのファイルをDatabricksワークスペース上に用意し、Databricksアプリコンソール上でデプロイします。
これで環境構築が終わりました。
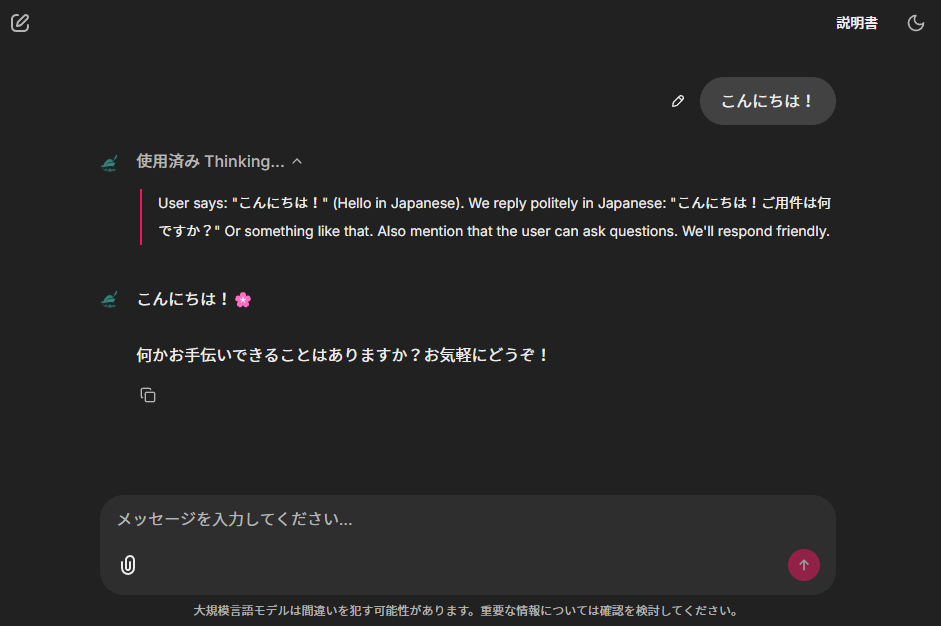
URLにアクセスするとちゃんと動作しているように見えます。
Chainlitはエージェントとのチャットも想定した機能を提供しているため、チャット形式に特化したアプリであればStreamlit等よりも高速にアプリ構築ができそうです。
終わりに
久しぶりにChainlitを触ってみたのですが、進化しており驚きました。
こういったフレームワークは数多く出ていますが、あまりカスタマイズ性を求めないシンプルなエージェントチャットであれば利用の選択肢にあがるのではないかと思います。
ドキュメントや以下のようなCookbookリポジトリも整理されていてわかりやすいですし。
またDatabricks Free Edition上で動くため、(アプリインスタンスの数に制限があるものの)初めてのチャットアプリ構築にはこのあたりから始めてもいいのではないかと思いました。
これでDeep Agentsのフロント作ってみるのも楽しそうだなあ。