この記事について
Neo4jを使ったグラフアルゴリズムの実装を紹介してみようという計画「グラフアルゴリズム入門 - javaとNeo4jで学ぶ -」の一部です(どこまで続くか・・・)
サンプルコードはこちらにおいた。
最短経路探索
幅優先・深さ優先探索は、頂点と辺のつながりの情報だけが与えられていたが、辺に移動コストの数値が定義されているときに、スタートするノードからゴールするノードまでの総コストが最小になるような経路と総コストを求める探索を最短経路探索と呼ぶ。最短経路探索には、有名なダイクストラのアルゴリズムがあり、ここではそれをNeo4jで実装してみる。コストはNeo4jのプロパティで表現することができる。プロパティグラフを容易に扱えるNeo4jにとって非常に役に立ち、わかりやすい例題である。
ダイクストラ法
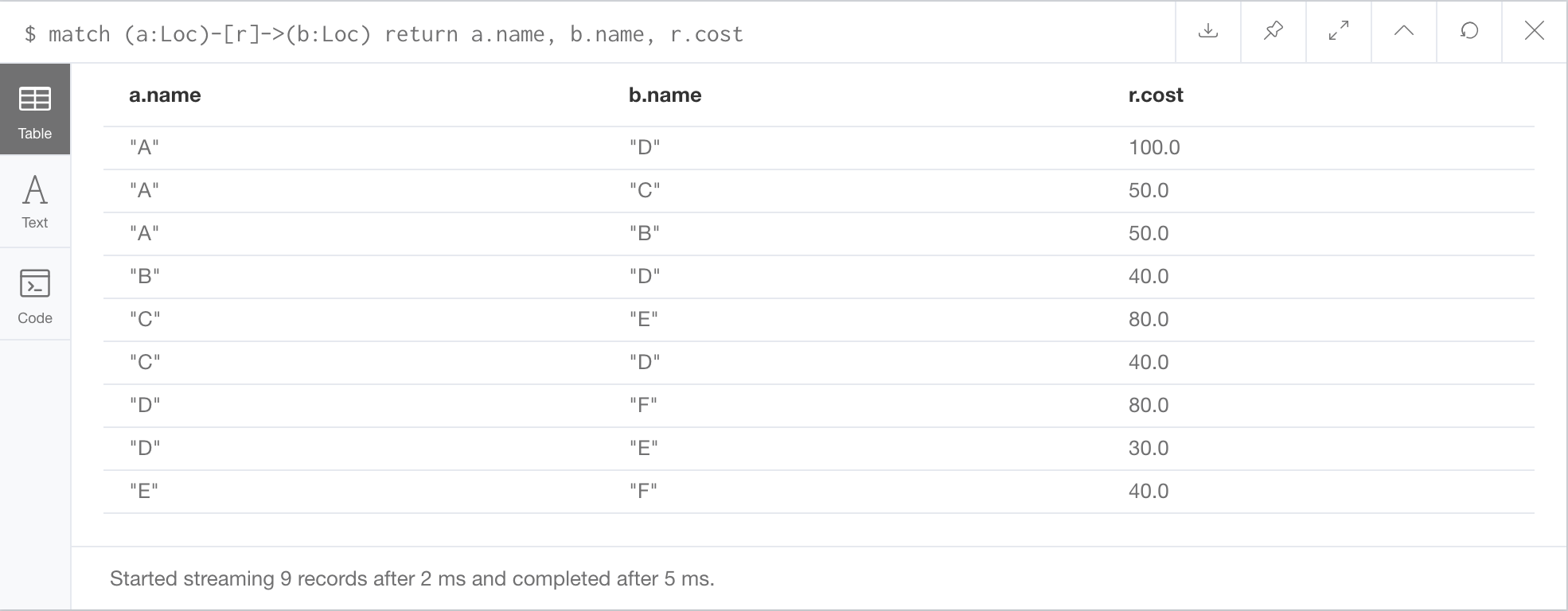
ダイクストラ法の簡単な解説とアルゴリズムは、こちらにあります(Qiitaは実装例は多いけど解説は意外と少ない)。スタートノードに隣接するノードを探し、その中で最もコストが小さいものは、そのノードへのコストの最小値として確定することができる。それを繰り返していき、コストの最小値を次々と確定させて、最終的にゴールのノードのコストが確定したら終了したらよい。下図にダイクストラ法の実行のイメージを示す。ここでは品川から久里浜に至る経路を探索している。左のコストテーブルが、コストが確定していく順番のイメージである。
自前でダイクストラ
実装例を下に示す。このプロシージャは、スタートとゴールのノードidをもらって、その最短経路のパスと総コストを求める。返却値は必ず一つで、複数同じコストのパスがあるケースには対応していない(最初に見つかったパスが返却される)。ダイクストラ法をナイーブに実装するとO(N^2)の計算量になるが、ノードをコストの小さい順に並べるプライオリティキューを利用することによって、計算量を減らすことができる。下のプログラムでは、ノードとコストの対応とノードのコストが確定済みかをクラスNodeInfoを利用して管理している。よって、プライオリティキューにはNodeInfoのオブジェクトを入れている。その順序はNodeInfoのcostの比較によって並べ替えられている(比較関数がラムダ式で定義されている)。NodeInfoの情報は、ノードと対応をつけてmapで管理している。また、パスを得るためのノードとその一つ手前の関連の対応を管理するマップも幅優先探索などと同様に使っている。コストを表すプロパティは、変数cost_propertyに定義している。ここでは"cost"という名前を使っている。データベース上にこのプロパティがあることが前提とされる。この文字列をプロシージャのパラメータに入れるほうが、柔軟になるが、その改造は容易である。
// sample8_1: djkstra
@Procedure(value = "example.sample8_1")
@Description("sample8_1: djkstra")
public Stream<Output> sample8_1( @Name("from_id") Long from_id, @Name("to_id") Long to_id )
{
Node from_nd = db.getNodeById(from_id);
Node to_nd = db.getNodeById(to_id);
// Priority Queue by cost property value
PriorityQueue<NodeInfo> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((n1,n2)->Double.compare(n1.cost,n2.cost));
// map for keeping node and cost
Map<Node, NodeInfo> nodes = new HashMap<>();
// map for keeping Node and parent relationship
Map<Node, Relationship> parent = new HashMap<>();
// current node(info)
NodeInfo cur_ni = new NodeInfo(from_nd, 0.0);
pq.add(cur_ni);
nodes.put(from_nd, cur_ni);
// if to_node's cost is fixed, exit
NodeInfo to_ni = null;
while(to_ni == null || to_ni.done != true){
// if queue is empty, no route exit
if(cur_ni == null){
return new ArrayList<Output>().stream();
}
// top node of queue's cost is fixed
cur_ni = pq.poll();
cur_ni.done = true;
// get adjacent nodes and add them to queue
// Property for cost: type must be double
String cost_property = "cost";
Iterable<Relationship> rels = cur_ni.nd.getRelationships();
for(Relationship rel: rels){
// get adjacent nodes and their costs
Node o_nd = rel.getOtherNode(cur_ni.nd);
double cost_rel = (double)rel.getProperty(cost_property);
// check whether the node was found
NodeInfo next_ni = nodes.get(o_nd);
// not found -> 1st appearance of the node, add it to map
if(next_ni == null){
next_ni = new NodeInfo(o_nd, cur_ni.cost+cost_rel);
pq.add(next_ni);
nodes.put(o_nd, next_ni);
parent.put(o_nd, rel);
}
// found but cost is't fixed and has lower cost -> overwrite cost
else if(next_ni.done == false){
if(next_ni.cost > cur_ni.cost+cost_rel){
next_ni.cost = cur_ni.cost+cost_rel;
parent.put(o_nd, rel);
}
}
// found and cost was fixed -> do nothing
}
// get to_node from map
to_ni = nodes.get(to_nd);
}
// output construction
Output o = new Output();
o.path = getPath(from_nd, to_nd, parent);
o.cost = to_ni.cost;
// list for result
List<Output> o_l = new ArrayList<>();
o_l.add(o);
return o_l.stream();
}
// Node and cost to it
public class NodeInfo {
public Node nd; // Neo4j Node
public double cost; // cost summation from start node
public boolean done; // flag for cost fixed
// constructor
public NodeInfo(Node nd, double cost) {
super();
this.nd = nd;
this.cost = cost;
done = false;
}
}
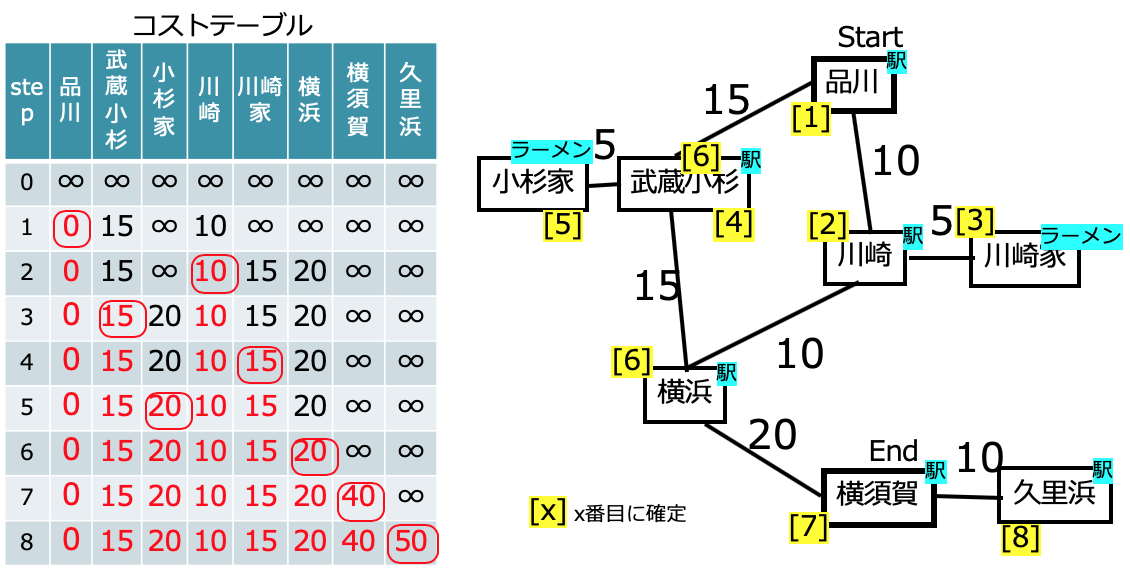
幅優先探索のときと同じサンプルでこのプログラムを実行してみよう。以下のサンプルである。
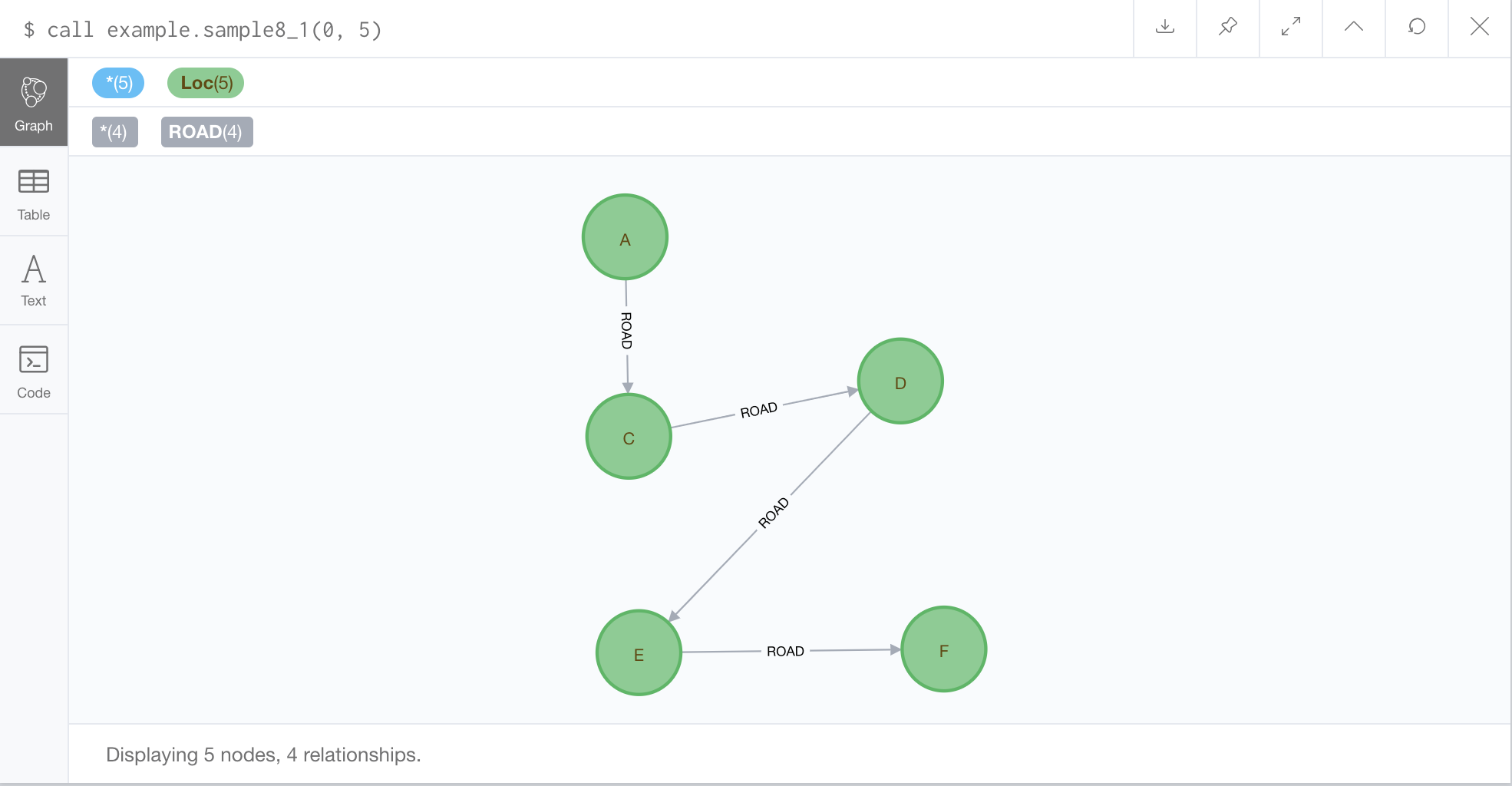
A(idは0)からF(idは5)へ至る最短経路を求める実行結果は、以下の通りである。
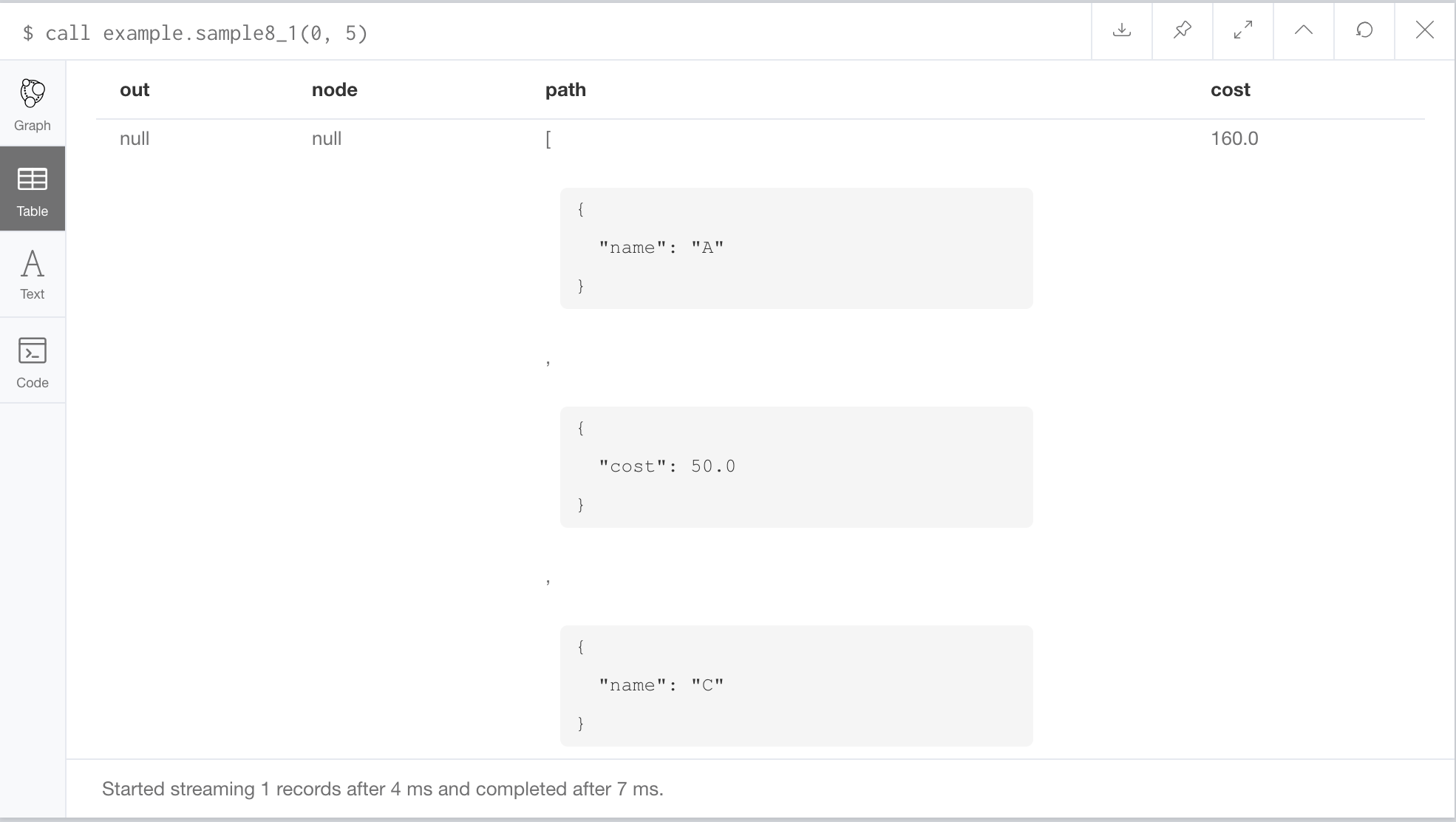
(幅優先などと同じようにすべてのノードへの最短経路を求める例題も追加するかもしれない。最短経路木が同様に書ける)
組み込み関数でダイクストラ
Neo4jには組み込みでダイクストラ法は実装されている。それを利用する方法は、こちらにある。