はじめに
私の記事Djangoが他のPolymorphicと挙動が異なる件
でDjangoのPolymorphicModelがいわゆるポリモーフィック関連と異なることを記事にしました。
今回は、「ではDjangoでポリモーフィック関連を実装するにはどうすのか」という点について解説します。
環境
- Python 3.7.5
- Django 2.2.1
- SQLite
ゴール
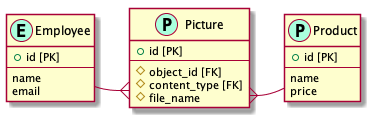
RailsGuideのPolymorphicAssociationsの章では以下のようにポリモーフィック関連が実装されています。
class Picture < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :imageable, polymorphic: true
end
class Employee < ApplicationRecord
has_many :pictures, as: :imageable
end
class Product < ApplicationRecord
has_many :pictures, as: :imageable
end
これに以下のERのような属性を持たせたModelを実装することをゴールにします。
coontent_typeはどのテーブルと関連しているかを示し、object_idはどのレコードを関連しているかを示します。
実装
モデル作成
from django.db import models
from django.contrib.contenttypes.models import ContentType
class Picture(models.Model):
object_id = models.IntegerField(db_index=True)
content_type = models.ForeignKey(ContentType, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
file_name = models.CharField()
class Employee(models.Model):
name = models.CharField()
email = models.EmailField()
class Product(models.Model):
name = models.CharField()
price = models.IntegerField()
Imageableクラスの実装
from django.db import models
from django.contrib.contenttypes.fields import GenericRelation, GenericForeignKey
from django.contrib.contenttypes.models import ContentType
class Picture(models.Model):
object_id = models.IntegerField(db_index=True)
content_type = models.ForeignKey(ContentType, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
file_name = models.CharField(max_length=256)
content_object = GenericForeignKey('content_type', 'object_id')
class Imageable(models.Model):
class Meta:
abstract = True
pictures = GenericRelation(Picture)
class Employee(Imageable):
name = models.CharField(max_length=256)
email = models.EmailField()
class Product(Imageable):
name = models.CharField(max_length=256)
price = models.IntegerField()
動作確認
# マイグレーション
$ python manage.py makemigrations polymorphic_associations
$ python manage.py migrate polymorphic_associations
$ python manage.py shell
# データ作成
>>> from polymorphic_associations.models import Employee, Product
>>>
>>> employee = Employee(name='John', email='test@example.com')
>>> employee.save()
>>> employee.pictures.create(file_name='employee.jpg')
<Picture: Picture object (1)>
>>>
>>> product = Product(name='Desk', price=1000)
>>> product.save()
>>> product.pictures.create(file_name='product.jpg')
<Picture: Picture object (2)>
# データ取得
>>> employee.pictures.all()
<QuerySet [<Picture: Picture object (1)>]>
>>> employee.pictures.first().file_name
'employee.jpg'
>>>
>>> product.pictures.all()
<QuerySet [<Picture: Picture object (2)>]>
>>> product.pictures.first().file_name
'product.jpg'
# SQL確認
>>> str(employee.pictures.all().query)
'SELECT
"polymorphic_associations_picture"."id",
"polymorphic_associations_picture"."object_id",
"polymorphic_associations_picture"."content_type_id",
"polymorphic_associations_picture"."file_name"
FROM
"polymorphic_associations_picture"
WHERE
(
"polymorphic_associations_picture"."content_type_id" = 2
AND "polymorphic_associations_picture"."object_id" = 1
)'
>>>
>>> str(product.pictures.all().query)
'SELECT
"polymorphic_associations_picture"."id",
"polymorphic_associations_picture"."object_id",
"polymorphic_associations_picture"."content_type_id",
"polymorphic_associations_picture"."file_name"
FROM
"polymorphic_associations_picture"
WHERE
(
"polymorphic_associations_picture"."content_type_id" = 3
AND "polymorphic_associations_picture"."object_id" = 1
)'
作成されたデータは、content_type_id、object_idによってテーブル、レコードを特定できていることがわかります。
これによって画像をもつテーブルはすべてImageableを継承することで素早く実装することができます。また画像に関する処理をImageableに実装することで、ロジックが各モデルやサービスに分散することを防ぐことができます。
このソースコードはGitに上げてあります。