- Source: SECCON Beginners CTF 2025
- Author: Yu_212
AES-CBCモードで1ブロックの暗号化と復号化を3回ずつ行うことができ、6ブロックからなるchallengeの暗号化ができるか、という問題。
golden-ticket.py
import os
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.Padding import pad
flag = os.environ.get("FLAG", "ctf4b{dummy_flag}")
iv = os.urandom(16)
key = os.urandom(16)
challenge = os.urandom(16 * 6)
ENC_TICKET = 3
DEC_TICKET = 3
GOLDEN_TICKET = 0
def menu() -> int:
print("Your tickets:")
if ENC_TICKET > 0:
print(f"{ENC_TICKET} encryption ticket(s)")
if DEC_TICKET > 0:
print(f"{DEC_TICKET} decryption ticket(s)")
if GOLDEN_TICKET > 0:
print(f"{GOLDEN_TICKET} golden ticket(s)")
print()
print(f"1. Encrypt")
print(f"2. Decrypt")
print(f"3. Get ticket")
print(f"4. Get flag")
print(f"5. Quit")
while True:
i = int(input("> "))
if 1 <= i <= 5:
return i
print("Invalid input!")
def consume_ticket(enc: int = 0, dec: int = 0, golden: int = 0):
global ENC_TICKET, DEC_TICKET, GOLDEN_TICKET
if ENC_TICKET < enc or DEC_TICKET < dec or GOLDEN_TICKET < golden:
print("Not enough tickets.")
exit(1)
ENC_TICKET -= enc
DEC_TICKET -= dec
GOLDEN_TICKET -= golden
while True:
i = menu()
if i == 1:
consume_ticket(enc=1)
pt = bytes.fromhex(input("pt> "))
if len(pt) > 16:
print("Input must not be longer than 16 bytes.")
continue
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv=iv)
print(f"ct:", cipher.encrypt(pad(pt, 16)).hex())
if i == 2:
consume_ticket(dec=1)
ct = bytes.fromhex(input("ct> "))
if len(ct) > 16:
print("Input must not be longer than 16 bytes.")
continue
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv=iv)
print("pt:", cipher.decrypt(pad(ct, 16)).hex())
if i == 3:
print("challenge:", challenge.hex())
answer = bytes.fromhex(input("answer> "))
if len(answer) != len(challenge) + 16:
print("Wrong length.")
continue
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv=answer[:16])
if cipher.decrypt(answer[16:]) == challenge:
print("Correct!")
GOLDEN_TICKET += 1337
else:
print("Wrong :(")
if i == 4:
consume_ticket(golden=1)
print("flag:", flag)
if i == 5:
print("Bye!")
exit(0)
脆弱性は復号化処理の部分で、本来はAES-CBCで復号してからunpadすべきだが、padしてから復号している。
if i == 2:
consume_ticket(dec=1)
ct = bytes.fromhex(input("ct> "))
if len(ct) > 16:
print("Input must not be longer than 16 bytes.")
continue
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv=iv)
print("pt:", cipher.decrypt(pad(ct, 16)).hex())
PKCS#7では長さが16の倍数になるように1~16byteのパディングを付加するので、暗号文として'\x10'*16を送信すると'\x10'*32になり、2ブロック分の復号結果が得られる。
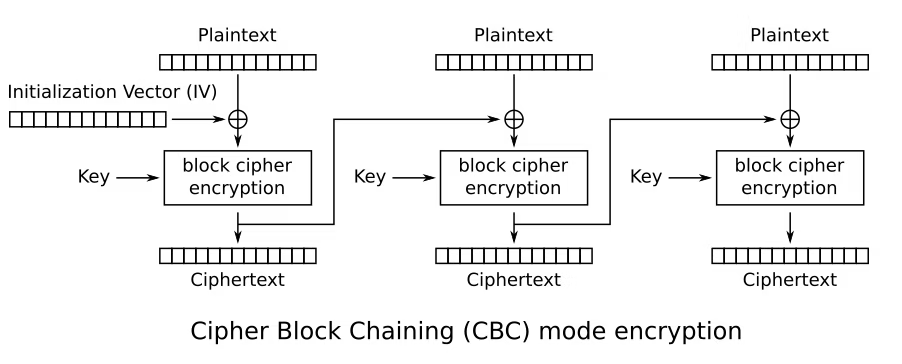
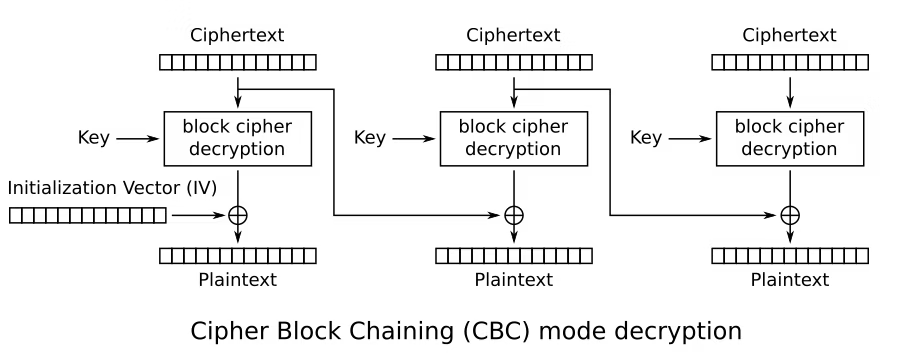
ここでAES-CBCのブロックの暗号化/復号化の仕組みを考える。
暗号文の各ブロックをc0とc1、平文の各ブロックをp0,p1と置くと、以下の式が成り立つ。
\displaylines{
p0=c0⊕key⊕iv
\\
p1=c1⊕key⊕c0
}
'\x10'*16を$pad$とすると、$c0=c1=pad$であるから、ivは$p0⊕p1⊕pad$で得ることができる。
pad16 = b"\x10" * 16
pt = decrypt(pad16)
iv = strxor(strxor(pt[:16], pt[16:]), pad16) # p0 = c0^key^iv, p1=c1^key^c0, c0=c1=pad16 -> iv = p0^p1^pad16
あと暗号化3回と復号化2回が使えるので、どこかのブロックの値を固定してからAESとして正しい前後のブロックおよびivを決定していく。この問題と同じ考え方でやっていく。(計算式は下のプログラムのコメントを参照)
これには6ブロックの計算が必要だが、'\x10'*16を3ブロック目に固定することでivを求めた時の復号結果を流用することができる。
ans2 = pad16
ans3 = encrypt(strxor(strxor(cha[3], ans2), iv))[:16] # ans3 = cha3^ans2^key, E(p) = p^key^iv -> E(cha3^ans2^iv) = ans3
ans4 = encrypt(strxor(strxor(cha[4], ans3), iv))[:16] # ans4 = cha4^ans3^key, E(p) = p^key^iv -> E(cha4^ans3^iv) = ans4
ans5 = encrypt(strxor(strxor(cha[5], ans4), iv))[:16] # ans5 = cha5^ans4^key, E(p) = p^key^iv -> E(cha5^ans4^iv) = ans5
ans1 = strxor(strxor(pt, cha[2]), iv)[:16] # ans2 = cha2^ans1^key, D(c) = c^key^iv -> D(ans2)^cha2^iv = ans1
ans0 = strxor(strxor(decrypt(ans1), cha[1]), iv)[:16] # ans1 = cha1^ans0^key, D(c) = c^key^iv -> D(ans1)^cha1^iv = ans0
ans_iv = strxor(strxor(decrypt(ans0), cha[0]), iv)[:16] # ans0 = cha0^ans_iv^key, D(c) = c^key^iv -> D(ans0)^cha0^iv = ans_iv
最終的なsolverはこうなる。
from pwn import *
io = remote("localhost", 9999)
def encrypt(pt: bytes) -> bytes:
assert len(pt) == 16
io.sendlineafter(b"> ", b"1")
io.sendlineafter(b"pt> ", pt.hex().encode())
io.recvuntil(b"ct: ")
ct = bytes.fromhex(io.recvline().strip().decode())
return ct
def decrypt(ct: bytes) -> bytes:
assert len(ct) == 16
io.sendlineafter(b"> ", b"2")
io.sendlineafter(b"ct> ", ct.hex().encode())
io.recvuntil(b"pt: ")
pt = bytes.fromhex(io.recvline().strip().decode())
return pt
def strxor(a: bytes, b: bytes) -> bytes:
return bytes(x ^ y for x, y in zip(a, b))
# recover iv
pad16 = b"\x10" * 16
pt = decrypt(pad16)
iv = strxor(strxor(pt[:16], pt[16:]), pad16) # p0 = c0^key^iv, p1=c1^key^c0, c0=c1=pad16 -> iv = p0^p1^pad16
print(f"iv: {iv.hex()}")
# get challenge
io.sendlineafter(b"> ", b"3")
io.recvuntil(b"challenge: ")
raw = bytes.fromhex(io.recvline().strip().decode())
cha = [raw[i:i+16] for i in range(0, len(raw), 16)]
io.sendlineafter(b"answer> ", b"00" * (16 * 7)) # dummy
# solve
ans2 = pad16
ans3 = encrypt(strxor(strxor(cha[3], ans2), iv))[:16] # ans3 = cha3^ans2^key, E(p) = p^key^iv -> E(cha3^ans2^iv) = ans3
ans4 = encrypt(strxor(strxor(cha[4], ans3), iv))[:16] # ans4 = cha4^ans3^key, E(p) = p^key^iv -> E(cha4^ans3^iv) = ans4
ans5 = encrypt(strxor(strxor(cha[5], ans4), iv))[:16] # ans5 = cha5^ans4^key, E(p) = p^key^iv -> E(cha5^ans4^iv) = ans5
ans1 = strxor(strxor(pt, cha[2]), iv)[:16] # ans2 = cha2^ans1^key, D(c) = c^key^iv -> D(ans2)^cha2^iv = ans1
ans0 = strxor(strxor(decrypt(ans1), cha[1]), iv)[:16] # ans1 = cha1^ans0^key, D(c) = c^key^iv -> D(ans1)^cha1^iv = ans0
ans_iv = strxor(strxor(decrypt(ans0), cha[0]), iv)[:16] # ans0 = cha0^ans_iv^key, D(c) = c^key^iv -> D(ans0)^cha0^iv = ans_iv
answer = ans_iv + ans0 + ans1 + ans2 + ans3 + ans4 + ans5
# get flag
io.sendlineafter(b"> ", b"3")
io.sendlineafter(b"answer> ", answer.hex().encode())
res = io.recvline().strip()
print(res.decode())
io.sendlineafter(b"> ", b"4")
print(io.recvline().decode())
これを実行するとflagが得られた。
ctf4b{u_wi11_b3_1nv173d_t0_7h3_ch0c0l4t3_f4c70ry_1337_t1m35}