最近お世話になる機会が増えてきたので忘れないようまとめておく。
以前自分で検証した内容も踏まえて。
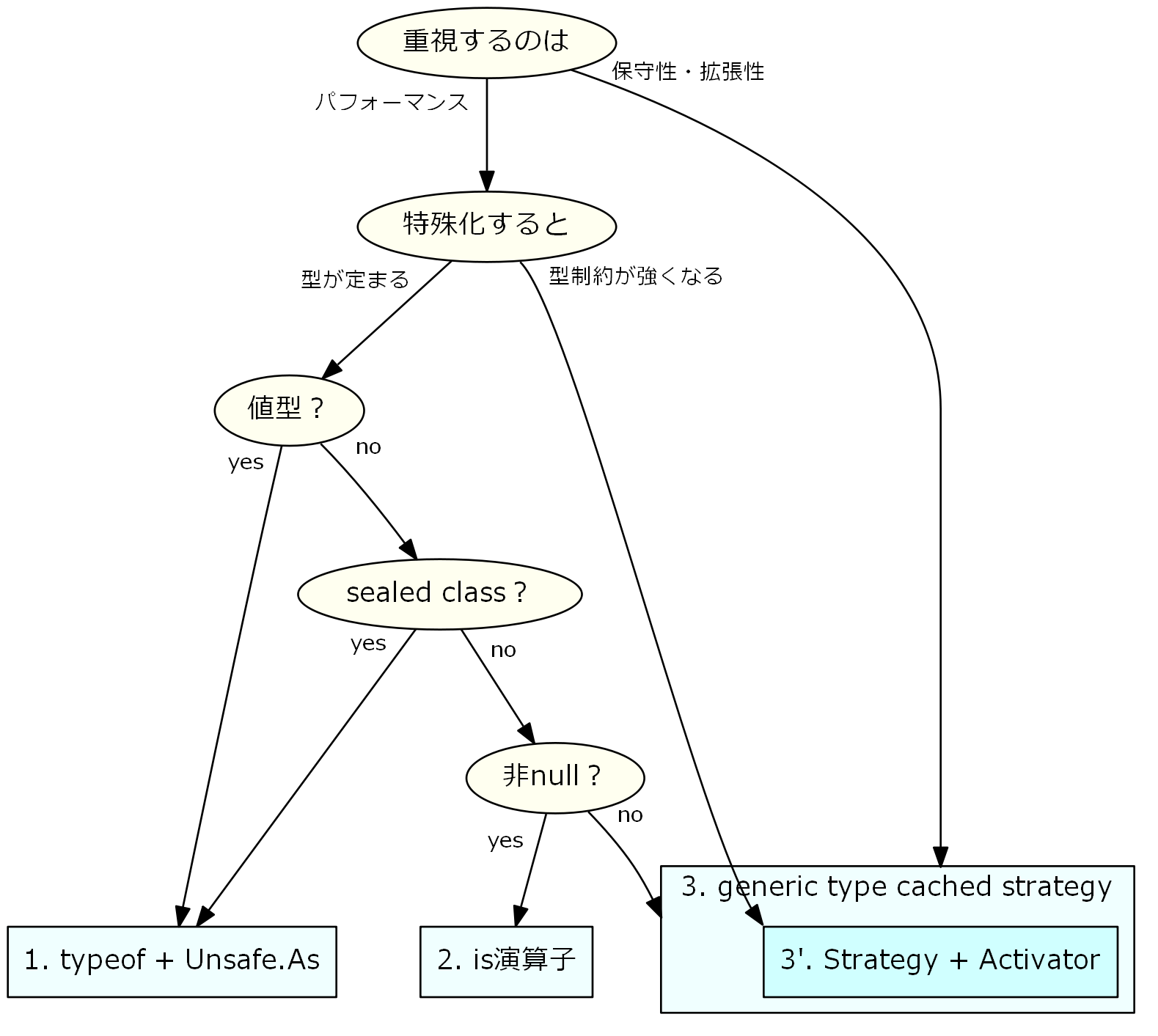
手法選択フローチャート
サンプルコード
using System;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
public static class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
DoSomething(123);
DoSomething(0.123);
DoSomething(new Bar());
DoSomething("hogehoge");
}
public static T DoSomething<T>(T value)
{
// 1. typeof & Unsafe.As
if(typeof(T) == typeof(int))
{
var value_int = Unsafe.As<T, int>(ref value);
var return_int = DoSomething_int(value_int);
return Unsafe.As<int, T>(ref return_int);
}
// 2. is operator
if(value is Foo value_Foo)
{
return DoSomething_Foo(value_Foo) is T return_Foo
? return_Foo
: throw new InvalidOperationException();
}
// 3. Generic type cached strategy
return DoSomethingStrategy<T>.Instance.Invoke(value);
}
public static int DoSomething_int(int value)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{value} -> specialized on int");
return value;
}
public static Foo DoSomething_Foo(Foo value)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{value} -> specialized on Foo");
return value;
}
private class DoSomethingStrategy<T>
{
// 3'. strategy pattern & Activator
public static DoSomethingStrategy<T> Instance { get; }
= typeof(T).IsValueType
? (DoSomethingStrategy<T>)Activator
.CreateInstance(typeof(DoSomethingStrategy_struct<>)
.MakeGenericType(typeof(T)))
: new DoSomethingStrategy<T>();
public virtual T Invoke(T value)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{value} -> default");
return value;
}
}
private class DoSomethingStrategy_struct<T> : DoSomethingStrategy<T>
where T : struct
{
public override T Invoke(T value)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{value} -> specialized on struct");
return value;
}
}
}
public class Foo {}
public class Bar : Foo {}
1., 2., 3. の手法は1つのジェネリックメソッド内で共存可能だが、サンプルのように順序を守ること。
解説
1. typeof & Unsafe
if(typeof(T) == typeof(int))
{
var value_int = Unsafe.As<T, int>(ref value);
var return_int = DoSomething_int(value_int);
return Unsafe.As<int, T>(ref return_int);
}
Tのtypeofを取って特殊化先の型と等値比較し、分岐の際には型変換にUnsafe.Asを用いる。
特殊化先が値型であれば、JIT後にはなんとゼロオーバーヘッドという素敵性能。
2. is演算子
if(value is Foo value_Foo)
{
return DoSomething_Foo(value_Foo) is T return_Foo
? return_Foo
: throw new InvalidOperationException();
}
C#における最も標準的なダウンキャストを用いる手法。
派生型もまとめてディスパッチできるが、nullをスルーしてしまうので非null限定であることに注意。
3. generic type cached strategy
return DoSomethingStrategy<T>.Instance.Invoke(value);
private class DoSomethingStrategy<T>
{
// 外部からデフォルトインスタンスを流し込む場合にはsetアクセサも公開する必要がある
public static DoSomethingStrategy<T> Instance { get; set; }
= new DoSomethingStrategy<T>();
public virtual T Invoke(T value)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{value} -> default");
return value;
}
}
Generic type cachingによりストックしたStrategyを用いる手法。
特殊化型ごとに独立したクラスを定義できるため特殊化実装間の疎結合を保ちやすい。
特殊化先の型ごとにデフォルトインスタンスの初期化をする必要があることに注意。
3'. strategy + Activator
private class DoSomethingStrategy<T>
{
// Activatorによるインスタンス生成をすることで型制約を回避する
public static DoSomethingStrategy<T> Instance { get; }
= typeof(T).IsValueType
? (DoSomethingStrategy<T>)Activator
.CreateInstance(typeof(DoSomethingStrategy_struct<>)
.MakeGenericType(typeof(T)))
: new DoSomethingStrategy<T>();
public virtual T Invoke(T value)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{value} -> default");
return value;
}
}
private class DoSomethingStrategy_struct<T> : DoSomethingStrategy<T>
where T : struct
{
public override T Invoke(T value)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{value} -> specialized on struct");
return value;
}
}
stragetyのデフォルトインスタンスを生成するときに、Activatorを介することで型制約を回避するテクニック。
C#では型制約の弱いメソッドから強いメソッドを呼ぶことが(アンセーフな手法でも)できないので、その代替手段として利用できる。
class制約、struct制約、new制約、複数のインターフェース制約など、どんなものにも対応できる。