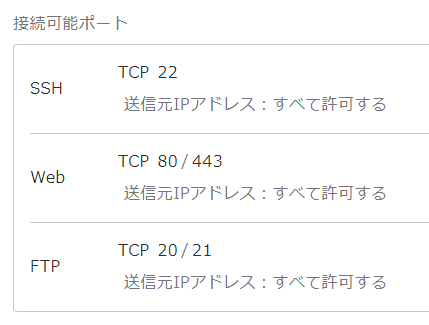
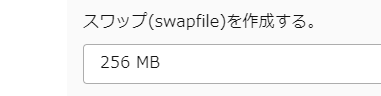
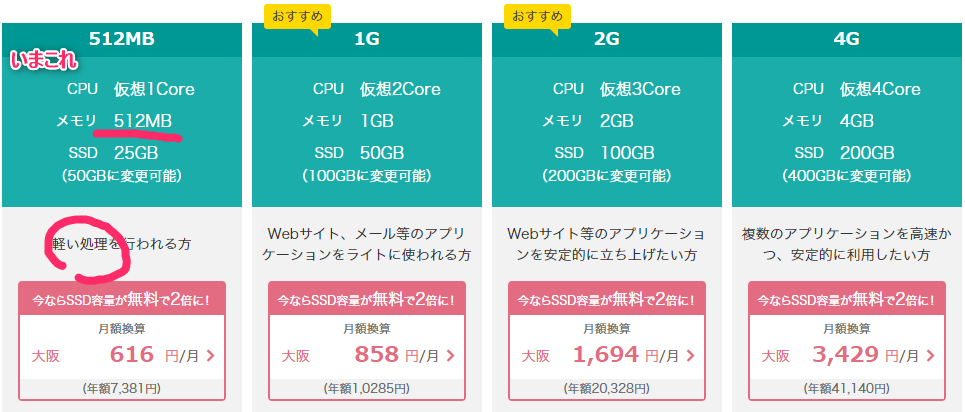
はじめに
pure python版 と書いているのは、この記事の前の記事のときにたしか...CentOSであったのと同時にanacondaだったから
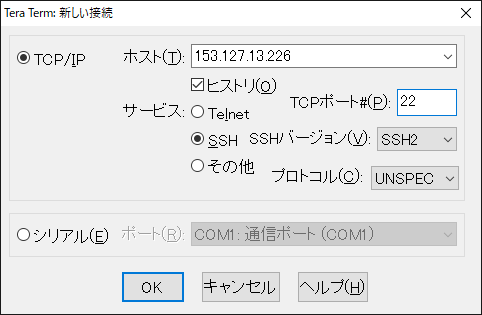
Ubuntu 24.04LTS
インストール
LTS版を入れる
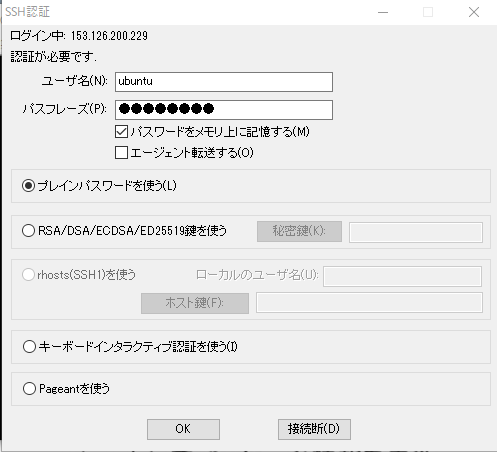
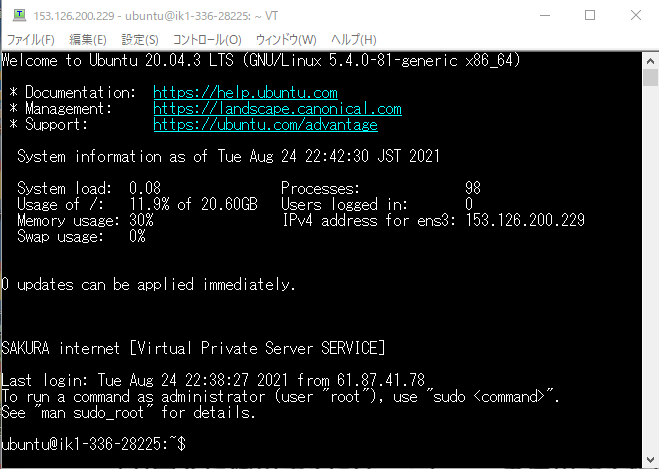
ユーザー名が ubuntu になっていることに注意(最初はrootにパスワードが設定されていなくてrootが使えないようだ。そしてできるだけrootで入らず sudo -s でroot化するのが基本だそうだ)


スタートアップスクリプト設定は Setup and update
Swap増設
ステップ1 – システムのスワップ情報を確認
さくらのVPSのサポートに問い合わせたらubuntuは標準ではswapが設定されていないとのこと。つまりメモリがパンクしてバツンと落ちてた可能性が高い。
メモリが足りないならハードディスクを使えばいいじゃない!
ubuntu@ik1-336-28225:~$ sudo swapon --show
freeユーティリティを使用して、アクティブなスワップがないことを確認
$ free -h
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 961Mi 889Mi 78Mi 1.5Mi 135Mi 71Mi
Swap: 0B 0B 0B
ステップ2 – ハードドライブパーティションの使用可能なスペースを確認
スワップファイルを作成する前に、現在のディスク使用量をチェックして、十分なスペースがあることを確認します。
Mounted on 列に / が表示されているデバイスがディスク。6GBしか使ってないから5GBぐらいアサインしてもいいね
$ df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
tmpfs 97M 948K 96M 1% /run
/dev/vda2 50G 6.0G 41G 13% /
tmpfs 481M 0 481M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 5.0M 0 5.0M 0% /run/lock
tmpfs 97M 8.0K 97M 1% /run/user/1000
ステップ3 – スワップファイルの作成
$ sudo fallocate -l 5G /swapfile
$ ls -lh /swapfile
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 5.0G 12月 24 19:11 /swapfile
ステップ4 – スワップファイルの有効化
適切なサイズのファイルが使用可能となったので、実際にこれをスワップ領域に変換する必要があります。
まず、root権限を持つユーザーのみが内容を読み取ることができるように、ファイルのアクセス許可をロックする必要があります。これにより通常のユーザーがファイルにアクセスできなくなるため、セキュリティにとって重要な意味を持ちます。
$ sudo chmod 600 /swapfile
$ sudo mkswap /swapfile
スワップ空間バージョン 1 を設定します。サイズ = 5 GiB (5368705024 バイト)
ラベルはありません, UUID=bc058b64-2f02-47fa-86bc-b2843087cdee
$ sudo swapon /swapfile
$ sudo swapon --show
NAME TYPE SIZE USED PRIO
/swapfile file 5G 0B -2
$ free -h
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 961Mi 883Mi 62Mi 1.5Mi 159Mi 78Mi
Swap: 5.0Gi 0B 5.0Gi
ステップ5 – スワップファイルの永続化
現在のセッションのスワップファイルが有効になりました。しかし、再起動すると、サーバーはスワップ設定を自動的に保持しません。これを変更するには、スワップファイルを/etc/fstabファイルに追加します。
※「/etc/fstab」ファイルは、マウントするファイルシステムの情報を記述するファイル
$ sudo cp /etc/fstab /etc/fstab.bak
$ echo '/swapfile none swap sw 0 0' | sudo tee -a /etc/fstab
/swapfile none swap sw 0 0
ステップ6 – スワップ設定の調整
Swappinessプロパティの調整
swappinessパラメーターは、システムがRAMからスワップ領域にデータをスワップする頻度を設定します。これは、パーセンテージを表す0~100の値です。
値が0に近い場合、カーネルは絶対に必要な場合を除いて、データをディスクにスワップしません。スワップにあまり依存しないようにシステムに指示すると、通常、システムの動作が高速になります。
$ cat /proc/sys/vm/swappiness
60
$ sudo sysctl vm.swappiness=40
vm.swappiness = 40
$ sudo vi /etc/sysctl.conf
vm.swappiness=40
vm.vfs_cache_pressure=50
Teraterm
※Linuxの記号の意味
Linux初心者は、コンソール上の「$」とか「#」がよくわかんなかったりする
| 記号 | 意味 |
|---|---|
| $ | 一般ユーザ権限で操作中 |
| # | root権限権限で操作中 |
ログインチェック
スーパーユーザーになる
(すぐexitするけどね)
$ sudo -s
[sudo] password for ubuntu:
# exit
公開鍵でログインできるようにする
作った公開鍵を置く(teratermにドラッグアンドドロップでOK)
$ pwd
/home/ubuntu
$ ls
id_rsa_henojiya.pub
許可する鍵としてさっきの公開鍵を登録する(先頭にドットがつくのは隠しフォルダ)
$ mkdir ~/.ssh
$ chmod 700 ~/.ssh
$ mv id_rsa_henojiya.pub ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
$ chmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
※SCPを使う場合(※慣れてから)
C:\Users\yoshi\.ssh> scp .\id_rsa_henojiya.pub ubuntu@153.126.200.229:/home/ubuntu
ubuntu@153.126.200.229's password:
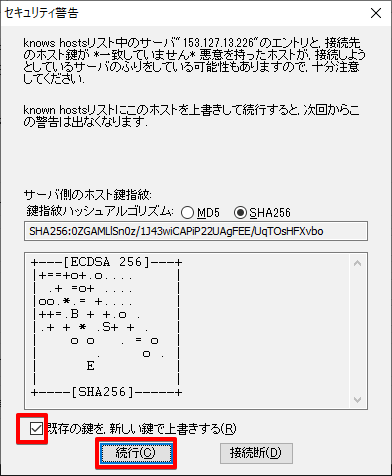
※sshログインで怒られたら
クライアントPC(今回はWin)からknown_hosts C:\Users\yoshi\.ssh\known_hosts を削除。サーバーのOS入れ直したんデショ?
$ ssh example.com
@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
@ WARNING: REMOTE HOST IDENTIFICATION HAS CHANGED! @
@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
Apache2
インストール
$ sudo -s
# cd ~
# apt -y install apache2 apache2-dev
# systemctl status apache2
設定
# vi /etc/apache2/conf-enabled/security.conf
:set number
- ServerTokens OS
+ ServerTokens Prod
# vi /etc/apache2/mods-enabled/dir.conf
- DirectoryIndex index.html index.cgi index.pl index.php index.xhtml index.htm
+ DirectoryIndex index.html
# vi /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/000-default.conf
apache2.conf(9行目)サーバー名追記
- #ServerName www.example.com
+ ServerName www.henojiya.net
+ # httpsの設定が済むまではコメントアウトしておく
+ # Redirect permanent / https://www.henojiya.net
# systemctl restart apache2
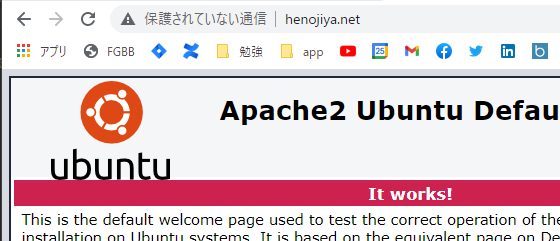
確認
http://www.henojiya.net でつながった!

ロケールの変更
WSGI アプリを Apache 配下で動かす場合、www-data ユーザーのロケールが C(ASCII)になっていると、
ZIP 展開やファイルアップロード時に日本語ファイル名で UnicodeEncodeError が発生することがあります。
そのため、Apache の環境変数で UTF-8(C.UTF-8)を明示しておくと安全です。
C.UTF-8 は locale の生成が不要で、システムを汚さず簡潔に設定できます。
Apache の環境変数で UTF-8 を明示
echo 'export LANG=C.UTF-8' | sudo tee -a /etc/apache2/envvars
echo 'export LC_ALL=C.UTF-8' | sudo tee -a /etc/apache2/envvars
sudo systemctl restart apache2
確認(任意): www-data 視点で UTF-8 になっているか
sudo -u www-data -H bash -lc 'locale'
LANG=C.UTF-8 と表示されれば OK。
これで日本語を含む ZIP 展開やファイルアップロードでも UnicodeEncodeError は発生しません。
バーチャルホスト
いったんパス もとの記事
# vi /etc/apache2/sites-available/virtual.host.conf
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName www.henojiya.net
DocumentRoot /var/www/html
</VirtualHost>
自分メモ(エントリポイントを増やすときはこう書く)
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName www.henojiya.net
DocumentRoot /var/www/html/portfolio
</VirtualHost>
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName app.henojiya.net
DocumentRoot /var/www/html/soil_analysis
</VirtualHost>
# a2ensite virtual.host
# systemctl restart apache2
ネームサーバーを設定
いったんパス もとの記事
https
ポートをあける
ubuntuの443ポートを開け、ファイアウォールを起動する
# ufw allow in "Apache Full"
# ufw allow in "OpenSSH"
# ufw enable
Command may disrupt existing ssh connections. Proceed with operation (y|n)? y
# ufw status
Status: active
To Action From
-- ------ ----
Apache Full ALLOW Anywhere
OpenSSH ALLOW Anywhere
Apache Full (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
OpenSSH (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
サイト設定を有効化する
# a2ensite default-ssl
Enabling site default-ssl. // 設定を読み込む
# a2enmod ssl
Module setenvif already enabled // apache に SSL モジュールを読み込む
# systemctl restart apache2 // Apache2 を再起動
SSL
Let’s Encryptについて
- Let’s Encrypt は、できるだけ多くの人がフェアにサービスを利用できるように、レート制限を設けています
- もしあなたが Let’s Encrypt クライアントの開発やテストを活発に行なっている場合には、本番 API を使用する代わりに、私たちが用意したステージング環境を利用するようにしてください
- 主なレート制限としては、登録ドメインごとの証明書数 (1週間に50個まで) があります
- 登録ドメインとは、一般に言うと、あなたがドメイン名レジストラから購入したドメインの一部のことです。たとえば、
www.example.comの場合、登録ドメインはexample.comです。new.blog.example.co.ukの場合、登録ドメインはexample.co.ukです。 - 証明書ごとのドメイン名はできるだけ少ない方がよいです。
certbotのインストール
# apt -y install certbot python3-certbot-apache
証明書を取得
# certbot delete --cert-name henojiya.net
Are you sure you want to delete the above certificate(s)?
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
(Y)es/(N)o: Y
# certbot certificates
No certificates found.
# cd ~
# certbot certonly --apache --dry-run
IMPORTANT NOTES:
- The dry run was successful.
# cd ~
# certbot certonly --apache
Enter email address: your_cool_email@gmail.com
(Y)es/(N)o: Y ←利用条件に同意する?
(Y)es/(N)o: N ←メーリングリストに登録する?
Which names would you like to activate HTTPS for?
We recommend selecting either all domains, or all domains in a VirtualHost/server block.
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
1: www.henojiya.net
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Select the appropriate numbers separated by commas and/or spaces, or leave input
blank to select all options shown (Enter 'c' to cancel): 1 ←何番をhttps化するの?
FQDNをメモ
/etc/letsencrypt/live/www.henojiya.net をメモする。cert.pem privkey.pem chain.pem も覚えとく
# ls /etc/letsencrypt/live/
README www.henojiya.net
# ls /etc/letsencrypt/live/www.henojiya.net
README cert.pem chain.pem fullchain.pem privkey.pem
# openssl x509 -in /etc/letsencrypt/live/www.henojiya.net/fullchain.pem -noout -dates
notBefore=Aug 29 03:05:54 2021 GMT
notAfter=Nov 27 03:05:53 2021 GMT
エディタのデフォルトをviに
export EDITOR=vi
# vi /etc/environment
VISUAL=/usr/bin/vim
EDITOR=/usr/bin/vim
保存してターミナルに入り直したら恒久的にviになった
https
# vi /etc/apache2/sites-available/default-ssl.conf
31,32行目:取得した証明書に変更
- SSLCertificateFile /etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cert-snakeoil.pem
+ SSLCertificateFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/www.henojiya.net/cert.pem
- SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/ssl/private/ssl-cert-snakeoil.key
+ SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/www.henojiya.net/privkey.pem
41行目:
- #SSLCertificateChainFile /etc/apache2/ssl.crt/server-ca.crt
+ SSLCertificateChainFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/www.henojiya.net/chain.pem
# systemctl restart apache2
確認
# certbot renew
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Processing /etc/letsencrypt/renewal/www.henojiya.net.conf
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Certificate not yet due for renewal
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
The following certificates are not due for renewal yet:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/www.henojiya.net/fullchain.pem expires on 2024-10-11 (skipped)
No renewals were attempted.
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
root@ik1-336-28225:~#
Certificate not yet due for renewal
は、まだ更新は必要ないよ、という意味
確認
https://henojiya.net/ でつながった!
※httpsの設定をしたらApacheが止まる??
たくさんやり直したでしょ m9(^Д^)プギャー
発行済の証明書が更新 (または複製) の対象とみなされるのは、全く同じホスト名の集合が指定されているときです (大文字・小文字、順序は区別しない)。たとえば、[www.example.com, example.com] というドメイン名に対する証明書をリクエストした場合、同じ週に [www.example.com, example.com] に対する証明書を重複して発行できるのは、追加で 4 つまでです。
レート制限に引っかかった場合、制限を一時的にリセットする方法はありません。レート制限が解消されるまで1週間後まで待つ必要があります。
参考)レート制限がかかると、以下のエラーメッセージが出るので1日待ってから行う。
Obtaining a new certificate
An unexpected error occurred:
There were too many requests of a given type :: Error creating new order :: too many certificates already issued for exact set of domains: yoursite.com: see https://letsencrypt.org/docs/rate-limits/
Please see the logfiles in /var/log/letsencrypt for more details.
IMPORTANT NOTES:
- Your account credentials have been saved in your Certbot
configuration directory at /etc/letsencrypt. You should make a
secure backup of this folder now. This configuration directory will
also contain certificates and private keys obtained by Certbot so
making regular backups of this folder is ideal.
httpからのhttpsリダイレクトの対応
# vi /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/000-default.conf
# httpsの設定が済むまではコメントアウトしておく
- # Redirect permanent / https://www.henojiya.net
+ Redirect permanent / https://www.henojiya.net
# systemctl restart apache2
定例更新化
cd /root
vi certbot.sh
# /bin/sh
/usr/local/bin/certbot-auto renew
today=$(date "+%Y/%m/%d %H:%M:%S")
echo ${today} certbot-auto >> result.log
export EDITOR=vi
# vi /etc/environment
VISUAL=/usr/bin/vim
EDITOR=/usr/bin/vim
保存してターミナルに入り直したら恒久的にviになった
chmod 755 certbot.sh
crontab -e
0 0 1 * * /root/certbot.sh
crontab -l
MySQL8
mariadbの削除
# apt purge mariadb-* mysql-*
インストール
# apt -y install mysql-server-8.0
# mysql --version
mysql Ver 8.0.37-0ubuntu0.24.04.1 for Linux on x86_64 ((Ubuntu))
# service mysql status
Active: active (running)
初期設定
# mysql_secure_installation
# パスワード品質チェックを有効にするか否か
Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No: y
# パスワード品質チェックを有効にした場合は強度を選択
Please enter 0 = LOW, 1 = MEDIUM and 2 = STRONG: 0
# 匿名ユーザーを削除するか否か
Remove anonymous users? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
Disallow root login remotely? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
# テストデータベースを削除するか否か
Remove test database and access to it? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
# 特権情報をリロードするか否か
Reload privilege tables now? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
All done!
確認
# mysql -u root -p
Welcome to the MySQL monitor.
UTF8mb4がデフォルト文字コードみたいなのでそのままでよい
mysql> status
Server characterset: utf8mb4
Db characterset: utf8mb4
Client characterset: utf8mb4
Conn. characterset: utf8mb4
データベースを作成
Ubuntuをお使いの場合、デフォルトでrootユーザーはsudoを使ってのみアクセス可能となっています。これは、セキュリティを強化するための設定です
つまりmysqlは root にしてから設定しろってことか。。?
mysql> CREATE DATABASE portfolio_db DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8mb4;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> show databases;
ユーザを作成
% の権限にするとWindowsからのリモートログインができるようになる。本来はこの部分を localhost にして、セキュリティを高める。
mysql> SELECT User, Host FROM mysql.user;
mysql> CREATE USER 'python'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'python123';
mysql> grant CREATE, DROP, SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT, DELETE, ALTER, REFERENCES, INDEX on portfolio_db.* to 'python'@'%';
特にローカルパソコンで手順をなぞるときは 'python'@'%' でユーザ作ったのに 'python'@'localhost' で権限を与えようとしてハマることがある(最初の1回しかやらないからパソコン買い替え時にハマった)。'python'@'%' でユーザ作ったら'python'@'%' で権限を与える。まぁローカルパソコンなら'python'@'localhost' でユーザ作ったらええか
mysql> exit
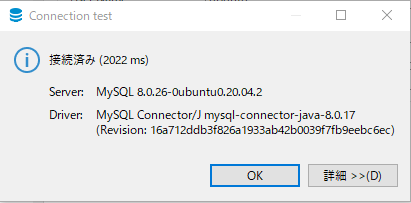
DBeaver
最近MySQLWorkbenchよりDBeaver好きなのよ。FK逆追いできるから。
かんたんにできるはず(失敗するとしたらportかぶり起こしてる)
MySQLのPORTを変える理由
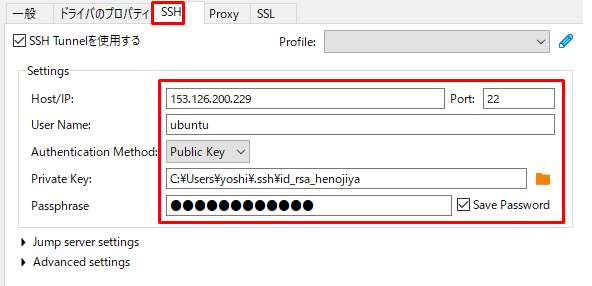
SSHタブの設定
| 入力箇所 | 入力値 |
|---|---|
| Host/IP | 153.126.200.229 |
| Port | 22 |
| User Name | ubuntu |
| Authentication Method | Public Key |
| Private Key | (VPSでのログイン時に指定する rsa 秘密鍵) |
| Passphrase | (ubuntu ユーザーのパスワード) |
Test tunnel configuration を押して、サーバにつながったことを確認する
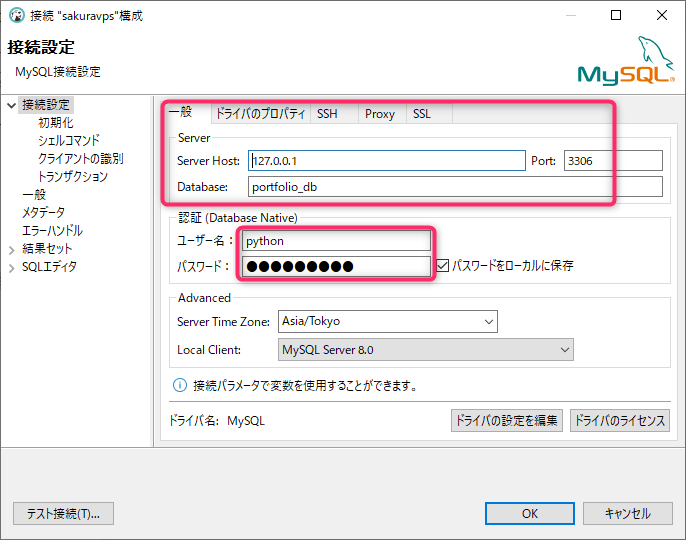
一般タブの設定
| 入力箇所 | 入力値 |
|---|---|
| Server Host | 127.0.0.1 |
| Port | 3306 |
| Database | portfolio_db |
| ユーザー名 | python |
| パスワード | (MySQLのrootユーザーのパスワード) |
※Public Key Retrieval is not allowedのエラーが出力される
DBeaverからローカルのMySQLに接続できない問題への対処法
サンプルのhtmlを作ってみる
デフォルトの「ドキュメントルート」が /var/www/html/ なんだってさ。httpd.conf を探すとあるよ。
# vi /var/www/html/index.html
あ、Ubuntuはあのスタートページが(CentOSと違って)ここにあるのね。
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1
-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
Python
起動確認
いままでは python ってコマンドでバージョンとか見てたけど python3 ってバージョン付きコマンドでなれたほうがよさそう
# python3 -V
Python 3.12.3
python 3.12
https://iohk.zendesk.com/hc/en-us/articles/16724475448473-Install-Python-3-11-on-ubuntu
# apt update && apt upgrade
# apt install wget build-essential libncursesw5-dev libssl-dev libsqlite3-dev tk-dev libgdbm-dev libc6-dev libbz2-dev libffi-dev zlib1g-dev
# add-apt-repository ppa:deadsnakes/ppa
# apt install Python3.12 python3.12-dev
venv
インストール
# apt -y install python3.12-venv
仮想環境の作成
# cd /var/www/html
# python3.12 -m venv venv (※ここに venv フォルダができて3.12がinstallされる)
activate
# source /var/www/html/venv/bin/activate
# python -V
Python 3.12.4
deactivate
# deactivate
Git
バージョン確認
そのままでいいと思うけどね
$ git --version
git version 2.43.0
公開鍵の作成
VPSに公開鍵を作成して、それをgithubに登録することでpullができるようになる(windowsに作った公開鍵と混同しないように)
$ cd ~/.ssh
$ ls
authorized_keys
$ git config --global user.name "yoshi"
$ git config --global user.email "your_cool_email@gmail.com"
$ ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -C "your_cool_email@gmail.com"
Enter file in which to save the key (/home/ubuntu/.ssh/id_ed25519): ←ここに作るよ? ←enter押す
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): ←カラでenter押す
Enter same passphrase again: ←カラでenter押す
$ ls
authorized_keys id_ed25519 id_ed25519.pub
公開鍵をgitHubにアップ
$ cat id_ed25519.pub
ssh-rsa AAAAB3N ...
確認
このコマンドを打つことで認証が済むのでこれをやらないと push できない。
$ ssh -T git@github.com
Warning: Permanently added the RSA host key for IP address '13.114.40.48' to the list of known hosts.
Hi duri0214! You've successfully authenticated, but GitHub does not provide shell access.
Django4
※Cloneから始めるときの前提になっている。新規は下の方に書いた
Cloneする
# chown -R ubuntu:ubuntu /var/www/html
# exit
$ cd /var/www/html
$ git clone git@github.com:duri0214/portfolio.git
$ service apache2 restart
$ cd portfolio
$ sudo apt-get install libmysqlclient-dev pkg-config python3-dev
$ source /var/www/html/venv/bin/activate
$ pip install -r requirements.txt
自分メモ
.env を FTP で移すのを忘れずに
※Cloneできないときはこれをチェック
-
ls ~/.sshに github 登録したカギがあるか(rootに.sshフォルダはない。$だとある) -
gitに公開鍵を登録していない 対git用公開鍵の作成
mod_wsgi
インストール
apache2-dev が入ってないとだめみたいね
$ source /var/www/html/venv/bin/activate
$ pip install mod_wsgi
Requirement already satisfied: mod_wsgi in /var/www/html/venv/lib/python3.12/site-packages (5.0.0)
LoadModule
これをメモして次のステップで 000-default.conf に書き込む
# find / -name mod_wsgi*.so
/var/www/html/venv/lib/python3.12/site-packages/mod_wsgi/server/mod_wsgi-py312.cpython-312-x86_64-linux-gnu.so
python-home
これをメモして次のステップで 000-default.conf に書き込む
# find /var/www/html -name '*venv*'
/var/www/html/venv
httpd.conf
# vi /etc/apache2/sites-available/000-default.conf
# VirtualHostは変更しません
<VirtualHost *:80>
・・・省略・・・
</VirtualHost>
# 以下に書き込む
LoadModule wsgi_module /var/www/html/venv/lib/python3.12/site-packages/mod_wsgi/server/mod_wsgi-py312.cpython-312-x86_64-linux-gnu.so
WSGIScriptAlias / /var/www/html/portfolio/config/wsgi.py
WSGIDaemonProcess wsgi_app python-home=/var/www/html/venv python-path=/var/www/html/portfolio
WSGIProcessGroup wsgi_app
WSGISocketPrefix /var/run/wsgi
WSGIApplicationGroup %{GLOBAL}
# css, javascript etc
Alias /static/ /var/www/html/portfolio/static/
<Directory /var/www/html/portfolio/static>
Require all granted
</Directory>
# service apache2 restart
LoadModule: mod_wsgiの本体ファイルの位置。Apacheがwsgiを認識するために必要
WSGIScriptAlias: 1つめの引数のURLでアクセスされたら、2つめの引数のwsgiスクリプトに移動する
WSGIDaemonProcess: Linuxではデーモン(=サービス)として動かすのが推奨されている
WSGIProcessGroup: 「サービス」に名前をつける
WSGISocketPrefix: 「※Socketの問題」を参照
(対応済み)
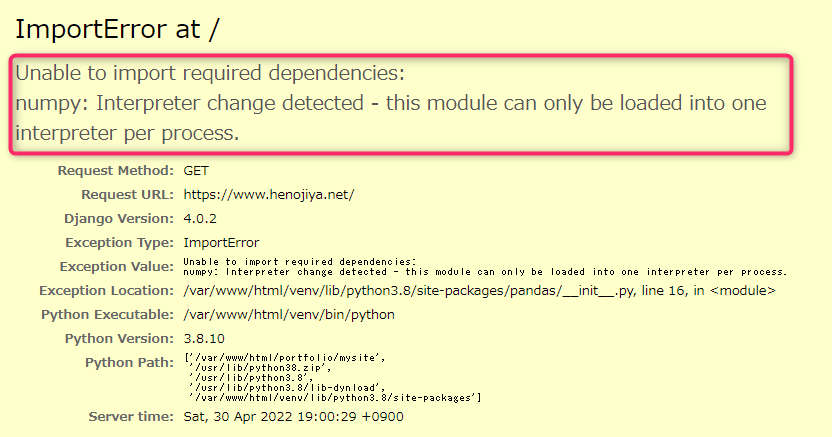
※numpy: Interpreter change detected
どうもこの記事にたどり着いた。
仮説
- numpyはインタープリタ(実行環境)の変化を許容しない
- wsgiはバーチャルホストの違いでインタープリタを分ける仕組みがある
https://tech-blog.monotaro.com/entry/2018/07/04/084733
# vi /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/000-default.conf
LoadModule wsgi_module /var/www/html/venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages/mod_wsgi/server/mod_wsgi-py38.cpython-38-x86_64-linux-gnu.so
WSGIScriptAlias / /var/www/html/portfolio/config/wsgi.py
WSGIDaemonProcess wsgi_app python-home=/var/www/html/venv python-path=/var/www/html/portfolio
WSGIProcessGroup wsgi_app
+ WSGIApplicationGroup %{GLOBAL}
WSGISocketPrefix /var/run/wsgi
# service apache2 restart
エラーが発生した場合はApacheのログをみれば原因がわかります
# vi /var/log/apache2/error.log
Cron(タスクスケジューラ)
CronはWindowsでいうタスクスケジューラだ。決まった時間に決まったコマンドを実行してくれる。CentOSとの操作の差はないみたい。
Cron(crontab)の設定
定期実行するプログラムの作成
# cd /var/www/html
# vi hello-cron.py
import codecs
from datetime import datetime
log_file_path = '/var/www/html/hello-cron.log'
txt = datetime.now().strftime("%Y/%m/%d %H:%M:%S") + ' hello-cron.py'
with codecs.open(log_file_path, 'a', 'utf-8') as f:
f.writelines('\n' + txt)
# python3 hello-cron.py
# vi hello-cron.log
2021/08/29 16:10:39 hello-cron.py
Cronの設定
10分ごとに Hello-cron.py を実行するスケジュールを作成します。気をつける点は、pythonプログラムが書き込む場所の権限とpythonプログラム自体へのパス(フルパスなんよね)。あとは相対パスでプログラムを書いている場合の「カレントディレクトリ」に注意。windowsとlinuxのディレクトリ構造は違うことが多いし。
export EDITOR=vi
# vi /etc/environment
VISUAL=/usr/bin/vim
EDITOR=/usr/bin/vim
保存してターミナルに入り直したら恒久的にviになった
# crontab -e
*/10 * * * * root /var/www/html/venv/bin/python /var/www/html/hello-cron.py
0 * * * * root /var/www/html/venv/bin/python /var/www/html/hello-cron.py
* * * * * root /var/www/html/venv/bin/python /var/www/html/hello-cron.py
0 0 1 * * /root/certbot.sh
0 18 * * * /var/www/html/venv/bin/python /var/www/html/portfolio/manage.py daily_import_from_vietkabu
5 18 * * * /var/www/html/venv/bin/python /var/www/html/portfolio/manage.py daily_import_from_sbi
6 18 * * * /var/www/html/venv/bin/python /var/www/html/portfolio/manage.py daily_import_from_bloomberg
15 18 * * * /var/www/html/venv/bin/python /var/www/html/portfolio/manage.py daily_industry_chart_and_uptrend
20 18 * * * /var/www/html/venv/bin/python /var/www/html/portfolio/manage.py daily_industry_stacked_bar_chart
25 18 * * * /var/www/html/venv/bin/python /var/www/html/portfolio/manage.py daily_download_edinet
30 18 * * * /var/www/html/venv/bin/python /var/www/html/portfolio/manage.py fetch_weather_forecast
35 18 * * * /var/www/html/venv/bin/python /var/www/html/portfolio/manage.py fetch_weather_warning
40 18 * * * /var/www/html/venv/bin/python /var/www/html/portfolio/manage.py collectstatic --noinput
15 18 1 * * /var/www/html/venv/bin/python /var/www/html/portfolio/manage.py monthly_fao_food_balance_chart
20 18 1 * * /var/www/html/venv/bin/python /var/www/html/portfolio/manage.py monthly_vietnam_statistics
15 19 1 * * /var/www/html/venv/bin/python /var/www/html/portfolio/manage.py monthly_cleanup_linebot_engine
バッチファイルには実行権限を忘れずに与える
cd /var/www/html/portfolio/vietnam_research/management/commands
chmod +x daily_import_from_vietkabu.py
chmod +x daily_import_from_sbi.py
chmod +x daily_import_from_bloomberg.py
chmod +x daily_industry_chart_and_uptrend.py
chmod +x daily_industry_stacked_bar_chart.py
chmod +x monthly_fao_food_balance_chart.py
chmod +x monthly_vietnam_statistics.py
ls -l
cd /var/www/html/portfolio/soil_analysis/management/commands
chmod +x fetch_weather_forecast.py
chmod +x fetch_weather_warning.py
ls -l
cd /var/www/html/portfolio/linebot_engine/management/commands
chmod +x monthly_cleanup_linebot_engine.py
ls -l
cd /var/www/html/portfolio/home/management/commands
chmod +x monthly_cleanup_home.py
ls -l
# vi hello-cron.log
2020/03/28 02:18:26 hello-cron.py
2020/03/28 02:28:26 hello-cron.py
# chown -R ubuntu:ubuntu /var/www/html
- cronで失敗するのは、staticを置き換える(python manage.py collectstatic)ときに置き換え先のpermissionがrootになってて上書きミスってるのとかがありそう。権限をまとめてubuntu扱いに、を忘れずに
cronを試し打ちしようとしたらこんなエラーが出たよ
(venv) root@ik1-336-28225:/var/www/html# /var/www/html/venv/bin/python /var/www/html/portfolio/manage.py daily_import_from_vietkabu
Traceback (most recent call last): File "/var/www/html/portfolio/manage.py", line 15, in <module> ..."/var/www/html/venv/lib/python3.12/site-packages/fastkml/__init__.py", line 28, in <module> from pkg_resources import
DistributionNotFound ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'pkg_resources'
pip install -U setuptools
Reset(※必要に応じて)
まず各appディレクトリのmigrationsディレクトリを消してまわります- dbを消します(=portfolio_db)
- dbを作ります
※migrationsは .gitignore に含めないで!
上記1番に取り消し線を引いた理由
なんかしらねーけどCIでのテストが通らなくて困っていた
ぼく「もしかしてだけど migrations フォルダを .ignore すると python manage.py test で影響ある?」
gpt「はい、.gitignore に migrations フォルダを含めていると、python manage.py test に影響を与える可能性があります。特に以下のような影響があります」
影響
マイグレーションファイルが存在しない:
migrations フォルダ内にはマイグレーションファイル(例えば 0001_initial.py など)が含まれています。これらのファイルはデータベースのスキーマを管理し、Djangoが適用するマイグレーションの履歴を保持します。もしこのフォルダが .gitignore されていて、CI環境などでマイグレーションファイルが存在しない場合、テスト実行時にデータベーススキーマが適用されず、エラーになります。
テスト用データベースにスキーマが反映されない:
テスト用データベースは、マイグレーションを適用することでスキーマが反映されますが、マイグレーションファイルがないと、Djangoは適切にデータベーススキーマを作成できません。その結果、auth_user のようなテーブルが存在せず、django.db.utils.OperationalError が発生する可能性があります。
解決策
migrations フォルダを .gitignore から外す: 開発やテスト環境で正しく動作するために、migrations フォルダはバージョン管理システムに含めておくことが推奨されます。これにより、CI/CD 環境でも正しいマイグレーションが適用され、テスト用データベースが正しく構築されます。
ぼく「ほんとだ 解決したわ。。。」
ぼく「じゃあdjangoの test コマンドはマイグレーションファイルを作成せずに既存のマイグレーションファイルを利用するということね?(ローカルでうまくいくのは無視されるファイルが存在するから)」
gpt「はい、その通りです。python manage.py test コマンドは、既存のマイグレーションファイルを利用してテスト環境にデータベースをセットアップします。」
gpt「つまり、migrations フォルダにあるマイグレーションファイルがテストの際に使われるため、もしそのフォルダが .gitignore などで無視されていたり、CI環境で存在していないと、マイグレーションが実行されずにエラーが発生する可能性があります。」
gpt「一方で、ローカル環境では .gitignore によって無視されるファイルが存在しているので、マイグレーションが正常に動作しているため、問題なくテストが通るということですね。」
なんで migrations フォルダを .gitignore したの?
ぼく「モデルなんてゴロゴロ変わるからさ!」
migrationとcreatesuperuser
$ cd /var/www/html/portfolio
$ python manage.py makemigrations vietnam_research gmarker shopping linebot_engine warehouse taxonomy soil_analysis securities
$ python3 manage.py migrate
なんか migrationで止まるケースがあって、そのときに root で実行すると通るみたいな状況が発生している ほんとに root 権限が解決しているのかは不明。
いや、一般ユーザでmigrationできた。メモリでVPSが落ちているようだから止まったらサーバーを強制再起動だな
$ python3 manage.py createsuperuser
Email address:
Password:
Password (again):
Superuser created successfully.
確認
djangoがシステム的に作ったテーブルと、アプリケーションを作っていればアプリケーション名が先頭についたテーブルが作成される(赤枠)
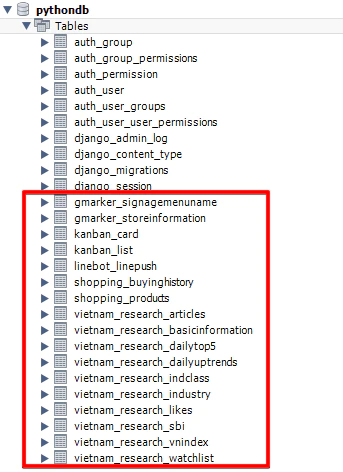
MySQLデータのインポート
https://qiita.com/YoshitakaOkada/items/45ebdc00cc923d970638
リストアのみならこれ
※自分メモ(ローカルからVPSのインポートは事故るから、マイグレーション済んだらsuperuserを手で追加したあと、ダンプからDrop・Create命令を除外したものを作って)
vi /etc/my.cnf
[mysqld]
wait_timeout = 86400
max_allowed_packet = 1G
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 1G
service mysql restart
# mysql -u root -p
mysql> use portfolio_db
mysql> source mysql_dump.sql
権限 chown -R ubuntu:ubuntu /var/www/html
さんざん root のままディレクトリとか作りまくってると access denied というか permission error になってることがあるので注意
FTP
いったんパス もとの記事
Djangoのバッチをつくる
Djangoで自動テストをする
バッチのテストもこっち
Ubuntuのmatplotlib、日本語問題
# sudo apt install -y fonts-ipafont
# ls ~/.cache/matplotlib/
# rm ~/.cache/matplotlib/fontlist-v330.json
# fc-cache -fv
# fc-list | grep -i ipa
/usr/share/fonts/opentype/ipafont-mincho/ipam.ttf: IPAMincho,IPA明朝:style=Regular
/usr/share/fonts/opentype/ipafont-gothic/ipagp.ttf: IPAPGothic,IPA Pゴシック:style=Regular
/usr/share/fonts/opentype/ipafont-mincho/ipamp.ttf: IPAPMincho,IPA P明朝:style=Regular
/usr/share/fonts/opentype/ipafont-gothic/ipag.ttf: IPAGothic,IPAゴシック:style=Regular
/usr/share/fonts/truetype/fonts-japanese-mincho.ttf: IPAMincho,IPA明朝:style=Regular
/usr/share/fonts/truetype/fonts-japanese-gothic.ttf: IPAGothic,IPAゴシック:style=Regular
font_path = '/usr/share/fonts/opentype/ipafont-mincho/ipam.ttf'
if Path.exists(Path(font_path).resolve()):
# for ubuntu jp font
plt.legend(loc='upper left', labels=df.columns, prop={"family": "IPAMincho"})
else:
plt.legend(loc='upper left', labels=df.columns, prop={"family": "MS Gothic"})
windowsにも入れちゃったほうがいいや
PdfMiner
- SBI topics で使用している
- pdfminer.six へライブラリを変更したら解決した
pip install pdfminer.six
CI環境を整える
Djangoプロジェクトを新規で始める場合
Djangoインストール
# source /var/www/html/venv/bin/activate
# pip3 install django
# django-admin --version
4.0.2
pip list
# pip list
Package Version
------------- -------
asgiref 3.4.1
Django 4.0.2
mod-wsgi 4.9.0
pip 20.0.2
pkg-resources 0.0.0
pytz 2021.1
setuptools 44.0.0
sqlparse 0.4.1
よく使うライブラリ
# pip3 install wheel numpy pandas sqlalchemy beautifulsoup4 matplotlib pillow lxml stripe
# chown -R ubuntu:ubuntu /var/www/html
わかりやすいプロジェクト構成
新規作成時のみ
- ベースディレクトリ名と設定ディレクトリ名が同じでややこしい
- テンプレートと静的ファイルがアプリケーションごとにバラバラに配置されてしまう
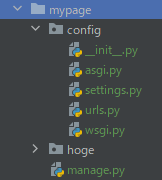
これらを解決する。ベースディレクトリを作成したあとにベースディレクトリの下に移動し、設定ディレクトリ名と . を指定する
$ mkdir mypage
$ cd mypage
$ django-admin startproject config .
$ python manage.py startapp hoge
$ python manage.py runserver
settings.py
ALLOWED_HOSTS(許可するドメイン)を編集する
# vi /var/www/html/portfolio/config/settings.py
- ALLOWED_HOSTS = []
+ ALLOWED_HOSTS = ['.henojiya.net', '127.0.0.1', 'localhost', '153.126.200.229']
loggerを有効にする(loggingモジュールでコンソールに情報が出せるようになる)
:
LOGGING = {
"version": 1,
"disable_existing_loggers": False,
"handlers": {
"console": {
"class": "logging.StreamHandler",
},
},
"root": {
"handlers": ["console"],
"level": "INFO",
},
}
mysqlclient
(venv)# apt -y install build-essential libssl1.1 libssl1.1=1.1.1f-1ubuntu2 libssl-dev libmysqlclient-dev
(venv)# pip3 install mysqlclient environ
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.sqlite3',
'NAME': BASE_DIR / 'db.sqlite3',
}
}
DATABASES = {
'default': {
- 'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.sqlite3',
- 'NAME': BASE_DIR / 'db.sqlite3',
+ 'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql',
+ 'NAME': 'portfolio_db',
+ 'USER': 'python',
+ 'PASSWORD': 'python123',
}
}
# service apache2 restart
Django
ログイン機能
セットアップのタイミング的にここに書いておくけどアプリケーション作るのに慣れてからやること。ログイン機能は、ログイン機能としてのアプリケーションを別個につくるのがベスト・プラクティスだ。
Reset(※必要に応じて)
- まず各appディレクトリのmigrationsディレクトリを消してまわります
- dbを消します(=portfolio_db)
- dbを作ります
startapp
# cd /var/www/html/portfolio
# python3 manage.py startapp register
from django.db import models
from django.core.mail import send_mail
from django.contrib.auth.models import PermissionsMixin, UserManager
from django.contrib.auth.base_user import AbstractBaseUser
from django.utils.translation import ugettext_lazy as _
from django.utils import timezone
class CustomUserManager(UserManager):
"""ユーザーマネージャー"""
use_in_migrations = True
def _create_user(self, email, password, **extra_fields):
if not email:
raise ValueError('The given email must be set')
email = self.normalize_email(email)
user = self.model(email=email, **extra_fields)
user.set_password(password)
user.save(using=self._db)
return user
def create_user(self, email, password=None, **extra_fields):
extra_fields.setdefault('is_staff', False)
extra_fields.setdefault('is_superuser', False)
return self._create_user(email, password, **extra_fields)
def create_superuser(self, email, password, **extra_fields):
extra_fields.setdefault('is_staff', True)
extra_fields.setdefault('is_superuser', True)
if extra_fields.get('is_staff') is not True:
raise ValueError('Superuser must have is_staff=True.')
if extra_fields.get('is_superuser') is not True:
raise ValueError('Superuser must have is_superuser=True.')
return self._create_user(email, password, **extra_fields)
class User(AbstractBaseUser, PermissionsMixin):
"""カスタムユーザーモデル."""
email = models.EmailField(_('email address'), unique=True)
first_name = models.CharField(_('first name'), max_length=30, blank=True)
last_name = models.CharField(_('last name'), max_length=150, blank=True)
is_staff = models.BooleanField(
_('staff status'),
default=False,
help_text=_(
'Designates whether the user can log into this admin site.'),
)
is_active = models.BooleanField(
_('active'),
default=True,
help_text=_(
'Designates whether this user should be treated as active. '
'Unselect this instead of deleting accounts.'
),
)
date_joined = models.DateTimeField(_('date joined'), default=timezone.now)
objects = CustomUserManager()
EMAIL_FIELD = 'email'
USERNAME_FIELD = 'email'
REQUIRED_FIELDS = []
class Meta:
verbose_name = _('user')
verbose_name_plural = _('users')
def get_full_name(self):
"""Return the first_name plus the last_name, with a space in
between."""
full_name = '%s %s' % (self.first_name, self.last_name)
return full_name.strip()
def get_short_name(self):
"""Return the short name for the user."""
return self.first_name
def email_user(self, subject, message, from_email=None, **kwargs):
"""Send an email to this user."""
send_mail(subject, message, from_email, [self.email], **kwargs)
@property
def username(self):
"""username属性のゲッター
他アプリケーションが、username属性にアクセスした場合に備えて定義
メールアドレスを返す
"""
return self.email
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
+ 'register.apps.RegisterConfig',
]
+ # login
+ LOGIN_URL = 'register:login'
+ LOGIN_REDIRECT_URL = 'vnm:index' #ログイン後にリダイレクトしたい先
+ LOGOUT_REDIRECT_URL = "vnm:index" #ログアウト後にリダイレクトしたい先
+ AUTH_USER_MODEL = 'register.User'
# mkdir -p templates/register
# vi templates/register/base.html
{% load static %}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="ja">
<head>
<!-- Global site tag (gtag.js) - Google Analytics -->
<script async src="https://www.googletagmanager.com/gtag/js?id=UA-43097095-9"></script>
<script>
window.dataLayer = window.dataLayer || [];
function gtag(){dataLayer.push(arguments);}
gtag('js', new Date());
gtag('config', 'UA-43097095-9');
</script>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>VNMビューア</title>
<!-- css -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static 'register/css/reset.css' %}">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static 'register/css/index.css' %}">
<!-- font -->
<link href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Sawarabi+Gothic" rel="stylesheet">
<!-- fontawesome -->
<link href="https://use.fontawesome.com/releases/v5.6.1/css/all.css" rel="stylesheet">
<!-- favicon -->
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="{% static 'register/images/c_r.ico' %}">
</head>
<body>
<!-- nav -->
<h1></h1>
<div id="main">
{% block content %}{% endblock %}
</div>
<footer>
<p>© 2019 henojiya. / <a href="https://github.com/duri0214" target="_blank">github portfolio</a></p>
</footer>
</body>
</html>
"""views.py"""
from django.conf import settings
from django.contrib.auth import get_user_model
from django.contrib.auth.views import LoginView, LogoutView
from django.contrib.sites.shortcuts import get_current_site
from django.core.signing import BadSignature, SignatureExpired, loads, dumps
from django.http import HttpResponseBadRequest
from django.shortcuts import redirect
from django.template.loader import render_to_string
from django.views import generic
from .forms import UserCreateForm
# signup
class UserCreate(generic.CreateView):
"""ユーザー仮登録"""
template_name = 'register/user_create.html'
form_class = UserCreateForm
def form_valid(self, form):
"""仮登録と本登録用メールの発行."""
# 仮登録と本登録の切り替えは、is_active属性を使うと簡単です。
# 退会処理も、is_activeをFalseにするだけにしておくと捗ります。
user = form.save(commit=False)
user.is_active = False
user.save()
# アクティベーションURLの送付
current_site = get_current_site(self.request)
domain = current_site.domain
context = {
'protocol': self.request.scheme,
'domain': domain,
'token': dumps(user.pk),
'user': user,
}
folder = settings.BASE_DIR + '/register/templates/register/mail_template/'
subject = render_to_string(folder + 'subject.txt', context)
message = render_to_string(folder + 'message.txt', context)
user.email_user(subject, message)
return redirect('register:user_create_done')
class UserCreateDone(generic.TemplateView):
"""ユーザー仮登録したよ"""
template_name = 'register/user_create_done.html'
class UserCreateComplete(generic.TemplateView):
"""メール内URLアクセス後のユーザー本登録"""
template_name = 'register/user_create_complete.html'
timeout_seconds = getattr(settings, 'ACTIVATION_TIMEOUT_SECONDS', 60*60*24) # デフォルトでは1日以内
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""tokenが正しければ本登録."""
token = kwargs.get('token')
try:
user_pk = loads(token, max_age=self.timeout_seconds)
# 期限切れ
except SignatureExpired:
return HttpResponseBadRequest()
# tokenが間違っている
except BadSignature:
return HttpResponseBadRequest()
# tokenは問題なし
else:
try:
user = get_user_model().objects.get(pk=user_pk)
except get_user_model().DoesNotExist:
return HttpResponseBadRequest()
else:
if not user.is_active:
# 問題なければ本登録とする
user.is_active = True
user.save()
return super().get(request, **kwargs)
return HttpResponseBadRequest()
class Login(LoginView):
"""ログインページ"""
template_name = 'register/login.html'
"""forms.py"""
from django.contrib.auth.forms import UserCreationForm
from django.contrib.auth import get_user_model
class UserCreateForm(UserCreationForm):
"""ユーザー登録用フォーム"""
class Meta:
model = get_user_model()
fields = ('email',)
def clean_email(self):
"""clean_email"""
email = self.cleaned_data['email']
get_user_model().objects.filter(email=email, is_active=False).delete()
return email
{% extends "register/base.html" %}
{% block content %}
<div class="card col-md-6">
<div class="card-body">
<form action="{% url 'register:login' %}" method="POST">
{{ form.non_field_errors }}
{% for field in form %}
{{ field }}
{{ field.errors }}
<hr>
{% endfor %}
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-success btn-lg btn-block" >ログイン</button>
<input type="hidden" name="next" value="{{ next }}" />
{% csrf_token %}
</form>
</div>
</div>
<div class="">
<div class="card-body">
<a href="{% url 'register:user_create' %}" class="" >会員登録</a>
</div>
</div>
{% endblock %}
"""urls.py"""
from django.urls import path
from . import views
from django.contrib.auth.views import LoginView, LogoutView
app_name = 'register'
urlpatterns = [
path('login/', LoginView.as_view(template_name='register/login.html'), name='login'),
path('logout/', LogoutView.as_view(), name='logout'),
path('user_create/', views.UserCreate.as_view(), name='user_create'),
path('user_create/done', views.UserCreateDone.as_view(), name='user_create_done'),
path('user_create/complete/<str:token>/', views.UserCreateComplete.as_view(), name='user_create_complete'),
]
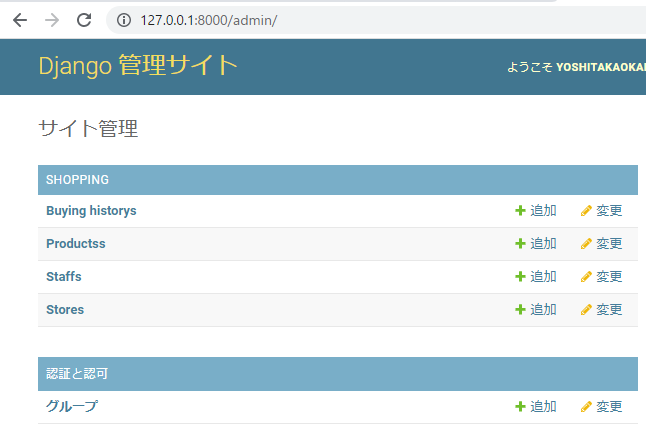
admin管理画面にテーブルを追加表示する
実体としてどれだけテーブルがあろうと、管理画面には表示されないので設定する必要がある。
from django.contrib import admin
+ from .models import Staff, Store, Products, BuyingHistory
# Register your models here.
+ admin.site.register(Staff)
+ admin.site.register(Store)
+ admin.site.register(Products)
+ admin.site.register(BuyingHistory)
Djangoアプリケーションの新規作成
# cd /var/www/html/portfolio
# python3 manage.py startapp vietnam_research
非公開情報を.envに移す(GitGuardian対策)
view作成
# vi vietnam_research/views.py
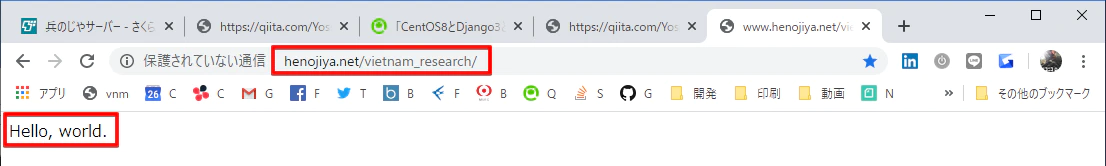
from django.http import HttpResponse
def index(request):
return HttpResponse("Hello, world.")
settings.py
# vi config/settings.py
INSTALLED_APPS = [
...,
'vietnam_research.apps.VietnamResearchConfig'
]
httpd.conf(wsgi.conf)
staticディレクトリ配下は開放。
※あくまで DEBUG = True のときの設定です。慣れてきて DEBUG = False にするときは こっち を参照
# vi /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/000-default.conf
+ # css, javascript etc
+ Alias /static/ /var/www/html/portfolio/static/
+ <Directory /var/www/html/portfolio/static>
+ Require all granted
+ </Directory>
# systemctl restart apache2
vietnam_research/urls.py を編集
URLの紐づけをロケットアニメのHelloWorldから変えるために、urls.py を新規作成する(作る場所は「vietnam_research」フォルダ)。便宜上「子供のurls.py」と呼ぶことがある。「urls.py」には「s」をつけろよデコ助野郎。
from django.urls import path
# 現在のフォルダの「views.py」を import する!さっき "Hello, world." したやつ!
from . import views
# views.py には「index」という関数を作りましたね!それを呼んでます
urlpatterns = [
path('', views.index, name='index'),
]
urls.py(共通Configのほう)
NTTの配電盤みたいなイメージね。便宜上「親のurls.py」と呼ぶことがある。(※この英語部分もよく読むと実はさっき子供のurls.pyに書いたようなことをやれって書いてあったりする)
"""portfolio URL Configuration
The `urlpatterns` list routes URLs to views. For more information please see:
https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.2/topics/http/urls/
Examples:
Function views
1. Add an import: from my_app import views
2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: path('', views.home, name='home')
Class-based views
1. Add an import: from other_app.views import Home
2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: path('', Home.as_view(), name='home')
Including another URLconf
1. Import the include() function: from django.urls import include, path
2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: path('blog/', include('blog.urls'))
"""
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import include, path
urlpatterns = [
path('vietnam_research/', include('vietnam_research.urls')),
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
]
# systemctl restart apache2
HelloWorld!
model.py
ここはデータベースとテーブルの話だからね。好きにやってちょうだい
"""このファイル内に、必要なテーブルがすべて定義されます"""
from django.db import models
class Industry(models.Model):
"""
viet-kabuで取得できる業種つき個社情報
closing_price: 終値(千ドン)
volume: 出来高(株)
trade_price_of_a_day: 売買代金(千ドン)
marketcap: 時価総額(億円)
"""
market_code = models.CharField(max_length=4)
symbol = models.CharField(max_length=10)
company_name = models.CharField(max_length=50)
industry1 = models.CharField(max_length=10)
industry2 = models.CharField(max_length=20)
open_price = models.DecimalField(max_digits=10, decimal_places=2, default=0.00)
high_price = models.DecimalField(max_digits=10, decimal_places=2, default=0.00)
low_price = models.DecimalField(max_digits=10, decimal_places=2, default=0.00)
closing_price = models.DecimalField(max_digits=10, decimal_places=2, default=0.00)
volume = models.DecimalField(max_digits=10, decimal_places=2, default=0.00)
trade_price_of_a_day = models.DecimalField(max_digits=20, decimal_places=2, default=0.00)
marketcap = models.DecimalField(max_digits=10, decimal_places=2, default=0.00)
per = models.DecimalField(max_digits=10, decimal_places=2, default=0.00)
pub_date = models.DateField()
migrations
makemigrationsは台帳登録みたいなイメージ
# python3 manage.py makemigrations vietnam_research
migrate
migrateは「実効」みたいなイメージ
# python3 manage.py migrate
Operations to perform:
Apply all migrations: admin, auth, contenttypes, sessions
Running migrations:
Applying contenttypes.0001_initial... OK
Applying auth.0001_initial... OK
Applying admin.0001_initial... OK
Applying admin.0002_logentry_remove_auto_add... OK
Applying admin.0003_logentry_add_action_flag_choices... OK
Applying contenttypes.0002_remove_content_type_name... OK
Applying auth.0002_alter_permission_name_max_length... OK
Applying auth.0003_alter_user_email_max_length... OK
Applying auth.0004_alter_user_username_opts... OK
Applying auth.0005_alter_user_last_login_null... OK
Applying auth.0006_require_contenttypes_0002... OK
Applying auth.0007_alter_validators_add_error_messages... OK
Applying auth.0008_alter_user_username_max_length... OK
Applying auth.0009_alter_user_last_name_max_length... OK
Applying auth.0010_alter_group_name_max_length... OK
Applying auth.0011_update_proxy_permissions... OK
Applying sessions.0001_initial... OK
アプリケーションとして認識させる
(このステップ忘れるべからず)
このsettingでアプリケーションとして認識させることで、index.htmlを開きにいったときの「templates/{アプリケーション名}/index.html」を自動的に識別して読みにいってくれる。
DjangoでTemplateDoesNotExistと言われたら
「各アプリケーションの配下にあるtemplatesディレクトリ」を探索するということは、アプリケーションと認識されていなければ探索されないということだ。
今回はそもそもここに原因があった。settings.pyのINSTALLED_APPSにmyappを登録するのを忘れていた。
INSTALLED_APPS に設定を追加するんだが、、え?VietnamResearchConfigに覚えがないって?
そうなんだよ、アプリケーションフォルダ(test_chartjs)配下にある、「apps.py」を開いてみると書いてあるんだよね。わかりにくいなぁこれ。
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
+ 'test_chartjs.apps.VietnamResearchConfig',
]
templates ディレクトリを作成
最初に、アプリケーションフォルダの中に「templates」フォルダを作成。さらにその中に、(Djangoのテンプレート読み込みルールに則り)アプリケーションフォルダと同じ名前のフォルダを作成してから index.html というファイルを作成する。
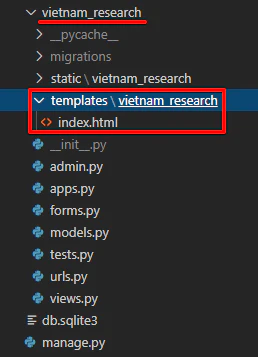
つまり、テンプレートは「vietnam_research/templates/vietnam_research/index.html」に書く必要がある。「テンプレートフォルダのなかにアプリケーション名がある」というの自体はほかのWeb言語にもあったような気がする?![]()
これは文化的なもので「名前空間」という意味合いに過ぎない。
「templates」には「s」をつけろよデコ助野郎。
テンプレートを編集
vscodeのhtmlファイル上で「!」って入力すると、vscodeのちょっとした機能でこのテンプレートが出てくる。すごい
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="ja">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>vietnam_research</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>vietnam_research</h1>
</body>
</html>
static ディレクトリを作成
- static(黄色の四角)
- static/vietnam_research(オレンジ)
- static/vietnam_research/js
などのフォルダやファイルは、手で作る必要があります。
(templateと同じ階層にstaticをつくります)
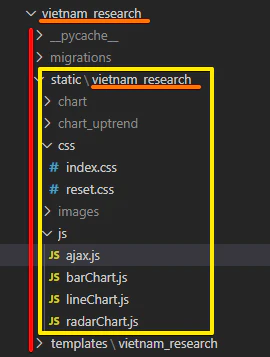
- htmlの最初に {% load static %} を忘れるな!
- javascript を読み込むときのパスは {% static 'vietnam_research/js/script.js' %} だ
- このフォルダの「指定方法」と「そしてどうなる」を脳筋になるまで繰り返して感覚をつかめ!
google analytics
headタグの一番最初に取り付ける
<!-- Global site tag (gtag.js) - Google Analytics -->
<script async src="https://www.googletagmanager.com/gtag/js?id=UA-43097095-9"></script>
<script>
window.dataLayer = window.dataLayer || [];
function gtag(){dataLayer.push(arguments);}
gtag('js', new Date());
gtag('config', 'UA-43097095-9');
</script>
index.html
{% load static %}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="ja">
<head>
<!-- Global site tag (gtag.js) - Google Analytics -->
<script async src="https://www.googletagmanager.com/gtag/js?id=UA-43097095-9"></script>
<script>
window.dataLayer = window.dataLayer || [];
function gtag(){dataLayer.push(arguments);}
gtag('js', new Date());
gtag('config', 'UA-43097095-9');
</script>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>shopping</title>
<!-- css -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static 'vietnam_research/css/reset.css' %}">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static 'vietnam_research/css/index.css' %}">
<!-- favicon -->
<link rel="icon" href="{% static 'vietnam_research/c_v.ico' %}">
<!-- javascript -->
<script src="{% static 'vietnam_research/js/script.js' %}"></script>
<!-- font -->
<link href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Sawarabi+Gothic" rel="stylesheet">
<!-- fontawesome -->
<link href="https://use.fontawesome.com/releases/v5.6.1/css/all.css" rel="stylesheet">
<!-- for ajax -->
<script>let myurl = {"base": "{% url 'vnm:index' %}"}</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>vietnam_research</h1>
</body>
</html>
views.pyがテンプレートへ向けて置換をかけて返却する流れを作る
"""views.py"""
from django.shortcuts import render
def index(request):
"""いわばhtmlのページ単位の構成物です"""
# htmlとして返却します
return render(request, 'vietnam_research/index.html')
ローカル環境でのテスト
フォームでのファイルアップロードを実装する
いやー stackoverflowで質問しても 回答つかなくて困った困った。settings.pyの MEDIA の役割がわかってなかったんだよね。
# これの追記で permissionerror 回避を確認ok
MEDIA_ROOT = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'media')
MEDIA_URL = '/media/'
上記の settings.py の追記に加えて、下記のように models.py で upload_to='shopping/ にすると、[example.com]/media/shopping/xxx.jpg と保存されるようになる
class Products(models.Model):
"""商品"""
code = models.CharField('商品コード', max_length=200)
name = models.CharField('商品名', max_length=200)
price = models.IntegerField('金額', default=0)
description = models.TextField('説明')
picture = models.ImageField('商品写真', upload_to='shopping/')
class UploadSingleView(FormView):
"""UploadSingleView"""
form_class = SingleRegistrationForm
success_url = reverse_lazy('shp:index')
def form_valid(self, form):
# prepare
code = form.cleaned_data.get('code')
Products.objects.filter(code=code).delete()
# save
form.save()
# delete if file is exists as same.
orgname, ext = os.path.splitext(form.cleaned_data["picture"].name)
mvfilepath = settings.BASE_DIR + '/shopping/static/shopping/img/' + code + ext.lower()
if os.path.exists(mvfilepath):
os.remove(mvfilepath)
# move file as rename
uploadfilepath = settings.BASE_DIR + '/media/shopping/' + orgname + ext.lower()
os.rename(uploadfilepath, mvfilepath)
return super().form_valid(form)
DEBUGをFalseにしてみて?
公式:本番環境における静的ファイルの配信
DEBUGをTrueにしているあいだは気にすることはないが、本番環境にしようとしてDEBUGをFalseにすると /static/ (settings.pyのSTATIC_URL)は各アプリケーション内のstaticディレクトリを読みにいきません。
(非効率であったり、セキュリティ上の理由らしい)
DEBUG = False
パス参考:/var/www/html/portfolio/static/
STATIC_ROOT = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, "static")
# python3 manage.py collectstatic
# chown -R ubuntu:ubuntu /var/www/html
# systemctl restart apache2