はじめに
TypeScript を使っていて「tsconfig.json の設定がよくわからない...」と感じたことはありませんか?
特にtarget / lib / moduleの三つの設定項目は、TypeScriptの動作を大きく左右する重要な設定ですが、それぞれの違いや使い分けが分かりにくいですよね。
この記事では、実際のサンプルコードを使いながら、これら3つの設定項目の役割を整理します。
開発環境
開発環境は以下の通りです。
- Windows11
- TypeScript 5.9.2
- Node.js 22.18.0
- npm 11.5.2
結論
| 設定項目 | 役割 | 設定値の例 |
|---|---|---|
| target | コンパイルする JavaScript のバージョン |
ES2020, ES2024
|
| lib | 利用する JavaScript API |
ES2022, DOM
|
| module | 利用するモジュールシステム |
ESNext, CommonJS
|
1. target:コンパイル後の JavaScript バージョンを決める
targetは「TypeScript をどのバージョンの JavaScript にコンパイルするか」を指定します。
サンプルコード
今回は、target に ES5 (ECMAScript 5) と ES2024 (ECMAScript 2024) を設定して、動作確認をします。
以下の TypeScript コードをコンパイルして確認します。
コードには、複数の JavaScript バージョンの機能が含まれています。target 設定によって TypeScript がどのように異なる JavaScript コードへ変換されるか確認します。
const users = ["Alice", "Bob", "Charlie"];
// Optional chaining(ES2020の機能)
const user = { profile: { name: "Alice" } };
const userName = user?.profile?.name;
// Arrow function
const getMessage = (name: string) => `Hello, ${name}!`;
// Array.includes(ES2016の機能)
const hasAlice = users.includes("Alice");
console.log(userName, getMessage("World"), hasAlice);
target: "ES5" の場合
古い JavaScript (ES5)バージョンに対応するため、新しい構文がどう変換されるかを確認します。
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "ES5"
}
}
コンパイル結果は、以下の通りです。
var _a;
var users = ["Alice", "Bob", "Charlie"];
// Optional chaining(ES2020の機能)
var user = { profile: { name: "Alice" } };
var userName = (_a = user === null || user === void 0 ? void 0 : user.profile) === null || _a === void 0 ? void 0 : _a.name;
// Arrow function
var getMessage = function (name) { return "Hello, ".concat(name, "!"); };
// Array.includes(ES2016の機能)
var hasAlice = users.includes("Alice");
console.log(userName, getMessage("World"), hasAlice);
変換された部分の詳細は以下の通りです。
-
const→var: ES5 ではconstが存在しないため -
Optional chaining: 複雑な条件分岐とヘルパー変数(_a)で安全にアクセス -
Arrow function→function: ES5 の関数定義に変換 -
Template literal→.concat(): ES5の文字列結合メソッドに変換 -
Array.includes: そのまま残る(ポリフィルが必要)
target: "ES2024" の場合
最新の JavaScript バージョンの設定で、現在の構文がそのまま残ることを確認します。
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "ES2024"
}
}
コンパイル結果は、以下の通りです。
const users = ["Alice", "Bob", "Charlie"];
// Optional chaining(ES2020の機能)
const user = { profile: { name: "Alice" } };
const userName = user?.profile?.name; // そのまま残る
const getMessage = (name) => `Hello, ${name}!`; // そのまま残る
// Array.includes(ES2016の機能)
const hasAlice = users.includes("Alice"); // そのまま残る
console.log(userName, getMessage("World"), hasAlice);
ES2024 で利用可能な機能がそのまま残っています。
このように target の設定値によって、コンパイル後の JavaScript が変わります。
2. lib:使用可能なAPIを指定する
lib は「どの JavaScript API や DOM API を使えるようにするか」を指定します。
DOM操作のサンプル
lib 設定によって TypeScript の型チェック対象となる API が変わることを確認します。
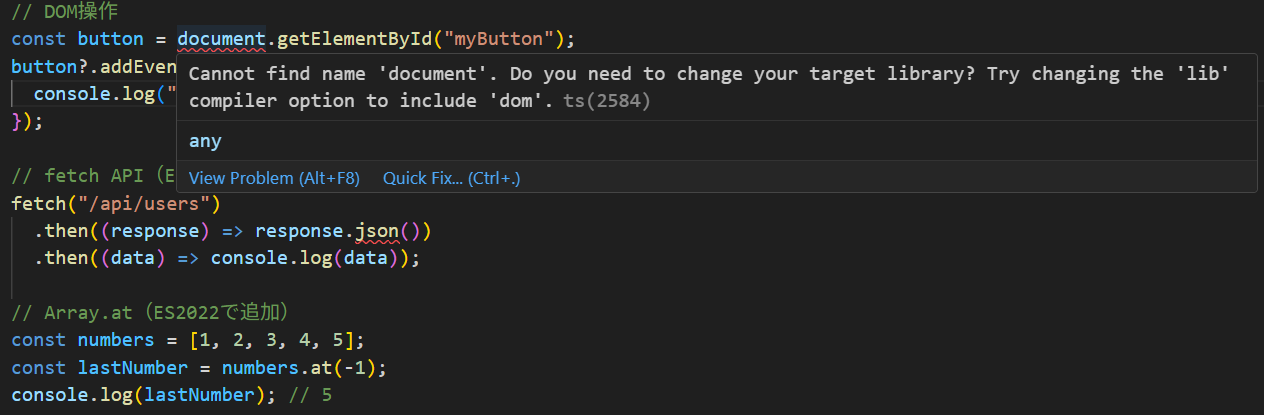
// DOM操作
const button = document.getElementById('myButton');
button?.addEventListener('click', () => {
console.log('Clicked!');
});
// fetch API(ES2017で追加)
fetch('/api/users')
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => console.log(data));
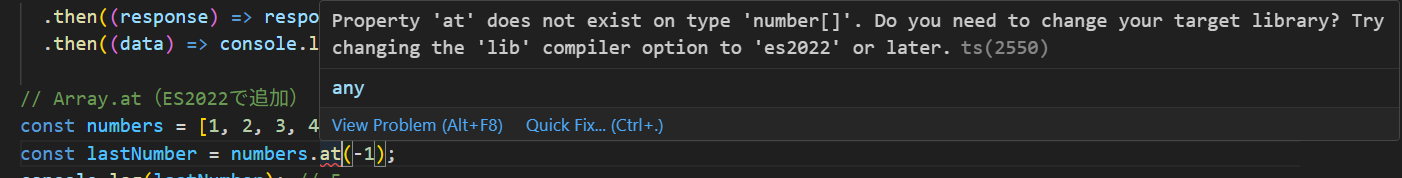
// Array.at(ES2022で追加)
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const lastNumber = numbers.at(-1);
console.log(lastNumber); // 5
lib指定なし(デフォルト)
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "ES2020"
// libの指定なし
}
}
この場合、target に基づいて自動的に lib が決まります。
-
target: "ES2020"→lib: ["ES2020"]が自動設定 -
問題点:
Array.atで TypeScript エラーが発生
lib: ["ES2022", "DOM"] を指定
適切な lib 設定により、必要な API が使用可能になることを確認します。
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "ES2020",
"lib": ["ES2022", "DOM"]
}
}
結果:
- DOM API(
document、addEventListenerなど)が使える - fetch API が使える
-
Array.atが使える - TypeScript エラーが解消される
3. module:モジュールシステムを指定する
module は「出力される JavaScript でどのモジュールシステムを使うか」を指定します。
モジュールシステムとは、TypeScript(または JavaScript)のコード内で、あるファイルが別のファイル(モジュール)の機能や変数を利用するためのルールと構文の集合のことです。コードを分割し、整理し、依存関係を管理するための仕組みであり、主に CommonJS (CJS) と ES Modules (ESM) の2種類があります。
モジュールのサンプル
module 設定によって、同じ TypeScript コードが異なるモジュール形式の JavaScript に出力されることを確認します。
export const add = (a: number, b: number) => a + b;
export const multiply = (a: number, b: number) => a * b;
export default class Calculator {
calculate(a: number, b: number, operation: "+" | "*") {
return operation === "+" ? add(a, b) : multiply(a, b);
}
}
import Calculator, { add, multiply } from "./math";
const calc = new Calculator();
console.log(add(2, 3)); // 5
console.log(multiply(4, 5)); // 20
console.log(calc.calculate(10, 20, "+")); // 30
module: "CommonJS" の場合
TypeScript の ES モジュール構文(import / export)が CommonJS 形式(require / exports)にどのように変換されるか確認します。
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "ES2024",
"module": "CommonJS"
}
}
math.js は以下の通りです。
"use strict";
Object.defineProperty(exports, "__esModule", { value: true });
exports.multiply = exports.add = void 0;
const add = (a, b) => a + b;
exports.add = add;
const multiply = (a, b) => a * b;
exports.multiply = multiply;
class Calculator {
calculate(a, b, operation) {
return operation === "+" ? (0, exports.add)(a, b) : (0, exports.multiply)(a, b);
}
}
exports.default = Calculator;
-
export const add→exports.add = add:名前付きエクスポートがexports割り当てに変換 -
export default class→exports.default = Calculator:デフォルトエクスポートがexports.defaultに変換 -
"use strict"と__esModuleフラグが自動追加される
index.js は以下の通りです。
"use strict";
Object.defineProperty(exports, "__esModule", { value: true });
const math_1 = require("./math");
const calc = new math_1.default();
console.log((0, math_1.add)(2, 3)); // 5
console.log((0, math_1.multiply)(4, 5)); // 20
console.log(calc.calculate(10, 20, "+")); // 30
-
import Calculator, { add } from './math'→const math_1 = require("./math"):import が require に変換 - デフォルトインポート →
math_1.defaultでアクセス - 名前付きインポート →
math_1.addでアクセス、関数呼び出し時は(0, math_1.add)()形式
module: "nodenext"の場合
TypeScript の ES モジュール構文がそのまま ES モジュール形式で出力されることを確認します。
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "ES2024",
"module": "nodenext",
"moduleResolution": "nodenext"
}
}
math.js は以下の通りです。
export const add = (a, b) => a + b;
export const multiply = (a, b) => a * b;
export default class Calculator {
calculate(a, b, operation) {
return operation === "+" ? add(a, b) : multiply(a, b);
}
}
index.js は以下の通りです。
import Calculator, { add, multiply } from "./math";
const calc = new Calculator();
console.log(add(2, 3)); // 5
console.log(multiply(4, 5)); // 20
console.log(calc.calculate(10, 20, "+")); // 30
TypeScript の ES モジュール構文がそのまま残り、export、export default、import が変換されずに出力されます。
まとめ
tsconfig.json の target / lib / module は、TypeScript の動作を決定する重要な設定項目です。
target はコンパイル後の JavaScript のバージョンを指定し、ES5 では古い構文に、ES2024 では新しい構文に変換されます。lib は型チェックで使用する JavaScript や DOM の API を定義し、記述がないと必要な API の型情報が不足しエラーになる可能性があります。module は出力される JavaScript のモジュール形式を指定し、CommonJS や nodenext などの形式を選択できます。
これらの設定を適切に行うことで、TypeScript のコンパイル結果を開発環境や実行環境に合わせて細かく制御できます。