CSGAdventCalendar最終日です。
ChainerRLを使ってブロック崩しの学習をさせるチュートリアルをやりました。
実装はGoogleColaboratoryを使いました。
ChainerRLとは
Chainerを使って実装していた深層強化学習アルゴリズムを”ChainerRL”というライブラリとしてまとめて公開したもの。
以下のような最近の深層強化学習アルゴリズムを共通のインタフェースで使えるよう実装している。
- Deep Q-Network (Mnih et al., 2015)
- Double DQN (Hasselt et al., 2016)
- Normalized Advantage Function (Gu et al., 2016)
- (Persistent) Advantage Learning (Bellemare et al., 2016)
- Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (Lillicrap et al., 2016)
- SVG(0) (Heese et al., 2015)
- Asynchronous Advantage Actor-Critic (Mnih et al., 2016)
- Asynchronous N-step Q-learning (Mnih et al., 2016)
- Actor-Critic with Experience Replay (Wang et al., 2017)
- etc.
準備
ChainerRLのインストール
!apt-get -qq -y update
# Install Chainer and CuPy!
!apt-get -qq -y install libcusparse8.0 libnvrtc8.0 libnvtoolsext1 > /dev/null
!ln -snf /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libnvrtc-builtins.so.8.0 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libnvrtc-builtins.so
!pip install cupy-cuda80 chainer
# Install ChainerRL and OpenAI Gym
!apt-get -qq -y install xvfb freeglut3-dev ffmpeg cmake swig zlib1g-dev> /dev/null
!pip -q install chainerrl atari-py gym 'gym[atari]' 'gym[box2d]' pyglet pyopengl pyvirtualdisplay
Google driveとの接続
atari のゲームを DQNで学習させると、とても時間がかかります。そのため、Google drive に経過を保存できるようする。
次のコードセルを実行し、以下の手順で Google アカウントの認証を行います。
- URLが表示されるのでそれをクリック
- Google アカウントにログイン
- 表示されるトークンをコピー
- このノートに戻って、テキストボックスにそのトークンを貼り付け
- 再度URLが表示されるのでそれをクリック
- このノートに戻って、テキストボックスにそのトークンを貼り付け
!apt-get install -y -qq software-properties-common python-software-properties module-init-tools > /dev/null
!add-apt-repository -y ppa:alessandro-strada/ppa 2>&1 > /dev/null
!apt-get update -qq 2>&1 > /dev/null
!apt-get -y install -qq google-drive-ocamlfuse fuse > /dev/null
from google.colab import auth
auth.authenticate_user()
# Generate creds for the Drive FUSE library.
from oauth2client.client import GoogleCredentials
creds = GoogleCredentials.get_application_default()
import getpass
!google-drive-ocamlfuse -headless -id={creds.client_id} -secret={creds.client_secret} < /dev/null 2>&1 | grep URL
vcode = getpass.getpass()
!echo {vcode} | google-drive-ocamlfuse -headless -id={creds.client_id} -secret={creds.client_secret}
!mkdir -p drive
!google-drive-ocamlfuse drive
環境の準備
import chainer
from chainer import functions as F
from chainer import links as L
import chainerrl
from chainerrl.envs import ale
import numpy as np
chainerrl.experiments.prepare_output_dir ではログ出力のディレクトリを設定します。
ale.ALEで環境を作ります。学習用の環境と、バリデーション用の環境を作ります。
また、学習用の環境は、報酬を -1〜1の範囲にクリップするため、chainerrl.misc.env_modifiers.make_reward_clippedを呼び出します。
outdir = chainerrl.experiments.prepare_output_dir(None, "drive/dqn_out")
ROM = "breakout"
TRAIN_SEED = 0
TEST_SEED = 2 ** 16 - 1 - TRAIN_SEED
env = ale.ALE(ROM, use_sdl=False, seed=TRAIN_SEED)
chainerrl.misc.env_modifiers.make_reward_clipped(env, -1, 1)
eval_env = ale.ALE(ROM, use_sdl=False,
treat_life_lost_as_terminal=False,
seed=TEST_SEED)
n_actions = env.number_of_actions
q_func = chainerrl.links.Sequence(
chainerrl.links.NatureDQNHead(),
L.Linear(512, n_actions),
chainerrl.action_value.DiscreteActionValue)
# Use the same hyper parameters as the Nature paper's
optimizer = chainer.optimizers.RMSpropGraves(lr=2.5e-4, alpha=0.95, momentum=0.0, eps=1e-2)
optimizer.setup(q_func)
rbuf = chainerrl.replay_buffer.ReplayBuffer(10 ** 6)
explorer = chainerrl.explorers.LinearDecayEpsilonGreedy(
1.0, 0.1,
10 ** 6,
lambda: np.random.randint(n_actions))
# In testing DQN, randomly select 5% of actions
eval_explorer = chainerrl.explorers.ConstantEpsilonGreedy(5e-2, lambda: np.random.randint(n_actions))
def dqn_phi(screens):
assert len(screens) == 4
assert screens[0].dtype == np.uint8
raw_values = np.asarray(screens, dtype=np.float32)
# [0,255] -> [0, 1]
raw_values /= 255.0
return raw_values
agent = chainerrl.agents.DQN(q_func, optimizer, rbuf, gpu=0, gamma=0.99,
explorer=explorer, replay_start_size=5 * 10 ** 4,
target_update_interval=10 ** 4,
clip_delta=True,
update_interval=4,
batch_accumulator='sum', phi=dqn_phi)
学習
import sys
STEPS = 10 ** 7
def step_hook(env, agent, step):
sys.stdout.write("\r{} / {} steps.".format(step, STEPS))
sys.stdout.flush()
chainerrl.experiments.train_agent_with_evaluation(
agent=agent, env=env, steps=STEPS,
eval_n_runs=10, eval_interval=10 ** 5,
outdir=outdir, eval_explorer=eval_explorer,
eval_env=eval_env, step_hooks=[step_hook])
モデルのリロード
import pandas as pd
import glob
import os
model_files = glob.glob("drive/dqn_out/*/*/model.npz")
model_files.sort(key=os.path.getmtime)
last_model_dir = os.path.dirname(model_files[-1])
last_model_dir
import chainer
from chainer import functions as F
from chainer import links as L
import chainerrl
from chainerrl.envs import ale
import numpy as np
ROM = "breakout"
TRAIN_SEED = 0
TEST_SEED = 2 ** 16 - 1 - TRAIN_SEED
env = ale.ALE(ROM, use_sdl=False, seed=TRAIN_SEED)
chainerrl.misc.env_modifiers.make_reward_clipped(env, -1, 1)
eval_env = ale.ALE(ROM, use_sdl=False,
treat_life_lost_as_terminal=False,
seed=TEST_SEED)
n_actions = env.number_of_actions
q_func = chainerrl.links.Sequence(
chainerrl.links.NatureDQNHead(),
L.Linear(512, n_actions),
chainerrl.action_value.DiscreteActionValue)
# Use the same hyper parameters as the Nature paper's
optimizer = chainer.optimizers.RMSpropGraves(lr=2.5e-4, alpha=0.95, momentum=0.0, eps=1e-2)
optimizer.setup(q_func)
rbuf = chainerrl.replay_buffer.ReplayBuffer(10 ** 6)
explorer = chainerrl.explorers.LinearDecayEpsilonGreedy(
1.0, 0.1,
10 ** 6,
lambda: np.random.randint(n_actions))
def dqn_phi(screens):
assert len(screens) == 4
assert screens[0].dtype == np.uint8
raw_values = np.asarray(screens, dtype=np.float32)
# [0,255] -> [0, 1]
raw_values /= 255.0
return raw_values
agent = chainerrl.agents.DQN(q_func, optimizer, rbuf, gpu=0, gamma=0.99,
explorer=explorer, replay_start_size=5 * 10 ** 4,
target_update_interval=10 ** 4,
clip_delta=True,
update_interval=4,
batch_accumulator='sum', phi=dqn_phi)
agent.load(last_model_dir)
学習結果の確認
import pandas as pd
import glob
import os
score_files = glob.glob("drive/dqn_out/*/scores.txt")
score_files.sort(key=os.path.getmtime)
score_file = score_files[-1]
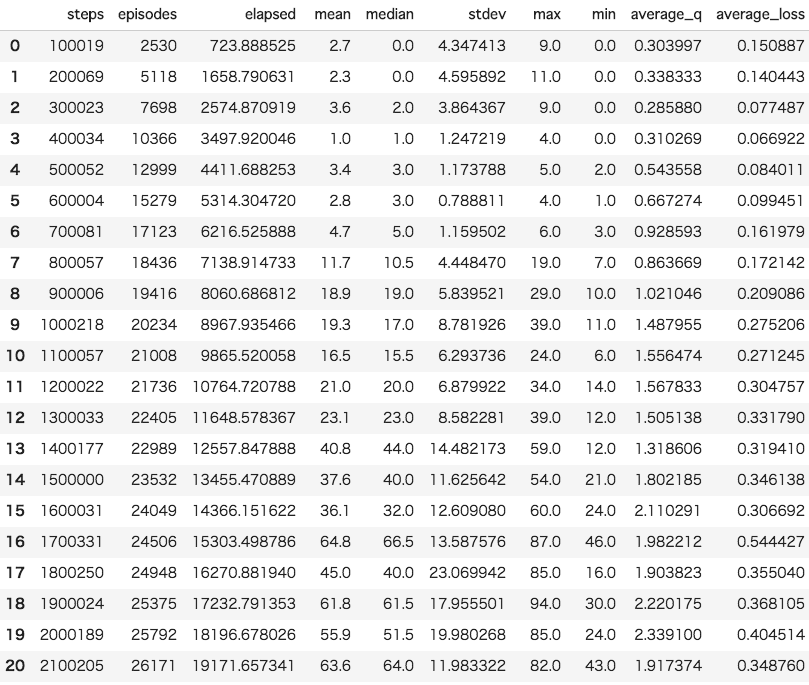
df = pd.read_csv(score_file, delimiter='\t' )
df
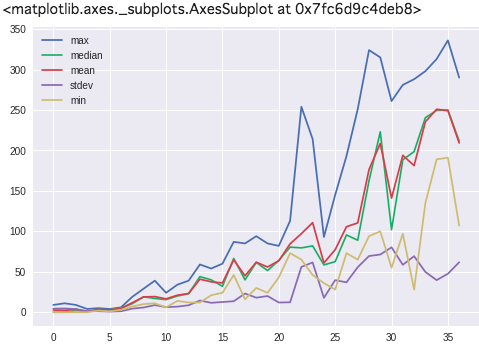
グラフ化します。
df[["max", "median", "mean", "stdev", "min"]].plot()
実行結果の確認
frames = []
for i in range(10):
obs = env.reset()
done = False
R = 0
t = 0
while not done:
action = agent.act(obs)
obs, r, done, _ = env.step(action)
frames.append(env.ale.getScreenRGB())
R += r
t += 1
print('test episode:', i, 'R:', R)
agent.stop_episode()
アニメーションの作成
最初のやつです。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.animation
import numpy as np
from IPython.display import HTML
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
plt.axis('off')
images = []
for f in frames:
image = plt.imshow(f)
images.append([image])
ani = matplotlib.animation.ArtistAnimation(fig, images, interval=30, repeat_delay=1)
HTML(ani.to_jshtml())
終わりに
チュートリアルそのまま行うだけで簡単にDQNで学習とわかりやすい形で結果の可視化ができました。
色々いじって遊びたいと思います。