はじめに
この記事は3編構成になっていて、
①環境構築編
②Functions編
③アプリ編
になっています。
Functions編では、実際にFirebase Cloud Functionsを使ってサーバー側でRealtime Databaseのイベントを読み込んで、新たにデータリストを追加します。
具体的には、ユーザーがじゃんけんの手を出して、サーバー側がじゃんけんの勝ち負けをデータとして追加します。
準備
まず、ターミナルからnpmを使ってfirebase-toolsをインストールします。
npm install -g firebase-tools
次に、適当なディレクトリ(今後Functionsにデプロイするためのjsファイルなどが格納される)を作成して、そのディレクトリの中に移動し以下のコマンドを打ちます。
firebase login
を実行します。Allow Firebase to collect anonymous CLI usage and error reporting information?と聞かれますが収集されたくない方はnで。許可を進めると

Successful!となります。プロキシをつけてネットに繋いでるとsuccessしないことがあるので注意です。
次に、initで関連ファイルを生成します。loginと同じようにターミナルで以下のコマンドを実行します。
firebase init functions
その後に、自分で作成したプロジェクトを選ぶ

あといくつか確認が出てきますが、以下の通りで自分はやりました。
? What language would you like to use to write Cloud Functions? JavaScript
? Do you want to use ESLint to catch probable bugs and enforce style? Yes
✔ Wrote functions/package.json
✔ Wrote functions/.eslintrc.json
✔ Wrote functions/index.js
? Do you want to install dependencies with npm now? Yes
無事終わると、✔ Firebase initialization complete!が表示されます。
生成されたファイルの構成は以下のようになると思います。
自分で作成したディレクトリ名/
├ firebase.json
└ functions/
├ index.js
├ package-lock.json package.json
└ node_module/
この中のindex.jsを書き換えます。
'use strict';
const functions = require('firebase-functions');
const admin = require('firebase-admin');
admin.initializeApp();
exports.judgeMatch = functions.database.ref('/room/{roomId}/owner').onWrite((change) => {
var handArray ={};
var winArray ={};
const parentRef = change.after.ref.parent;
const currentRef = change.after.ref;
const countRef = parentRef.child('owner/count');
var handtoRef = 0;
const testRef = currentRef.parent.child('result');
return parentRef.once('value').then((snapshot) => {
var isstart = snapshot.child("owner/isStart").val();
var count = snapshot.child("owner/count").val();
var handNum = snapshot.child("hand").numChildren();
if(isstart && count === handNum){
snapshot.child("hand").forEach((child) =>{
handArray[child.key] = child.val(); //連想配列に追加
});
winArray = calculateHand(handArray);
return testRef.transaction((current) => {
console.log("winarray",winArray);
return winArray;
});
}
return null;
});
});
function calculateHand(hand){
var result = {};
var r = 0;
var p = 0;
var s = 0;
Object.keys(hand).forEach(function(key) {
var val = this[key]; // this は obj
console.log(key, val);
if(val === "rock"){
r += 1;
}else if (val === "paper") {
p += 1;
}else if (val === "scissors") {
s += 1;
}else{
return null;
}
}, hand);
console.log(r,p,s);
if((r >= 1 && p >= 1 && s>= 1) || (r >= 1 && p === 0 && s === 0) || (r === 0 && p >= 1 && s === 0) || (r === 0 && p === 0 && s >= 1)){ //draw
Object.keys(hand).forEach(function(key) {
var val = this[key];
result[key] = 'draw';
}, hand);
}else if(r === 0){ //win scissors
Object.keys(hand).forEach(function(key) {
var val = this[key];
var tmp = '';
if(val === 'scissors'){
tmp = 'win';
}else if(val === 'paper'){
tmp = 'lose'
}else{
return null;
}
result[key] = tmp;
}, hand);
}else if(p === 0){ // win rock
Object.keys(hand).forEach(function(key) {
var val = this[key];
var tmp = '';
if(val === 'rock'){
tmp = 'win';
}else if(val === 'scissors'){
tmp = 'lose'
}else{
return null;
}
result[key] = tmp;
}, hand);
}else if(s === 0){ //win paper
Object.keys(hand).forEach(function(key) {
var val = this[key];
var tmp = '';
if(val === 'paper'){
tmp = 'win';
}else if(val === 'rock'){
tmp = 'lose'
}else{
return null;
}
result[key] = tmp;
}, hand);
}
r = 0; p = 0; s = 0;
return result;
}
プログラムの説明
内部では、Realtime Databaseから手を受け取ってじゃんけんの勝者を判定します。
その結果をデータとして追加するという処理を行っています。
handCalculateには、ユーザー名と手を渡してどのユーザーが勝ちか負けか連想配列で返します。
その結果をRealtime Databaseに追加しています。
デプロイ
次に、デプロイします。
firebase deploy
少し待って✔ Deploy complete!が表示されたら成功です。
Firebaseの画面に戻って、Functionsのダッシュボードを開くと、judgeMatchが関数として現れています。

Realtime Databaseで動作を確認
ただの動作確認ですので、面倒な方は次に進んで大丈夫です!
次にデータベースの追加を行います。Realtime Databaseの画面に移ります。
まず、プロジェクト名の横から+ボタンを押してroomというデータを追加します。
さらに、
room/部屋名(何でも良い)/hand
を追加し、ユーザー名と手を格納します。
room/部屋名/owner
を追加し、手の数とオーナー名とisStart(最初はfalse)を追加します。
下の画像を参考に

正しくデータの追加が終わったら次に、isStartをtrueにします。
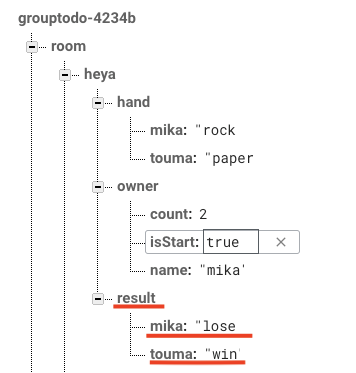
すると!勝手にresultというデータが追加され、じゃんけんの結果が格納されています。
手の数とownerの子であるcountの値が一致していれば何人でも結果を返します。(1人でもできちゃいます...)
さいごに
次はアプリ編ですが、アプリで手をデータベースに追加してやれば後は勝手に結果を追加してくれるのでそれを表示すれば終わりです。
③アプリ編