はじめに
基盤モデル×RoboticsのAdventCalendarの4日目です!
カレンダーものぞいてみてくださいー!(私は計3投稿目らしい笑)
https://qiita.com/advent-calendar/2022/robot-ai
一日目に基盤モデルのお話を書いてますので、ぜひ!
【🎉基盤モデル×Robotics 1日目 投稿🎉】
— るっと🐨 Ph.D. 🤖 (@MeRTcooking) December 1, 2022
タイトル:基盤モデルとは
東京大学 松尾研究室が主催する「基盤モデル×Robotics」に関するAdvent Calendarの1日目を投稿しました!
リンクのカレンダー(12/1)から記事を是非読んでください🎄#拡散希望RT #adventcalendar2022 https://t.co/mcTe4RAEMD
拡散RT&いいね何卒です(モチベあがります!)
【🎉基盤モデル×Robotics 4日目 投稿🎉】
— るっと🐨 Ph.D. 🤖 (@MeRTcooking) December 3, 2022
タイトル:ChatGPTでロボットコード「PythonRobotics」を解読できるのか?
ゆるめの記事ですが今後共よろしくお願いします!!!!!(基盤モデル×Robotics アドカレ計3投稿目)#ChatGPT #AdventCalendar #PythonRobotics https://t.co/KQQM8rlf5j
おさらい
本記事は【後編】ChatGPTでロボットコード「PythonRobotics」を解読できるのか?となり、前編があります!
以下から前編を良ければご覧ください!
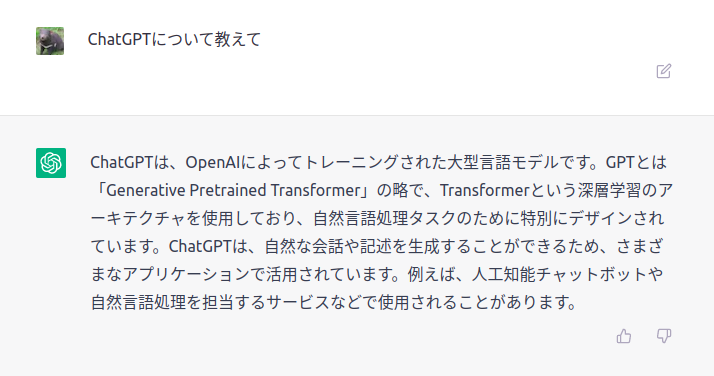
ChatGPTとは
OpenAIが開発するGPT-3(※)という大規模言語モデルをベースとしたチャットアプリです。
実際のにどんな事ができるか見てみましょう!
ChatGPTに聞いてみよう!
ChatGPTにChatGPTについて聞く
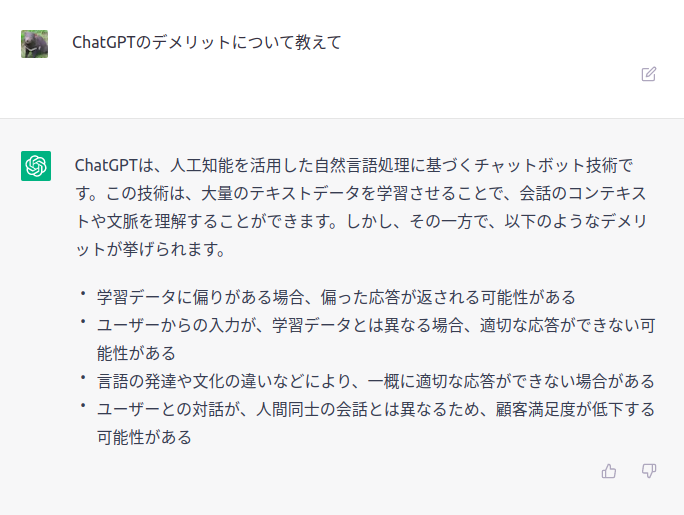
ChatGPTにChatGPTのデメリットについて聞く
何ができるのか(返答がくるのか)?
沢山のユーザの報告により、以下ができるみたいです。
質問に対する応答
架空のものに対する返答
架空の食べ物のレシピ
料理やお菓子のレシピ(正確性については?)
特定の材料を指定してレシピや料理の提示
レシピの量の換算(1人前のレシピを3人前になど)
Wikipedia風の文章
お店の人気料理(有名店)
お店のメニュー(有名店)
シナリオのあらすじ
遊園地のおすすめアトラクション
要約
哲学的な質問への応答
特定の語尾にする
キャラクターの言いそうなこと、言わなそうなこと
タスクの作成
リストを文章化する
スケジュール
プログラミングコードの生成
DB設計
以下記事ともに、なんとなくChatGPTのイメージはついたでしょうか?
【前編】ChatGPTでロボットのコード生成はできるのか?
では、本題へいきましょう!
【後編】ChatGPTでロボットコード「PythonRobotics」を解読できるのか?
今回は、プログラミングコードの解読に着目しています。
コード与えて説明してくれたらめっちゃありがたいなあと思いまして。。。
結論
ほどほどに解読してくれた!!!!
衝撃!!!
いざ、本題へ!!!
PythonRoboticsのDWA:dynamic window approach(自律移動手法)を解読できるのか?
PythonRoboticsとは、Sakaiさんが開発している「ロボティクスの代表的な様々なアルゴリズムをPythonで実装したOSS」です。
PythonRoboticsについては以下を参考にしてください。
- PythonRobotics
- PythonRobotics:a Python code collection of robotics algorithms
- PythonRobotics’s documentation!
PythonRoboticsのDWA:dynamic window approach(自律移動手法)をChatGPTに解読を頼んでみた
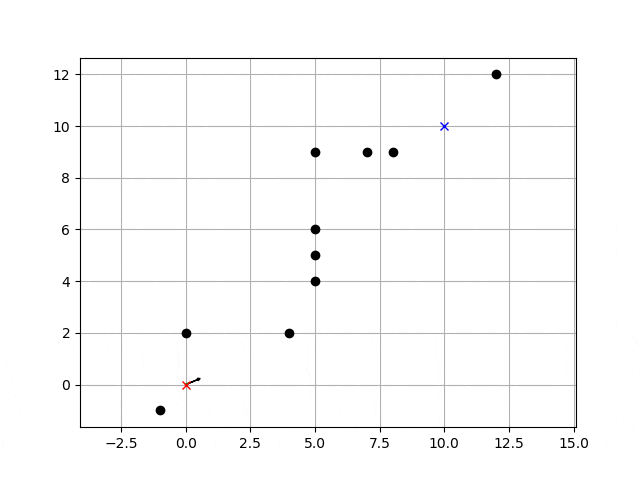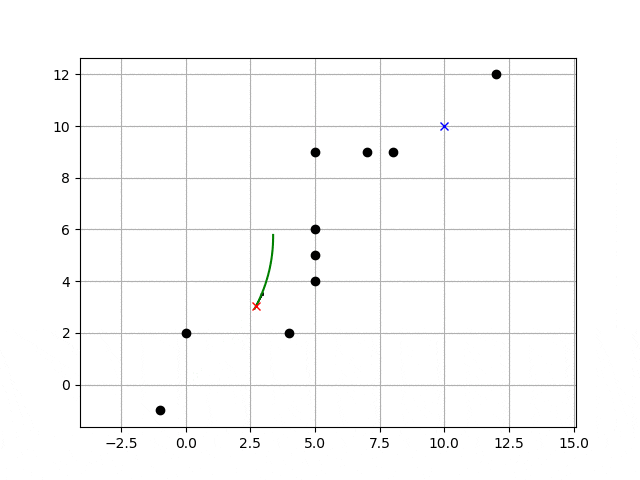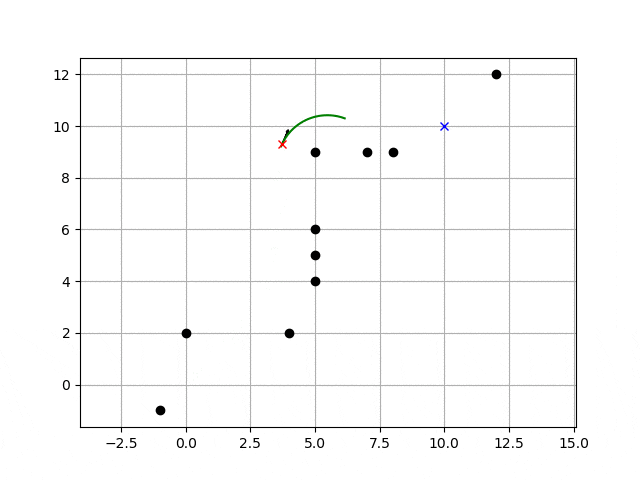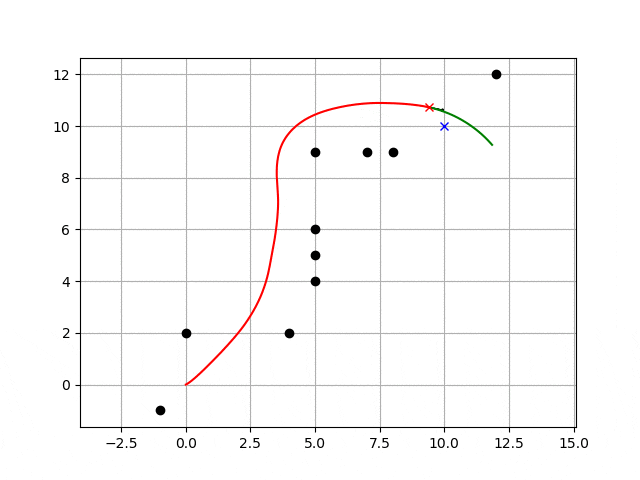
DWA:dynamic window approach(自律移動手法)の動作例
以下の動画のように障害物を避けながら、ゴール地点へ向かう自律移動手法です。
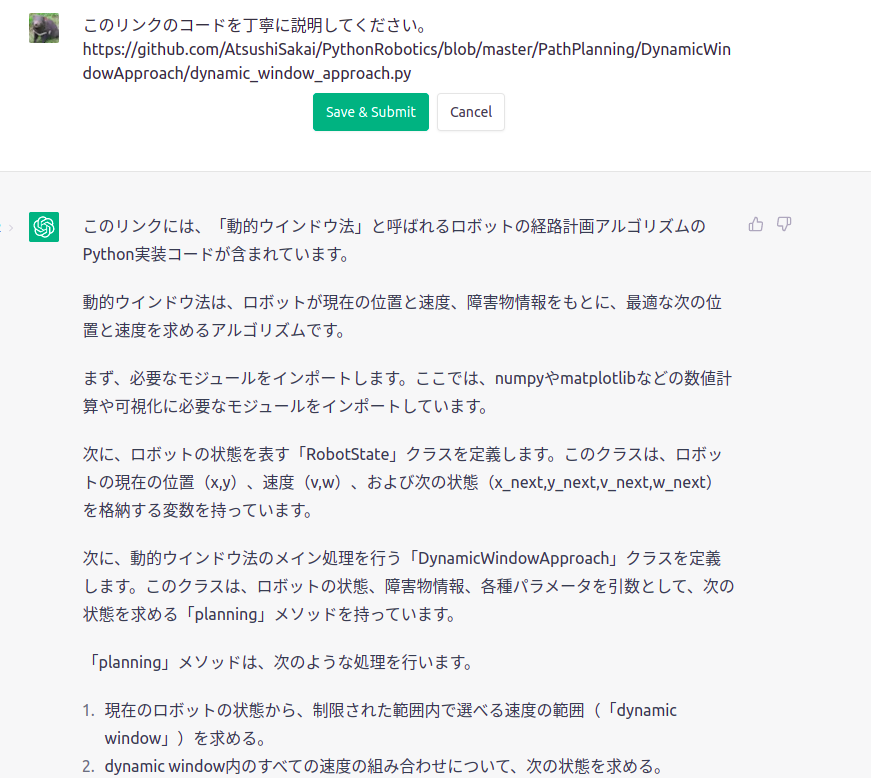
上の動作例のコードをいざChatGPTへ!
実際にいれてみた。。。。。。。
このリンクのコードを丁寧に説明してください。
https://github.com/AtsushiSakai/PythonRobotics/blob/master/PathPlanning/DynamicWindowApproach/dynamic_window_approach.py
実際のコード一部
"""
Mobile robot motion planning sample with Dynamic Window Approach
author: Atsushi Sakai (@Atsushi_twi), Göktuğ Karakaşlı
"""
import math
from enum import Enum
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
show_animation = True
def dwa_control(x, config, goal, ob):
"""
Dynamic Window Approach control
"""
dw = calc_dynamic_window(x, config)
u, trajectory = calc_control_and_trajectory(x, dw, config, goal, ob)
return u, trajectory
class RobotType(Enum):
circle = 0
rectangle = 1
class Config:
"""
simulation parameter class
"""
def __init__(self):
# robot parameter
self.max_speed = 1.0 # [m/s]
self.min_speed = -0.5 # [m/s]
self.max_yaw_rate = 40.0 * math.pi / 180.0 # [rad/s]
self.max_accel = 0.2 # [m/ss]
self.max_delta_yaw_rate = 40.0 * math.pi / 180.0 # [rad/ss]
self.v_resolution = 0.01 # [m/s]
self.yaw_rate_resolution = 0.1 * math.pi / 180.0 # [rad/s]
self.dt = 0.1 # [s] Time tick for motion prediction
self.predict_time = 3.0 # [s]
self.to_goal_cost_gain = 0.15
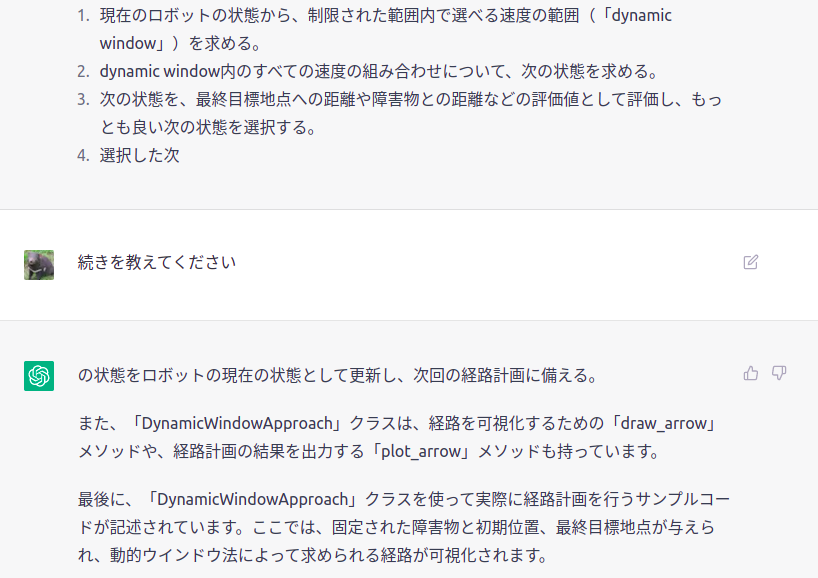
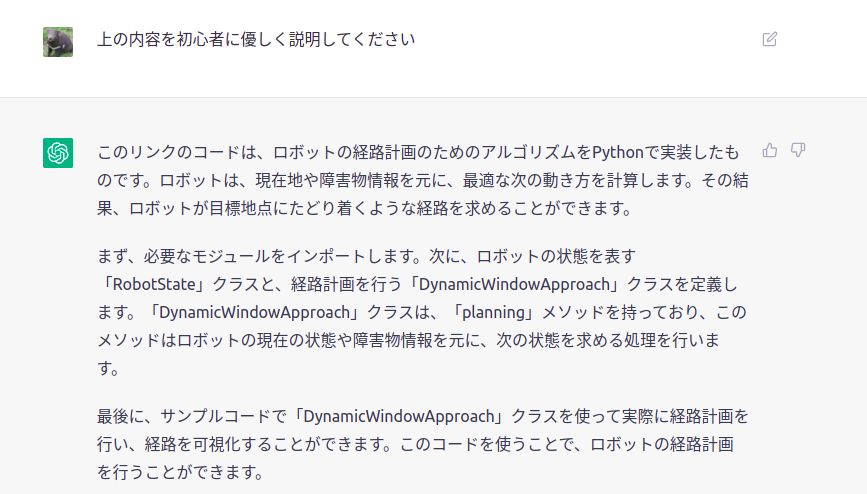
どうなるのか・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
なんと!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
上記が解読結果です!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
ところどころ間違っている所もありますが、大方あっていますね!!!!!!!
これはすごいですね。。。言葉がでません。。。。
おわりに
お読み頂きありがとうございました!
引き続き、ご投稿「基盤モデル×Robotics」のAdvent Calendarへのご投稿もお待ちしております!!!(12/6)の人がまだいません。。。
本日は軽めの記事ですみませんが、今後共何卒よろしくお願いします!
拡散RT&いいね何卒です(モチベあがります!)
【🎉基盤モデル×Robotics 4日目 投稿🎉】
— るっと🐨 Ph.D. 🤖 (@MeRTcooking) December 3, 2022
タイトル:ChatGPTでロボットコード「PythonRobotics」を解読できるのか?
ゆるめの記事ですが今後共よろしくお願いします!!!!!(基盤モデル×Robotics アドカレ計3投稿目)#ChatGPT #AdventCalendar #PythonRobotics https://t.co/KQQM8rlf5j
おまけ
DWA:dynamic window approachの改良手法
謝辞
PythonRobotics様に深く感謝を申し上げます。
参考コード(ChatGPTに入れたコード)
以下がDWAのpythonコードです。
"""
Mobile robot motion planning sample with Dynamic Window Approach
author: Atsushi Sakai (@Atsushi_twi), Göktuğ Karakaşlı
"""
import math
from enum import Enum
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
show_animation = True
def dwa_control(x, config, goal, ob):
"""
Dynamic Window Approach control
"""
dw = calc_dynamic_window(x, config)
u, trajectory = calc_control_and_trajectory(x, dw, config, goal, ob)
return u, trajectory
class RobotType(Enum):
circle = 0
rectangle = 1
class Config:
"""
simulation parameter class
"""
def __init__(self):
# robot parameter
self.max_speed = 1.0 # [m/s]
self.min_speed = -0.5 # [m/s]
self.max_yaw_rate = 40.0 * math.pi / 180.0 # [rad/s]
self.max_accel = 0.2 # [m/ss]
self.max_delta_yaw_rate = 40.0 * math.pi / 180.0 # [rad/ss]
self.v_resolution = 0.01 # [m/s]
self.yaw_rate_resolution = 0.1 * math.pi / 180.0 # [rad/s]
self.dt = 0.1 # [s] Time tick for motion prediction
self.predict_time = 3.0 # [s]
self.to_goal_cost_gain = 0.15
self.speed_cost_gain = 1.0
self.obstacle_cost_gain = 1.0
self.robot_stuck_flag_cons = 0.001 # constant to prevent robot stucked
self.robot_type = RobotType.circle
# if robot_type == RobotType.circle
# Also used to check if goal is reached in both types
self.robot_radius = 1.0 # [m] for collision check
# if robot_type == RobotType.rectangle
self.robot_width = 0.5 # [m] for collision check
self.robot_length = 1.2 # [m] for collision check
# obstacles [x(m) y(m), ....]
self.ob = np.array([[-1, -1],
[0, 2],
[4.0, 2.0],
[5.0, 4.0],
[5.0, 5.0],
[5.0, 6.0],
[5.0, 9.0],
[8.0, 9.0],
[7.0, 9.0],
[8.0, 10.0],
[9.0, 11.0],
[12.0, 13.0],
[12.0, 12.0],
[15.0, 15.0],
[13.0, 13.0]
])
@property
def robot_type(self):
return self._robot_type
@robot_type.setter
def robot_type(self, value):
if not isinstance(value, RobotType):
raise TypeError("robot_type must be an instance of RobotType")
self._robot_type = value
config = Config()
def motion(x, u, dt):
"""
motion model
"""
x[2] += u[1] * dt
x[0] += u[0] * math.cos(x[2]) * dt
x[1] += u[0] * math.sin(x[2]) * dt
x[3] = u[0]
x[4] = u[1]
return x
def calc_dynamic_window(x, config):
"""
calculation dynamic window based on current state x
"""
# Dynamic window from robot specification
Vs = [config.min_speed, config.max_speed,
-config.max_yaw_rate, config.max_yaw_rate]
# Dynamic window from motion model
Vd = [x[3] - config.max_accel * config.dt,
x[3] + config.max_accel * config.dt,
x[4] - config.max_delta_yaw_rate * config.dt,
x[4] + config.max_delta_yaw_rate * config.dt]
# [v_min, v_max, yaw_rate_min, yaw_rate_max]
dw = [max(Vs[0], Vd[0]), min(Vs[1], Vd[1]),
max(Vs[2], Vd[2]), min(Vs[3], Vd[3])]
return dw
def predict_trajectory(x_init, v, y, config):
"""
predict trajectory with an input
"""
x = np.array(x_init)
trajectory = np.array(x)
time = 0
while time <= config.predict_time:
x = motion(x, [v, y], config.dt)
trajectory = np.vstack((trajectory, x))
time += config.dt
return trajectory
def calc_control_and_trajectory(x, dw, config, goal, ob):
"""
calculation final input with dynamic window
"""
x_init = x[:]
min_cost = float("inf")
best_u = [0.0, 0.0]
best_trajectory = np.array([x])
# evaluate all trajectory with sampled input in dynamic window
for v in np.arange(dw[0], dw[1], config.v_resolution):
for y in np.arange(dw[2], dw[3], config.yaw_rate_resolution):
trajectory = predict_trajectory(x_init, v, y, config)
# calc cost
to_goal_cost = config.to_goal_cost_gain * calc_to_goal_cost(trajectory, goal)
speed_cost = config.speed_cost_gain * (config.max_speed - trajectory[-1, 3])
ob_cost = config.obstacle_cost_gain * calc_obstacle_cost(trajectory, ob, config)
final_cost = to_goal_cost + speed_cost + ob_cost
# search minimum trajectory
if min_cost >= final_cost:
min_cost = final_cost
best_u = [v, y]
best_trajectory = trajectory
if abs(best_u[0]) < config.robot_stuck_flag_cons \
and abs(x[3]) < config.robot_stuck_flag_cons:
# to ensure the robot do not get stuck in
# best v=0 m/s (in front of an obstacle) and
# best omega=0 rad/s (heading to the goal with
# angle difference of 0)
best_u[1] = -config.max_delta_yaw_rate
return best_u, best_trajectory
def calc_obstacle_cost(trajectory, ob, config):
"""
calc obstacle cost inf: collision
"""
ox = ob[:, 0]
oy = ob[:, 1]
dx = trajectory[:, 0] - ox[:, None]
dy = trajectory[:, 1] - oy[:, None]
r = np.hypot(dx, dy)
if config.robot_type == RobotType.rectangle:
yaw = trajectory[:, 2]
rot = np.array([[np.cos(yaw), -np.sin(yaw)], [np.sin(yaw), np.cos(yaw)]])
rot = np.transpose(rot, [2, 0, 1])
local_ob = ob[:, None] - trajectory[:, 0:2]
local_ob = local_ob.reshape(-1, local_ob.shape[-1])
local_ob = np.array([local_ob @ x for x in rot])
local_ob = local_ob.reshape(-1, local_ob.shape[-1])
upper_check = local_ob[:, 0] <= config.robot_length / 2
right_check = local_ob[:, 1] <= config.robot_width / 2
bottom_check = local_ob[:, 0] >= -config.robot_length / 2
left_check = local_ob[:, 1] >= -config.robot_width / 2
if (np.logical_and(np.logical_and(upper_check, right_check),
np.logical_and(bottom_check, left_check))).any():
return float("Inf")
elif config.robot_type == RobotType.circle:
if np.array(r <= config.robot_radius).any():
return float("Inf")
min_r = np.min(r)
return 1.0 / min_r # OK
def calc_to_goal_cost(trajectory, goal):
"""
calc to goal cost with angle difference
"""
dx = goal[0] - trajectory[-1, 0]
dy = goal[1] - trajectory[-1, 1]
error_angle = math.atan2(dy, dx)
cost_angle = error_angle - trajectory[-1, 2]
cost = abs(math.atan2(math.sin(cost_angle), math.cos(cost_angle)))
return cost
def plot_arrow(x, y, yaw, length=0.5, width=0.1): # pragma: no cover
plt.arrow(x, y, length * math.cos(yaw), length * math.sin(yaw),
head_length=width, head_width=width)
plt.plot(x, y)
def plot_robot(x, y, yaw, config): # pragma: no cover
if config.robot_type == RobotType.rectangle:
outline = np.array([[-config.robot_length / 2, config.robot_length / 2,
(config.robot_length / 2), -config.robot_length / 2,
-config.robot_length / 2],
[config.robot_width / 2, config.robot_width / 2,
- config.robot_width / 2, -config.robot_width / 2,
config.robot_width / 2]])
Rot1 = np.array([[math.cos(yaw), math.sin(yaw)],
[-math.sin(yaw), math.cos(yaw)]])
outline = (outline.T.dot(Rot1)).T
outline[0, :] += x
outline[1, :] += y
plt.plot(np.array(outline[0, :]).flatten(),
np.array(outline[1, :]).flatten(), "-k")
elif config.robot_type == RobotType.circle:
circle = plt.Circle((x, y), config.robot_radius, color="b")
plt.gcf().gca().add_artist(circle)
out_x, out_y = (np.array([x, y]) +
np.array([np.cos(yaw), np.sin(yaw)]) * config.robot_radius)
plt.plot([x, out_x], [y, out_y], "-k")
def main(gx=10.0, gy=10.0, robot_type=RobotType.circle):
print(__file__ + " start!!")
# initial state [x(m), y(m), yaw(rad), v(m/s), omega(rad/s)]
x = np.array([0.0, 0.0, math.pi / 8.0, 0.0, 0.0])
# goal position [x(m), y(m)]
goal = np.array([gx, gy])
# input [forward speed, yaw_rate]
config.robot_type = robot_type
trajectory = np.array(x)
ob = config.ob
while True:
u, predicted_trajectory = dwa_control(x, config, goal, ob)
x = motion(x, u, config.dt) # simulate robot
trajectory = np.vstack((trajectory, x)) # store state history
if show_animation:
plt.cla()
# for stopping simulation with the esc key.
plt.gcf().canvas.mpl_connect(
'key_release_event',
lambda event: [exit(0) if event.key == 'escape' else None])
plt.plot(predicted_trajectory[:, 0], predicted_trajectory[:, 1], "-g")
plt.plot(x[0], x[1], "xr")
plt.plot(goal[0], goal[1], "xb")
plt.plot(ob[:, 0], ob[:, 1], "ok")
plot_robot(x[0], x[1], x[2], config)
plot_arrow(x[0], x[1], x[2])
plt.axis("equal")
plt.grid(True)
plt.pause(0.0001)
# check reaching goal
dist_to_goal = math.hypot(x[0] - goal[0], x[1] - goal[1])
if dist_to_goal <= config.robot_radius:
print("Goal!!")
break
print("Done")
if show_animation:
plt.plot(trajectory[:, 0], trajectory[:, 1], "-r")
plt.pause(0.0001)
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main(robot_type=RobotType.rectangle)
# main(robot_type=RobotType.circle)