経緯
- 顔抽出アプリを作成する機会があり、画面は Streamlit か Gradio で作成する事にしました
- どちらも使った事が無かったのでどちらを選択するか悩んだのですが、触っている中で Streamlit が今回作るアプリに向いていない事が分かったので、違いをまとめました
先にまとめ
- 以下のような場合は Streamlit が向いている
- Streamlit で使いたい UI パーツがある
(特に私が触れていない部分で、表やグラフなどのデータ可視化のパーツはどちらが充実しているか・楽に実装出来るか分からない) - UI のレイアウトが好み
- GitHub にコードをアップロードしていて、そこから公開したい
- Streamlit で使いたい UI パーツがある
- 以下のような場合は Gradio が向いている
- 画面上で画像クリックなどの選択操作がある
- css を使ってある程度自由にレイアウトを変更したい
- ちょびっと画面見てもらいたい時にいちいちアカウントを登録するのが面倒(share=trueとすれば3日間ローカル PC から公開可能)
アプリ詳細
Streamlit の画像選択でハマる
-
顔認識したギャラリーの写真をクリックした時にどの画像が選択されたか判断する必要があったが Streamlit の標準機能で画像の選択が出来ないため、どの画像が選択されたか判断する処理を作りにくかった
-
別のライブラリ(streamlit_image_select)を入れる事で「画像の選択・indexの取得」は出来るようになるけど、レイアウト面が扱いにくい
(少し調べた限りまず列数の指定が出来なかった)import streamlit as st from streamlit_image_select import image_select images = ["./web/imgOrig/1.jpg", "./web/imgOrig/2.jpg", "./web/imgOrig/3.jpg",] selected = image_select( "streamlit", images, index=0, use_container_width=[False], return_value="index",) print(f"selectedIndex: {selected}") -
Gradio だと以下のようになります
- Gallery の標準機能で select イベントが用意されているので、簡単に実装出来る
- 列数の指定も Gallery の引数で簡単に設定出来る
import gradio as gr # gallery の画像が選択された時のイベント def on_select(evt: gr.SelectData): print(f"selectedIndex: {evt.index}") images = ["./web/imgOrig/1.jpg", "./web/imgOrig/2.jpg", "./web/imgOrig/3.jpg",] with gr.Blocks() as demo: gallery = gr.Gallery(value=images, label="gradio", columns=6, show_download_button=False, allow_preview=False) gallery.select(fn=on_select, inputs=[], outputs=[]) demo.launch()
その他の機能比較
CSS の適用
- 画面の項目ごとに CSS で細かくレイアウトをしたい!という時にどちらがやりやすいのか比較をしました
Streamlit の CSS 適用
- Streamlit では .markdown(または .write) を使って css を埋め込む事で各要素の見た目を設定出来ます
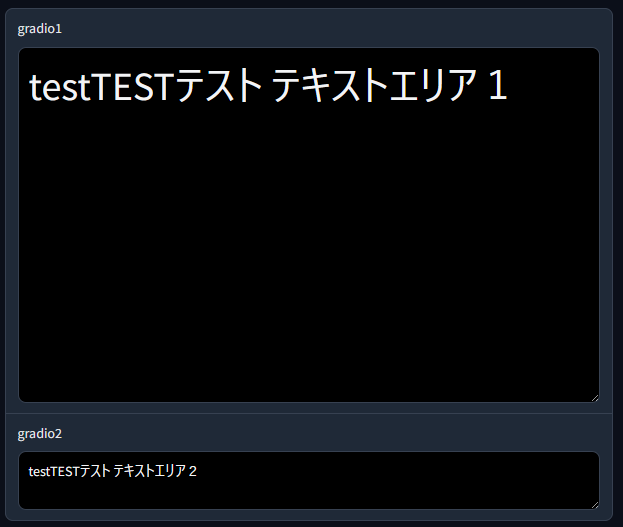
- Streamlit の css 適用で問題になるのが、下記のように複数の要素を配置した時、個別に id, class を設定出来ないので同じ要素は全て一括で変更になります
- つまり textarea1 は 20px, textarea2 は 30px といった細かい調整が難しいです
import streamlit as st css = """ <style> .stTextArea textarea {font-size: 40px;} </style> """ st.markdown(css, unsafe_allow_html=True) st.text_area(label="streamlit textarea1", value="testTESTテスト テキストエリア1") st.text_area(label="streamlit textarea2", value="testTESTテスト テキストエリア2")
Gradio の CSS 適用
- Gradio では Block に css を読み込ませる事で各要素の見た目を設定出来ます
- Gradio では要素ごとに id, class を指定出来るので柔軟なレイアウト設定が出来ます
import gradio as gr
css = """
#test1 textarea {font-size: 40px;}
.textareaclass textarea {background: black !important;}
"""
with gr.Blocks(css=css) as demo:
gr.Textbox(label="gradio1", value= "testTESTテスト テキストエリア1", elem_id="test1", elem_classes="textareaclass")
gr.Textbox(label="gradio2", value= "testTESTテスト テキストエリア2", elem_classes="textareaclass")
demo.launch()
認証機能
- Streamlit は追加のライブラリを用いる事で認証画面を作成出来ます
- Gradio はデフォルト機能で認証画面をサポートしています
Streamlit のログイン画面
- streamlit_authenticator を使用する事で認証機能を追加できます
- yaml を別途用意したり、追加するコード量が結構多いです
cookie: expiry_days: 0 key: random_signature_key name: random_cookie_name credentials: usernames: test1: email: test1@t.com logged_in: false name: test1 aaa password: $2b$12$CGtVjuca1.dM7hYPZ7Vqre/CcwivKF8f2IrQ6Lo0tTOZ1Yhn45D8Gimport streamlit as st import streamlit_authenticator as stauth import yaml from yaml.loader import SafeLoader with open('./web/auth.yaml') as file: config = yaml.load(file, Loader=SafeLoader) authenticator = stauth.Authenticate( config['credentials'], config['cookie']['name'], config['cookie']['key'], config['cookie']['expiry_days'], config['preauthorized'] ) authenticator.login() if st.session_state["authentication_status"]: st.write(f'Welcome *{st.session_state["name"]}*') authenticator.logout() elif st.session_state["authentication_status"] is False: st.error('Username/password is incorrect') elif st.session_state["authentication_status"] is None: st.warning('Please enter your username and password')
Gradio のログイン画面
- Gradio では標準機能として認証機能が用意されています
- .launch()の引数に auth を渡すだけで認証機能が追加されるので楽です
import gradio as gr
with gr.Blocks() as demo:
gr.Textbox(label="gradio1", value= "testTESTテスト テキストエリア1", elem_id="test1", elem_classes="textareaclass")
gr.Textbox(label="gradio2", value= "testTESTテスト テキストエリア2", elem_classes="textareaclass")
demo.launch(auth=[("username", "password"),("111","222")])
外部への公開
- 作成したアプリを外部へ簡単に公開する機能もそれぞれ用意されています
Streamlit の公開方法
- Streamlit のアカウントと Github のアカウントを作成して連携する事で公開出来る
- HuggingFace の Spaces に Streamlit アプリをデプロイする
Gradio の公開方法
ホットリロード
- どちらのアプリもホットリロード機能が備わっているので、開発中にコードを変更してアプリを起動し直す必要はありません
- Streamlit では通常の起動(streamlit run app.py)でホットリロードされます
- Gradio ではリロードモード(gradio app.py)でアプリを実行するとホットリロードされます
======
顔抽出ツールのプログラム
# import json
import os
from io import BytesIO
from zipfile import ZipFile
from PIL import Image
from skimage import io
import gradio as gr
from retinaface import RetinaFace
# def main():
class face_area_information:
def __init__(self, idx, path, gallery_image, x1, y1, x2, y2):
self.idx = idx
self.path = path
self.gallery_image = gallery_image
self.x1 = x1
self.y1 = y1
self.x2 = x2
self.y2 = y2
def getFileNameAndExtention(self):
name = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(self.path))[0]
file_extension = os.path.splitext(self.path)[1]
return name, file_extension
class StateModel:
def __init__(self):
self.face_area_informations = []
def add(self, face_area_informations):
self.face_area_informations = face_area_informations
# ギャラリに追加する画像の生成
def getGalleryImage(path, x1, y1, x2, y2):
# # skimage で読み込み
imagenp = io.imread(path)
# PIL に変換
image = Image.fromarray(imagenp)
return image.crop((x1, y1, x2, y2))
# ギャラリ用画像の取得
def getGalleryImages(state):
# ギャラリ用のイメージリストの作成
images = []
for face_area_info in state.face_area_informations:
images.append(face_area_info.gallery_image)
return images
# 解像度の計算
def calcResolution(x1, x2, y1, y2):
x = x2 - x1
y = y2 - y1
return x, y
# アスペクト比計算
def calcAspectRatio(x, y):
def gcd(x, y):
if(y == 0): return x
return gcd(y, x % y)
g = gcd(x, y)
ratio_x = x / g
ratio_y = y / g
return round(ratio_x), round(ratio_y)
# イメージギャラリーで画像を選択
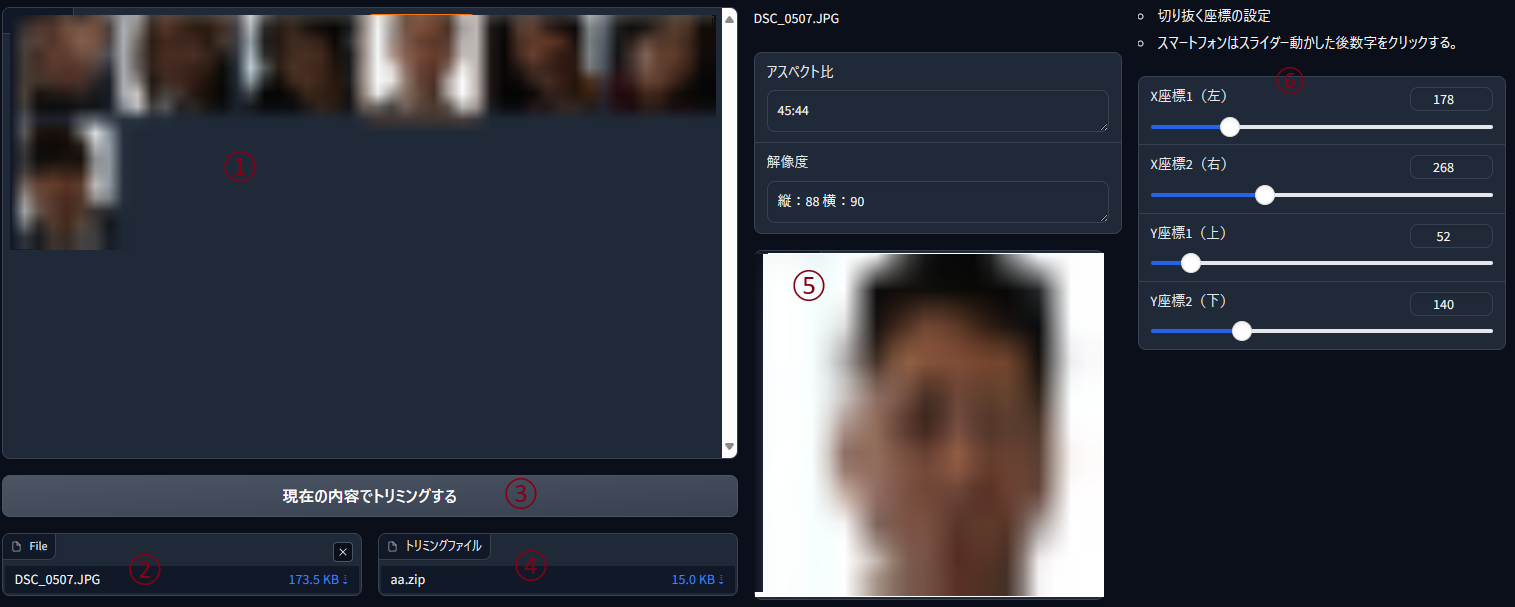
def on_select(evt: gr.SelectData, state): # SelectData is a subclass of EventData
# skimage で読み込み
face_area_information = state.face_area_informations[evt.index]
imagenp = io.imread(face_area_information.path)
# PIL に変換
image = Image.fromarray(imagenp)
# 画像の高さ・幅取得
height = image.height
width = image.width
print(f"You selected {evt.value} at {evt.index} from {evt.target}")
x, y = calcResolution(face_area_information.x1, face_area_information.x2, face_area_information.y1, face_area_information.y2)
aspect_x, aspect_y = calcAspectRatio(x, y)
name, file_extention = face_area_information.getFileNameAndExtention()
return (gr.Image(value=image.crop((face_area_information.x1, face_area_information.y1, face_area_information.x2, face_area_information.y2))),
gr.Markdown(value="- 切り抜く座標の設定\n- スマートフォンはスライダー動かした後数字をクリックする。",visible=True),
gr.Textbox(value=f"{aspect_x}:{aspect_y}", visible=True),
gr.Textbox(value=f"縦:{y} 横:{x}", visible=True),
gr.Slider(minimum=0, maximum=width, value=face_area_information.x1, visible=True),
gr.Slider(minimum=1, maximum=width + 1, value=face_area_information.x2, visible=True),
gr.Slider(minimum=0, maximum=height, value=face_area_information.y1, visible=True),
gr.Slider(minimum=1, maximum=height+1, value=face_area_information.y2, visible=True),
gr.Markdown(value=str(face_area_information.idx)),
gr.Markdown(value=f"{name}{file_extention}", visible=True),
gr.Markdown(value=face_area_information.path)
)
# img, sliderText, aspect_ratio, resolution, imgX1, imgX2, imgY1, imgY2, idxText, nameText, imgPathText
# slider の値チェック
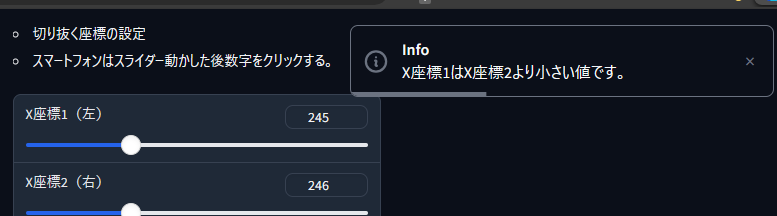
def slider_check(x1, x2, y1, y2):
if x1 >= x2:
x1 = x2 - 1
gr.Info("X座標1はX座標2より小さい値です。")
if y1 >= y2:
y1 = y2 - 1
gr.Info("Y座標1はY座標2より小さい値です。")
return (gr.Slider(value=x1),
gr.Slider(value=x2),
gr.Slider(value=y1),
gr.Slider(value=y2)
)
# スライダーをリリース
def slider_release(state, x1, x2, y1, y2, idx, imgPath):
state.face_area_informations[int(idx)] = face_area_information(idx, imgPath, getGalleryImage(imgPath, x1, y1, x2, y2), x1, y1, x2, y2)
images = getGalleryImages(state)
# skimage で読み込み
imagenp = io.imread(imgPath)
# PIL に変換
image = Image.fromarray(imagenp)
x, y = calcResolution(x1, x2, y1, y2)
aspect_x, aspect_y = calcAspectRatio(x, y)
return (gr.Gallery(value=images),
gr.Image(value=image.crop((x1, y1, x2, y2))),
gr.Textbox(value=f"{aspect_x}:{aspect_y}", visible=True),
gr.Textbox(value=f"縦:{y} 横:{x}", visible=True)
)
# ファイルアップロードした時
def file_uploaded(state, files):
if files is None:
raise gr.Error("ファイルを選択して下さい。")
print(files)
face_area_informations = []
idx = 0
for file in files:
imagenp = io.imread(file)
img_faces = RetinaFace.detect_faces(imagenp)
height = imagenp.shape[0]
width = imagenp.shape[1]
if not type(img_faces) is dict:
print(f"未検出:{file}")
continue
for i in img_faces.keys():
facial_parts = img_faces[i]
recognize_face_area = facial_parts["facial_area"]
# 顔部分の座標を分解
x1, y1, x2, y2 = recognize_face_area
print(f"face_area_y1:{y1}")
print(f"face_area_x1:{x1}")
print(f"face_area_y2:{y2}")
print(f"face_area_x2:{x2}")
# 顔座標の大きさを取得
xsize = x2 - x1
ysize = y2 - y1
# 顔座標の x と y の中央座標を取得
xx = xsize // 2 + x1
yy = ysize // 2 + y1
# トリミングサイズを大きい方に合わせる
if xsize > ysize:
trimming_size = xsize * 1.5
else:
trimming_size = ysize * 1.5
# トリミング座標を決定する
xx1 = xx - trimming_size / 2
yy1 = yy - trimming_size / 2
xx2 = xx + trimming_size / 2
yy2 = yy + trimming_size / 2
# トリミング座標が画像サイズをオーバーしている場合の処理
if trimming_size > width:
xx1 = 0
xx2 = width
elif xx1 < 0:
xx1 = 0
xx2 = trimming_size
elif xx2 > width:
xx1 = width - trimming_size
xx2 = width
if trimming_size > height:
yy1 = 0
yy2 = height
elif yy1 < 0:
yy1 = 0
yy2 = trimming_size
elif yy2 > height:
yy1 = height - trimming_size
yy2 = height
# face_region = imagenp[y1:y2, x1:x2]
face_area_informations.append(face_area_information(idx,
file,
getGalleryImage(file, round(xx1), round(yy1), round(xx2), round(yy2)),
round(xx1),
round(yy1),
round(xx2),
round(yy2)))
idx += 1
state.add(face_area_informations)
images = getGalleryImages(state)
return(gr.Gallery(value=images),
gr.Image(value=None),
gr.Markdown(value=None, visible=False), # sliderText
gr.Textbox(value=None, visible=False), # aspect_ratio
gr.Textbox(value=None, visible=False), # resolution
gr.Slider(value=None, visible=False), # imgX1
gr.Slider(value=None, visible=False), # imgX2
gr.Slider(value=None, visible=False), # imgY1
gr.Slider(value=None, visible=False), # imgY2
gr.Markdown(value=None, visible=False), # idxText
gr.Markdown(value=None, visible=False), # imgPathText
)
# gallery, img, sliderText, aspect_ratio, resolution, imgX1, imgX2, imgY1, imgY2, idxText, imgPathText
def zip_files(state):
# images = getGalleryImages(state)
# if images == []:
# raise gr.Error("ファイルを選択して下さい。")
# for face_area_info in state.face_area_informations:
# images.append(face_area_info.gallery_image)
if len(state.face_area_informations) == 0:
raise gr.Error("ファイルを選択して下さい。")
with ZipFile("aa.zip", "w") as zipObj:
for idx, face_area_info in enumerate(state.face_area_informations):
name, file_extention = face_area_info.getFileNameAndExtention()
output = BytesIO()
face_area_info.gallery_image.save(output, format='JPEG')
image_jpg = output.getvalue()
zipObj.writestr(f"{name}_{idx}.jpg", image_jpg)
return "aa.zip"
with gr.Blocks() as demo:
state = gr.State(StateModel())
images = []
with gr.Row():
with gr.Column(scale=2):
gallery = gr.Gallery(value=images,
columns=6,
show_download_button=False,
allow_preview=False)
trimmingBtn = gr.Button(value="現在の内容でトリミングする")
with gr.Row():
with gr.Column(scale=1):
inputFiles = gr.File(file_count="multiple",
file_types=["image"],
type="filepath",
interactive=True,
visible=True)
with gr.Column(scale=1):
outputFiles = gr.File(height=50,
interactive=False,
visible=True,
label="トリミングファイル")
with gr.Column(scale=1):
idxText = gr.Markdown("-",
visible=False)
nameText = gr.Markdown("-",
visible=False)
imgPathText = gr.Markdown("-",
visible=False)
aspect_ratio = gr.Textbox("",
label="アスペクト比",
interactive=False,
visible=False)
resolution = gr.Textbox("",
label="解像度",
interactive=False,
visible=False)
img = gr.Image(type="pil",
show_download_button=False,
interactive=False,
width=350,
height=350)
with gr.Column(scale=1):
sliderText = gr.Markdown(visible=False)
imgX1 = gr.Slider(label="X座標1(左)",
interactive=True,
visible=False)
imgX2 = gr.Slider(label="X座標2(右)",
interactive=True,
visible=False)
imgY1 = gr.Slider(label="Y座標1(上)",
interactive=True,
visible=False)
imgY2 = gr.Slider(label="Y座標2(下)",
interactive=True,
visible=False)
# gallery の画像が選択された時のイベント
gallery.select(fn=on_select, inputs=[state], outputs=[img, sliderText, aspect_ratio, resolution, imgX1, imgX2, imgY1, imgY2, idxText, nameText, imgPathText])
# スライダーリリース時のイベント
imgX1.release(fn=slider_check, inputs=[imgX1, imgX2, imgY1, imgY2], outputs=[imgX1, imgX2, imgY1, imgY2]
).then(fn=slider_release, inputs=[state, imgX1, imgX2, imgY1, imgY2, idxText, imgPathText], outputs=[gallery, img, aspect_ratio, resolution])
imgX2.release(fn=slider_check, inputs=[imgX1, imgX2, imgY1, imgY2], outputs=[imgX1, imgX2, imgY1, imgY2]
).then(fn=slider_release, inputs=[state, imgX1, imgX2, imgY1, imgY2, idxText, imgPathText], outputs=[gallery, img, aspect_ratio, resolution])
imgY1.release(fn=slider_check, inputs=[imgX1, imgX2, imgY1, imgY2], outputs=[imgX1, imgX2, imgY1, imgY2]
).then(fn=slider_release, inputs=[state, imgX1, imgX2, imgY1, imgY2, idxText, imgPathText], outputs=[gallery, img, aspect_ratio, resolution])
imgY2.release(fn=slider_check, inputs=[imgX1, imgX2, imgY1, imgY2], outputs=[imgX1, imgX2, imgY1, imgY2]
).then(fn=slider_release, inputs=[state, imgX1, imgX2, imgY1, imgY2, idxText, imgPathText], outputs=[gallery, img, aspect_ratio, resolution])
# ファイルアップロード時のイベント
inputFiles.upload(lambda: gr.File(interactive=False), None, inputFiles
).success(fn=file_uploaded, inputs=[state, inputFiles], outputs=[gallery, img, sliderText, aspect_ratio, resolution, imgX1, imgX2, imgY1, imgY2, idxText, imgPathText]
).then(lambda: gr.File(interactive=True), None, inputFiles)
# inputFiles.clear(lambda: gr.Files(interactive=True), None, inputFiles)
# トリミング処理済みのファイルを zip にまとめてダウンロード可能にする。
trimmingBtn.click(lambda: gr.Button(interactive=False), None, trimmingBtn
).success(fn=zip_files, inputs=[state], outputs=[outputFiles]
).then(lambda: gr.Button(interactive=True), None, trimmingBtn)
if __name__ == "__main__":
demo.launch()
```
</details>