はじめに
この記事では、LLMを用いてテキストデータを2次元に投影し、クラスタリングを行います。
LLM: DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-14B(Paper, Hugging Face, Kaggle Models)
テキストデータ: 数学の公式名("Pythagorean Theorem", "Quadratic Formula", "Binomial Theorem", "Fundamental Theorem of Calculus", "Euler's Formula", etc.)
クラスタリング手法: HDBSCAN(Paper, GitHub, PyPI)
昨年一人アドカレを完走した際に、25記事のタイトルをLLMでクラスタリングしてみました。昨年の記事のLLMとしては、Llama-3.1-8Bを用いました。こちらのコードを参考にしています。
実装
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import torch
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModel
import umap.umap_ as umap
import hdbscan
import plotly.graph_objs as go
math_formulas = [
"Pythagorean Theorem", # ピタゴラスの定理
"Quadratic Formula", # 二次方程式の解の公式
"Binomial Theorem", # 二項定理
"Fundamental Theorem of Calculus", # 微積分の基本定理
"Euler's Formula", # オイラーの公式
"Law of Cosines", # 余弦定理
"Law of Sines", # 正弦定理
"L'Hôpital's Rule", # ロピタルの定理
"Taylor Series Expansion", # テイラー展開
"Fourier Transform", # フーリエ変換
"Cauchy-Schwarz Inequality", # コーシー・シュワルツの不等式
"Bayes' Theorem", # ベイズの定理
"Central Limit Theorem", # 中心極限定理
"Green's Theorem", # グリーンの定理
"Stokes' Theorem", # ストークスの定理
"Divergence Theorem", # 発散定理(ガウスの定理)
"De Moivre's Formula", # ド・モアブルの公式
"Vieta's Formulas", # ヴィエタの公式
"Heron's Formula", # ヘロンの公式
"Newton's Method", # ニュートン法
"Chain Rule", # 連鎖律(合成関数の微分)
"Product Rule", # 積の微分法則
"Quotient Rule", # 商の微分法則
"Integration by Parts", # 部分積分法
"Stirling's Approximation", # スターリングの近似
"Leibniz Rule", # ライプニッツの法則
"Mean Value Theorem", # 平均値の定理
"Intermediate Value Theorem", # 中間値の定理
"Squeeze Theorem", # はさみうちの定理
"Laplace Transform" # ラプラス変換
]
# ================ LLMモデルの準備 ================
# モデルとトークナイザの読み込み
model_name = "deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-14B"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(model_name, torch_dtype="half", device_map="auto")
def get_embedding(text: str) -> np.ndarray:
inputs = tokenizer(text, return_tensors="pt")
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(**inputs)
# 平均プーリング
embedding = outputs.last_hidden_state.mean(dim=1).squeeze().numpy()
return embedding
# 埋め込み取得
X = np.array([get_embedding(title) for title in math_formulas])
# ================ UMAPによる次元削減 ================
umap_reducer = umap.UMAP(n_neighbors=5, min_dist=0.1, n_components=2, random_state=42)
X_2d = umap_reducer.fit_transform(X)
# ================ クラスタリング ================
# HDBSCANでクラスタリング(自動で適切なクラスタ数を抽出)
clusterer = hdbscan.HDBSCAN(min_cluster_size=2, metric='euclidean', cluster_selection_epsilon=0.1)
labels = clusterer.fit_predict(X_2d)
# ノイズ(-1)はクラスタ外として扱われる
# ================ 可視化 ================
def visualize_2d_data(points, labels, texts, title="UMAP + HDBSCAN Clustering"):
unique_labels = np.unique(labels)
color_map = {}
for lbl in unique_labels:
if lbl == -1:
color_map[lbl] = "rgba(128,128,128,0.8)"
else:
color_map[lbl] = f"hsl({(lbl * 60) % 360}, 70%, 50%)"
data_traces = []
for lbl in unique_labels:
mask = (labels == lbl)
data_traces.append(go.Scatter(
x=points[mask, 0],
y=points[mask, 1],
mode='markers+text',
text=[texts[i] for i in np.where(mask)[0]],
textposition='top center',
textfont=dict(size=8),
marker=dict(color=color_map[lbl], size=10),
name=f"Cluster {lbl}" if lbl != -1 else "Noise"
))
fig = go.Figure(data=data_traces)
fig.update_layout(
title=title,
xaxis_title='UMAP Component 1',
yaxis_title='UMAP Component 2',
showlegend=True,
hovermode='closest'
)
fig.show()
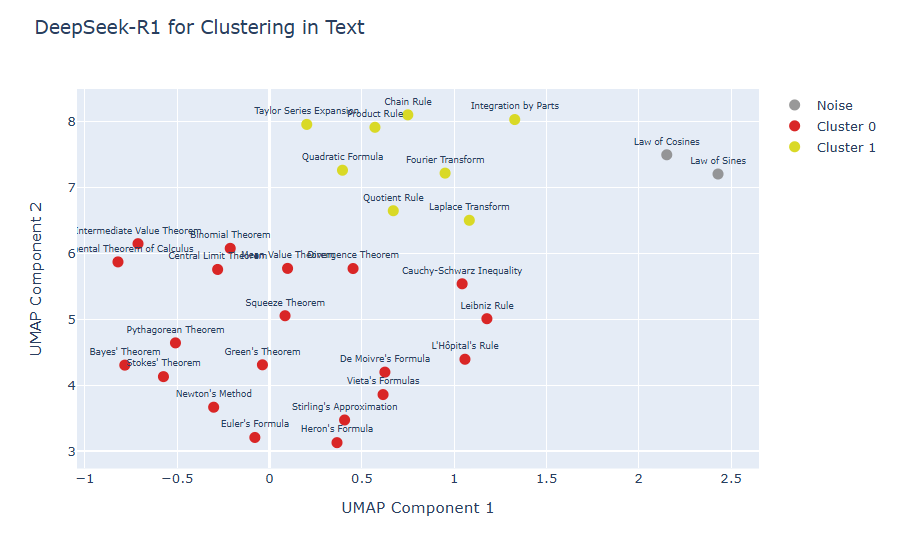
visualize_2d_data(X_2d, labels, math_formulas, title="DeepSeek-R1 for Clustering in Text ")
クラスタリング可視化結果
まとめ
クラスタリング結果は、Cluster 0に微積分の基本定理や平均値の定理、ピタゴラスの定理など、基礎解析学および古典的な定理が集まり、Cluster 1へはChain Rule(連鎖律)、Product Rule(積の微分法則)、Integration by Parts(部分積分法)など具体的な微分・積分の計算規則や手法が分離しました。
DeepSeek-R1 を使った embedding → UMAP → HDBSCAN により、数学公式名の集合を 意味的に近い公式群でまとまりを作る ことが多少可能であるように見えました。ただし、DeepSeek-R1 は本来「生成/推論用 LLM」であって、embedding 特化モデルではないです。そのため、埋め込みの信頼性や普遍性には限界があります。
本記事で使用したソースコードは、Kaggle環境で動作を確認しています。