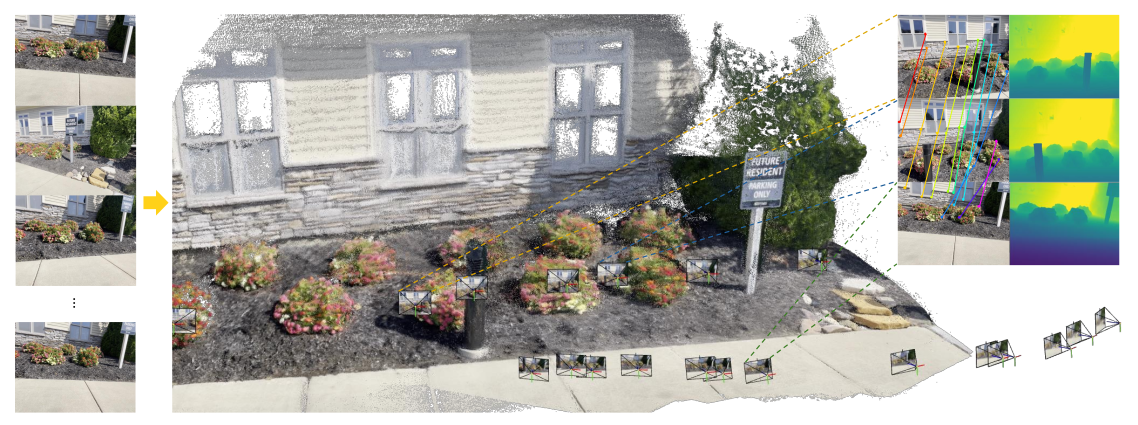
当記事では複数の画像からニューラルネットワーク(ViT)を用いて3D再構成を行うVGGT(Visual Geometry Grounded Transformer)の論文とPyTorch実装の確認を行います。
VGGTの論文
概要
VGGT(Visual Geometry Grounded Transformer)では上図のように複数の画像(上図の左)から3DのPointmap(上図の中央)を構築し、ピクセルマッチング(上図の右の左側)や深度推定(上図の右の右側)などに活用します。
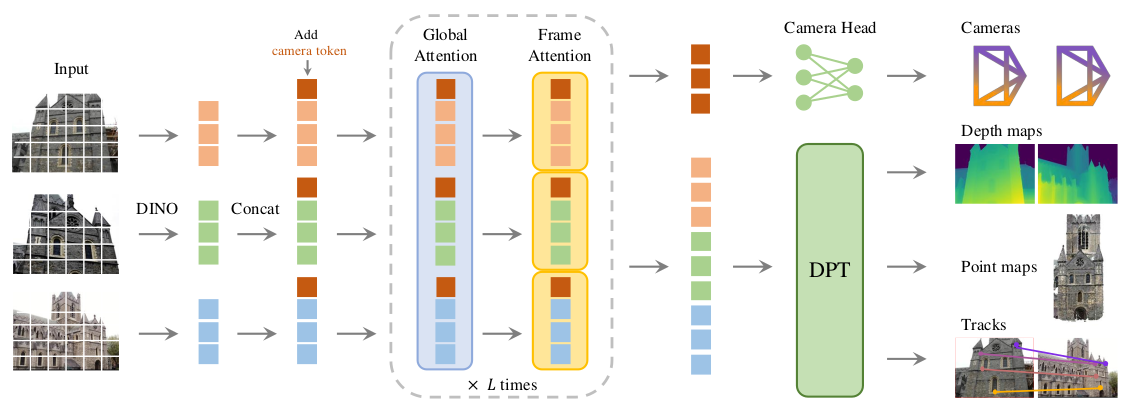
VGGTの処理の流れ
VGGTの処理の流れの大枠は上図より確認することができます。詳しい処理については以下で確認します。
問題定義
\begin{align}
(\mathbf{g}_{i}, D_{i}, P_{i}, T_{i})_{i=1}^{N} &= f((I_{i})_{i=1}^{n}) \\
I_{i} & \in \mathbb{R}^{W \times H \times 3} \\
\mathbf{g}_{i} & \in \mathbb{R}^{9} \\
D_{i} & \in \mathbb{R}^{W \times H} \\
P_{i} & \in \mathbb{R}^{W \times H \times 3} \\
T_{i} & \in \mathbb{R}^{W \times H \times C}
\end{align}
まず問題定義については上記の数式より確認することができます。N枚の入力画像についてそれぞれカメラパラメータ、深度マップ($D_{i}$)、Pointmap($P_{i}$)、$C$次元の特徴量マップ($T_{i}$)を取得する関数$f$の学習を行うことが目的になります。
・カメラパラメータ$\mathbf{g}_{i}$
9次元のカメラパラメータ$\mathbf{g}$は下記のように定義されます。
\begin{align}
\mathbf{g} = [ \mathbf{q}, \mathbf{t}, \mathbf{f} ]
\end{align}
| 文字 | 解釈 |
|---|---|
| $\mathbf{q} \in \mathbb{R}^{4}$ | 3次元回転(rotation)に対応するクオータニオン(quaternion) |
| $\mathbf{t} \in \mathbb{R}^{3}$ | 並進ベクトル(translation vector) |
| $\mathbf{t} \in \mathbb{R}^{2}$ | field of view |
・深度マップ$D_{i}$
\begin{align}
D_{i}(\mathbf{y}) & \in \mathbb{R}^{3} \\
\mathbf{y} & \in \mathcal{I}(I_{i}) \\
\mathcal{I}(I_{i}) &= \{ 1, \cdots , W \} \times \{ 1, \cdots , H \}
\end{align}
・Pointmap$P_{i}$
\begin{align}
P_{i}(\mathbf{y}) & \in \mathbb{R}^{+} \\
\mathbf{y} & \in \mathcal{I}(I_{i}) \\
\mathcal{I}(I_{i}) &= \{ 1, \cdots , W \} \times \{ 1, \cdots , H \}
\end{align}
上記のPointmapは1番目の入力画像の視点である$\mathbf{g}_{1}$に基づいて得られていることに注意しておくと良いです。
・$C$次元特徴量マップ$T_{i}$
$C$次元の特徴量マップである$T_{i}$は特徴点トラッキングなどに用いられます。
\begin{align}
T_{i}(\mathbf{y}) & \in \mathbb{R}^{C} \\
\mathbf{y} & \in \mathcal{I}(I_{i}) \\
\mathcal{I}(I_{i}) &= \{ 1, \cdots , W \} \times \{ 1, \cdots , H \}
\end{align}
・入力画像の順序
基本的には入力画像の順序については任意ですが、1番目の入力がreference frame(world coordinateの基準)となる点に注意が必要です。
特徴量抽出(Backbone Network)とPrediction Heads(DPT Heads)
特徴量抽出はViT(Vision Transformer)に基づいて行われます。内部処理にGlobal AttentionとFrame-wise Attentionから構成されるAlternating-Attentionが用いられている点について抑えておくと良いです。
VGGTの学習
\begin{align}
\mathcal{L} &= \mathcal{L}_{\mathrm{camera}} + \mathcal{L}_{\mathrm{depth}} + \mathcal{L}_{\mathrm{pmap}} + \lambda \mathcal{L}_{\mathrm{track}} \\
\mathcal{L}_{\mathrm{camera}} &= \sum_{i=1}^{N} \mathrm{Huber} \left( \hat{\mathbf{g}}_i - \mathbf{g}_i \right) \\
\mathcal{L}_{\mathrm{depth}} &= \sum_{i=1}^{N} \left[ || \Sigma_i^D \odot (\hat{D}_i - D_i) || + || \Sigma_i^D \odot (\nabla \hat{D}_i - \nabla D_i) || - \alpha \log{\Sigma_i^D} \right] \\
\mathcal{L}_{\mathrm{pmap}} &= \sum_{i=1}^{N} \left[ || \Sigma_i^P \odot (\hat{P}_i - P_i) || + || \Sigma_i^P \odot (\nabla \hat{P}_i - \nabla P_i) || \right] \\
\mathcal{L}_{\mathrm{track}} &= \sum_{j=1}^{M} \sum_{i=1}^{N} || \mathbf{y}_{j,i} - \hat{\mathbf{y}}_{j,i} ||
\end{align}
| 文字 | 解釈 |
|---|---|
| $\odot$ | channel-broadcast element-wise product |
VGGTの実装
VGGTの実行
$ python demo_gradio.py
demo_gradio.pyの確認
当項ではVGGTのdemo_gradio.pyの実装の確認を行います。
Gradioの基本的なトピックについては上記でまとめたので当記事では省略します。
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 6) Build Gradio UI
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
theme = gr.themes.Ocean()
theme.set(
checkbox_label_background_fill_selected="*button_primary_background_fill",
checkbox_label_text_color_selected="*button_primary_text_color",
)
with gr.Blocks(
...
) as demo:
# Instead of gr.State, we use a hidden Textbox:
is_example = gr.Textbox(label="is_example", visible=False, value="None")
num_images = gr.Textbox(label="num_images", visible=False, value="None")
gr.HTML(
"""
<h1>🏛️ VGGT: Visual Geometry Grounded Transformer</h1>
<p>
<a href="https://github.com/facebookresearch/vggt">🐙 GitHub Repository</a> |
<a href="#">Project Page</a>
</p>
<div style="font-size: 16px; line-height: 1.5;">
<p>Upload a video or a set of images to create a 3D reconstruction of a scene or object. VGGT takes these images and generates a 3D point cloud, along with estimated camera poses.</p>
<h3>Getting Started:</h3>
<ol>
<li><strong>Upload Your Data:</strong> Use the "Upload Video" or "Upload Images" buttons on the left to provide your input. Videos will be automatically split into individual frames (one frame per second).</li>
<li><strong>Preview:</strong> Your uploaded images will appear in the gallery on the left.</li>
<li><strong>Reconstruct:</strong> Click the "Reconstruct" button to start the 3D reconstruction process.</li>
<li><strong>Visualize:</strong> The 3D reconstruction will appear in the viewer on the right. You can rotate, pan, and zoom to explore the model, and download the GLB file. Note the visualization of 3D points may be slow for a large number of input images.</li>
<li>
<strong>Adjust Visualization (Optional):</strong>
After reconstruction, you can fine-tune the visualization using the options below
<details style="display:inline;">
<summary style="display:inline;">(<strong>click to expand</strong>):</summary>
<ul>
<li><em>Confidence Threshold:</em> Adjust the filtering of points based on confidence.</li>
<li><em>Show Points from Frame:</em> Select specific frames to display in the point cloud.</li>
<li><em>Show Camera:</em> Toggle the display of estimated camera positions.</li>
<li><em>Filter Sky / Filter Black Background:</em> Remove sky or black-background points.</li>
<li><em>Select a Prediction Mode:</em> Choose between "Depthmap and Camera Branch" or "Pointmap Branch."</li>
</ul>
</details>
</li>
</ol>
<p><strong style="color: #0ea5e9;">Please note:</strong> <span style="color: #0ea5e9; font-weight: bold;">VGGT typically reconstructs a scene in less than 1 second. However, visualizing 3D points may take tens of seconds due to third-party rendering, which are independent of VGGT's processing time. </span></p>
</div>
"""
)
target_dir_output = gr.Textbox(label="Target Dir", visible=False, value="None")
with gr.Row():
with gr.Column(scale=2):
input_video = gr.Video(label="Upload Video", interactive=True)
input_images = gr.File(file_count="multiple", label="Upload Images", interactive=True)
image_gallery = gr.Gallery(
label="Preview",
columns=4,
height="300px",
show_download_button=True,
object_fit="contain",
preview=True,
)
with gr.Column(scale=4):
with gr.Column():
gr.Markdown("**3D Reconstruction (Point Cloud and Camera Poses)**")
log_output = gr.Markdown(
"Please upload a video or images, then click Reconstruct.", elem_classes=["custom-log"]
)
reconstruction_output = gr.Model3D(height=520, zoom_speed=0.5, pan_speed=0.5)
with gr.Row():
submit_btn = gr.Button("Reconstruct", scale=1, variant="primary")
clear_btn = gr.ClearButton(
[input_video, input_images, reconstruction_output, log_output, target_dir_output, image_gallery],
scale=1,
)
with gr.Row():
prediction_mode = gr.Radio(
["Depthmap and Camera Branch", "Pointmap Branch"],
label="Select a Prediction Mode",
value="Depthmap and Camera Branch",
scale=1,
elem_id="my_radio",
)
with gr.Row():
conf_thres = gr.Slider(minimum=0, maximum=100, value=50, step=0.1, label="Confidence Threshold (%)")
frame_filter = gr.Dropdown(choices=["All"], value="All", label="Show Points from Frame")
with gr.Column():
show_cam = gr.Checkbox(label="Show Camera", value=True)
mask_sky = gr.Checkbox(label="Filter Sky", value=False)
mask_black_bg = gr.Checkbox(label="Filter Black Background", value=False)
mask_white_bg = gr.Checkbox(label="Filter White Background", value=False)
...
まず、上記のgr.HTML()内のHTMLが前項で確認した画面の文面と対応することを確認すると良いです。次にgr.Row()以下に2つのgr.Columnがあり、scaleがそれぞれ2と4であることと画面が1:2に左右に分割されていることについて着目すると良いと思います。
左のコンポーネントのlabelでUpload Video、Upload Images、Previewが指定されており、画面出力と対応することが確認できます。基本的にはUpload Imagesに画像をアップロードし、Previewで確認する流れになります。
右側のコンポーネントではgr.ButtonでReconstructボタン、gr.ClearButtonでClearボタンがそれぞれ実装されています。また、gr.Radioやgr.Slider、gr.Dropdown、gr.Checkboxなどを元に表示にあたっての諸パラメータの指定を行うことができます。
from visual_util import predictions_to_glb
with gr.Blocks(
...
) as demo:
...
with gr.Row():
with gr.Column(scale=2):
...
with gr.Column(scale=4):
...
with gr.Row():
conf_thres = gr.Slider(minimum=0, maximum=100, value=50, step=0.1, label="Confidence Threshold (%)")
frame_filter = gr.Dropdown(choices=["All"], value="All", label="Show Points from Frame")
with gr.Column():
show_cam = gr.Checkbox(label="Show Camera", value=True)
mask_sky = gr.Checkbox(label="Filter Sky", value=False)
mask_black_bg = gr.Checkbox(label="Filter Black Background", value=False)
mask_white_bg = gr.Checkbox(label="Filter White Background", value=False)
...
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Real-time Visualization Updates
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
conf_thres.change(
update_visualization,
[
target_dir_output,
conf_thres,
frame_filter,
mask_black_bg,
mask_white_bg,
show_cam,
mask_sky,
prediction_mode,
is_example,
],
[reconstruction_output, log_output],
)
次に画面からのパラメータ指定を出力に反映させる流れについて確認します。パラメータ指定を出力に反映させるにあたっては上記のようにgr.Slider.changeでupdate_visualizationを実行します。update_visualizationはdemo_gradio.pyに下記のように実装されています。
def update_visualization(
target_dir, conf_thres, frame_filter, mask_black_bg, mask_white_bg, show_cam, mask_sky, prediction_mode, is_example
):
"""
Reload saved predictions from npz, create (or reuse) the GLB for new parameters,
and return it for the 3D viewer. If is_example == "True", skip.
"""
...
predictions_path = os.path.join(target_dir, "predictions.npz")
if not os.path.exists(predictions_path):
return None, f"No reconstruction available at {predictions_path}. Please run 'Reconstruct' first."
key_list = [
"pose_enc",
"depth",
"depth_conf",
"world_points",
"world_points_conf",
"images",
"extrinsic",
"intrinsic",
"world_points_from_depth",
]
loaded = np.load(predictions_path)
predictions = {key: np.array(loaded[key]) for key in key_list}
glbfile = os.path.join(
target_dir,
f"glbscene_{conf_thres}_{frame_filter.replace('.', '_').replace(':', '').replace(' ', '_')}_maskb{mask_black_bg}_maskw{mask_white_bg}_cam{show_cam}_sky{mask_sky}_pred{prediction_mode.replace(' ', '_')}.glb",
)
if not os.path.exists(glbfile):
glbscene = predictions_to_glb(
predictions,
conf_thres=conf_thres,
filter_by_frames=frame_filter,
mask_black_bg=mask_black_bg,
mask_white_bg=mask_white_bg,
show_cam=show_cam,
mask_sky=mask_sky,
target_dir=target_dir,
prediction_mode=prediction_mode,
)
glbscene.export(file_obj=glbfile)
return glbfile, "Updating Visualization"
上記のプログラムは「出力されたPointmapなどを保存したpredictions.npzを都度読み込み、それぞれの出力を辞書形式でpredictionsに保存し、predictions_to_glbでしきい値に基づいた出力の調整とglb形式での可視化を行う」のように理解すると良いです。predictions_to_glbはvisual_util.pyに下記のように実装されています。
def predictions_to_glb(
predictions,
conf_thres=50.0,
filter_by_frames="all",
mask_black_bg=False,
mask_white_bg=False,
show_cam=True,
mask_sky=False,
target_dir=None,
prediction_mode="Predicted Pointmap",
) -> trimesh.Scene:
"""
Converts VGGT predictions to a 3D scene represented as a GLB file.
Args:
predictions (dict): Dictionary containing model predictions with keys:
- world_points: 3D point coordinates (S, H, W, 3)
- world_points_conf: Confidence scores (S, H, W)
- images: Input images (S, H, W, 3)
- extrinsic: Camera extrinsic matrices (S, 3, 4)
conf_thres (float): Percentage of low-confidence points to filter out (default: 50.0)
filter_by_frames (str): Frame filter specification (default: "all")
mask_black_bg (bool): Mask out black background pixels (default: False)
mask_white_bg (bool): Mask out white background pixels (default: False)
show_cam (bool): Include camera visualization (default: True)
mask_sky (bool): Apply sky segmentation mask (default: False)
target_dir (str): Output directory for intermediate files (default: None)
prediction_mode (str): Prediction mode selector (default: "Predicted Pointmap")
Returns:
trimesh.Scene: Processed 3D scene containing point cloud and cameras
Raises:
ValueError: If input predictions structure is invalid
"""
if not isinstance(predictions, dict):
raise ValueError("predictions must be a dictionary")
if conf_thres is None:
conf_thres = 10.0
print("Building GLB scene")
selected_frame_idx = None
if filter_by_frames != "all" and filter_by_frames != "All":
try:
# Extract the index part before the colon
selected_frame_idx = int(filter_by_frames.split(":")[0])
except (ValueError, IndexError):
pass
if "Pointmap" in prediction_mode:
print("Using Pointmap Branch")
if "world_points" in predictions:
pred_world_points = predictions["world_points"] # No batch dimension to remove
pred_world_points_conf = predictions.get("world_points_conf", np.ones_like(pred_world_points[..., 0]))
else:
print("Warning: world_points not found in predictions, falling back to depth-based points")
pred_world_points = predictions["world_points_from_depth"]
pred_world_points_conf = predictions.get("depth_conf", np.ones_like(pred_world_points[..., 0]))
else:
print("Using Depthmap and Camera Branch")
pred_world_points = predictions["world_points_from_depth"]
pred_world_points_conf = predictions.get("depth_conf", np.ones_like(pred_world_points[..., 0]))
# Get images from predictions
images = predictions["images"]
# Use extrinsic matrices instead of pred_extrinsic_list
camera_matrices = predictions["extrinsic"]
...
vertices_3d = pred_world_points.reshape(-1, 3)
# Handle different image formats - check if images need transposing
if images.ndim == 4 and images.shape[1] == 3: # NCHW format
colors_rgb = np.transpose(images, (0, 2, 3, 1))
else: # Assume already in NHWC format
colors_rgb = images
colors_rgb = (colors_rgb.reshape(-1, 3) * 255).astype(np.uint8)
conf = pred_world_points_conf.reshape(-1)
# Convert percentage threshold to actual confidence value
if conf_thres == 0.0:
conf_threshold = 0.0
else:
conf_threshold = np.percentile(conf, conf_thres)
conf_mask = (conf >= conf_threshold) & (conf > 1e-5)
...
vertices_3d = vertices_3d[conf_mask]
colors_rgb = colors_rgb[conf_mask]
if vertices_3d is None or np.asarray(vertices_3d).size == 0:
vertices_3d = np.array([[1, 0, 0]])
colors_rgb = np.array([[255, 255, 255]])
scene_scale = 1
else:
# Calculate the 5th and 95th percentiles along each axis
lower_percentile = np.percentile(vertices_3d, 5, axis=0)
upper_percentile = np.percentile(vertices_3d, 95, axis=0)
# Calculate the diagonal length of the percentile bounding box
scene_scale = np.linalg.norm(upper_percentile - lower_percentile)
colormap = matplotlib.colormaps.get_cmap("gist_rainbow")
# Initialize a 3D scene
scene_3d = trimesh.Scene()
# Add point cloud data to the scene
point_cloud_data = trimesh.PointCloud(vertices=vertices_3d, colors=colors_rgb)
scene_3d.add_geometry(point_cloud_data)
# Prepare 4x4 matrices for camera extrinsics
num_cameras = len(camera_matrices)
extrinsics_matrices = np.zeros((num_cameras, 4, 4))
extrinsics_matrices[:, :3, :4] = camera_matrices
extrinsics_matrices[:, 3, 3] = 1
if show_cam:
# Add camera models to the scene
for i in range(num_cameras):
world_to_camera = extrinsics_matrices[i]
camera_to_world = np.linalg.inv(world_to_camera)
rgba_color = colormap(i / num_cameras)
current_color = tuple(int(255 * x) for x in rgba_color[:3])
integrate_camera_into_scene(scene_3d, camera_to_world, current_color, scene_scale)
# Align scene to the observation of the first camera
scene_3d = apply_scene_alignment(scene_3d, extrinsics_matrices)
print("GLB Scene built")
return scene_3d
基本的にはconf_threshold = np.percentile(conf, conf_thres)やconf_mask = (conf >= conf_threshold) & (conf > 1e-5)などによってどの点を可視化してどの点を可視化しないかを指定するのように理解すると良いと思います。また、出力のglbファイルはtrimeshを用いて作成されます。
VGGTのネットワークの確認
...
from vggt.models.vggt import VGGT
...
model = VGGT()
...
def run_model(target_dir, model) -> dict:
...
with torch.no_grad():
with torch.cuda.amp.autocast(dtype=dtype):
predictions = model(images)
...
demo_gradio.pyでは上記のようにvggt/model/vggt.pyからVGGTクラスを読み込んで推論処理を行います。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from huggingface_hub import PyTorchModelHubMixin # used for model hub
from vggt.models.aggregator import Aggregator
from vggt.heads.camera_head import CameraHead
from vggt.heads.dpt_head import DPTHead
from vggt.heads.track_head import TrackHead
class VGGT(nn.Module, PyTorchModelHubMixin):
def __init__(self, img_size=518, patch_size=14, embed_dim=1024,
enable_camera=True, enable_point=True, enable_depth=True, enable_track=True):
super().__init__()
self.aggregator = Aggregator(img_size=img_size, patch_size=patch_size, embed_dim=embed_dim)
self.camera_head = CameraHead(dim_in=2 * embed_dim) if enable_camera else None
self.point_head = DPTHead(dim_in=2 * embed_dim, output_dim=4, activation="inv_log", conf_activation="expp1") if enable_point else None
self.depth_head = DPTHead(dim_in=2 * embed_dim, output_dim=2, activation="exp", conf_activation="expp1") if enable_depth else None
self.track_head = TrackHead(dim_in=2 * embed_dim, patch_size=patch_size) if enable_track else None
def forward(self, images: torch.Tensor, query_points: torch.Tensor = None):
"""
Forward pass of the VGGT model.
Args:
images (torch.Tensor): Input images with shape [S, 3, H, W] or [B, S, 3, H, W], in range [0, 1].
B: batch size, S: sequence length, 3: RGB channels, H: height, W: width
query_points (torch.Tensor, optional): Query points for tracking, in pixel coordinates.
Shape: [N, 2] or [B, N, 2], where N is the number of query points.
Default: None
Returns:
dict: A dictionary containing the following predictions:
- pose_enc (torch.Tensor): Camera pose encoding with shape [B, S, 9] (from the last iteration)
- depth (torch.Tensor): Predicted depth maps with shape [B, S, H, W, 1]
- depth_conf (torch.Tensor): Confidence scores for depth predictions with shape [B, S, H, W]
- world_points (torch.Tensor): 3D world coordinates for each pixel with shape [B, S, H, W, 3]
- world_points_conf (torch.Tensor): Confidence scores for world points with shape [B, S, H, W]
- images (torch.Tensor): Original input images, preserved for visualization
If query_points is provided, also includes:
- track (torch.Tensor): Point tracks with shape [B, S, N, 2] (from the last iteration), in pixel coordinates
- vis (torch.Tensor): Visibility scores for tracked points with shape [B, S, N]
- conf (torch.Tensor): Confidence scores for tracked points with shape [B, S, N]
"""
# If without batch dimension, add it
if len(images.shape) == 4:
images = images.unsqueeze(0)
if query_points is not None and len(query_points.shape) == 2:
query_points = query_points.unsqueeze(0)
aggregated_tokens_list, patch_start_idx = self.aggregator(images)
predictions = {}
with torch.cuda.amp.autocast(enabled=False):
if self.camera_head is not None:
pose_enc_list = self.camera_head(aggregated_tokens_list)
predictions["pose_enc"] = pose_enc_list[-1] # pose encoding of the last iteration
predictions["pose_enc_list"] = pose_enc_list
if self.depth_head is not None:
depth, depth_conf = self.depth_head(
aggregated_tokens_list, images=images, patch_start_idx=patch_start_idx
)
predictions["depth"] = depth
predictions["depth_conf"] = depth_conf
if self.point_head is not None:
pts3d, pts3d_conf = self.point_head(
aggregated_tokens_list, images=images, patch_start_idx=patch_start_idx
)
predictions["world_points"] = pts3d
predictions["world_points_conf"] = pts3d_conf
if self.track_head is not None and query_points is not None:
track_list, vis, conf = self.track_head(
aggregated_tokens_list, images=images, patch_start_idx=patch_start_idx, query_points=query_points
)
predictions["track"] = track_list[-1] # track of the last iteration
predictions["vis"] = vis
predictions["conf"] = conf
if not self.training:
predictions["images"] = images # store the images for visualization during inference
return predictions
入力画像に対応するimagesのメイン処理に用いられるクラスとメソッドはそれぞれ下記のように理解すると良いです。
| クラスとメソッド | 実装されているファイル | 動作 |
|---|---|---|
Aggregator(self.aggregator) |
vggt/models/aggregator.py |
Alternating-Attention(Global Attention + Frame Attention)による特徴量抽出 |
CameraHead(self.camera_head) |
vggt/heads/camera_head.py |
カメラパラメータの計算 |
DPTHead(self.point_head) |
vggt/heads/dpt_head.py |
Dense Prediction(Pointmap) |
DPTHead(self.depth_head) |
vggt/heads/dpt_head.py |
Dense Prediction(Depth) |
TrackHead(self.track_head) |
vggt/heads/track_head.py |
Dense Prediction(Tracking) |
以下ではそれぞれのクラスについて詳しく確認します。
Aggregatorクラス
class Aggregator(nn.Module):
"""
The Aggregator applies alternating-attention over input frames,
as described in VGGT: Visual Geometry Grounded Transformer.
Remember to set model.train() to enable gradient checkpointing to reduce memory usage.
Args:
img_size (int): Image size in pixels.
patch_size (int): Size of each patch for PatchEmbed.
embed_dim (int): Dimension of the token embeddings.
depth (int): Number of blocks.
num_heads (int): Number of attention heads.
mlp_ratio (float): Ratio of MLP hidden dim to embedding dim.
num_register_tokens (int): Number of register tokens.
block_fn (nn.Module): The block type used for attention (Block by default).
qkv_bias (bool): Whether to include bias in QKV projections.
proj_bias (bool): Whether to include bias in the output projection.
ffn_bias (bool): Whether to include bias in MLP layers.
patch_embed (str): Type of patch embed. e.g., "conv" or "dinov2_vitl14_reg".
aa_order (list[str]): The order of alternating attention, e.g. ["frame", "global"].
aa_block_size (int): How many blocks to group under each attention type before switching. If not necessary, set to 1.
qk_norm (bool): Whether to apply QK normalization.
rope_freq (int): Base frequency for rotary embedding. -1 to disable.
init_values (float): Init scale for layer scale.
"""
def __init__(
self,
img_size=518,
patch_size=14,
embed_dim=1024,
depth=24,
num_heads=16,
mlp_ratio=4.0,
num_register_tokens=4,
block_fn=Block,
qkv_bias=True,
proj_bias=True,
ffn_bias=True,
patch_embed="dinov2_vitl14_reg",
aa_order=["frame", "global"],
aa_block_size=1,
qk_norm=True,
rope_freq=100,
init_values=0.01,
):
super().__init__()
...
self.depth = depth
...
self.aa_block_size = aa_block_size
...
self.aa_block_num = self.depth // self.aa_block_size
...
def forward(self, images: torch.Tensor) -> Tuple[List[torch.Tensor], int]:
"""
Args:
images (torch.Tensor): Input images with shape [B, S, 3, H, W], in range [0, 1].
B: batch size, S: sequence length, 3: RGB channels, H: height, W: width
Returns:
(list[torch.Tensor], int):
The list of outputs from the attention blocks,
and the patch_start_idx indicating where patch tokens begin.
"""
...
for _ in range(self.aa_block_num):
for attn_type in self.aa_order:
if attn_type == "frame":
tokens, frame_idx, frame_intermediates = self._process_frame_attention(
tokens, B, S, P, C, frame_idx, pos=pos
)
elif attn_type == "global":
tokens, global_idx, global_intermediates = self._process_global_attention(
tokens, B, S, P, C, global_idx, pos=pos
)
else:
raise ValueError(f"Unknown attention type: {attn_type}")
for i in range(len(frame_intermediates)):
# concat frame and global intermediates, [B x S x P x 2C]
concat_inter = torch.cat([frame_intermediates[i], global_intermediates[i]], dim=-1)
output_list.append(concat_inter)
Aggregatorクラスではforwardメソッド内のfor _ in range(self.aa_block_num)のループ内のself._process_frame_attentionとself._process_global_attentionでFrame AttentionとGlobal Attentionの処理をself.aa_block_num回実行します。
class Aggregator(nn.Module):
...
def _process_frame_attention(self, tokens, B, S, P, C, frame_idx, pos=None):
"""
Process frame attention blocks. We keep tokens in shape (B*S, P, C).
"""
# If needed, reshape tokens or positions:
if tokens.shape != (B * S, P, C):
tokens = tokens.view(B, S, P, C).view(B * S, P, C)
if pos is not None and pos.shape != (B * S, P, 2):
pos = pos.view(B, S, P, 2).view(B * S, P, 2)
intermediates = []
# by default, self.aa_block_size=1, which processes one block at a time
for _ in range(self.aa_block_size):
if self.training:
tokens = checkpoint(self.frame_blocks[frame_idx], tokens, pos, use_reentrant=self.use_reentrant)
else:
tokens = self.frame_blocks[frame_idx](tokens, pos=pos)
frame_idx += 1
intermediates.append(tokens.view(B, S, P, C))
return tokens, frame_idx, intermediates
def _process_global_attention(self, tokens, B, S, P, C, global_idx, pos=None):
"""
Process global attention blocks. We keep tokens in shape (B, S*P, C).
"""
if tokens.shape != (B, S * P, C):
tokens = tokens.view(B, S, P, C).view(B, S * P, C)
if pos is not None and pos.shape != (B, S * P, 2):
pos = pos.view(B, S, P, 2).view(B, S * P, 2)
intermediates = []
# by default, self.aa_block_size=1, which processes one block at a time
for _ in range(self.aa_block_size):
if self.training:
tokens = checkpoint(self.global_blocks[global_idx], tokens, pos, use_reentrant=self.use_reentrant)
else:
tokens = self.global_blocks[global_idx](tokens, pos=pos)
global_idx += 1
intermediates.append(tokens.view(B, S, P, C))
return tokens, global_idx, intermediates
DPTHeadクラス
下記で詳しく取り扱いましたので当記事では省略します。