この記事の内容:
「力学系のリアプノフ指数を求める標準的な数値計算は,RNNを使ったKerasのModelとして完全に書ける.」
Tensorflow のKeras RNNレイヤーを使って計算の流れを実装してみます.
すでに微分可能な関数$f$がわかっている場合を扱います.リカレントニューラルネットワークを時系列データから学習させ力学系を同定し,リアプノフ指数を推定する,という内容ではありません.
環境:
- python 3.8
- tensorflow 2.4
問題
状態量$x \in R^{d}$ の時間発展が
x_{n+1}=f(x_{n})
で表される力学系を考えて,その軌道のリアプノフ指数をすべて数値的に求めます.
QR分解(グラム・シュミット直交化)を行い基底を変換しながら接空間内の互いに直交する方向ごとの伸び率を推定するという標準的な数値計算法を使います. リアプノフ指数の定義については力学系に関するテキスト等を参考にしてください.
Hénon写像
(x_{n+1}, y_{n+1}) = ( 1 -a x_{n}^2+y_{n}, bx_{n})
を例にして行います.
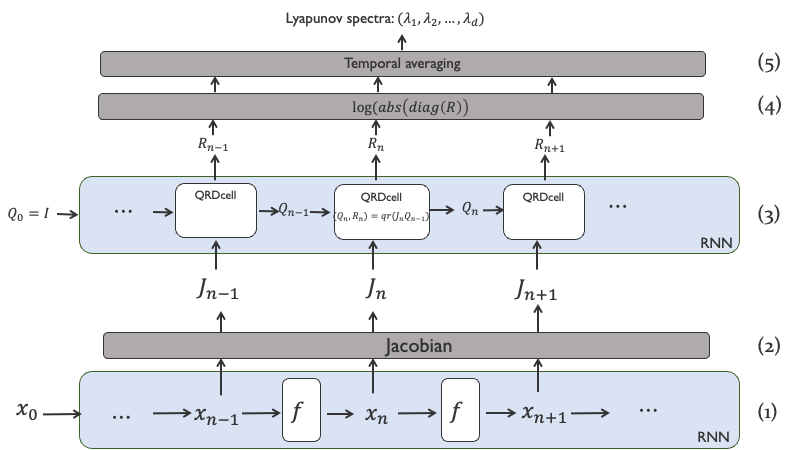
計算フロー
全体の計算フローはこの図のようになります. tenorflowでの実装はすべてbatch計算に対応した形になり,複数の軌道の同時計算できることを前提にしています.
下からみていきます.
(1) 軌道の計算
初期値$x_0$ から軌道$(x_1, x_2,.., x_L)$ を求めます. 実装上は写像をRNNのcellとして定義して,軌道計算をRNNとして実装することで行うことができます. 前回に書いた記事でここまでやっています. RNNクラスの使い方は前回の記事参照してください.
(2) Jacobianの計算
各$x_n$ からヤコビアン$J_{f}(x_n)=...$ を求めます. ヤコビアンを求める部分をKerasレイヤー化しておきます.
(3) Jacobianの積をQR分解しながら計算
$Q_0$ を単位行列として準備します.
nステップでは,ヤコビアン$J_{n}$を$Q_{n-1}$に掛け,結果をQR分解します:
Q_{n}R_{n}=J_{n}Q_{n-1}
そして$Q_{n}$を次のステップに送ります.
この結果Jacobianの積$J_{L}\cdots J_{2}J_{1}$は
Q_{L}R_{L}\cdots R_{2}R_{1}=J_{L}\cdots J_{2}J_{1}
となります.
この流れもRNNレイヤーとして実装できます.
$Q_{n}$がRNNの内部状態(state), $J_{n}$が入力,$R_{n}$ が出力となります.
(4) Rの対角項をとり,絶対値の対数をとる.
(5) 要素毎に時間方向の平均を取る.
これがリアプノフ指数の推定値になります.
コード
準備
倍精度を使います.
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras import layers
import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
tf.keras.backend.set_floatx('float64')
mydtype = tf.float64
Hénon写像の定義・軌道を計算するRNN
前回に書いた記事 とやってることは同じなので省略します.
公開したgithubのコードでは実際は実装を少し変えてtf.stackを使わないようにしたため,見づらいですが速度は上がっています.
Jacobian Layer
Jacobianの計算を行うKerasレイヤーを定義します.(batch_size, 時間ステップ, 力学系の次元) のテンソル'X'を受け取って,各サンプル,各時刻ごとにヤコビアンを計算します. GradientTapeで記録するなかで各$x_n$で$f(x_n)$ をもう一度計算し,GradientTape.batch_jacobianを使いヤコビアンを出しますが,その仕様上,前後でreshapeをしています.
レイヤーはステップ数をオプションの引数で与えることにしておきます.
class Jacobian(layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, func, **kwargs):
''' input-output shapes of func should be (batch, dim) -> (batch, dim)
'''
self.func = func
super(Jacobian, self).__init__(**kwargs)
def call(self, X, t_length=None):
# x have (batch, timestep, dim)
if t_length == None:
t_length = X.shape[1]
batch_size = X.shape[0]
X = tf.reshape(X, [batch_size*t_length, X.shape[2]])
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
tape.watch(X)
X_next, _ = self.func(None, [X])
Jxs = tape.batch_jacobian(X_next, X)
Jxs = tf.reshape(Jxs, [batch_size, t_length, X.shape[1], X.shape[1]])
return Jxs
QR分解レイヤー
(3)に対応する計算を行うKerasレイヤーをRNNで作るため,1ステップ計算を実装するcellを作ります.
初期状態として単位行列を設定するための関数get_initial_stateを忘れないように書いておきます.
class QRDcell(layers.Layer):
'''
performing successive QR decomposition.
This class can be used as a RNN cell in Keras RNN Layer
'''
def __init__(self, dim=2, **kwargs):
super(QRDcell, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.dim = dim
# d x d dimension (d is a dimension of dynamical systems)
self.state_size = tf.TensorShape([dim, dim])
self.output_size = tf.constant(dim)
def get_initial_state(self, inputs=None, batch_size=None, dtype=mydtype):
''' return identity matrices'''
return tf.linalg.eye(self.dim, self.dim, batch_shape=[batch_size], dtype=mydtype)
def call(self, inputs, states):
# inputs is J_{n} (batch, dim, dim)
# states is Q_{n-1} (batch, dim,dim). Q_{0} is identity matrix
# Q_{n}R_{n} = J_{n}Q_{n-1}
# Q_{n} is the next state. (Q_new)
# R_{n} is the output. (R_new)
J = inputs
Q = states[0]
Q_new, R_new = tf.linalg.qr(J@Q)
return R_new, [Q_new]
モデルの構築
Keras Functional API を使って計算の流れを記述しモデルを作成します.
# parameters
batch_size = tf.constant(10, dtype=tf.int32)
dim = tf.constant(2, dtype=tf.int32)
t_length = tf.constant(10000, dtype=tf.int32)
# layers
hc = HenonCell(a=1.4, b=0.3)
henon_rnn = layers.RNN(hc, return_sequences=True)
jl = Jacobian(hc)
qrd_rnn = layers.RNN(QRDcell(), return_sequences=True)
# inputs (initial conditions and time length)
input_initial_condition = keras.Input(shape=(dim,), dtype=mydtype) # input object for keras model
tlength_inp = keras.Input(batch_shape=(1,), dtype=tf.int32) # passing model length of timesteps
# tracing forward calculation
dummy_input = tf.zeros(
shape=[batch_size, tlength_inp[0], dim], dtype=mydtype)
X = henon_rnn(dummy_input, initial_state=input_initial_condition) # 軌道の計算
js = jl(X, t_length=tlength_inp[0]) # reshapeするときに必要なため,明示的にt_length_inp[0] を渡す.(これはt_lengthが決まっているtensorのときは必要ない)
rs = qrd_rnn(js) # qr分解しながらRを集める.
log_diag_r = tf.math.log(tf.math.abs(
tf.linalg.diag_part(rs))) # Rの対角項をとって絶対値の対数を取る
m_log_r = tf.reduce_mean(log_diag_r, axis=1) # 平均
# functional APIによりモデル作成
# 軌道計算するモデル
gen_trj = keras.models.Model(inputs=[input_initial_condition, tlength_inp], outputs=X)
# リアプノフ指数の計算までするモデル
est_lyap = keras.models.Model(inputs=[input_initial_condition, tlength_inp], outputs=m_log_r)
# 高速化する関数
@tf.function
def calc_lyap(x0, t_length):
return est_lyap([x0, t_length])
計算実行・結果
実際に計算する部分です.
初期値が異なると有限の長さでは異なった値になるため,バッチ内のサンプル平均と標準偏差を表示しています.
g1 = tf.random.Generator.from_non_deterministic_state()
x0 = 0.1*g1.normal(shape=(batch_size, dim), dtype=mydtype)
lyaps_batch = calc_lyap(x0, t_length)
lyap_ave = tf.reduce_mean(lyaps_batch, axis=0)
lyap_std = tf.math.reduce_std(lyaps_batch, axis=0)
print(f'Estimation of lyapnov exponents (average over different trajectories +- std.):')
for i,(av,st) in enumerate(zip(lyap_ave, lyap_std)):
print(f'{i}: {av.numpy()} +- {st.numpy()} ')
Estimation of lyapnov exponents (average over different trajectories +- std.):
0: 0.41938474252452246 +- 0.002342227276169231
1: -1.6233575468504582 +- 0.0023422272761692764
memo
- 改良する点: 初期遷移のステップを計算から除くなど
- Jacobianの計算のために$f$を2度計算するのはコストがかかるので,一度でできるのではないか?
- RNNcell内でJacobianを計算すればそのようにできるが,使い勝手が悪いのでは.
- Jacobianを求めるときの$f$は並列的に計算できるので,実際の計算時間はほとんど変わらないのでは.
github
コードを下記に公開しています.
https://github.com/yymgch/sample_codes_public/blob/master/tf_lyapunov_exp.py