目的
pythonを用いてGUIを操作し、画像変換器を作成します。
実行環境
Python version: 3.9.13
OS: Windows 10
イメージ
完成したGUIをキャプチャしてます。画像を選択します。左には、加工前の画像(Base)と右には加工後の画像を(Effect)を表示するようにしています。タブを選択すると、設定してあるいくつかの加工ができるようにしています。
ライブラリ
GUI表示、画像処理ライブラリを選んだ背景です。また、モジュールを3つに分けてプログラムを作成しており、その背景について簡単に説明します。
GUI
以前の記事では、PySimpleGUIを使用していたのですが、違うGUIを使用してみたかったので、今回は、tkinterを使用することにしました。
GUIは、tkinterを使用してます。
画像処理
画像処理は、Pillow, NumPy, OpenCVなどいくつかありますが、今回は、画像処理を中心に行いたかったため、こちらの記事を参考にPillow(PIL)を使用するとにしました。
MVCモデル
今回、こちらの記事からMVC(Model View Controller)モデルを知りました。classやdefの使い方を知りたかったので、MVCモデルで作成することにしました。
プログラム
この記事を書いたときのプログラムは、githubのv0.1にあります。プログラムは、Model(GUI_model.py) View(run_gui.py) Controller(GUI_control.py)としています。run_gui.pyでは、GUIの外観のボタン、画像の配置をしています。GUI_control.pyでは、Comboboxで選択された加工をするための操作を分けています。GUI_model.pyでは、実際に画像を加工するためのプログラムを実行してます。
プログラム内のclass名と役割は下記のようにしています。
| Class名 | 役割 |
|---|---|
| Set_gui | GUIの外観(表示、イベント登録) |
| GUI_control | GUIの操作 |
| GUI_model | 画像処理 |
走行方法
プログラムは、githubに置いています。3つのファイル(GUI_model.py,run_gui.py,GUI_control.py)を同じディレクトリに置き、下記コマンドを実行すると、走行します。
$ python run_gui.py
run_gui.py
GUIの外観ボタンは、下記のように関数を設定しました。
| def | 概要 |
|---|---|
| init | Tkinterの部品生成 |
| on_click_close | main windowのclose |
| draw_default_image | entryに画像のpath表示、呼び出した画像をcanvasに表示する |
| effect_event | 画像の加工処理 |
| replace_effect_image | 加工処理をした画像をcanvas部分に反映する |
プログラムは、下記のようにしています。
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
from PIL import Image, ImageOps, ImageTk
from GUI_control import GUI_control
class Set_gui:
def __init__(self, main_window):
# controller Class生成
self.control = GUI_control()
# Variable setting
self.function_btn = [
"Gray_scale",
"Binarization",
"Sepia",
"Jagged_mosaic",
"Soft_mosaic",
"Quantize",
"Invert",
"Mirror",
"Flip",
"Posterize",
"Solarize",
"Equalize",
"Counter",
"Emboss",
"Find_emboss",
]
self.canvas_title = ["Base", "Effect"]
# Main window
self.main_window = main_window
self.main_window.geometry("1400x800")
self.main_window.title("Image Editor v0.10")
# Sub window
self.filepath_frame = tk.Frame(self.main_window, height=100, width=400)
self.func_frame = tk.Frame(self.main_window, height=450, width=400)
self.exit_frame = tk.Frame(self.main_window, height=100, width=400)
self.canvas_frame = tk.Frame(self.main_window, height=450, width=400)
# Widgetsmith
self.filepath_frame.place(relx=0.05, rely=0.8)
self.func_frame.place(relx=0.85, rely=0.15)
self.exit_frame.place(relx=0.85, rely=0.8)
self.canvas_frame.place(relx=0.05, rely=0.05)
# 1. Set file path
self.imp_path_btn = tk.Button(
self.filepath_frame,
text="Select_image_file",
command=self.draw_default_image,
)
self.imp_path_btn.grid(row=0, column=0, sticky=tk.W, padx=10, pady=5)
self.img_path_stvar = tk.StringVar()
self.imp_path_entry = tk.Entry(
self.filepath_frame, textvariable=self.img_path_stvar, width=70
)
self.imp_path_entry.grid(row=1, column=0, sticky=tk.EW, padx=10)
# 2. Set Function botton
self.func_combobox = ttk.Combobox(
self.func_frame,
text="combo_file",
state="readonly",
value=self.function_btn,
width=30,
)
self.func_combobox.set(self.function_btn[0])
self.func_combobox.bind("<<ComboboxSelected>>", self.effect_event)
self.func_combobox.pack()
# 3.1 canvas_frame title
for i in range(2):
label = tk.Label(
self.canvas_frame,
text=self.canvas_title[i],
bg="white",
relief=tk.RIDGE,
)
label.grid(row=0, column=i, sticky=tk.W + tk.E)
# 3.2 canvas_frame title
self.base_canvas = tk.Canvas(
self.canvas_frame, width=500, height=500, bg="#A9A9A9"
)
self.base_canvas.grid(row=1, column=0)
self.effect_canvas = tk.Canvas(
self.canvas_frame, width=500, height=500, bg="#A9A9A9"
)
self.effect_canvas.grid(row=1, column=1)
# 4 set to close the window
self.button = tk.Button(
self.exit_frame, text="Exit", width=10, command=self.on_click_close
)
self.button.grid(row=0, column=0, sticky=tk.SE, padx=10, pady=10)
# Function for closing window
def on_click_close(self):
self.main_window.destroy()
def draw_default_image(self):
self.img_path = self.control.get_image_path()
self.img_path_stvar.set(self.img_path)
(
self.effect_img,
self.base_canvas,
self.effect_canvas_create,
) = self.control.draw_image(self.img_path, self.base_canvas, self.effect_canvas)
def effect_event(self, arg):
self.converted_img = self.control.effect_image(
self.effect_img, self.func_combobox
)
self.replace_effect_image(self.converted_img)
def replace_effect_image(self, pic_img):
self.effect_canvas.photo = ImageTk.PhotoImage(pic_img)
self.effect_canvas.itemconfig(
self.effect_canvas_create, image=self.effect_canvas.photo
)
def main():
# Tk MainWindow
main_window = tk.Tk()
# Viewクラス生成
Set_gui(main_window)
# フレームループ処理
main_window.mainloop()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
tkinterについて
run_gui.pyで使われているtkinterのイメージを説明します。
1.main windowの作成
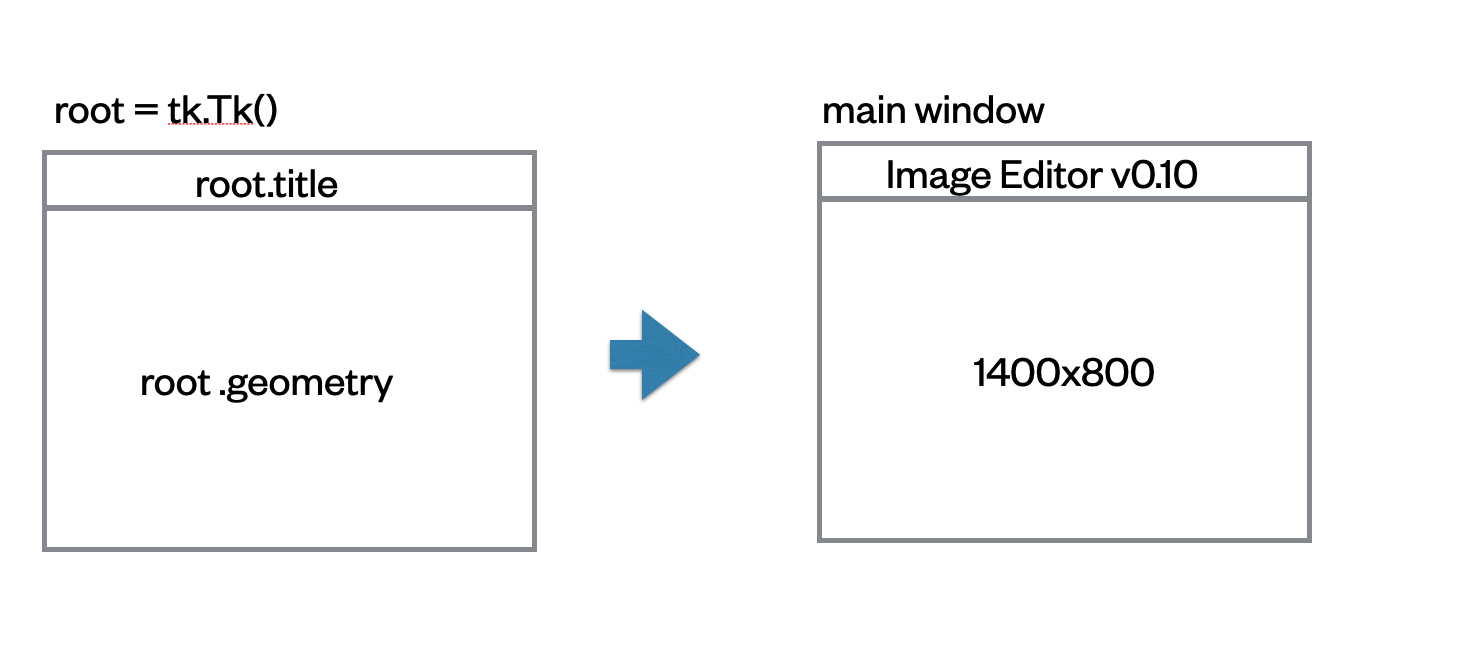
main windowの部分は、外観を作っています。タイトルは、上部の部分に出力されます。geometryは、main windowを開いた時の大きさを決めています。
2.frame(sub window)の作成

大枠の部分をいくつかの領域に分けるためframeを使っています。私は、canvas、func、file_path,quitと4つの領域に分けて作成しました。relx,relyは、フレームの幅を1として相対的な位置を示しています。
3.botton,entry,imageの作成
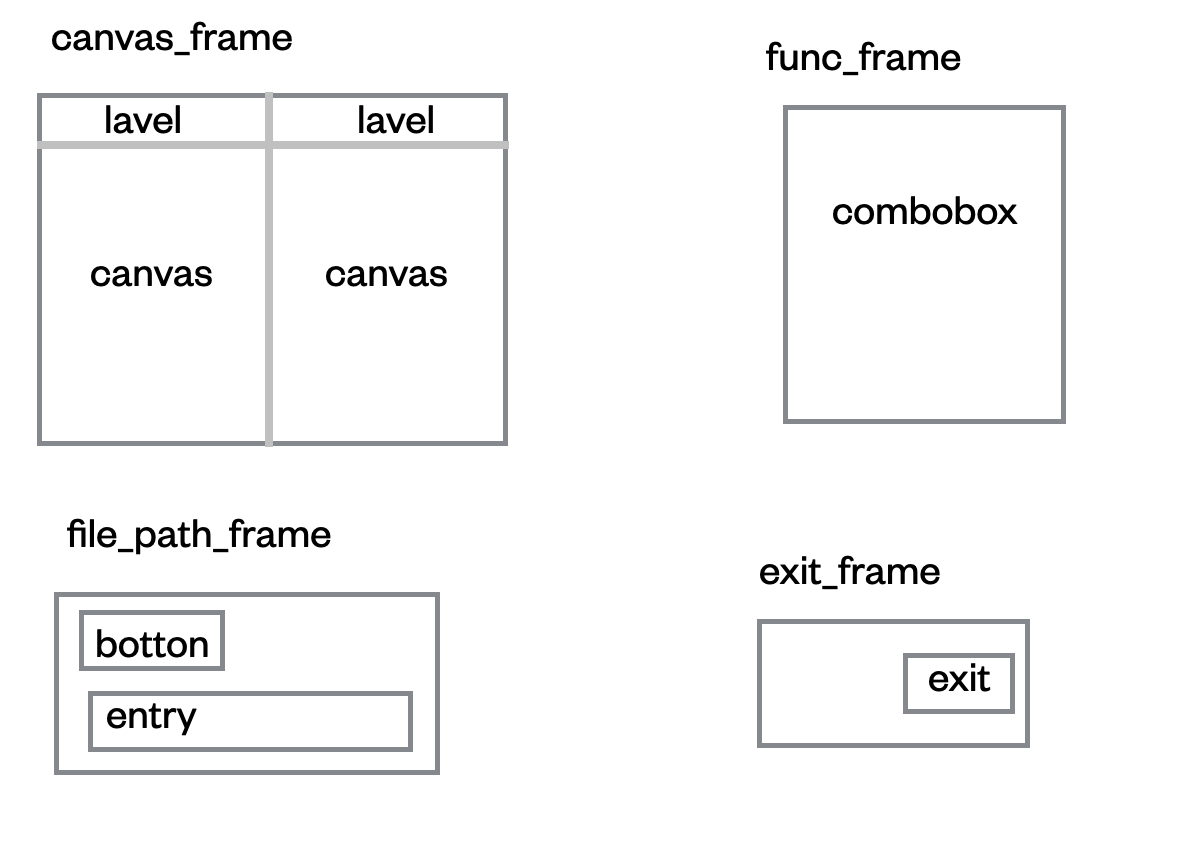
2.で各フレームごとに分けたので、どんなbotton、box、canvas を各フレームごとに決めていきます。
4.図形の変更

最後に描写した画像を変更する場合、.itemconfigを使用することで変更することができます。
GUI_control.py
GUIの操作は、下記のように関数を設定しました。
| def | 概要 |
|---|---|
| init | 初期化 |
| get_image_path | 画像ファイルのpath取得 |
| draw_image | 画像ファイルをcanvasのサイズに合わせて調整する。エフェクト加工前のファイルをcanvasに表示する。 |
| effect_image | comboxで選択した加工処理をmodelへ渡す。 |
プログラムは、下記のようにしています。
from GUI_model import GUI_model
class GUI_control:
def __init__(self):
self.model = GUI_model()
# Function for closing window
def get_image_path(self):
img_file_path = self.model.get_path()
return img_file_path
def draw_image(self, im_path, base_canvas, effect_canvas):
resize_img, base_img_canvas, effect_canvas_create = self.model.resize_image(
im_path, base_canvas, effect_canvas
)
return resize_img, base_img_canvas, effect_canvas_create
def effect_image(self, effect_img, func_combobox):
func_no = func_combobox.current()
func_name = func_combobox.get()
if func_no <= 2:
convert_img = self.model.retouch_gray_scale(effect_img)
if func_name == "Gray_scale":
converted_img = convert_img
elif func_name == "Binarization":
converted_img = self.model.retouch_binarization(convert_img)
elif func_name == "Sepia":
converted_img = self.model.retouch_sepia(convert_img)
elif func_name == "Jagged_mosaic":
converted_img = self.model.retouch_jagged_mosaic(effect_img)
elif func_name == "Soft_mosaic":
converted_img = self.model.retouch_soft_mosaic(effect_img)
elif func_name == "Quantize":
converted_img = self.model.retouch_alpha_blend(effect_img)
elif func_name == "Invert":
converted_img = self.model.retouch_invert(effect_img)
elif func_name == "Mirror":
converted_img = self.model.retouch_mirror(effect_img)
elif func_name == "Flip":
converted_img = self.model.retouch_flip(effect_img)
elif func_name == "Posterize":
converted_img = self.model.retouch_posterize(effect_img)
elif func_name == "Solarize":
converted_img = self.model.retouch_solarize(effect_img)
elif func_name == "Equalize":
converted_img = self.model.retouch_equalize(effect_img)
elif func_name == "Counter":
converted_img = self.model.retouch_counter(effect_img)
elif func_name == "Emboss":
converted_img = self.model.retouch_emboss(effect_img)
elif func_name == "Find_emboss":
converted_img = self.model.retouch_findemboss(effect_img)
return converted_img
GUI_model.py
画像処理は、下記のように関数を設定しました。実行処理については、PIL/Pillow チートシートを参考にしてます。
| def | 概要 |
|---|---|
| get_path | 画像ファイルのpath取得 |
| resize_image | 画像ファイルの大きさを調べて、キャンバスのサイズに合わせて調整する。 |
| retouch_gray_scale | グレイスケールに変換する(Imageモジュール) |
| retouch_binarization | 2値化(Imageモジュール) |
| retouch_sepia | セピアに変換する(Imageモジュール) |
| retouch_jagged_mosaic | ギザギザモザイク(Imageモジュール) |
| retouch_soft_mosaic | やわらかいモザイク(Imageモジュール) |
| retouch_alpha_blend | アルファブレンド(Imageモジュール) |
| retouch_invert | ネガポジ反転(ImageOpsモジュール) |
| retouch_mirror | 左右反転(ImageOpsモジュール) |
| retouch_flip | 上下反転(ImageOpsモジュール) |
| retouch_posterize | ポスタライズ(ImageOpsモジュール) |
| retouch_solarize | ソーラライズ(ImageOpsモジュール) |
| retouch_equalize | イコライズ(ImageOpsモジュール) |
| retouch_counter | counter表示(ImageFilterモジュール) |
| retouch_emboss | emboss表示(ImageFilterモジュール) |
| retouch_findemboss | findemboss表示(ImageFilterモジュール) |
プログラムは、下記のようにしています。
from tkinter import filedialog
from tkinter.filedialog import askopenfile
from PIL import Image, ImageFilter, ImageOps, ImageTk
class GUI_model:
def __init__(self):
self.file_filter = [("Image file", ".bmp .png .jpg .tif")]
def get_path(self):
return filedialog.askopenfilename(
title="Please select image file,", filetypes=self.file_filter
)
def resize_image(self, path, base_canvas, effect_canvas):
resize_img = Image.open(path)
w = resize_img.width
h = resize_img.height
w_offset = 250 - (w * (500 / h) / 2)
h_offset = 250 - (h * (500 / w) / 2)
if w > h:
resize_img = resize_img.resize((int(w * (500 / w)), int(h * (500 / w))))
else:
resize_img = resize_img.resize((int(w * (500 / h)), int(h * (500 / h))))
self.pil_base_img = ImageTk.PhotoImage(resize_img)
self.pil_effect_img = self.pil_base_img
if w > h:
base_img_canvas = base_canvas.create_image(
0, h_offset, anchor="nw", image=self.pil_base_img
)
effect_canvas_create = effect_canvas.create_image(
0, h_offset, anchor="nw", image=self.pil_effect_img
)
else:
base_img_canvas = base_canvas.create_image(
w_offset, 0, anchor="nw", image=self.pil_base_img
)
effect_canvas_create = effect_canvas.create_image(
w_offset, 0, anchor="nw", image=self.pil_effect_img
)
return resize_img, base_img_canvas, effect_canvas_create
# effect image model
def retouch_gray_scale(self, ef_img):
convert_img = ef_img.convert("L")
return convert_img
def retouch_binarization(self, ef_img):
converted_img = ef_img.point(lambda x: 0 if x < 230 else x)
return converted_img
def retouch_sepia(self, ef_img):
converted_img = Image.merge(
"RGB",
(
ef_img.point(lambda x: x * 240 / 255),
ef_img.point(lambda x: x * 200 / 255),
ef_img.point(lambda x: x * 145 / 255),
),
)
return converted_img
def retouch_jagged_mosaic(self, ef_img):
converted_img = ef_img.resize([x // 8 for x in ef_img.size]).resize(ef_img.size)
return converted_img
def retouch_soft_mosaic(self, ef_img):
gimg = ef_img.filter(ImageFilter.GaussianBlur(4))
converted_img = gimg.resize([x // 8 for x in ef_img.size]).resize(ef_img.size)
return converted_img
def retouch_alpha_blend(self, ef_img):
converted_img = ef_img.quantize(4)
return converted_img
def retouch_invert(self, ef_img):
converted_img = ImageOps.invert(ef_img.convert("RGB"))
return converted_img
def retouch_mirror(self, ef_img):
converted_img = ImageOps.mirror(ef_img.convert("RGB"))
return converted_img
def retouch_flip(self, ef_img):
converted_img = ImageOps.flip(ef_img.convert("RGB"))
return converted_img
def retouch_posterize(self, ef_img):
converted_img = ImageOps.posterize(ef_img.convert("RGB"), 2)
return converted_img
def retouch_solarize(self, ef_img):
converted_img = ImageOps.solarize(ef_img.convert("RGB"), 128)
return converted_img
def retouch_equalize(self, ef_img):
converted_img = ImageOps.equalize(ef_img.convert("RGB"))
return converted_img
def retouch_counter(self, ef_img):
converted_img = ef_img.filter(ImageFilter.CONTOUR)
return converted_img
def retouch_emboss(self, ef_img):
converted_img = ef_img.filter(ImageFilter.EMBOSS)
return converted_img
def retouch_findemboss(self, ef_img):
converted_img = ef_img.filter(ImageFilter.FIND_EDGES)
return converted_img
その他
作成時に参考にしたサイトをまとめておきます。
| 項目 | サイト名 |
|---|---|
| color codeの調査 | Modern browsers support 140 named colors |
| 変数について | グローバル変数とか |
| デバック | pythonで、ログ表示やデバック時に使う、行番号、関数名、ファイル名を表示 |
| 関数名を考える | Naming -名前付け- |
| 自動整形 | [Python]blackとisortで自動フォーマット |
補足
一人で適当にコードを書いたので、blackとisortで自動整形しました。実行コマンドは、下記です。
# black
black ファイル名
# isort
isort ファイル名
