概要
ハッカソンでRaspberry PiとGrove Pi+スターターキット、kintoneを活用することになり、Pythonで問題なく利用できるか調べました。結果、GitHubに公開しているgrovepi.pyには不具合があり修正する必要がありますが、付属センサは概ね利用できました。
Grove Pi+ スターターキット 初心者向け Raspberry Pi A+,B,B+&2,3適用 CE認証(写真はGrove Pi本体)
https://shop.dexterindustries.com/grovepi-starter-kit-raspberry-pi/

Grove Pi+ の設定と試験環境
使用OS
Raspbian Buster with desktop
Version:September 2019
Release date:2019-09-26
Kernel version:4.19
使用ライブラリィ
library supports this fw versions: 1.3.0
以下の情報を参考に設定
https://www.dexterindustries.com/GrovePi/get-started-with-the-grovepi/setting-software/
(重要)ライブラリィ不具合の修正
以下の__「Raspberry PiでGrove Pi+スターターキットとカメラを使う初期設定」の”Grove Pi+のライブラリィ不具合”を参照__し、grovepi.py を修正。
https://qiita.com/yukataoka/items/9df2c74f7cd514e04b97#grove-pi%E3%81%AE%E3%83%A9%E3%82%A4%E3%83%96%E3%83%A9%E3%83%AA%E3%82%A3%E4%B8%8D%E5%85%B7%E5%90%88
試験環境
デフォルトのアカウント pi のルート(/home/pi)配下に、以下の手順で設定。
$ mkdir ~/pgm
$ cd ~/pgm
$ cp ~/Dexter/GrovePi/Software/Python/grovepi.py ~/pgm
$ cp ~/Dexter/GrovePi/Software/Python/grove_rgb_lcd/grove_rgb_lcd.py ~/pgm
$ python grovepi.py
library supports this fw versions: 1.3.0
Grove Pi+ スターターキット付属のセンサを試す
1.Example Project: LED Fade(LEDのフェード)
https://www.dexterindustries.com/GrovePi/projects-for-the-raspberry-pi/
http://www.dexterindustries.com/GrovePi/projects-for-the-raspberry-pi/led-fade/
https://github.com/DexterInd/GrovePi/blob/master/Projects/LED_Fade/led_fade.py
コード
import time
import grovepi
# Connect the Rotary Angle Sensor to analog port A2
potentiometer = 2
# Connect the LED to digital port D5
led = 5
grovepi.pinMode(led,"OUTPUT")
time.sleep(1)
i = 0
while True:
try:
# Read resistance from Potentiometer
i = grovepi.analogRead(potentiometer)
print(i)
# Send PWM signal to LED
grovepi.analogWrite(led,i//4)
time.sleep(0.5)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
break
except (IOError,TypeError) as e:
print("Error")
break
結果
$ python led_fade.py
0
0
12
546
1023
1023
1023
945
0
0
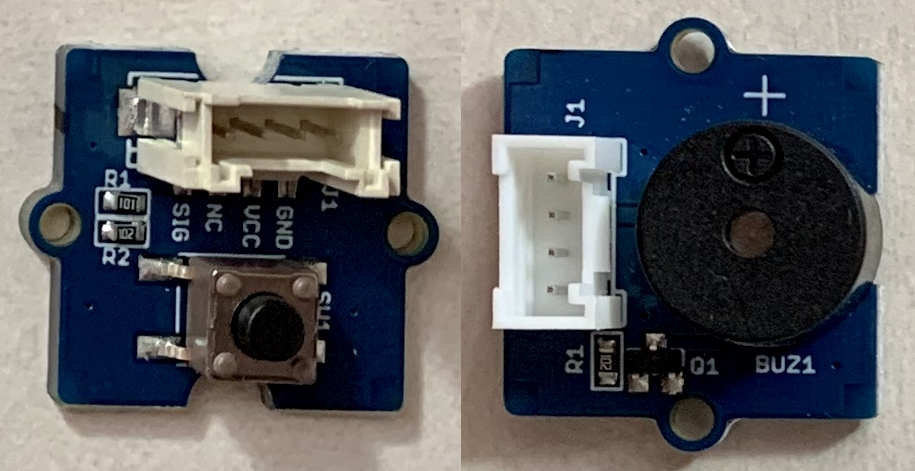
2.Example Project: Button And Buzzer(ボタンブザー)
https://www.dexterindustries.com/GrovePi/projects-for-the-raspberry-pi/
https://github.com/DexterInd/GrovePi/blob/master/Projects/Button_And_Buzzer/Button_And_Buzzer.py
コード
import time
from grovepi import *
import math
buzzer_pin = 2 #Port for buzzer
button = 4 #Port for Button
pinMode(buzzer_pin,"OUTPUT") # Assign mode for buzzer as output
pinMode(button,"INPUT") # Assign mode for Button as input
while True:
try:
button_status= digitalRead(button) #Read the Button status
if button_status: #If the Button is in HIGH position, run the program
digitalWrite(buzzer_pin,1)
print "Buzzing"
else: #If Button is in Off position, print "Off" on the screen
digitalWrite(buzzer_pin,0)
print "Off"
time.sleep(0.1)
except KeyboardInterrupt: # Stop the buzzer before stopping
digitalWrite(buzzer_pin,0)
break
except (IOError,TypeError) as e:
print("Error")
break
結果
$ python Button_And_Buzzer.py
Off
Off
Off
Buzzing
Buzzing
Off
Buzzing
Off
Off
Buzzing
Off
Buzzing
Off
Off
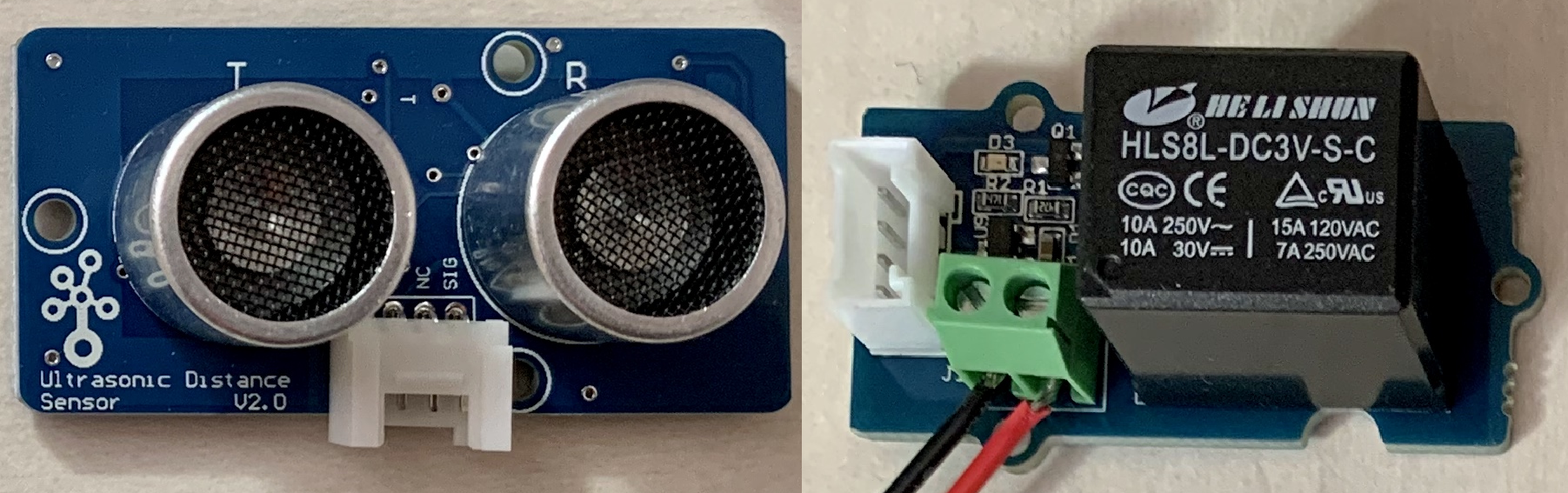
3.Example Project: Ultrasonic And Relay(距離センサとリレー)
https://www.dexterindustries.com/GrovePi/projects-for-the-raspberry-pi/
https://github.com/DexterInd/GrovePi/blob/master/Projects/Ultrasonic_And_Relay/Ultrasonic_And_Relay.py
コード
import time
from grovepi import *
# Connect the Grove Ultrasonic Ranger to digital port D4
# SIG,NC,VCC,GND
ultrasonic_ranger = 4
Relay_pin = 2
pinMode(Relay_pin,"OUTPUT")
digitalWrite(Relay_pin,0)
while True:
try:
# Read distance value from Ultrasonic
distant = ultrasonicRead(ultrasonic_ranger)
print(distant,'cm')
if distant <= 10:
digitalWrite(Relay_pin,1)
else:
digitalWrite(Relay_pin,0)
time.sleep(0.2)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
digitalWrite(Relay_pin,0)
break
except (IOError,TypeError) as e:
print("Error")
break
結果
$ python Ultrasonic_And_Relay.py
(93, 'cm')
(92, 'cm')
(92, 'cm')
(9, 'cm')
(8, 'cm')
(9, 'cm')
(9, 'cm')
(93, 'cm')
(94, 'cm')
(93, 'cm')
4.Example Project: Home Weather Display(家の気温と湿度を表示)
https://www.dexterindustries.com/GrovePi/projects-for-the-raspberry-pi/
https://www.dexterindustries.com/GrovePi/projects-for-the-raspberry-pi/raspberry-pi-temperature-sensor/
https://github.com/DexterInd/GrovePi/blob/master/Projects/Home_Weather_Display/Home_Weather_Display.py
コード
from grovepi import *
from grove_rgb_lcd import *
from time import sleep
from math import isnan
dht_sensor_port = 7 # connect the DHt sensor to port 7
dht_sensor_type = 0 # use 0 for the blue-colored sensor and 1 for the white-colored sensor
# set green as backlight color
# we need to do it just once
# setting the backlight color once reduces the amount of data transfer over the I2C line
setRGB(0,255,0)
setText("")
while True:
try:
# get the temperature and Humidity from the DHT sensor
[ temp,hum ] = dht(dht_sensor_port,dht_sensor_type)
print("temp =", temp, "C\thumidity =", hum,"%")
# check if we have nans
# if so, then raise a type error exception
if isnan(temp) is True or isnan(hum) is True:
raise TypeError('nan error')
t = str(temp)
h = str(hum)
# instead of inserting a bunch of whitespace, we can just insert a \n
# we're ensuring that if we get some strange strings on one line, the 2nd one won't be affected
setText_norefresh("Temp:" + t + "C\n" + "Humidity :" + h + "%")
time.sleep(1)
except (IOError, TypeError) as e:
print(str(e))
# and since we got a type error
# then reset the LCD's text
setText("")
break
except KeyboardInterrupt as e:
print(str(e))
# since we're exiting the program
# it's better to leave the LCD with a blank text
setText("")
break
# wait some time before re-updating the LCD
sleep(0.05)
結果
$ python Home_Weather_Display.py
('temp =', 21.0, 'C\thumidity =', 57.0, '%')
('temp =', 21.0, 'C\thumidity =', 57.0, '%')
('temp =', 21.0, 'C\thumidity =', 56.0, '%')
('temp =', 21.0, 'C\thumidity =', 56.0, '%')
('temp =', 21.0, 'C\thumidity =', 56.0, '%')
5.Example Project: Sensor Twitter Feed(センサ値のツイート)
https://www.dexterindustries.com/GrovePi/projects-for-the-raspberry-pi/
http://www.dexterindustries.com/GrovePi/projects-for-the-raspberry-pi/raspberry-pi-twitter-sensor-feed/
https://github.com/DexterInd/GrovePi/tree/master/Projects/Sensor_Twitter_Feed
ツイートには対応していません。
コード
# import twitter
import time
import grovepi
import math
# Connections
sound_sensor = 0 # port A0
light_sensor = 1 # port A1
temperature_sensor = 2 # port D2
led = 3 # port D3
intro_str = "DI Lab's"
# Connect to Twitter
"""
api = twitter.Api(
consumer_key='YourKey',
consumer_secret='YourKey',
access_token_key='YourKey',
access_token_secret='YourKey'
)
"""
grovepi.pinMode(led,"OUTPUT")
grovepi.analogWrite(led,255) #turn led to max to show readiness
while True:
# Error handling in case of problems communicating with the GrovePi
try:
# Get value from light sensor
light_intensity = grovepi.analogRead(light_sensor)
# Give PWM output to LED
#grovepi.analogWrite(led,light_intensity/4)
grovepi.analogWrite(led,light_intensity*20)
# Get sound level
sound_level = grovepi.analogRead(sound_sensor)
time.sleep(0.5)
# Get value from temperature sensor
[t,h]=[0,0]
[t,h] = grovepi.dht(temperature_sensor,0)
# Post a tweet
out_str ="%s Temp: %d C, Humidity: %d, Light: %d, Sound: %d" %(intro_str,t,h,light_intensity/10,sound_level)
print (out_str)
#api.PostUpdate(out_str)
#time.sleep(60)
time.sleep(2)
except IOError:
print("Error")
exit()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
exit()
except Exception as e:
print("Duplicate Tweet or Twitter Refusal: {}".format(e))
exit()
結果
$ python wifi_twit.py
DI Lab's Temp: 24 C, Humidity: 50, Light: 76, Sound: 593
DI Lab's Temp: 24 C, Humidity: 51, Light: 76, Sound: 196
DI Lab's Temp: 24 C, Humidity: 51, Light: 76, Sound: 195
DI Lab's Temp: 24 C, Humidity: 51, Light: 76, Sound: 197
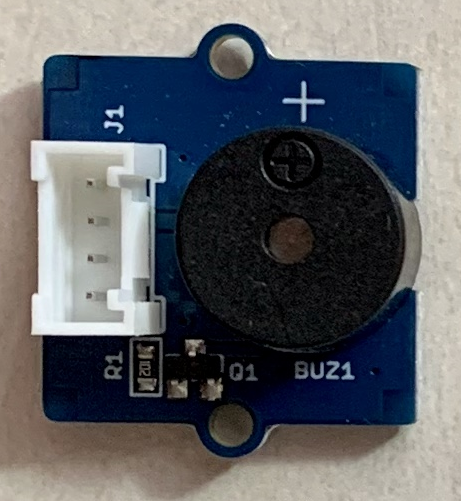
6.Grove - Buzzer(ブザー)
https://www.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Buzzer.html
http://wiki.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Buzzer/#play-with-raspberry-pi-with-grovepi_plus
コード
import time
import grovepi
# Connect the Grove Buzzer to digital port D8
# SIG,NC,VCC,GND
buzzer = 8
grovepi.pinMode(buzzer,"OUTPUT")
# Buzz for 1 second
grovepi.digitalWrite(buzzer,1)
print ('start')
time.sleep(1)
# Stop buzzing for 1 second and repeat
grovepi.digitalWrite(buzzer,0)
print ('stop')
結果
$ python grove_buzzer.py
start
stop
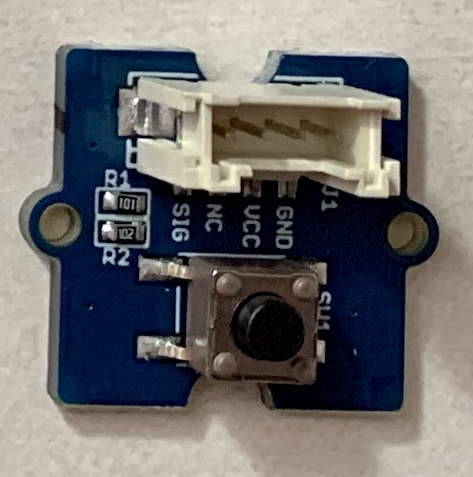
7.Grove - Button(ボタン)
https://www.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Button.html
http://wiki.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Button/#play-with-raspberry-piwith-grovepi_plus
コード
import time
import grovepi
# Connect the Grove Button to digital port D4
# SIG,NC,VCC,GND
button = 4
grovepi.pinMode(button,"INPUT")
while True:
try:
print(grovepi.digitalRead(button))
time.sleep(0.5)
except KeyboardInterrupt: # Stop the buzzer before stopping
break
except (IOError,TypeError) as e:
print("Error")
break
結果
$ python grove_button.py
0
0
0
1
1
1
0
0
1
0
0
0
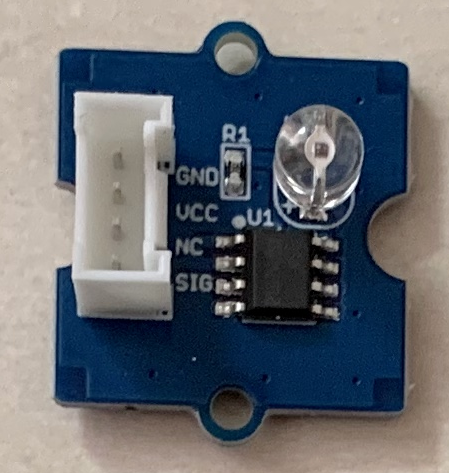
8.Grove - LED
https://www.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Green-LED.html
https://www.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Red-LED.html
https://www.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Blue-LED.html
http://wiki.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Red_LED/#play-with-raspberry-pi-with-grovepi_plus
コード
import time
from grovepi import *
# Connect the Grove LED to digital port D4
led = 4
pinMode(led,"OUTPUT")
time.sleep(1)
while True:
try:
#Blink the LED
digitalWrite(led,1) # Send HIGH to switch on LED
print ("LED ON!")
time.sleep(1)
digitalWrite(led,0) # Send LOW to switch off LED
print ("LED OFF!")
time.sleep(1)
except KeyboardInterrupt: # Turn LED off before stopping
digitalWrite(led,0)
break
except IOError: # Print "Error" if communication error encountered
print ("Error")
結果
$ python grove_led_blink.py
LED ON!
LED OFF!
LED ON!
LED OFF!
LED ON!
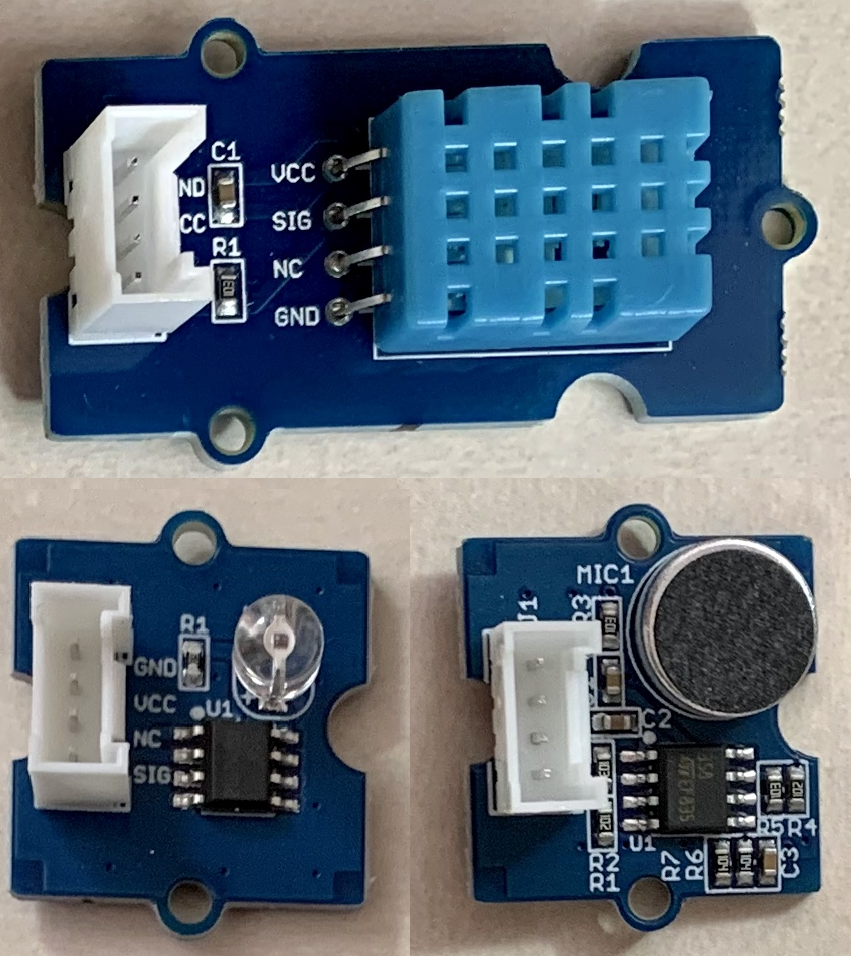
9.Grove - Sound Sensor(音センサ)
https://www.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Sound-Sensor.html
http://wiki.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Sound_Sensor/#play-with-raspberry-pi-with-grovepi_plus
コード
import time
import grovepi
# Connect the Grove Sound Sensor to analog port A0
# SIG,NC,VCC,GND
sound_sensor = 0
# Connect the Grove LED to digital port D5
# SIG,NC,VCC,GND
led = 5
grovepi.pinMode(sound_sensor,"INPUT")
grovepi.pinMode(led,"OUTPUT")
# The threshold to turn the led on 400.00 * 5 / 1024 = 1.95v
# threshold_value = 400
threshold_value = 40
while True:
try:
# Read the sound level
sensor_value = grovepi.analogRead(sound_sensor)
# If loud, illuminate LED, otherwise dim
if sensor_value > threshold_value:
grovepi.digitalWrite(led,1)
else:
grovepi.digitalWrite(led,0)
print("sensor_value = %d" %sensor_value)
time.sleep(0.5)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
break
except (IOError,TypeError) as e:
print("Error")
break
結果
$ python grove_sound_sensor.py
sensor_value = 580
sensor_value = 221
sensor_value = 270
sensor_value = 976
sensor_value = 755
sensor_value = 222
sensor_value = 222
sensor_value = 222
sensor_value = 222
sensor_value = 221
sensor_value = 222
10.Grove - Relay(リレー)
https://www.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Relay.html
http://wiki.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Relay/#play-with-raspberry-pi-with-grovepi_plus
コード
import time
import grovepi
# Connect the Grove Switch to digital port D3
# SIG,NC,VCC,GND
switch = 3
# Connect the Grove Relay to digital port D4
# SIG,NC,VCC,GND
relay = 4
grovepi.pinMode(switch,"INPUT")
grovepi.pinMode(relay,"OUTPUT")
grovepi.digitalWrite(relay,0)
while True:
try:
if grovepi.digitalRead(switch):
print("ON")
grovepi.digitalWrite(relay,1)
else:
grovepi.digitalWrite(relay,0)
print("OFF")
time.sleep(0.5)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
grovepi.digitalWrite(relay,0)
break
except (IOError,TypeError) as e:
print("Error")
break
結果
$ python grove_switch_relay.py
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
11.Grove - Ultrasonic Distance Sensor(距離センサ)
https://www.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Ultrasonic-Distance-Sensor.html
http://wiki.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Ultrasonic_Ranger/#play-with-raspberry-pi-with-grovepi_plus
コード
from grovepi import *
# Connect the Grove Ultrasonic Ranger to digital port D4
# SIG,NC,VCC,GND
ultrasonic_ranger = 4
while True:
try:
# Read distance value from Ultrasonic
print ultrasonicRead(ultrasonic_ranger)
time.sleep(0.2)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
break
except (IOError,TypeError) as e:
print("Error")
break
結果
$ python grove_ultrasonic.py
166
166
166
36
32
31
31
31
30
30
38
166
166
4
2
2
166
166
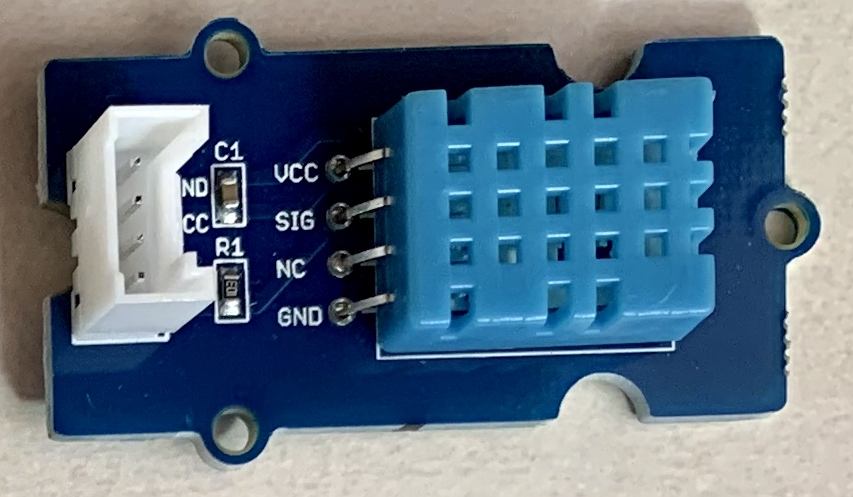
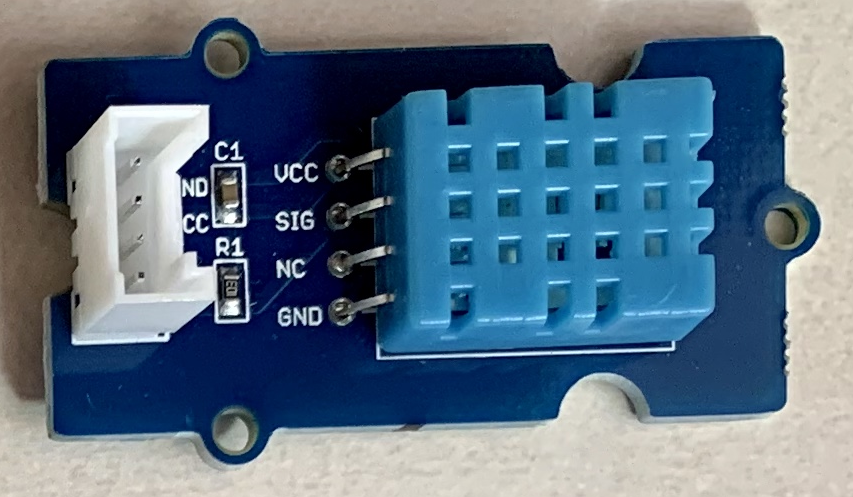
12.Grove - Temperature & Humidity Sensor (DHT11)(温湿度センサ)
https://www.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Temperature-Humidity-Sensor-DHT11.html
http://wiki.seeedstudio.com/Grove-TemperatureAndHumidity_Sensor/#play-with-raspberry-pi-with-grovepi_plus
コード
import grovepi
import math
import time
# Connect the Grove Temperature & Humidity Sensor Pro to digital port D4
# This example uses the blue colored sensor.
# SIG,NC,VCC,GND
sensor = 4 # The Sensor goes on digital port 4.
# temp_humidity_sensor_type
# Grove Base Kit comes with the blue sensor.
blue = 0 # The Blue colored sensor.
white = 1 # The White colored sensor.
while True:
try:
# This example uses the blue colored sensor.
# The first parameter is the port, the second parameter is the type of sensor.
[temp,humidity] = grovepi.dht(sensor,blue)
if math.isnan(temp) == False and math.isnan(humidity) == False:
print("temp = %.02f C humidity =%.02f%%"%(temp, humidity))
time.sleep(0.5)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
break
except (IOError,TypeError) as e:
print("Error")
break
結果
$ python grove_dht_pro.py
temp = 19.00 C humidity =63.00%
temp = 19.00 C humidity =63.00%
temp = 19.00 C humidity =63.00%
temp = 19.00 C humidity =62.00%
13.Grove - Rotary Angle Sensor(回転角度センサ)
https://www.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Rotary-Angle-Sensor.html
http://wiki.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Rotary_Angle_Sensor/#play-with-raspberry-pi-with-grovepi_plus
センサ
コード
import time
import grovepi
# Connect the Grove Rotary Angle Sensor to analog port A0
# SIG,NC,VCC,GND
potentiometer = 0
# Connect the LED to digital port D5
# SIG,NC,VCC,GND
led = 5
grovepi.pinMode(potentiometer,"INPUT")
grovepi.pinMode(led,"OUTPUT")
time.sleep(1)
# Reference voltage of ADC is 5v
adc_ref = 5
# Vcc of the grove interface is normally 5v
grove_vcc = 5
# Full value of the rotary angle is 300 degrees, as per it's specs (0 to 300)
full_angle = 300
while True:
try:
# Read sensor value from potentiometer
sensor_value = grovepi.analogRead(potentiometer)
# Calculate voltage
voltage = round((float)(sensor_value) * adc_ref / 1023, 2)
# Calculate rotation in degrees (0 to 300)
degrees = round((voltage * full_angle) / grove_vcc, 2)
# Calculate LED brightess (0 to 255) from degrees (0 to 300)
brightness = int(degrees / full_angle * 255)
# Give PWM output to LED
grovepi.analogWrite(led,brightness)
print("sensor_value = %d voltage = %.2f degrees = %.1f brightness = %d" %(sensor_value, voltage, degrees, brightness))
time.sleep(0.2)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
break
except (IOError,TypeError) as e:
print("Error")
break
結果
$ python grove_rotary_angle_sensor.py
sensor_value = 0 voltage = 0.00 degrees = 0.0 brightness = 0
sensor_value = 0 voltage = 0.00 degrees = 0.0 brightness = 0
sensor_value = 0 voltage = 0.00 degrees = 0.0 brightness = 0
sensor_value = 222 voltage = 1.09 degrees = 65.4 brightness = 55
sensor_value = 392 voltage = 1.92 degrees = 115.2 brightness = 97
sensor_value = 485 voltage = 2.37 degrees = 142.2 brightness = 120
sensor_value = 511 voltage = 2.50 degrees = 150.0 brightness = 127
sensor_value = 530 voltage = 2.59 degrees = 155.4 brightness = 132
sensor_value = 562 voltage = 2.75 degrees = 165.0 brightness = 140
sensor_value = 617 voltage = 3.02 degrees = 181.2 brightness = 154
sensor_value = 706 voltage = 3.45 degrees = 207.0 brightness = 175
sensor_value = 826 voltage = 4.04 degrees = 242.4 brightness = 206
sensor_value = 950 voltage = 4.64 degrees = 278.4 brightness = 236
sensor_value = 1021 voltage = 4.99 degrees = 299.4 brightness = 254
sensor_value = 1023 voltage = 5.00 degrees = 300.0 brightness = 255
sensor_value = 1023 voltage = 5.00 degrees = 300.0 brightness = 255
sensor_value = 1023 voltage = 5.00 degrees = 300.0 brightness = 255
sensor_value = 1022 voltage = 5.00 degrees = 300.0 brightness = 255
14.Grove - Light Sensor v1.2(光センサ)
https://www.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Light-Sensor-v1-2.html
http://wiki.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Light_Sensor/#play-with-raspberry-pi-with-grovepi_plus
コード
import time
import grovepi
# Connect the Grove Light Sensor to analog port A0
# SIG,NC,VCC,GND
light_sensor = 0
# Connect the LED to digital port D4
# SIG,NC,VCC,GND
led = 4
# Turn on LED once sensor exceeds threshold resistance
threshold = 10
grovepi.pinMode(light_sensor,"INPUT")
grovepi.pinMode(led,"OUTPUT")
while True:
try:
# Get sensor value
sensor_value = grovepi.analogRead(light_sensor)
# Calculate resistance of sensor in K
resistance = (float)(1023 - sensor_value) * 10 / sensor_value
if resistance > threshold:
# Send HIGH to switch on LED
grovepi.digitalWrite(led,1)
else:
# Send LOW to switch off LED
grovepi.digitalWrite(led,0)
print("sensor_value = %d resistance = %.2f" %(sensor_value, resistance))
time.sleep(0.5)
except KeyboardInterrupt: # Turn LED off before stopping
grovepi.digitalWrite(led,0)
break
except IOError: # Print "Error" if communication error encountered
print ("Error")
結果
$ python grove_light_sensor.py
sensor_value = 64 resistance = 149.84
sensor_value = 68 resistance = 140.44
sensor_value = 72 resistance = 132.08
sensor_value = 75 resistance = 126.40
sensor_value = 76 resistance = 124.61
sensor_value = 91 resistance = 102.42
sensor_value = 404 resistance = 15.32
sensor_value = 511 resistance = 10.02
sensor_value = 512 resistance = 9.98
sensor_value = 496 resistance = 10.62
sensor_value = 771 resistance = 3.27
sensor_value = 771 resistance = 3.27
sensor_value = 772 resistance = 3.25
sensor_value = 772 resistance = 3.25
15.Grove - LCD RGB Backlight
https://www.seeedstudio.com/Grove-LCD-RGB-Backlight.html
http://wiki.seeedstudio.com/Grove-LCD_RGB_Backlight/#play-with-raspberry-pi
コード
import time
import sys
if sys.platform == 'uwp':
import winrt_smbus as smbus
bus = smbus.SMBus(1)
else:
import smbus
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
rev = GPIO.RPI_REVISION
if rev == 2 or rev == 3:
bus = smbus.SMBus(1)
else:
bus = smbus.SMBus(0)
# this device has two I2C addresses
DISPLAY_RGB_ADDR = 0x62
DISPLAY_TEXT_ADDR = 0x3e
# set backlight to (R,G,B) (values from 0..255 for each)
def setRGB(r,g,b):
bus.write_byte_data(DISPLAY_RGB_ADDR,0,0)
bus.write_byte_data(DISPLAY_RGB_ADDR,1,0)
bus.write_byte_data(DISPLAY_RGB_ADDR,0x08,0xaa)
bus.write_byte_data(DISPLAY_RGB_ADDR,4,r)
bus.write_byte_data(DISPLAY_RGB_ADDR,3,g)
bus.write_byte_data(DISPLAY_RGB_ADDR,2,b)
# send command to display (no need for external use)
def textCommand(cmd):
bus.write_byte_data(DISPLAY_TEXT_ADDR,0x80,cmd)
# set display text \n for second line(or auto wrap)
def setText(text):
textCommand(0x01) # clear display
time.sleep(.05)
textCommand(0x08 | 0x04) # display on, no cursor
textCommand(0x28) # 2 lines
time.sleep(.05)
count = 0
row = 0
for c in text:
if c == '\n' or count == 16:
count = 0
row += 1
if row == 2:
break
textCommand(0xc0)
if c == '\n':
continue
count += 1
bus.write_byte_data(DISPLAY_TEXT_ADDR,0x40,ord(c))
# Update the display without erasing the display
def setText_norefresh(text):
textCommand(0x02) # return home
time.sleep(.05)
textCommand(0x08 | 0x04) # display on, no cursor
textCommand(0x28) # 2 lines
time.sleep(.05)
count = 0
row = 0
while len(text) < 32: #clears the rest of the screen
text += ' '
for c in text:
if c == '\n' or count == 16:
count = 0
row += 1
if row == 2:
break
textCommand(0xc0)
if c == '\n':
continue
count += 1
bus.write_byte_data(DISPLAY_TEXT_ADDR,0x40,ord(c))
# example code
if __name__=="__main__":
setText("Hello world\nThis is an LCD test")
setRGB(0,128,64)
time.sleep(2)
for c in range(0,255):
setText_norefresh("Going to sleep in {}...".format(str(c)))
setRGB(c,255-c,0)
time.sleep(0.1)
setRGB(0,255,0)
setText("Bye bye, this should wrap onto next line")
他のセンサを試してみた
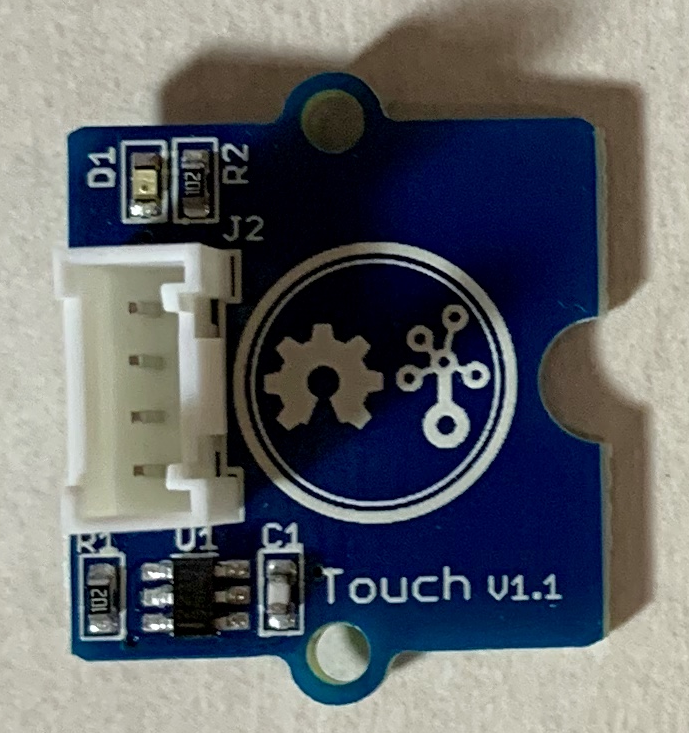
16.Grove - Touch Sensor(タッチセンサ)
https://www.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Touch-Sensor.html
http://wiki.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Touch_Sensor/#play-with-raspberry-pi-with-grovepi_plus
コード
import time
import grovepi
# Connect the Grove Button to digital port D4
# SIG,NC,VCC,GND
button = 4
grovepi.pinMode(button,"INPUT")
while True:
try:
print(grovepi.digitalRead(button))
time.sleep(0.5)
except KeyboardInterrupt: # Stop the buzzer before stopping
break
except (IOError,TypeError) as e:
print("Error")
break
結果
$ python grove_button.py
0
0
0
1
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
0
17.Grove - Magnetic Switch(磁気スイッチ)
https://www.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Magnetic-Switch-p-744.html
http://wiki.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Magnetic_Switch/#play-with-raspberry-pi
コード
import time
import grovepi
# Connect the Grove Tilt Switch to digital port D2
# SIG,NC,VCC,GND
tilt_switch = 2
grovepi.pinMode(tilt_switch,"INPUT")
while True:
try:
print grovepi.digitalRead(tilt_switch)
time.sleep(0.5)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
break
except IOError:
print ("Error")
結果
$ python grovepi_tilt_switch.py
0
0
0
1
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
18.Grove - Tilt Switch(傾きセンサ)
https://www.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Tilt-Switch.html
http://wiki.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Tilt_Switch/
コードと結果
「17.Grove - Magnetic Switch(磁気スイッチ)」と同じ。
19.Grove - 3 Axis Digital Accelerometer(±16g)(加速度計)
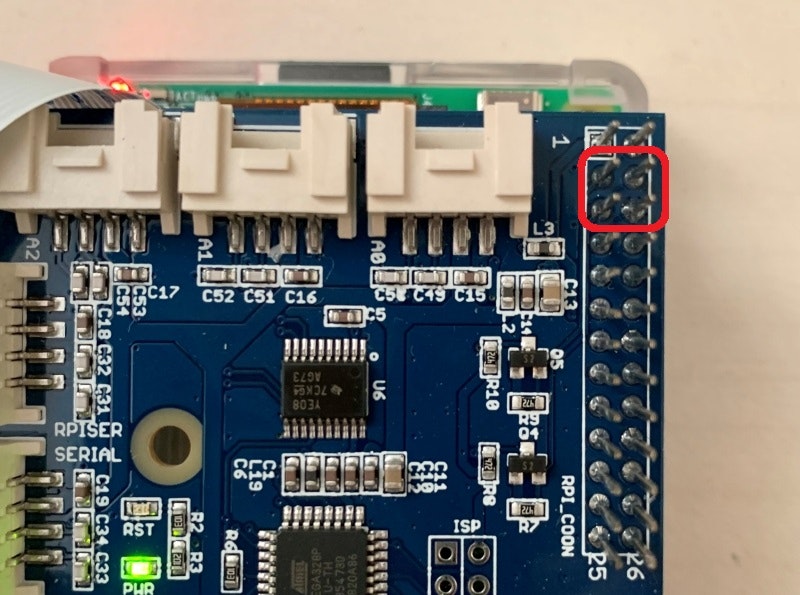
Grove Pi+ 経由のサンプルが無く、以下の赤囲みのI2Cと5V電源を直接使う。
コード
import smbus
from time import sleep
# select the correct i2c bus for this revision of Raspberry Pi
revision = ([l[12:-1] for l in open('/proc/cpuinfo','r').readlines() if l[:8]=="Revision"]+['0000'])[0]
bus = smbus.SMBus(1 if int(revision, 16) >= 4 else 0)
# ADXL345 constants
EARTH_GRAVITY_MS2 = 9.80665
SCALE_MULTIPLIER = 0.004
DATA_FORMAT = 0x31
BW_RATE = 0x2C
POWER_CTL = 0x2D
BW_RATE_1600HZ = 0x0F
BW_RATE_800HZ = 0x0E
BW_RATE_400HZ = 0x0D
BW_RATE_200HZ = 0x0C
BW_RATE_100HZ = 0x0B
BW_RATE_50HZ = 0x0A
BW_RATE_25HZ = 0x09
RANGE_2G = 0x00
RANGE_4G = 0x01
RANGE_8G = 0x02
RANGE_16G = 0x03
MEASURE = 0x08
AXES_DATA = 0x32
class ADXL345:
address = None
def __init__(self, address = 0x53):
self.address = address
self.setBandwidthRate(BW_RATE_100HZ)
self.setRange(RANGE_2G)
self.enableMeasurement()
def enableMeasurement(self):
bus.write_byte_data(self.address, POWER_CTL, MEASURE)
def setBandwidthRate(self, rate_flag):
bus.write_byte_data(self.address, BW_RATE, rate_flag)
# set the measurement range for 10-bit readings
def setRange(self, range_flag):
value = bus.read_byte_data(self.address, DATA_FORMAT)
value &= ~0x0F;
value |= range_flag;
value |= 0x08;
bus.write_byte_data(self.address, DATA_FORMAT, value)
# returns the current reading from the sensor for each axis
#
# parameter gforce:
# False (default): result is returned in m/s^2
# True : result is returned in gs
def getAxes(self, gforce = False):
bytes = bus.read_i2c_block_data(self.address, AXES_DATA, 6)
x = bytes[0] | (bytes[1] << 8)
if(x & (1 << 16 - 1)):
x = x - (1<<16)
y = bytes[2] | (bytes[3] << 8)
if(y & (1 << 16 - 1)):
y = y - (1<<16)
z = bytes[4] | (bytes[5] << 8)
if(z & (1 << 16 - 1)):
z = z - (1<<16)
x = x * SCALE_MULTIPLIER
y = y * SCALE_MULTIPLIER
z = z * SCALE_MULTIPLIER
if gforce == False:
x = x * EARTH_GRAVITY_MS2
y = y * EARTH_GRAVITY_MS2
z = z * EARTH_GRAVITY_MS2
x = round(x, 4)
y = round(y, 4)
z = round(z, 4)
return {"x": x, "y": y, "z": z}
if __name__ == "__main__":
# if run directly we'll just create an instance of the class and output
# the current readings
adxl345 = ADXL345()
while True:
try:
axes = adxl345.getAxes(True)
print("ADXL345 on address 0x%x:" % (adxl345.address))
print(" x = %.3fG" % ( axes['x'] ))
print(" y = %.3fG" % ( axes['y'] ))
print(" z = %.3fG" % ( axes['z'] ))
sleep(2)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
break
except (IOError,TypeError) as e:
print("Error")
break
結果
$ python grovepi_accelerometer.py
ADXL345 on address 0x53:
x = -0.072G
y = -0.136G
z = 0.908G
ADXL345 on address 0x53:
x = 0.252G
y = 0.752G
z = 0.024G
ADXL345 on address 0x53:
x = -0.204G
y = -0.200G
z = -1.012G
ADXL345 on address 0x53:
x = 0.088G
y = -0.356G
z = 0.828G
その他
今回試験していませんが、保有している以下のセンサも今後試してみるつもりです。
絶対圧センサ評価モジュール
https://www.switch-science.com/catalog/5329/
https://camp.isaax.io/ja/examples/2smpb-02e-raspberry-pi
https://github.com/isaaxug/2smpb02e-with-isaax
Grove - Temperature Sensor(温度センサ)
https://www.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Temperature-Sensor.html
http://wiki.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Temperature_Sensor_V1.2/#play-with-raspberry-pi-with-grovepi_plus
Grove - GPS Module
https://www.seeedstudio.com/Grove-GPS-Module.html
http://wiki.seeedstudio.com/Grove-GPS/#play-with-raspberry-pi
Grove - Water Sensor(水センサ)
https://www.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Water-Sensor-p-748.html
http://wiki.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Water_Sensor/#play-with-raspberry-piwith-grovepi_plus
Grove - Moisture Sensor(水分センサ)
https://www.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Moisture-Sensor.html
http://wiki.seeedstudio.com/Grove-Moisture_Sensor/#play-with-raspberry-piwith-grovepi_plus