はじめに
Tensorflow 2.0 Alpha上で画像認識サンプルを動作させた過程を記載します。
基本的にはこちらの公式チュートリアルの流れに沿って導入しています。
本記事は概要版となります。
詳細は最新版TensorFlow (2.0 Alpha) 画像認識編(詳細版)で紹介しています。
構成
MacBook Pro (13-inch, 2016, Two Thunderbolt 3 ports)
TensorFlowおよび各ライブラリの読み込み
Tensorflow 2.0 Alphaが導入されている前提で進めます。
未導入の方はこちらを参照してください:最新版TensorFlow (2.0 Alpha) 動作環境構築
Tensorflowおよび各ライブラリの読み込み
from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals
# TensorFlow and tf.keras
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
# Helper libraries
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
print(tf.__version__)
2.0.0-alpha0と出たらOKです。
Fashion MNISTデータセットの読み込み
Fashion MNISTとは10カテゴリ計7万枚の洋服の白黒画像(28x28ピクセル)が含まれているデータセットです。
fashion_mnist = keras.datasets.fashion_mnist
(train_images, train_labels), (test_images, test_labels) = fashion_mnist.load_data()
このコマンドを入力するとダウンロードが始まります。
ラベルごとのクラス名は以下の通りです。
| ラベル | クラス |
|---|---|
| 0 | T-shirt/top |
| 1 | Trouser |
| 2 | Pullover |
| 3 | Dress |
| 4 | Coat |
| 5 | Sandal |
| 6 | Shirt |
| 7 | Sneaker |
| 8 | Bag |
| 9 | Ankle boot |
ただし、データセットにクラス名は含まれていないため、
以下のように設定してあげましょう。
class_names = ['T-shirt/top', 'Trouser', 'Pullover', 'Dress', 'Coat','Sandal', 'Shirt', 'Sneaker', 'Bag', 'Ankle boot']
データの確認
train_images.shape
(60000, 28, 28)
len(train_labels)
60000
train_labels
array([9, 0, 0, ..., 3, 0, 5], dtype=uint8)
test_images.shape
(10000, 28, 28)
len(test_labels)
10000
データの準備
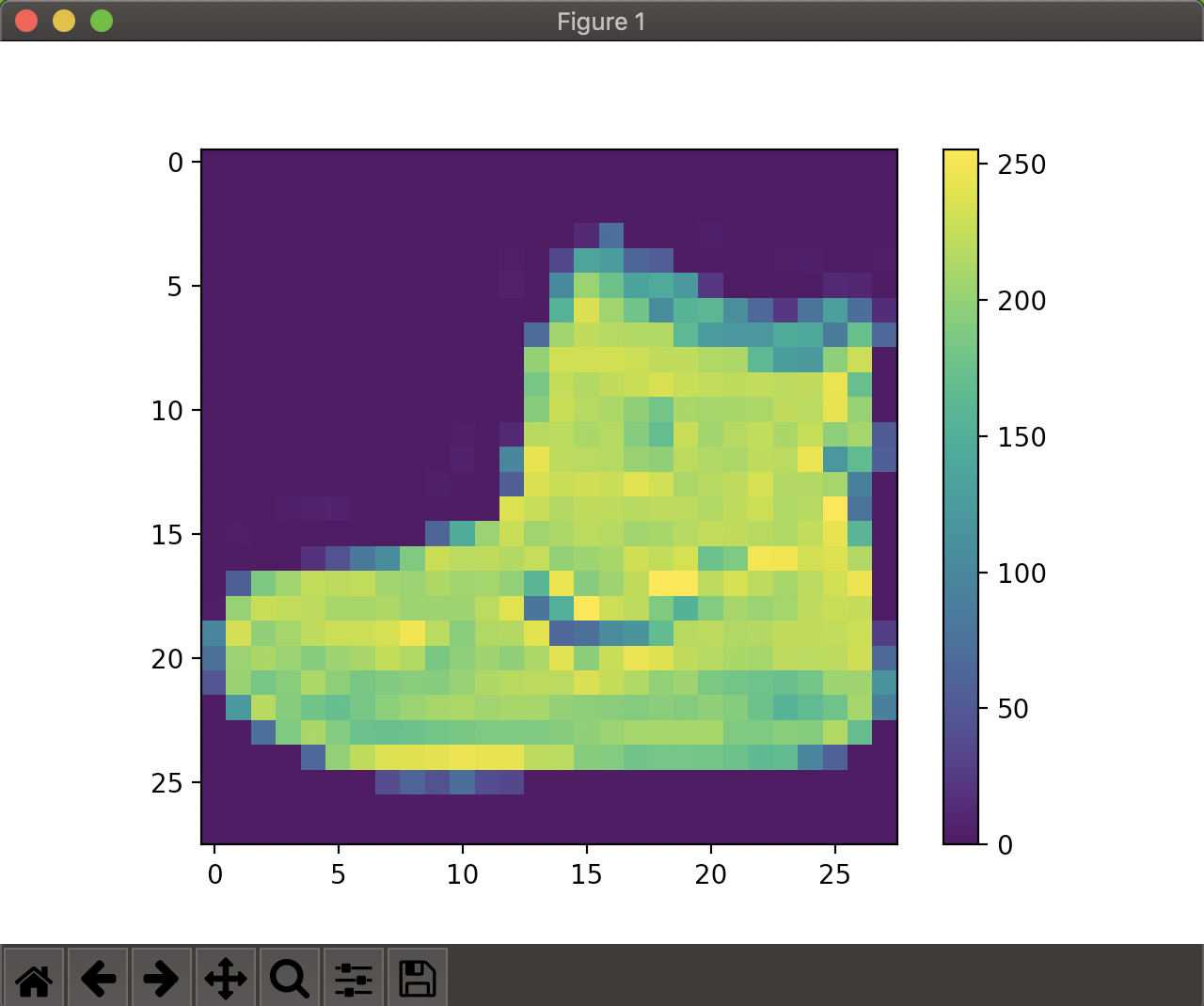
まずは画像の視覚化をしてみます。
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(train_images[0])
plt.colorbar()
plt.grid(False)
plt.show()
0~1の範囲にスケーリング
train_images = train_images / 255.0
test_images = test_images / 255.0
学習用セットの最初の25枚の画像を表示してみます。
plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))
for i in range(25):
plt.subplot(5,5,i+1)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.grid(False)
plt.imshow(train_images[i], cmap=plt.cm.binary)
plt.xlabel(class_names[train_labels[i]])
plt.show()

モデルの構築
いよいよ学習用モデルの構築に入ります。
model = keras.Sequential([
keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28)),
keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'),
keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')
])
モデルのコンパイル
ここでは以下のように設定しました。
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
モデルの学習
いよいよ学習を開始します。
以下のmodel.fitで訓練を開始します。
model.fit(train_images, train_labels, epochs=5)
Epoch 1/5
60000/60000 [==============================] - 4s 59us/sample - loss: 1.1019 - accuracy: 0.6589
Epoch 2/5
60000/60000 [==============================] - 3s 51us/sample - loss: 0.6481 - accuracy: 0.7669
Epoch 3/5
60000/60000 [==============================] - 3s 47us/sample - loss: 0.5701 - accuracy: 0.7957
Epoch 4/5
60000/60000 [==============================] - 3s 45us/sample - loss: 0.5260 - accuracy: 0.8134
Epoch 5/5
60000/60000 [==============================] - 3s 45us/sample - loss: 0.4973 - accuracy: 0.8231
<tensorflow.python.keras.callbacks.History object at 0x11d804b70>
精度としては82%程度となりました。
精度の評価
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(test_images, test_labels)
print('\nTest accuracy:', test_acc)
実行結果:
Test accuracy: 0.8173
学習モデルを使った予測
学習したモデルを使ってtest_imagesの予測をしてみます。
predictions = model.predict(test_images)
最初の画像の予測結果を見てみます。
predictions[0]
array([2.2446468e-06, 7.3107621e-08, 1.1268611e-05, 1.6483513e-05,
1.9317991e-05, 1.4457782e-01, 2.7507849e-05, 3.9779294e-01,
6.4411242e-03, 4.5111132e-01], dtype=float32)
これは0~9のラベルに対してのそれぞれの信頼度になります。
一番信頼度が高いラベルは以下でわかります。
np.argmax(predictions[0])
9
続いて各信頼度をグラフ化してみましょう。
def plot_image(i, predictions_array, true_label, img):
predictions_array, true_label, img = predictions_array[i], true_label[i], img[i]
plt.grid(False)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.imshow(img, cmap=plt.cm.binary)
predicted_label = np.argmax(predictions_array)
if predicted_label == true_label:
color = 'blue'
else:
color = 'red'
plt.xlabel("{} {:2.0f}% ({})".format(class_names[predicted_label],
100*np.max(predictions_array),
class_names[true_label]),
color=color)
def plot_value_array(i, predictions_array, true_label):
predictions_array, true_label = predictions_array[i], true_label[i]
plt.grid(False)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
thisplot = plt.bar(range(10), predictions_array, color="#777777")
plt.ylim([0, 1])
predicted_label = np.argmax(predictions_array)
thisplot[predicted_label].set_color('red')
thisplot[true_label].set_color('blue')
最初の画像の情報を表示してみます。
i = 0
plt.figure(figsize=(6,3))
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plot_image(i, predictions, test_labels, test_images)
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plot_value_array(i, predictions, test_labels)
plt.show()

まとめ
画像認識入門編としてFashion MNISTデータセットを使ったサンプル動作を一通り実現できました。
今後は、オリジナルの学習モデルの構築を目標に勉強したいと思います。
本記事は概要版となります。
詳細は最新版TensorFlow (2.0 Alpha) 画像認識編(詳細版)で紹介しています。