はじめに
AgentCoreのRuntime機能に続き、Gateway機能もやってみたいと思ったのでやっていこうと思います。
今回は公式ドキュメントの手順がかなりわかりやすかったのでそれに沿って実施してみました。
それに加えて私なりにGatewayの仕組みを解説していきたいと思います。
また、RuntimeとGatewayの統合にしようと思ったのですが、今回はシンプルにStrandsから利用する形にしようと思います。
そもそもGatewayってどんな機能?
公式ドキュメント曰く、API、Lambda 関数、および既存のサービスを Model Context Protocol (MCP) 互換ツールに変換し、簡単にエージェントが利用できるようになるとのことです。
また、入力タイプとしてSalesforce、Slack、Jiraといった有名どころのツールとの統合も可能になっています。(Teams派の私は涙が止まらん)
利用することによるメリット
ツールの統合を簡素化
これが一番大きい気がしますが、既存のリソースをエージェント対応ツールに変換することができ、簡単にエージェントをカスタマイズすることができます。
様々な人気のツールとワンクリックで統合できるだけでなく、ターゲットにLambda、GAとともに追加されたMCPサーバーなどの便利パーツとの連携を強化してくれます。
動的なツール検出
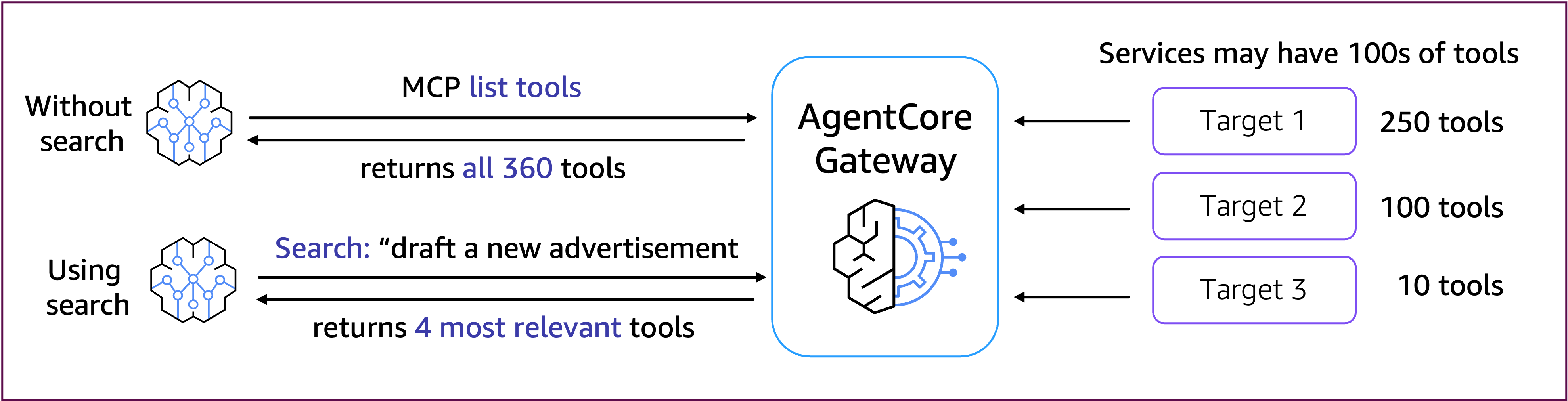
数百または数千もツールを追加しているとある時エージェントは「あれ、どのツール使えばいいんだ?」となり、コストの増加、レイテンシーの増大やツール選択精度の低下を招く恐れがあります。
そうなってくると、ツールを効率的に管理・選択するアプローチが必要になるわけですが、AgentCore Gatewayのセマンティック検索機能が解決してくれます。
この機能により、エージェントが特定のコンテキストや質問に最も関連性の高いツールのみを知的に発見・選択できるようにすることで、運用コストと応答時間を削減しながら、エージェントのパフォーマンスが劇的に向上します。
以下は公式ワークショップから拝借した画像ですが、Gatewayに対してツールの検索を行なっていい感じにツールを取得しているのがわかるかと思います。
興味ある方は、以下の公式ワークショップ「Diving Deep into Bedrock AgentCore」で体験できるので、ぜひお試しください〜
包括的な認証
GatewayはInbound認証(エージェントの身元確認)とOutbound認証(外部ツールへの接続)の両方をマネージドサービスIdentityで管理できます。
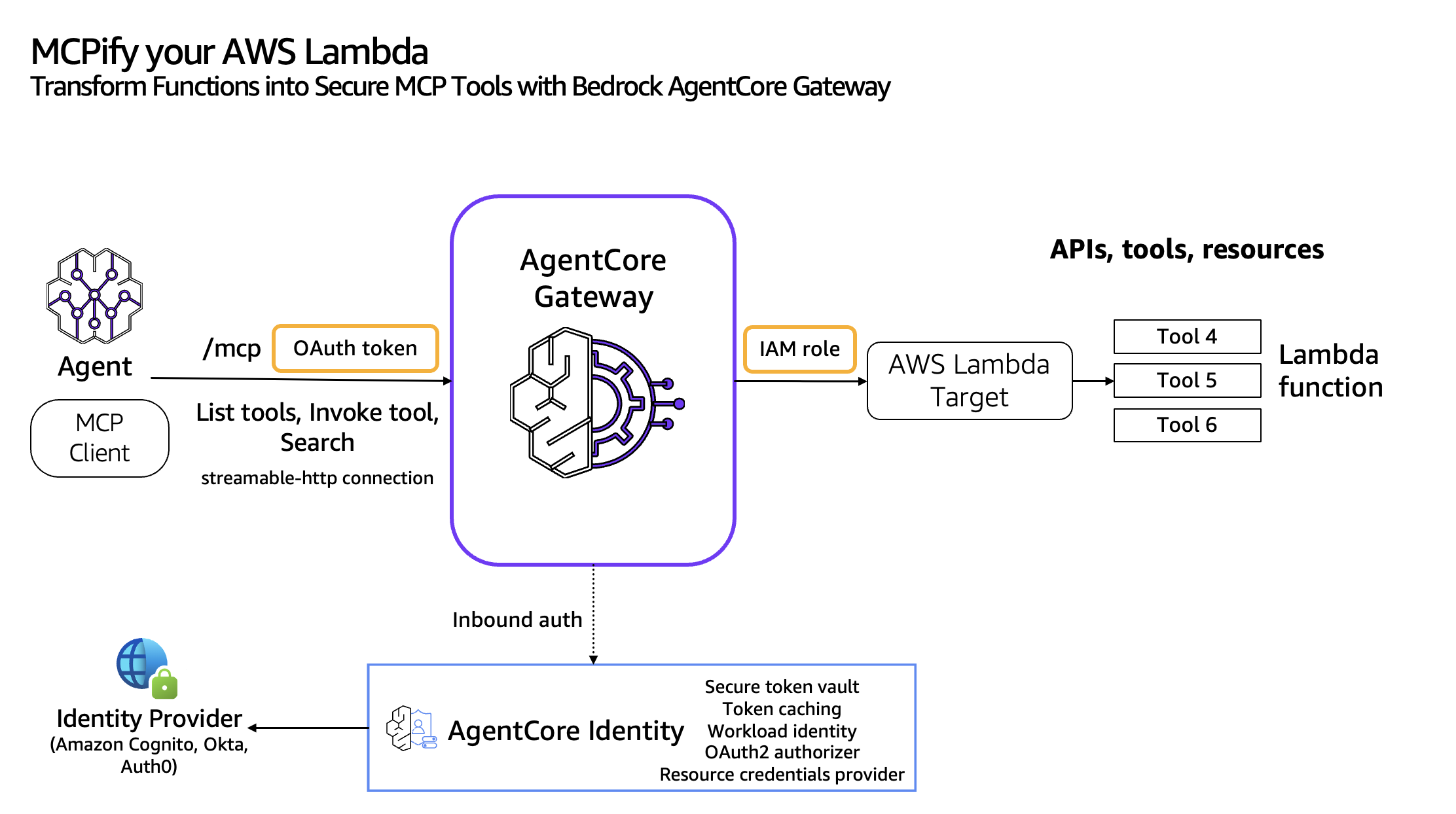
今回実装するLambda関数との統合についても同様に公式ワークショップに図があるので確認してみます。
大体以下のようなフローになっています。
1.エージェント→Gateway: OAuth tokenでの認証
2.Gateway→Identity: トークン検証
3.Gateway→Lambda: IAMロールでの実行権限
この辺の認証周りもがっつり書きたいのですが、流石に今回は記事を分けようと思います...
大体こういう認証処理を挟んでるんだな〜くらいで、大まかな流れを理解していただければと思います。
やってみる
ではこれからドキュメントのチュートリアルに従って実践していきます。
公式ドキュメントでは事前の環境構築や依存関係のインストールを行なっています。
Pythonの仮想環境の構築やBedrock AgentCoreのライブラリのインストールは下記の記事の手順でできます。
Gatewayを作成する
まずsetup_gateway.pyを新しく作成し、実行します。
コード全文
"""
Setup script to create Gateway with Lambda target and save configuration
Run this first: python setup_gateway.py
"""
from bedrock_agentcore_starter_toolkit.operations.gateway.client import GatewayClient
import json
import logging
import time
def setup_gateway():
# Configuration
region = "us-east-1" # Change to your preferred region
print("🚀 Setting up AgentCore Gateway...")
print(f"Region: {region}\n")
# Initialize client
client = GatewayClient(region_name=region)
client.logger.setLevel(logging.INFO)
# Step 2.1: Create OAuth authorizer
print("Step 2.1: Creating OAuth authorization server...")
cognito_response = client.create_oauth_authorizer_with_cognito("TestGateway")
print("✓ Authorization server created\n")
# Step 2.2: Create Gateway
print("Step 2.2: Creating Gateway...")
gateway = client.create_mcp_gateway(
# the name of the Gateway - if you don't set one, one will be generated.
name=None,
# the role arn that the Gateway will use - if you don't set one, one will be created.
# NOTE: if you are using your own role make sure it has a trust policy that trusts bedrock-agentcore.amazonaws.com
role_arn=None,
# the OAuth authorization server details. If you are providing your own authorization server,
# then pass an input of the following form: {"customJWTAuthorizer": {"allowedClients": ["<INSERT CLIENT ID>"], "discoveryUrl": "<INSERT DISCOVERY URL>"}}
authorizer_config=cognito_response["authorizer_config"],
# enable semantic search
enable_semantic_search=True,
)
print(f"✓ Gateway created: {gateway['gatewayUrl']}\n")
# If role_arn was not provided, fix IAM permissions
# NOTE: This is handled internally by the toolkit when no role is provided
client.fix_iam_permissions(gateway)
print("⏳ Waiting 30s for IAM propagation...")
time.sleep(30)
print("✓ IAM permissions configured\n")
# Step 2.3: Add Lambda target
print("Step 2.3: Adding Lambda target...")
lambda_target = client.create_mcp_gateway_target(
# the gateway created in the previous step
gateway=gateway,
# the name of the Target - if you don't set one, one will be generated.
name=None,
# the type of the Target
target_type="lambda",
# the target details - set this to define your own lambda if you pre-created one.
# Otherwise leave this None and one will be created for you.
target_payload=None,
# you will see later in the tutorial how to use this to connect to APIs using API keys and OAuth credentials.
credentials=None,
)
print("✓ Lambda target added\n")
# Step 2.4: Save configuration for agent
config = {
"gateway_url": gateway["gatewayUrl"],
"gateway_id": gateway["gatewayId"],
"region": region,
"client_info": cognito_response["client_info"]
}
with open("gateway_config.json", "w") as f:
json.dump(config, f, indent=2)
print("=" * 60)
print("✅ Gateway setup complete!")
print(f"Gateway URL: {gateway['gatewayUrl']}")
print(f"Gateway ID: {gateway['gatewayId']}")
print("\nConfiguration saved to: gateway_config.json")
print("\nNext step: Run 'python run_agent.py' to test your Gateway")
print("=" * 60)
return config
if __name__ == "__main__":
setup_gateway()
今回私は仮想環境をuvで構築しているので以下のように実行しました
uv run setup_gateway.py
やっていることの確認
OAuth認証サーバーを作成する
上で示したように、ゲートウェイはOAuth認可サーバーによって保護されており、許可されたユーザーのみがゲートウェイにアクセスできるようにします。
そのための認証情報をAmazon Cognitoを使用して作成しています。
# Step 2.1: Create OAuth authorizer
print("Step 2.1: Creating OAuth authorization server...")
cognito_response = client.create_oauth_authorizer_with_cognito("TestGateway")
print("✓ Authorization server created\n")
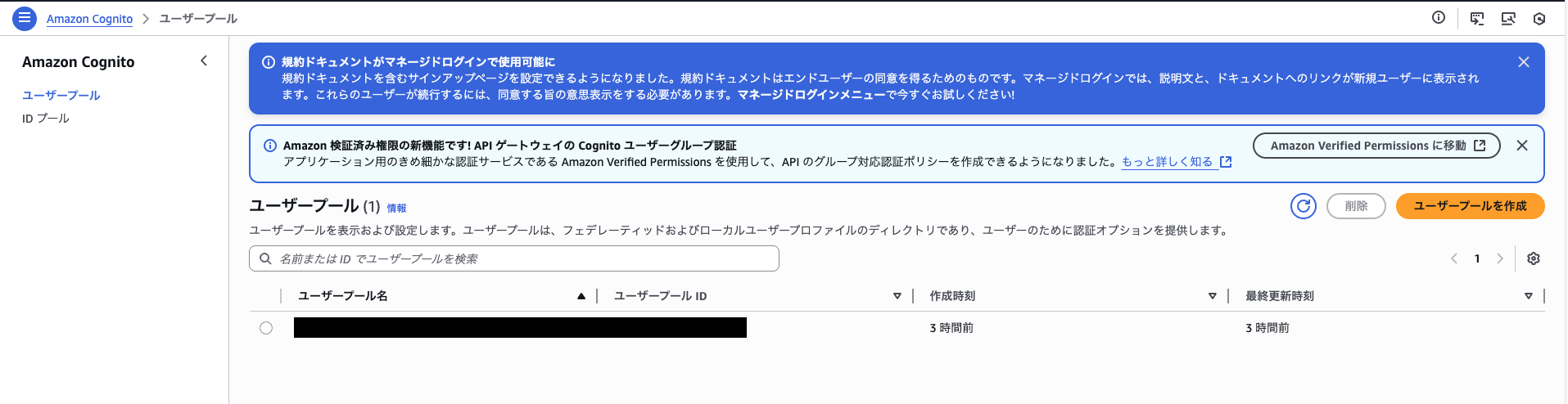
OAuth 2.0 クライアント認証情報フローが設定された Amazon Cognito ユーザープールが作成されます。
アクセストークンの取得に使用できるクライアント ID とシークレットが提供されます。
Cognitoユーザープールを確認すると、以下のように認証情報が作成されていました。
この情報が、エージェントからGatewayにお邪魔するときの認証に使われるわけです。
Gatewayの作成
ここでは実際にGatewayを作成しています。
また、セマンティック検索も有効にしています。
# Step 2.2: Create Gateway
print("Step 2.2: Creating Gateway...")
gateway = client.create_mcp_gateway(
# the name of the Gateway - if you don't set one, one will be generated.
name=None,
# the role arn that the Gateway will use - if you don't set one, one will be created.
# NOTE: if you are using your own role make sure it has a trust policy that trusts bedrock-agentcore.amazonaws.com
role_arn=None,
# the OAuth authorization server details. If you are providing your own authorization server,
# then pass an input of the following form: {"customJWTAuthorizer": {"allowedClients": ["<INSERT CLIENT ID>"], "discoveryUrl": "<INSERT DISCOVERY URL>"}}
authorizer_config=cognito_response["authorizer_config"],
# enable semantic search
enable_semantic_search=True,
)
print(f"✓ Gateway created: {gateway['gatewayUrl']}\n")
# If role_arn was not provided, fix IAM permissions
# NOTE: This is handled internally by the toolkit when no role is provided
client.fix_iam_permissions(gateway)
print("⏳ Waiting 30s for IAM propagation...")
time.sleep(30)
print("✓ IAM permissions configured\n")
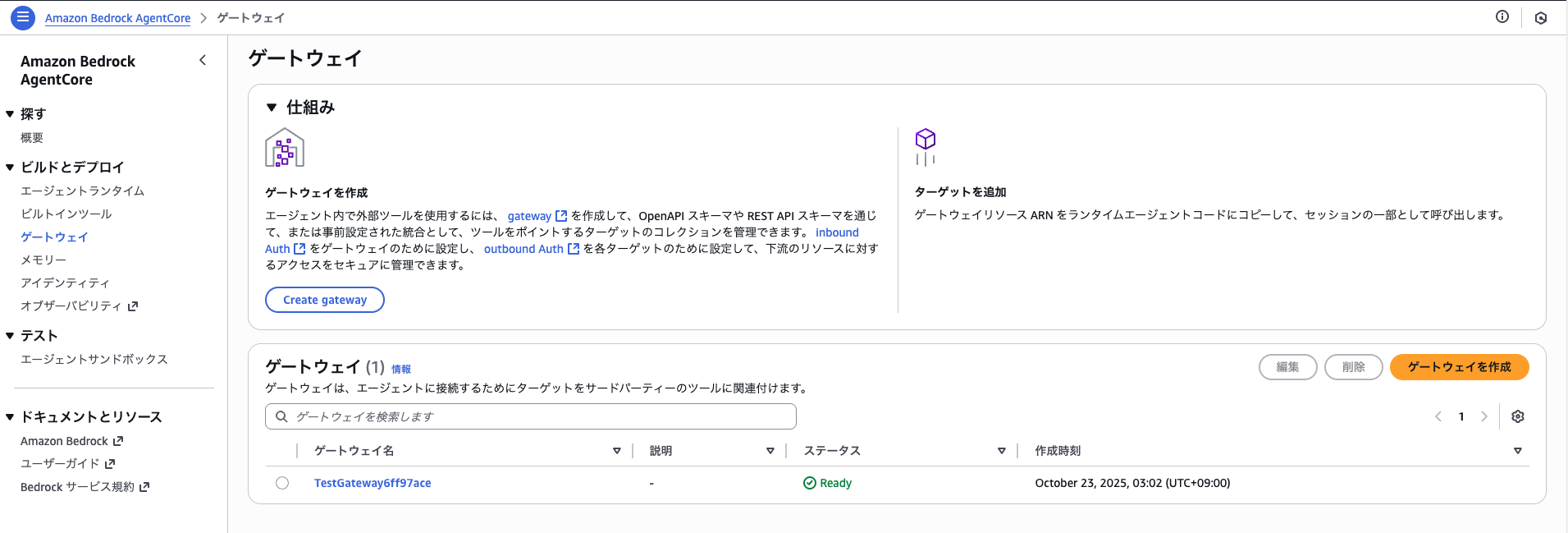
こちらも確認すると、Gatewayが作成されていることがわかります。
ターゲット関数の作成、追加
Lambda関数のターゲットを作成、追加しています。
天気と時間ツールを含むLambda関数を自動的に作成します。
# Step 2.4: Save configuration for agent
config = {
"gateway_url": gateway["gatewayUrl"],
"gateway_id": gateway["gatewayId"],
"region": region,
"client_info": cognito_response["client_info"]
}
with open("gateway_config.json", "w") as f:
json.dump(config, f, indent=2)
print("=" * 60)
print("✅ Gateway setup complete!")
print(f"Gateway URL: {gateway['gatewayUrl']}")
print(f"Gateway ID: {gateway['gatewayId']}")
print("\nConfiguration saved to: gateway_config.json")
print("\nNext step: Run 'python run_agent.py' to test your Gateway")
print("=" * 60)
return config
if __name__ == "__main__":
setup_gateway()
作成されるターゲット関数は以下になります。
天気と時間をそれぞれ固定値で返却するモック関数になっており、ツールとして登録しています。
import json
def lambda_handler(event, context):
# Extract tool name from context
tool_name = context.client_context.custom.get('bedrockAgentCoreToolName', 'unknown')
if 'get_weather' in tool_name:
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': json.dumps({
'location': event.get('location', 'Unknown'),
'temperature': '72°F',
'conditions': 'Sunny'
})
}
elif 'get_time' in tool_name:
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': json.dumps({
'timezone': event.get('timezone', 'UTC'),
'time': '2:30 PM'
})
}
else:
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': json.dumps({'message': 'Unknown tool'})
}
Gatewayに接続して実行してみる
では次に、実際にエージェントを作成し、Gatewayに接続して使用していきます
コード全文
"""
Agent script to test the Gateway
Run this after setup: python run_agent.py
"""
from strands import Agent
from strands.models import BedrockModel
from strands.tools.mcp.mcp_client import MCPClient
from mcp.client.streamable_http import streamablehttp_client
from bedrock_agentcore_starter_toolkit.operations.gateway.client import GatewayClient
import json
import sys
def create_streamable_http_transport(mcp_url: str, access_token: str):
return streamablehttp_client(mcp_url, headers={"Authorization": f"Bearer {access_token}"})
def get_full_tools_list(client):
"""Get all tools with pagination support"""
more_tools = True
tools = []
pagination_token = None
while more_tools:
tmp_tools = client.list_tools_sync(pagination_token=pagination_token)
tools.extend(tmp_tools)
if tmp_tools.pagination_token is None:
more_tools = False
else:
more_tools = True
pagination_token = tmp_tools.pagination_token
return tools
def run_agent():
# Load configuration
try:
with open("gateway_config.json", "r") as f:
config = json.load(f)
except FileNotFoundError:
print("❌ Error: gateway_config.json not found!")
print("Please run 'python setup_gateway.py' first to create the Gateway.")
sys.exit(1)
gateway_url = config["gateway_url"]
client_info = config["client_info"]
# Get access token for the agent
print("Getting access token...")
client = GatewayClient(region_name=config["region"])
access_token = client.get_access_token_for_cognito(client_info)
print("✓ Access token obtained\n")
# Model configuration - change if needed
model_id = "anthropic.claude-3-7-sonnet-20250219-v1:0"
print("🤖 Starting AgentCore Gateway Test Agent")
print(f"Gateway URL: {gateway_url}")
print(f"Model: {model_id}")
print("-" * 60)
# Setup Bedrock model
bedrockmodel = BedrockModel(
inference_profile_id=model_id,
streaming=True,
)
# Setup MCP client
mcp_client = MCPClient(lambda: create_streamable_http_transport(gateway_url, access_token))
with mcp_client:
# List available tools
tools = get_full_tools_list(mcp_client)
print(f"\n📋 Available tools: {[tool.tool_name for tool in tools]}")
print("-" * 60)
# Create agent
agent = Agent(model=bedrockmodel, tools=tools)
# Interactive loop
print("\n💬 Interactive Agent Ready!")
print("Try asking: 'What's the weather in Seattle?'")
print("Type 'exit', 'quit', or 'bye' to end.\n")
while True:
user_input = input("You: ")
if user_input.lower() in ["exit", "quit", "bye"]:
print("👋 Goodbye!")
break
print("\n🤔 Thinking...\n")
response = agent(user_input)
print(f"\nAgent: {response.message.get('content', response)}\n")
if __name__ == "__main__":
run_agent()
LLMが解釈して結果を返却
最後に問い合わせを実施すると、以下のような回答が想定できます。
実際に天気の問い合わせをしたところ、天気に関するツールを利用しています。
You: シアトルの天気はどうですか?
🤔 Thinking...
シアトルの天気をお調べします。
Tool #1: TestGatewayTarget74eb18fa___get_weather
シアトルの現在の天気は以下の通りです:
- **場所**: シアトル
- **気温**: 72°F(約22°C)
- **天候**: 晴れ
今日のシアトルは晴れて過ごしやすい気温ですね!
Agent: [{'text': 'シアトルの現在の天気は以下の通りです:\n\n- **場所**: シアトル\n- **気温**: 72°F(約22°C)\n- **天候**: 晴れ\n\n今日のシアトルは晴れて過ごしやすい気温ですね!'}]
ここまでで、Lambda関数をMCPツールとして登録し、エージェントから利用するという一通りGatewayの機能を試すことはできました。
Runtimeとの統合を試してみる
今までやっていたのはStrandsからGatewayを利用している形になっていました。
せっかくならRuntimeにエージェントをデプロイして、RuntimeからGatewayに接続して実行までやってみたいと思います。
公式のワークショップリポジトリにサンプルがありましたので、そちらを参考にしました。
コードをRuntime仕様に変更
作業としてはさほど多くなく、上で作成したrun_agent.pyをRuntime仕様に変更してあげればOKです。
コード全文
from __future__ import annotations
import json
import os
import sys
import logging
from typing import Any, Dict, List, Optional
from bedrock_agentcore import BedrockAgentCoreApp
from strands import Agent
from strands.models import BedrockModel
from strands.tools.mcp.mcp_client import MCPClient
from mcp.client.streamable_http import streamablehttp_client
from bedrock_agentcore_starter_toolkit.operations.gateway.client import GatewayClient
app = BedrockAgentCoreApp()
def _init_logging() -> None:
level_name = os.getenv("AGENT_LOG_LEVEL", "INFO").upper()
level = getattr(logging, level_name, logging.INFO)
root = logging.getLogger()
if not root.handlers:
handler = logging.StreamHandler(sys.stdout)
fmt = "%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s"
handler.setFormatter(logging.Formatter(fmt))
root.addHandler(handler)
root.setLevel(level)
logging.getLogger("urllib3").setLevel(logging.WARNING if level > logging.DEBUG else level)
logging.getLogger("botocore").setLevel(logging.INFO)
logging.getLogger("boto3").setLevel(logging.INFO)
logging.getLogger("bedrock_agentcore").setLevel(logging.INFO)
logging.getLogger("strands").setLevel(logging.INFO)
logging.getLogger("mcp").setLevel(logging.INFO)
try:
sys.stdout.reconfigure(line_buffering=True)
except Exception:
pass
_init_logging()
log = logging.getLogger("run_agent")
# -----------------------------
# Model configuration
# -----------------------------
DEFAULT_MODEL_ID = os.getenv(
"BEDROCK_MODEL_ID",
"us.anthropic.claude-haiku-4-5-20251001-v1:0",
)
def _load_gateway_config() -> Dict[str, Any]:
blob = os.getenv("GATEWAY_CONFIG_JSON")
if blob:
return json.loads(blob)
with open("gateway_config.json", "r") as f:
return json.load(f)
def _get_access_token(region: str, client_info: Dict[str, Any]) -> str:
log.info("Fetching test token from Cognito...")
client = GatewayClient(region_name=region)
token = client.get_access_token_for_cognito(client_info)
log.info("✓ Got test token successfully")
return token
def _create_streamable_http_transport(mcp_url: str, access_token: str):
return streamablehttp_client(
mcp_url,
headers={"Authorization": f"Bearer {access_token}"},
)
def _list_all_tools(mcp: MCPClient) -> List[Any]:
tools: List[Any] = []
token: Optional[str] = None
while True:
page = mcp.list_tools_sync(pagination_token=token)
tools.extend(page)
token = page.pagination_token
if token is None:
break
return tools
@app.entrypoint
def invoke(payload: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]:
cfg = _load_gateway_config()
gateway_url = cfg["gateway_url"]
region = cfg["region"]
client_info = cfg["client_info"]
print("Getting access token...")
access_token = _get_access_token(region, client_info)
print("✓ Access token obtained\n")
print("🤖 Starting AgentCore Gateway Test Agent")
print(f"Gateway URL: {gateway_url}")
print(f"Model: {DEFAULT_MODEL_ID}")
print("-" * 60)
additional_fields = {"inferenceProfileArn": INFERENCE_PROFILE_ARN} if INFERENCE_PROFILE_ARN else None
bedrock_model = BedrockModel(
model_id=DEFAULT_MODEL_ID,
streaming=True,
additional_request_fields=additional_fields,
)
prompt: Optional[str] = None
messages = payload.get("messages")
if isinstance(messages, list) and messages:
for m in reversed(messages):
if isinstance(m, dict) and m.get("role") == "user" and m.get("content"):
prompt = m["content"]
break
if not prompt:
prompt = payload.get("prompt") or "こんにちは!どうお手伝いできますか?"
mcp_client = MCPClient(lambda: _create_streamable_http_transport(gateway_url, access_token))
with mcp_client:
tools = _list_all_tools(mcp_client)
print(f"\n📋 Available tools: {[t.tool_name for t in tools]}")
print("-" * 60)
agent = Agent(
model=bedrock_model,
tools=tools,
)
print("\n💬 Interactive Agent Ready!")
print("Try asking: 'What's the weather in Seattle?'")
print("(runtime invoke)\n")
print("\n🤔 Thinking...\n")
log.info("Invoking agent with prompt: %s", prompt)
result = agent(prompt)
content = getattr(getattr(result, "message", {}), "get", lambda *_: None)("content") or result
print(f"\nAgent: {content}\n")
log.info("Invocation finished.")
return {"result": content}
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run()
その後、以下コマンドでRuntimeにデプロイして実行すると変わらずツールを実行してレスポンスが返却されるはずです。
uv run agentcore configure --entrypoint run_agent.py
uv run agentcore launch
uv run agentcore invoke '{"prompt": "シアトルの天気について教えて"}'
オブザーバビリティの確認
さいごにログやトレースの確認だけしてみます。
まず、「AgentCore.Gateway.ListTools」に注目してみると、Gatewayに登録されている利用可能なツールを取得しています。
見にくくて恐縮ですが、ログをそのまま抜き出すと以下のようになります。
「responseBody部」では、get_timeとget_weatherが利用可能なツールとして返却されていることがわかります。
{
"resource_arn": "arn:aws:bedrock-agentcore:us-west-2:017820658462:gateway/testgateway6ff97ace-x6wakfaq7e",
"event_timestamp": 1761430247527,
"body": {
"isError": false,
"responseBody": "{jsonrpc=2.0, id=1, result={tools=[{inputSchema={type=object, properties={query={type=string}}, required=[query]}, name=x_amz_bedrock_agentcore_search, description=A special tool that returns a trimmed down list of tools given a context. Use this tool only when there are many tools available and you want to get a subset that matches the provided context.}, {inputSchema={type=object, properties={timezone={type=string}}, required=[timezone]}, name=TestGatewayTarget74eb18fa___get_time, description=Get time for a timezone}, {inputSchema={type=object, properties={location={type=string}}, required=[location]}, name=TestGatewayTarget74eb18fa___get_weather, description=Get weather for a location}]}}",
"log": "Successfully processed request",
"id": "1"
},
"account_id": "017820658462",
"request_id": "a79b9900-9d86-4739-99d5-a39e25559a20",
"trace_id": "68fd4ae65e9784515c42aa192a72cc06",
"span_id": "53f7a7285f074c52"
}
下記は問い合わせに対して実際にツールを選んで実行している部分のログになります。
シアトルの天気を確認したい問い合わせに対して、toolUse句でget_weatherツールが利用されていることがわかります。
tool.result句では問い合わせを行い、Lambdaで登録している値がとれていることがわかりますね。
"body": {
"output": {
"messages": [
{
"content": {
"message": [
{
"text": "シアトルの天気を確認します。"
},
{
"toolUse": {
"toolUseId": "tooluse_Ppenr0ikQK-2KKyL6Ek69w",
"name": "TestGatewayTarget74eb18fa___get_weather",
"input": {
"location": "Seattle"
}
}
}
],
"tool.result": [
{
"toolResult": {
"status": "success",
"toolUseId": "tooluse_Ppenr0ikQK-2KKyL6Ek69w",
"content": [
{
"text": {
"statusCode": 200,
"body": {
"location": "Seattle",
"temperature": "72°F",
"conditions": "Sunny"
}
}
}
]
}
}
]
}
さいごに
ここまででAgentCore Gatewayの機能を一通り体験してみました。
Lambda関数をMCPツール化できるという面白い機能でした。
今回登録したツールはダミーのLamndaのみでしたが、他にも色々使えるようなので検証していこうと思います。
認証まわりの処理まであまり解説できなかったので、次回の記事でじっくり書いていきたいと思います。