データ型について
変数に入れるデータの種類のことを指し、①数値型(number「ナンバー」型)②文字列型(string「ストリング」型) ③ブール型(Boolean「ブーリアン」型)に分けデータを代入する際に、Go言語ではデータ型として指定する静的型付け言語が用いられる。逆に、変数にデータを入れる際にデータを指定する必要がなく自動的に判断してくれるプログラミング言語を動的型付け言語といいます。
数値型には、整数型と小数点型がある
| 数値型 | 説明 |
|---|---|
| int | コンピューターで表せるだけの範囲の整数値を表す(int8 int32等、-127〜127) |
| float64 | 64ビットのコンピューターで少数値を表す(32ビットの場合はfloat32型) |
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var a int
a = 4
b := 6
fmt.Println(2 * a)
fmt.Println(b - a)
}
前回までの応用で、データ型を自動判別させ変数を定義して値を代入し実行してみます。
・実行結果
./ints
8
2
変数自身の値に処理を加える
変数は「変」数という名前から伝わるように、一度値を代入したあとでも別の値を再代入することができ、前にあった変数の値は新しく上書きされて消されます。例えば、a := 100 の下にa = 50 と代入すれば、aの値は50になります。
変数自身の値にを処理して、新しく代入する
変数の元の値を処理してその変数に代入し直す事ができます。
a = 50 (↓のaには値50が用いられる)
(新しい値80が代入→)a = a + 30
代入演算子の右側では、元の値が使われたうえで処理が行われます。そして、代入演算子の左側の変数に新しい演算子が代入される仕組みです。更に、a = a + 30 は a += 30のように省略して書くことができます。
省略形には、加算代入(+=)、減算代入(-=)、乗算代入(*=)、除算代入(/=)、剰余代入(%=)があります。
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
a := 4
b := 6
fmt.Println(2 * a)
fmt.Println(b - a)
a = 50
b += a
fmt.Println(a)
fmt.Println(b)
}
変数自身の値を処理して再代入する処理を追記させて実行してみます。
・実行結果
./ints
8
2
50
56
float64型の宣言を省略した書き方
a := 4.0
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
a := 4
fmt.Println(2 * a)
fmt.Println(2.0 * a)
fmt.Println(2.2 * a)
}
floats.goというファイルを作り、数値の型を確認してみます。
・実行結果
./floats
8
8
8.8
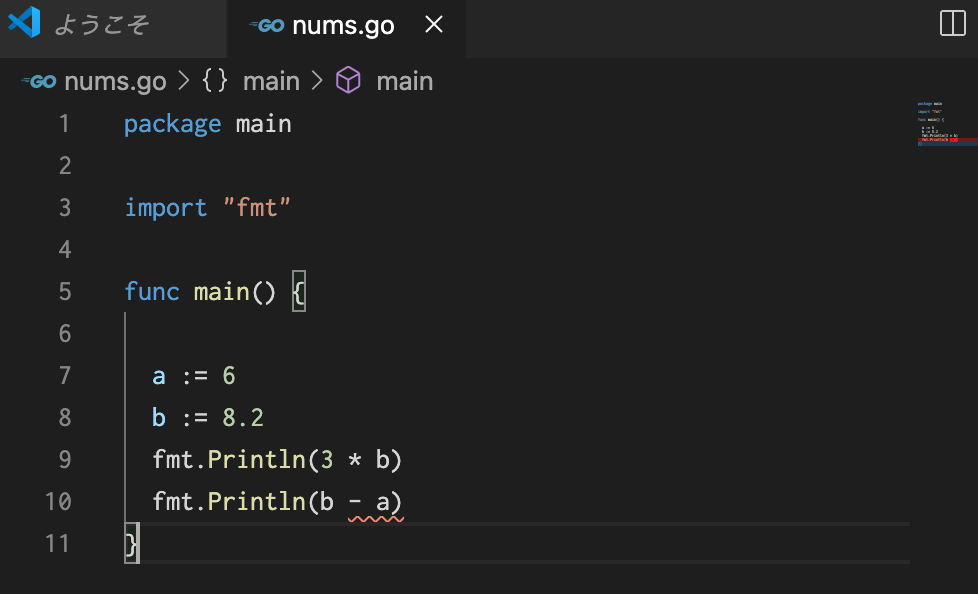
変数 a にはint型、変数 b にはfloat64型が渡されている場合、データ型の異なる値同士で減算するとエラーが乗じます。Go言語を始めとしたプログラミング言語の多くは、データ型が異なる数値同士での計算を禁じています。また、Go言語のデータ型は、**reflect(リフレクト)**のパッケージのTypeOf(タイプオフ)を使用して確認することが出来ます。
package main
import ("fmt" "reflect")
func main() {
num01 := 123
var num02 int = 123456789
num03 := 1.23
var num04 int = 1.23456789
fmt.Println(reflect.TypeOf(num01))
fmt.Println(reflect.TypeOf(num02))
fmt.Println(reflect.TypeOf(num03))
fmt.Println(reflect.TypeOf(num04))
}
・実行結果
./nums
int
int
float64
float64