Rで描いた、いろいろなビジュアライゼーションを集めました。
基本的には、ggplotで描いていますが、
ggplotでの表現が煩雑になる場合は、他のライブラリも使用しています。
- デフォルトで読み込むライブラリ
R
library(dplyr)
library(ggplot2)
属性間の比較
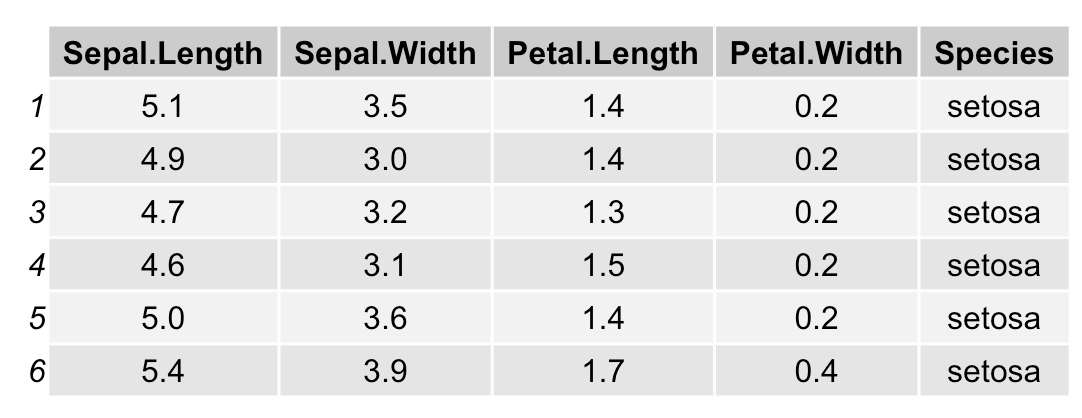
表(単純なもの)
R
library(gridExtra)
d <- head(iris)
grid.table(d)
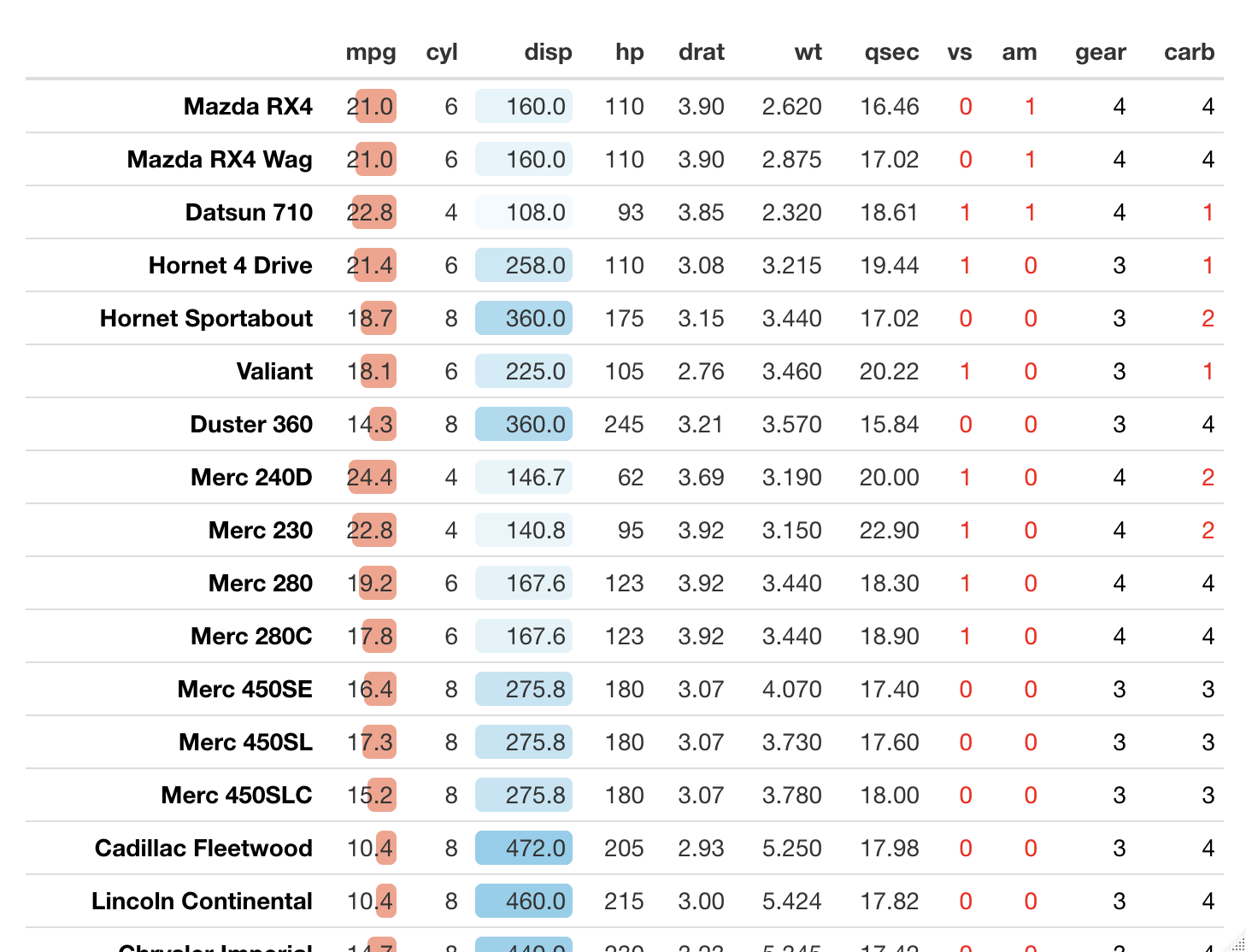
表(フォーマット指定)
R
library(formattable)
library(tibble)
data(mtcars)
mtcars <- rownames_to_column(mtcars, var=" ")
formattable(mtcars,
list(' ' = formatter("span", style = ~ style(color = "black", font.weight = "bold")),
'mpg' = color_bar("#FAA18B"),
'disp' = color_tile("white", "skyblue"),
area(col=c(9:12)) ~ formatter("span",
style = x ~ style(color = ifelse(x < 3, "red", "black")))
)
)
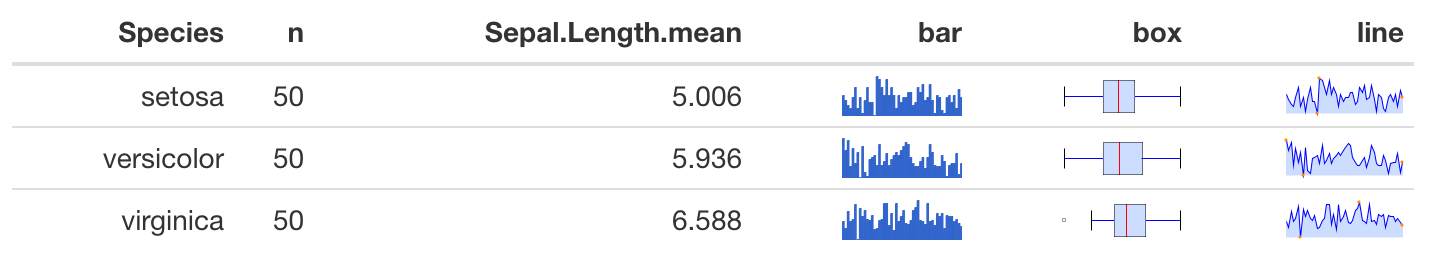
表(スパークライン付加)
R
library(formattable)
library(sparkline)
library(tidyverse)
# データ準備
data(iris)
iris %>%
group_by(Species) %>%
summarise(n=n(),
Sepal.Length.mean=mean(Sepal.Length)) -> df
# Speciesごとの数値データを、sparkline()に入れてオブジェクトを作成、
# それをhtml文字列に変換する
Sepal.Length.bySpecies <- split(iris, iris$Species)
for(type in c("bar", "box", "line")){
Sepal.Length.bySpecies %>%
map(~ sparkline(.$Sepal.Length, type = type)) %>%
map(~ as.character(htmltools::as.tags(.))) -> spakline.htmlstr
df[[type]] <- spakline.htmlstr
}
# formattable()でフォーマットし出力
out = as.htmlwidget(formattable(df))
out$dependencies = c(out$dependencies, htmlwidgets:::widget_dependencies("sparkline", "sparkline"))
out
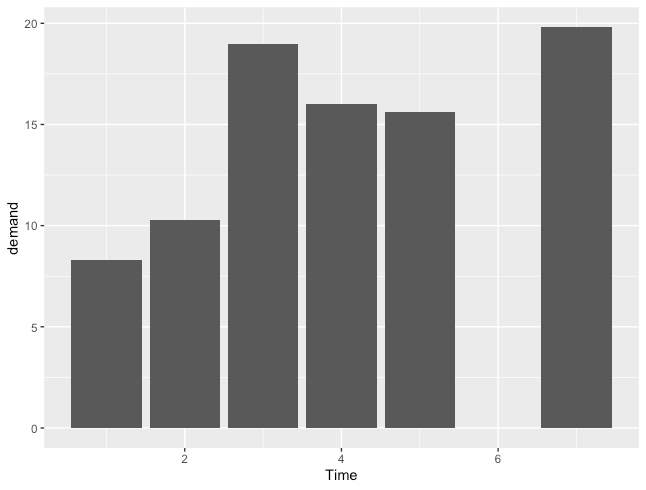
縦棒グラフ
R
ggplot(BOD, aes(x=Time, y=demand)) +
geom_col()
横棒グラフ
R
ggplot(BOD, aes(x=demand, y=Time)) +
geom_col()
クリーブランドのドットプロット
R
# 描画用データ準備
df <- data.frame(state.x77)
df["Name"] <- rownames(df)
# geom_segment と geom_point を組み合わせることで描画
df[df$Population < 3000, ] %>%
ggplot(aes(y=reorder(Name, Population), x=Population, color=Population)) +
geom_segment(aes(yend=Name), xend=0) +
geom_point(size=4) +
theme(panel.grid.major.y=element_blank()) +
ylab("U.S. state")
ヒートマップ
R
# 描画用データ準備
df <- data.frame(occupationalStatus)
# geom_rasterで描画。(geom_tileでも同じ図を描ける)
ggplot(df, aes(x=origin, y=destination, fill=Freq)) +
geom_raster()
ヒートマップ + グラフ
superheatを使った色々な描き方は、こちらでも少し詳しく記載しています。
R
library(superheat)
superheat(mtcars,scale=TRUE,
yr=mtcars$mpg,
yr.plot.type="bar",
yr.axis.name="mpg",
yr.plot.size=0.5)
時系列の比較
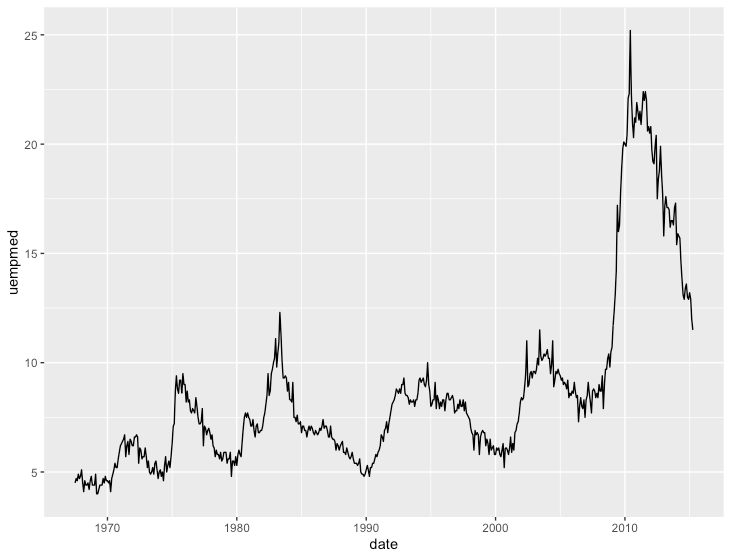
折れ線グラフ
R
ggplot(economics, aes(x=date, y=uempmed)) +
geom_line()
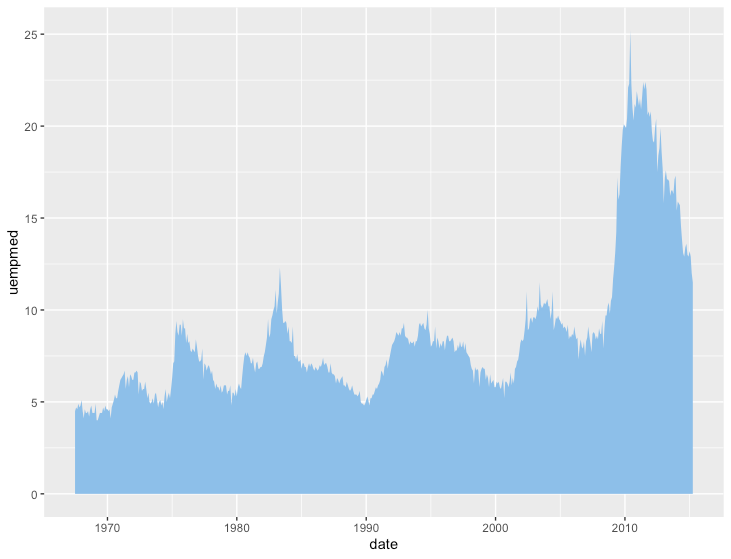
面グラフ
R
ggplot(economics, aes(x=date, y=uempmed)) +
geom_area(fill="skyblue2")
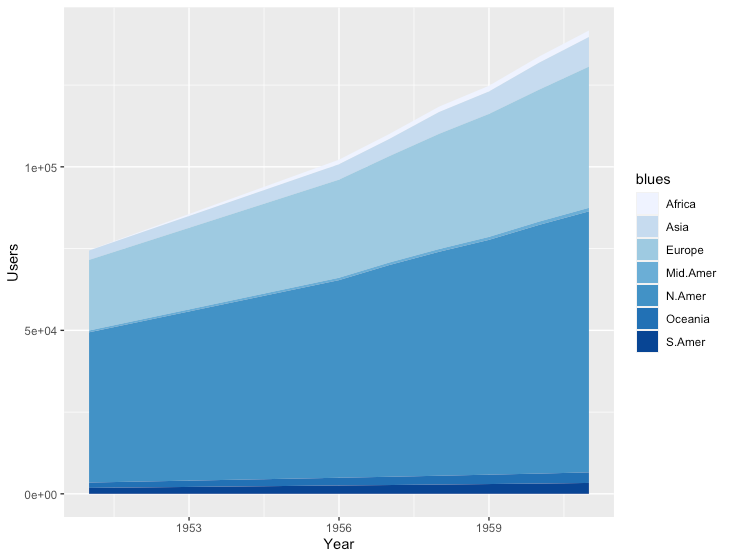
積み上げ面グラフ
R
library(tidyr)
# データ準備
# データが縦持ちの形式となっている必要がある
# WorldPhones
# N.Amer Europe Asia S.Amer Oceania Africa Mid.Amer
# 1951 45939 21574 2876 1815 1646 89 555
# 1956 60423 29990 4708 2568 2366 1411 733
# 1957 64721 32510 5230 2695 2526 1546 773
# ...
# ---↓↓↓---
# Year Country Users
# 1 1951 N.Amer 45939
# 2 1956 N.Amer 60423
# 3 1957 N.Amer 64721
# 4 1958 N.Amer 68484
# ...
df <- data.frame(WorldPhones) %>%
tibble::rownames_to_column("Year") %>%
gather(key="Country", value="Users", -Year)
df$Year <- as.integer(df$Year)
ggplot(df, aes(x=Year, y=Users, fill=Country)) +
geom_area() +
scale_fill_brewer("blues")
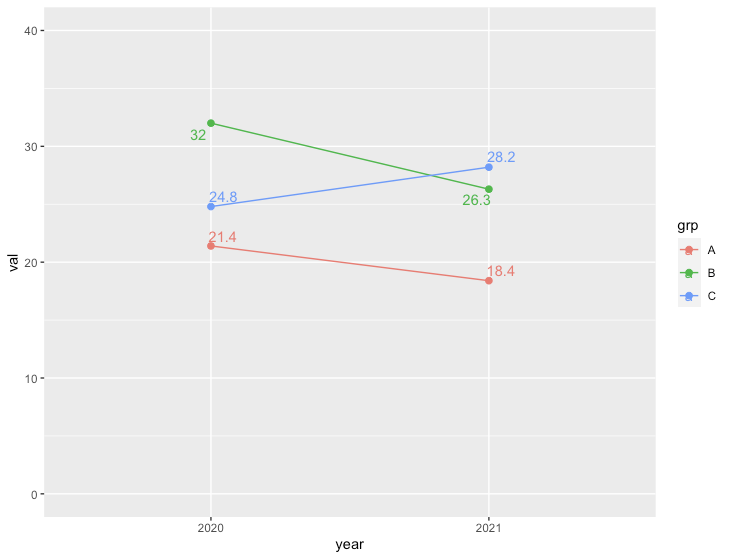
スロープグラフ
R
library("ggrepel") #geom_pointのラベル位置を適当に調整するために使用
# データ準備
df <- data.frame(year=c(2020, 2021, 2020, 2021, 2020, 2021),
grp=c("A", "A", "B", "B", "C", "C"),
val=c(21.4, 18.4, 32.0, 26.3, 24.8, 28.2))
ggplot(df, aes(x=factor(year), y=val, label=val, group=grp, colour=grp)) +
geom_line() +
geom_point(size=2) +
geom_text_repel() +
ylim(0, 40) +
xlab("year")
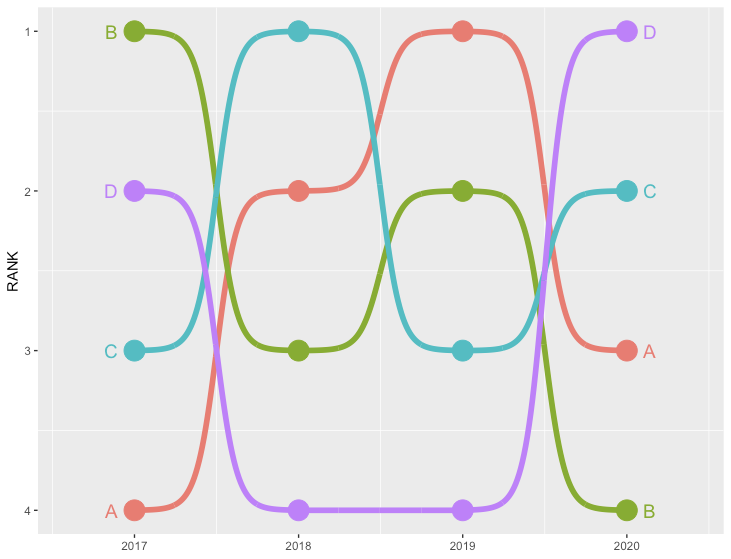
バンプチャート
R
library(ggbump) #install_github("davidsjoberg/ggbump")
# データ準備
df <- data.frame(country=c(rep("A", 4), rep("B", 4), rep("C", 4), rep("D", 4)),
year=rep(c(2017, 2018, 2019, 2020), 4),
rank=c(4,2,1,3, 1,3,2,4, 3,1,3,2, 2,4,4,1))
ggplot(df, aes(year, rank, color = country)) +
geom_point(size = 7) +
geom_text(data = df %>% filter(year == min(year)),
aes(x = year - .1, label = country), size = 5, hjust = 1) +
geom_text(data = df %>% filter(year == max(year)),
aes(x = year + .1, label = country), size = 5, hjust = 0) +
geom_bump(size = 2, smooth = 8) +
scale_x_continuous(limits = c(2016.6, 2020.4),
breaks = seq(2017, 2020, 1)) +
theme(legend.position = "none",
panel.grid.major = element_blank()) +
labs(y = "RANK",
x = NULL) +
scale_y_reverse()
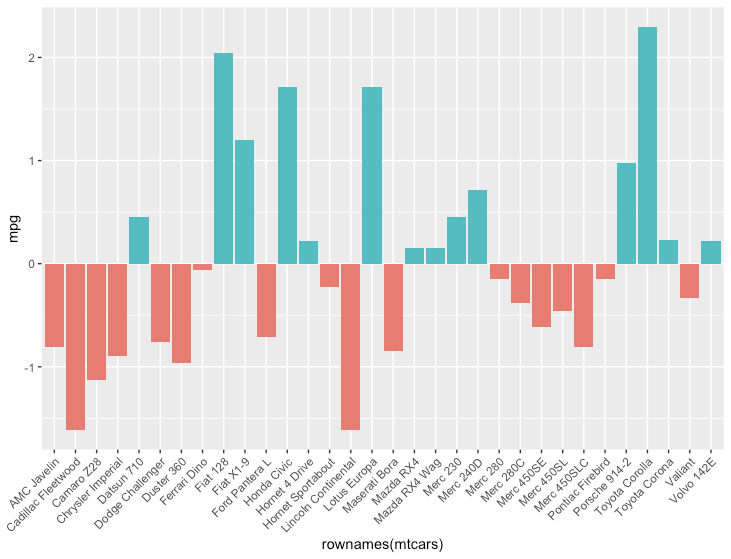
(分岐させた)色塗り線グラフ
R
# データ準備
scaled_mtcars <- mtcars %>%
scale() %>%
data.frame() %>%
mutate(positive=mpg>0)
ggplot(scaled_mtcars, aes(x=rownames(mtcars), y=mpg, fill=positive)) +
geom_col() +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 45, hjust = 1),
legend.position = 'none')
分布の把握
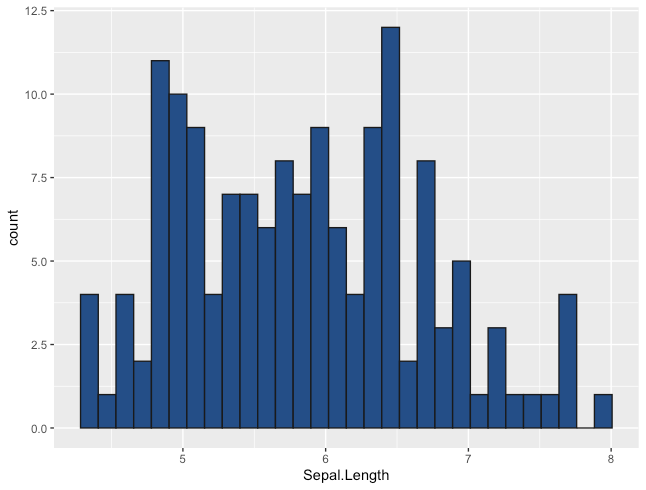
ヒストグラム
ggplotのヒストグラムについては、こちらにも少し詳しく記載しています。
R
ggplot(iris, aes(x=Sepal.Length)) +
geom_histogram(colour = "gray10", fill = "dodgerblue4")
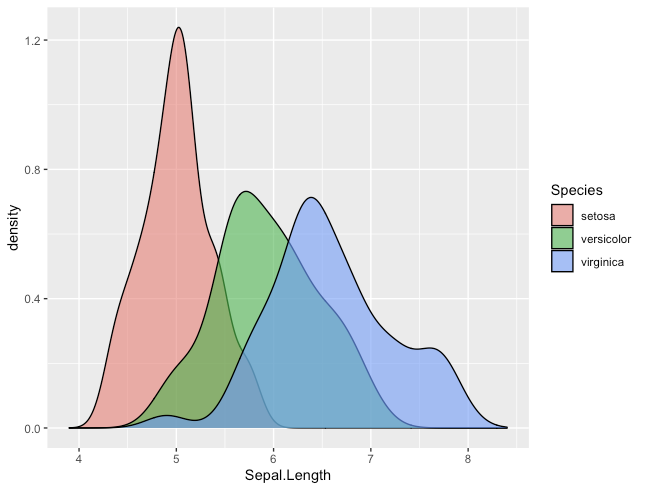
密度曲線
R
ggplot(iris, aes(x=Sepal.Length, fill=Species)) +
geom_density(position="identity", alpha=0.6) +
xlim(3.9, 8.4)
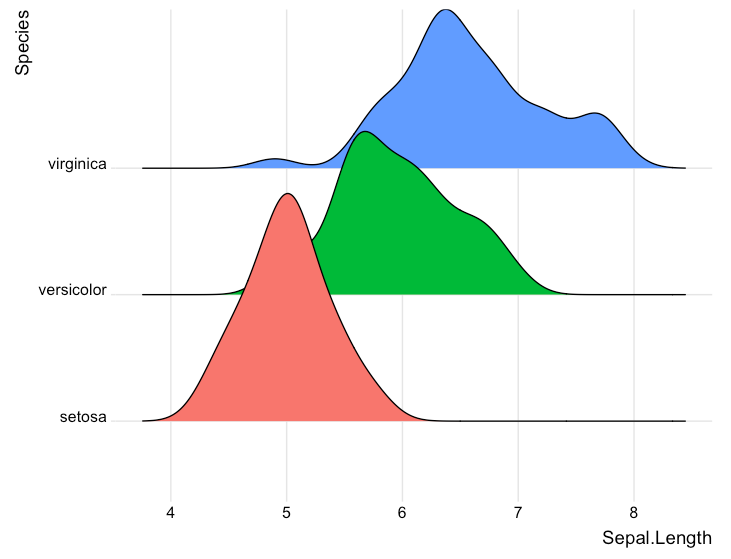
ジョイプロット
R
library(ggridges)
library(ggplot2)
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Species, fill = Species)) +
geom_density_ridges() +
theme_ridges() +
theme(legend.position = "none")
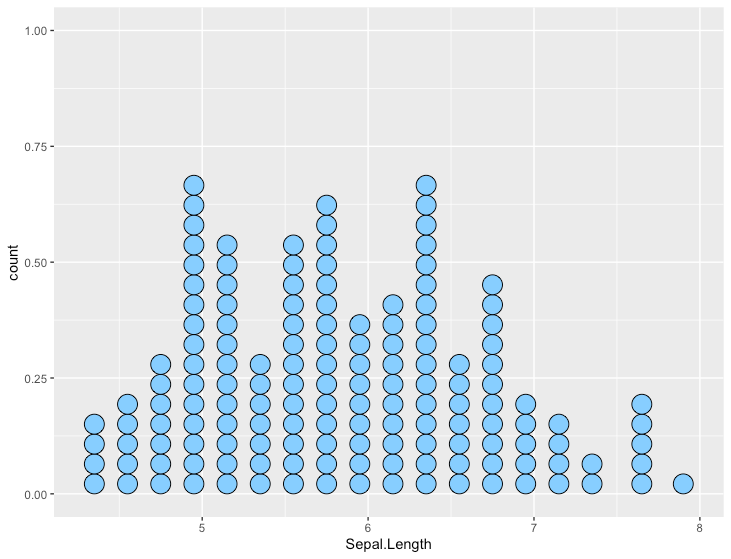
ドットプロット(ウィルキンソン)
R
ggplot(iris, aes(x=Sepal.Length)) +
geom_dotplot(fill="skyblue1")
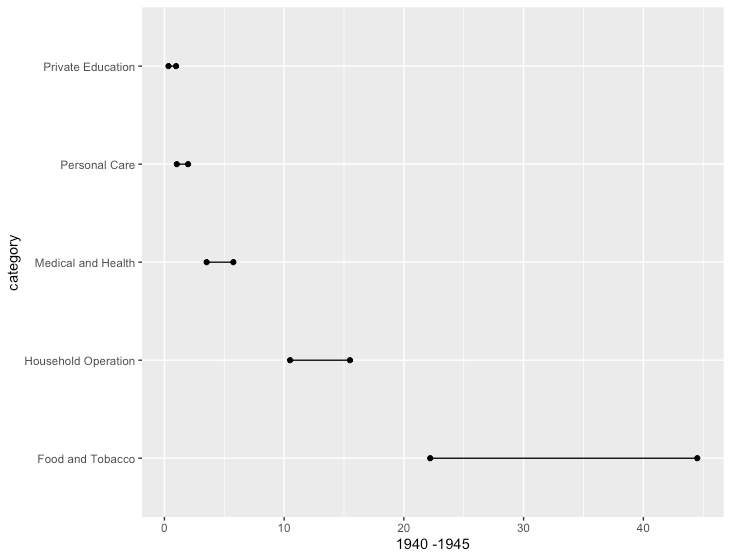
ダンベルチャート
R
library(ggalt) # install_github("hrbrmstr/ggalt")
data <- data.frame(USPersonalExpenditure)
data["category"] <- rownames(data)
ggplot(data, aes(x=X1940, xend=X1945, y=category, group=category)) +
geom_dumbbell(size_x = 1.5,
size_xend = 1.5) +
xlab("1940 -1945")
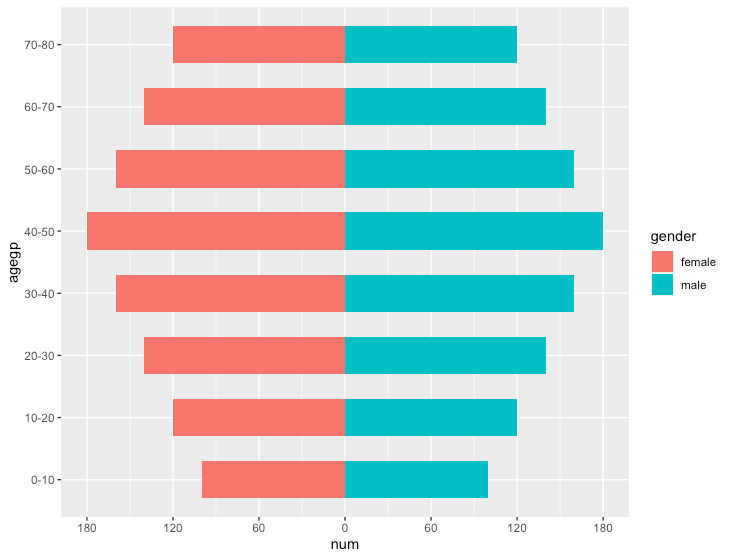
バタフライチャート
R
# データ作成
data <- data.frame(
agegp=rep(c("0-10", "10-20", "20-30", "30-40", "40-50", "50-60", "60-70", "70-80"), 2),
gender=c(rep("male", 8), rep("female", 8)),
num=rep(c(100, 120, 140, 160, 180, 160, 140, 120), 2))
# 片方の属性の値をマイナスにして「対」を表現する
data <- mutate(data, num=ifelse(gender=="female", -num, num))
# x軸のラベルをつくる
# 上でマイナスにした部分を加味して補正したbreakとラベルを作成
max_num <- max(abs(data$num))
d <- diff(range(-max_num, max_num))/6
brks <- seq(-max_num, max_num, d)
lbls = as.character(c(seq(max_num, 0, -d), seq(d, max_num, d)))
# geom_barで描画
ggplot(data, aes(x = num, y = agegp, fill = gender)) +
geom_bar(stat = "identity", width = .6) +
scale_x_continuous(breaks = brks,
labels = lbls)
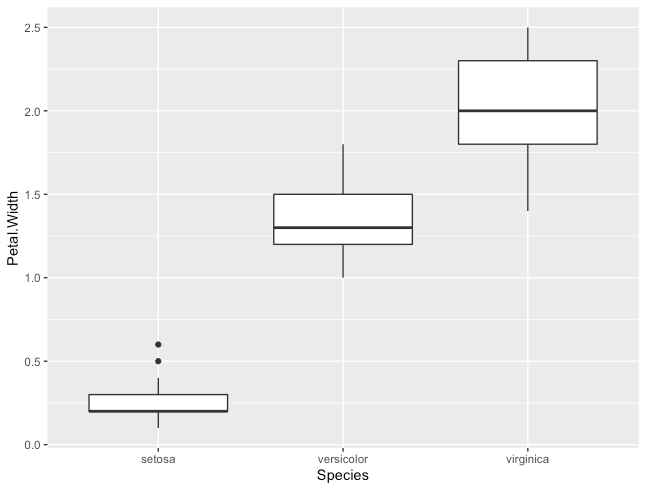
箱ひげ図
R
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Species, y=Petal.Width))+
geom_boxplot()
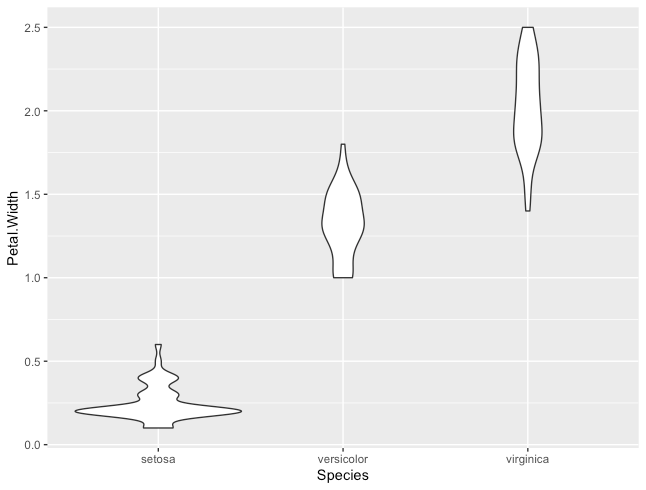
バイオリンプロット
R
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Species, y=Petal.Width))+
geom_violin()
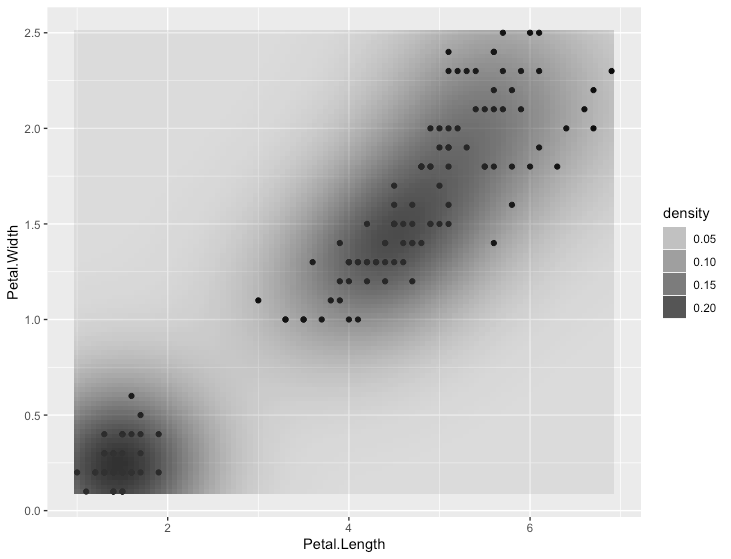
2次元の密度プロット
R
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Petal.Length, y=Petal.Width)) +
geom_point() +
stat_density2d(aes(alpha=..density..), geom="tile", contour = F)
相関の把握
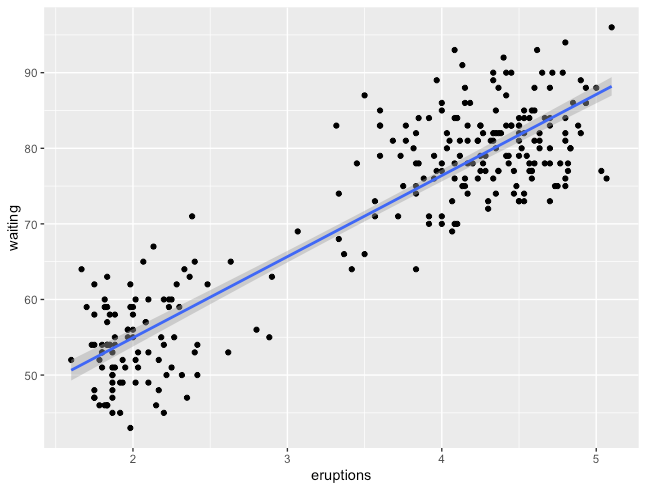
散布図
R
ggplot(faithful, aes(x=eruptions, y=waiting)) +
geom_point() +
stat_smooth(method=lm) # 傾向線をプロット
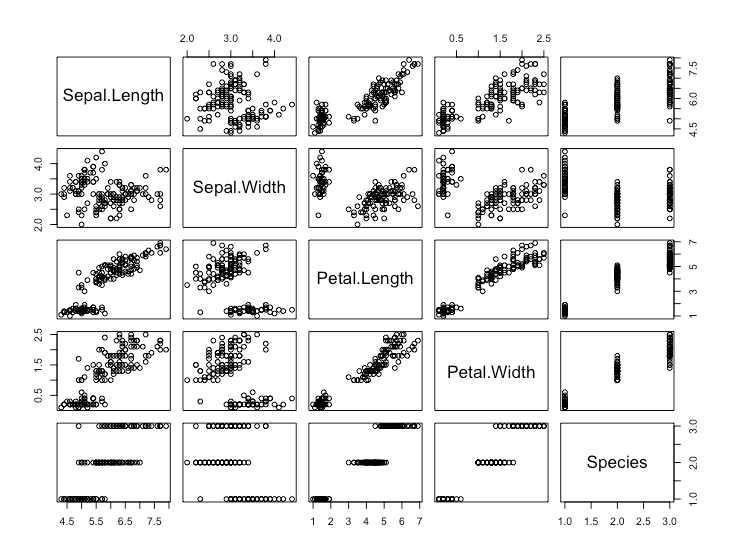
散布図行列
R
# ggplotでは散布図行列を作成できないの手軽なpairsを使用
pairs(iris)
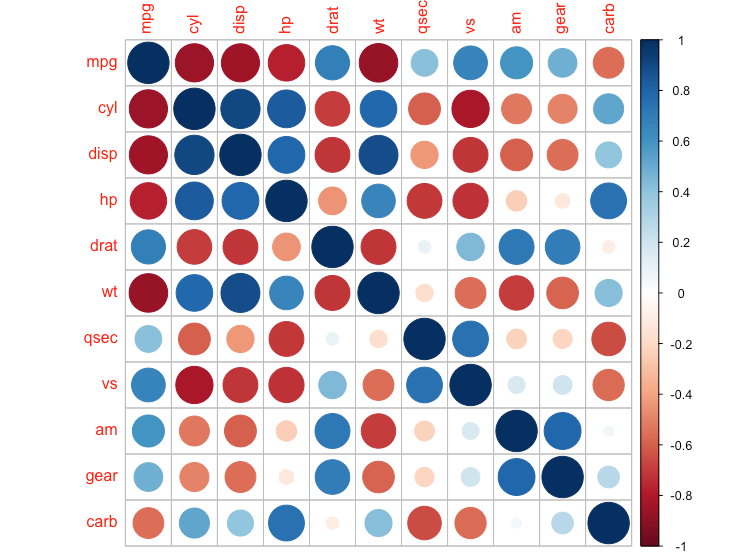
相関行列
R
library(corrplot)
cor_mtcars <- cor(mtcars)
corrplot(cor_mtcars)
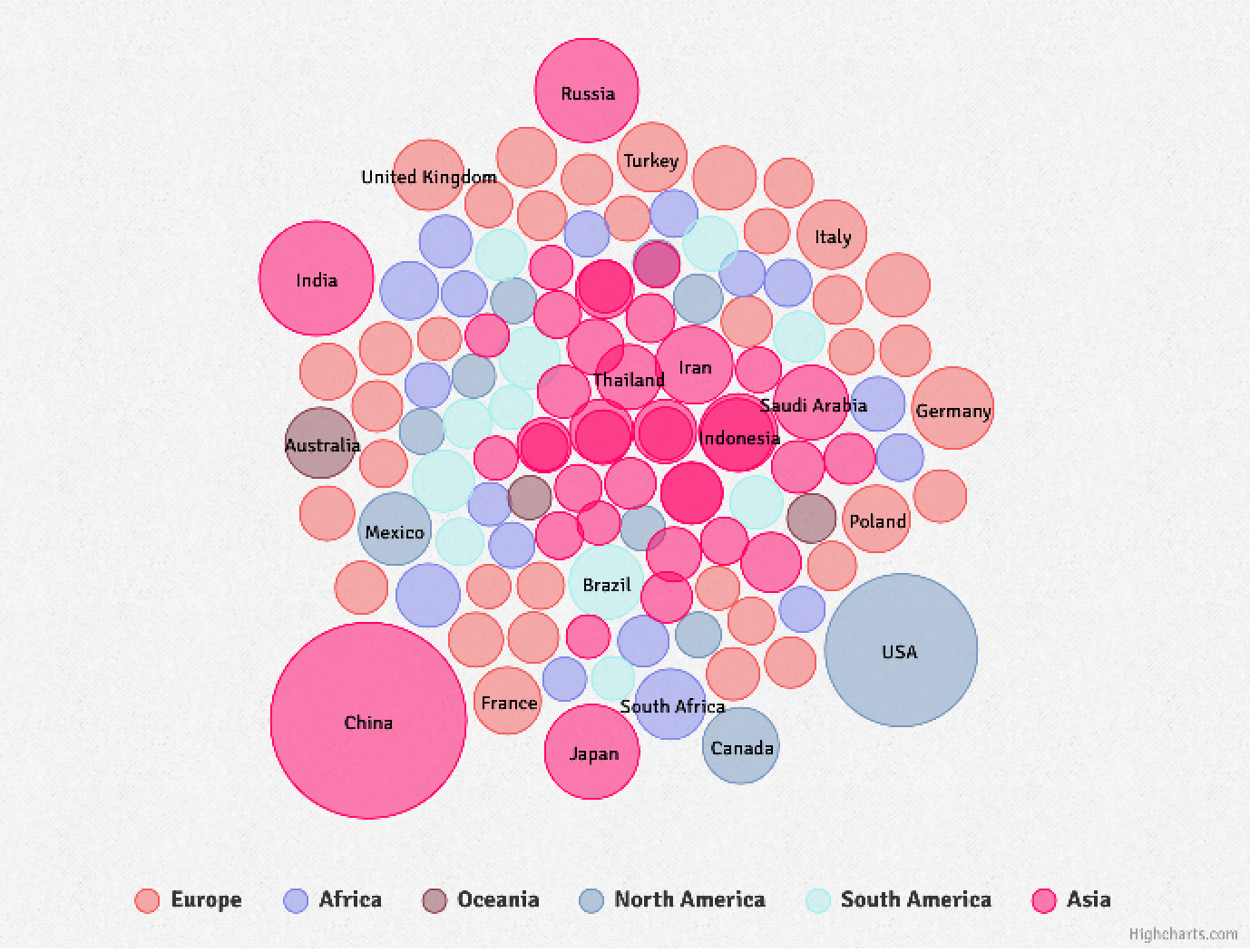
パックドバブルチャート
R
library(hpackedbubble)
hpackedbubble(CO2$continent, CO2$country, CO2$CO2,
packedbubbleZmax = 10000, split = 0)
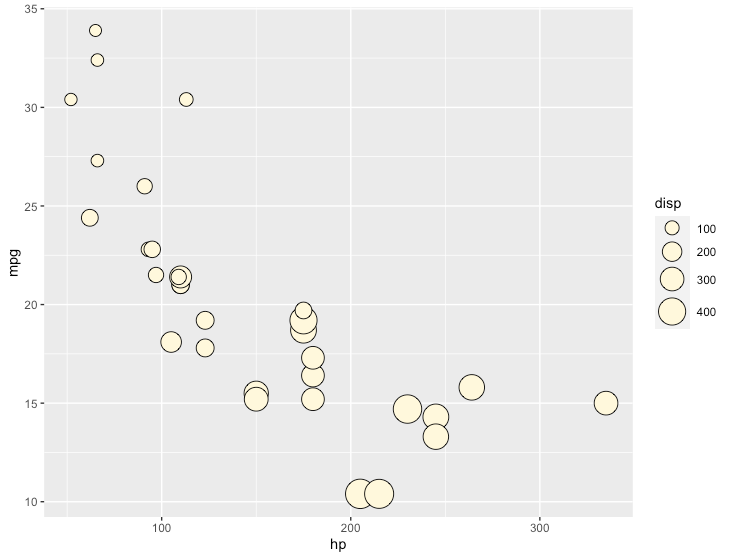
バルーンプロット
R
ggplot(mtcars, aes(x=hp, y=mpg, size=disp)) +
geom_point(shape=21, colour="black", fill="cornsilk") +
scale_size_area(max_size=10)
内訳の比較
積み上げ棒グラフ
R
# データ準備
df <- data.frame(Titanic) %>%
group_by(Survived, Class) %>%
summarize(n=n(), mean=mean(Freq))
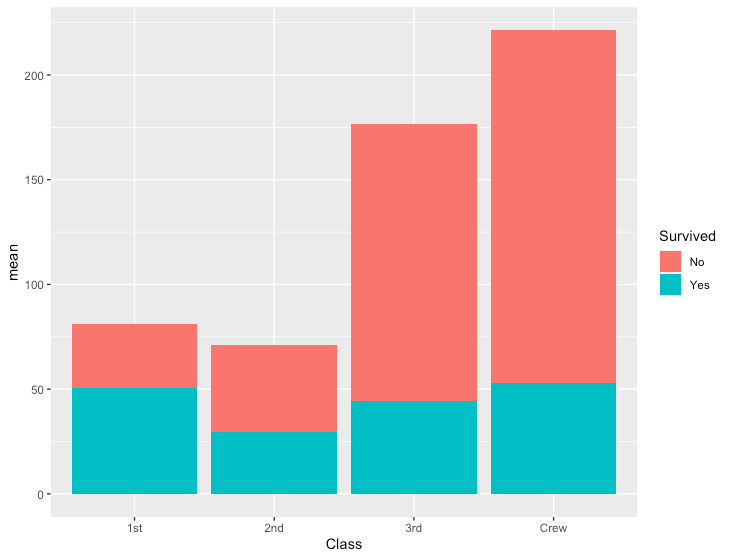
- 積み上げ縦棒グラフ
R
ggplot(df, aes(x=Class, y=mean, fill=Survived)) +
geom_col()
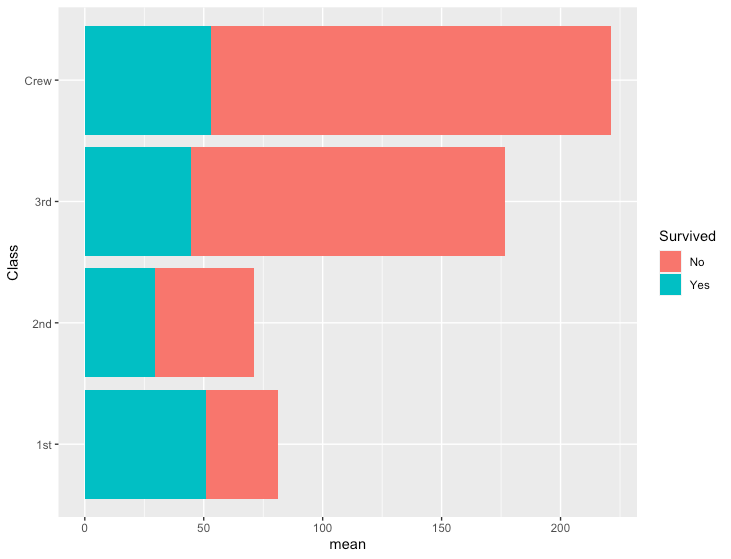
- 積み上げ横棒グラフ
R
ggplot(df, aes(x=mean, y=Class, fill=Survived)) +
geom_col()
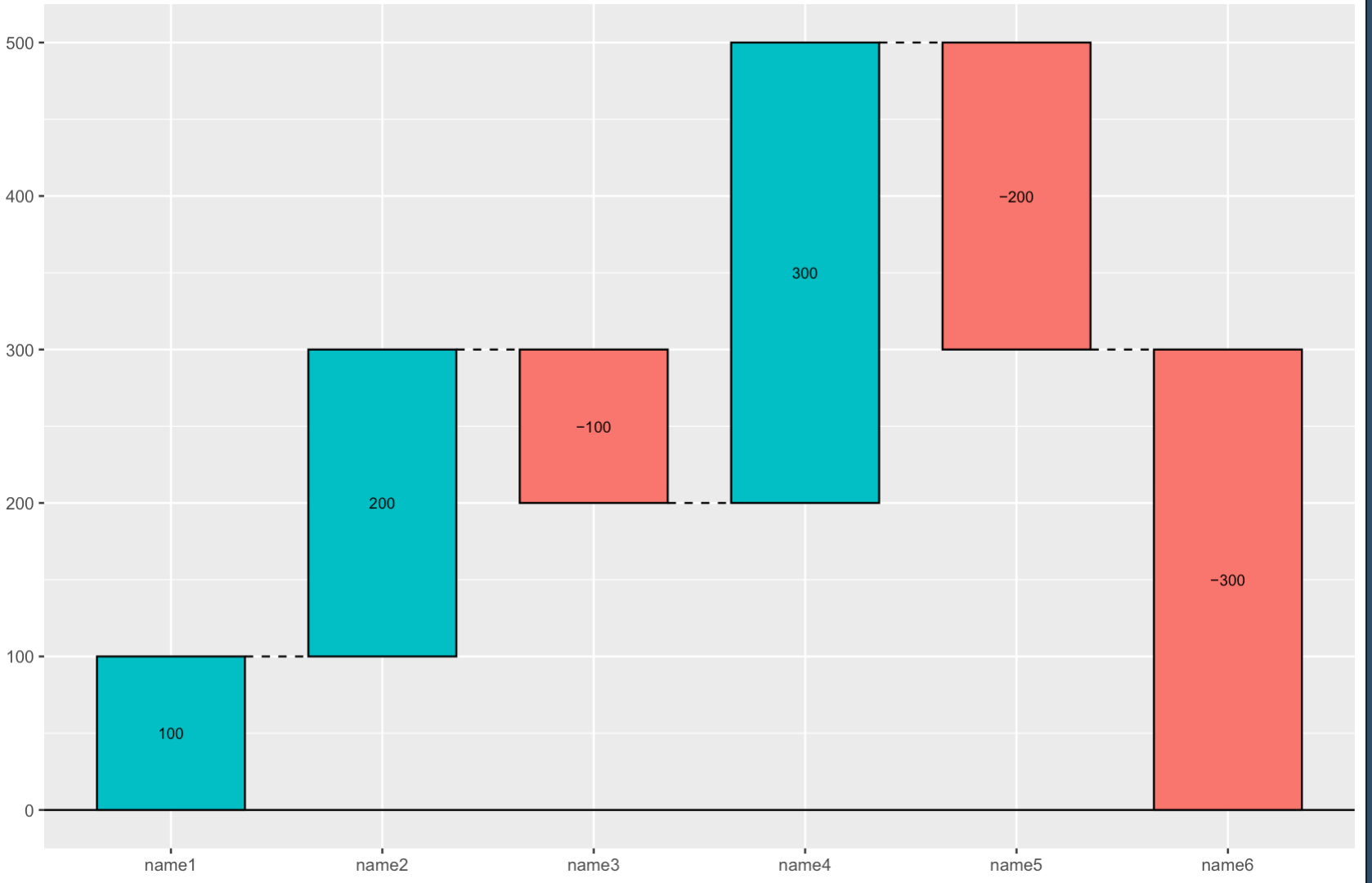
ウォーターフォールチャート
R
# install.packages("waterfalls")
library(waterfalls)
# ダミーデータ
df <- data.frame(x=c("name1", "name2", "name3", "name4", "name5", "name6"),
y=c(100, 200, -100, 300, -200, -300))
# 描画
waterfall(df)
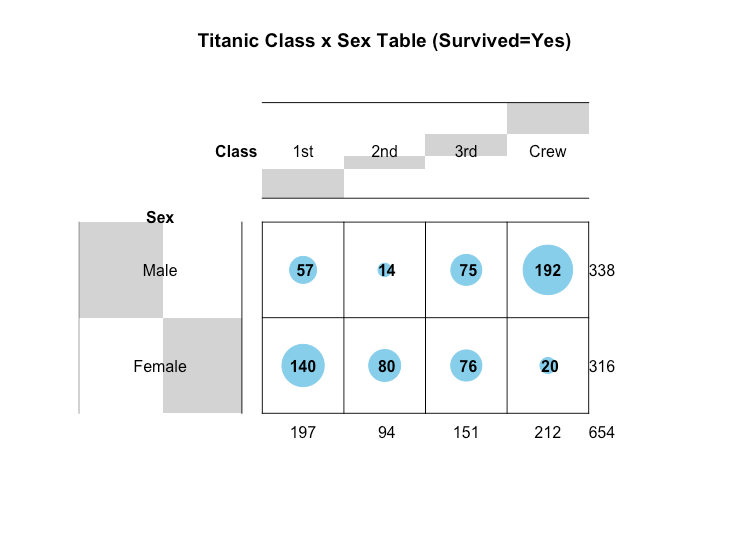
バルーンプロット
R
library(gplots)
balloonplot(Titanic[,, Age="Adult", Survived="Yes"],
main="Titanic Class x Sex Table (Survived=Yes)")
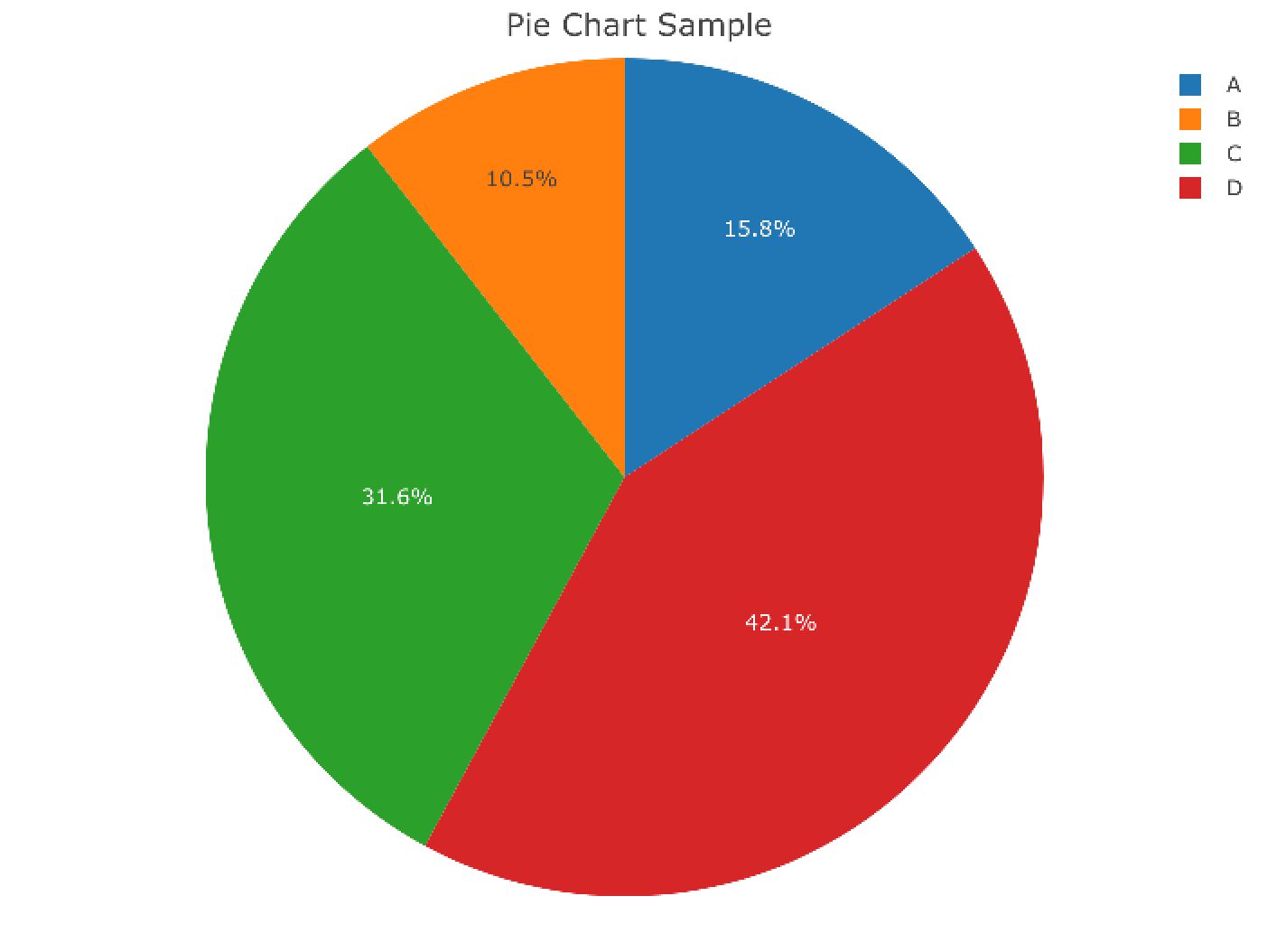
円グラフ
- ggplotで描くのが難しいため、plotlyで描く
R
library(plotly)
data <- data.frame(labels=c("A", "B", "C", "D"), values=c(30, 20, 60, 80))
# labels values
# 1 A 30
# 2 B 20
# 3 C 60
# 4 D 80
plot_ly(data, labels = ~labels, values = ~values, type = "pie", sort=F) %>%
layout(title="Pie Chart Sample")
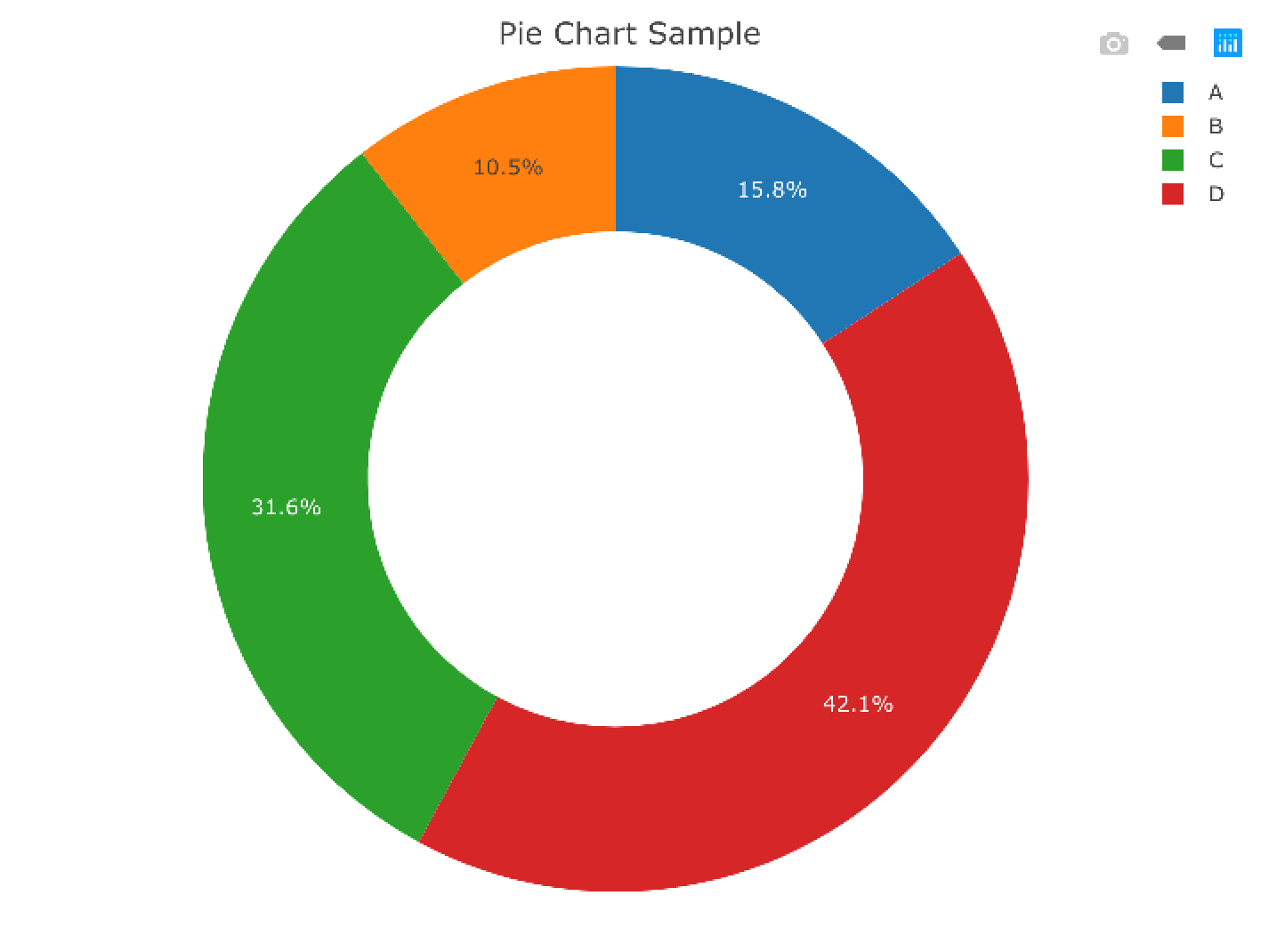
ドーナツグラフ
- 円グラフ同様、plotlyで描く
R
library(plotly)
data <- data.frame(labels=c("A", "B", "C", "D"), values=c(30, 20, 60, 80))
plot_ly(data, labels = ~labels, values = ~values, type = "pie", hole=0.6, sort=F) %>%
layout(title="Pie Chart Sample")
- ggplotで頑張るパターン
R
df <- data.frame(name=c("A", "B", "C", "D"),
ymin=c(0, 30, 60, 80),
ymax=c(30, 60, 80, 100))
ggplot(df) +
geom_rect(aes(fill=name, ymin=ymin, ymax=ymax, xmax=4, xmin=3)) +
coord_polar(theta="y") + xlim(c(0,4))
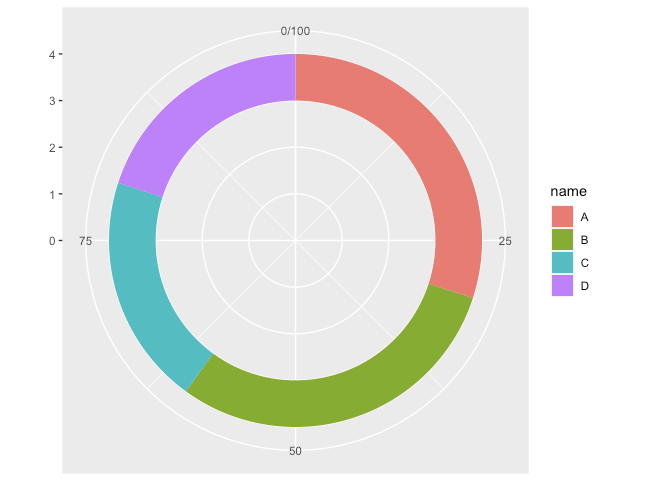
階層型ドーナツグラフ
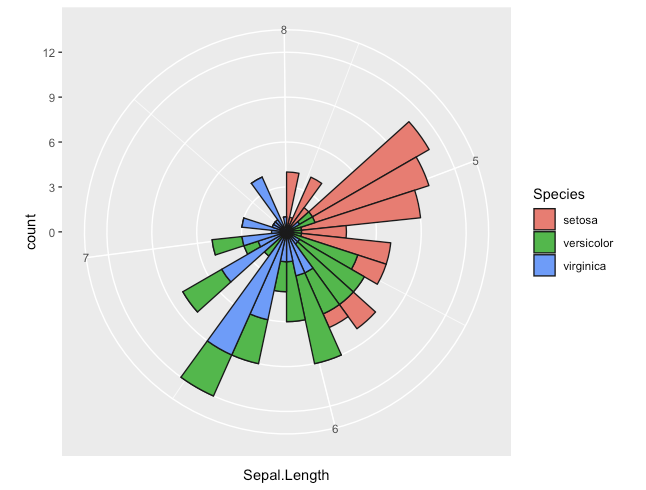
極座標プロット
R
ggplot(iris, aes(x=Sepal.Length, fill=Species)) +
geom_histogram(colour = "gray10") +
coord_polar()
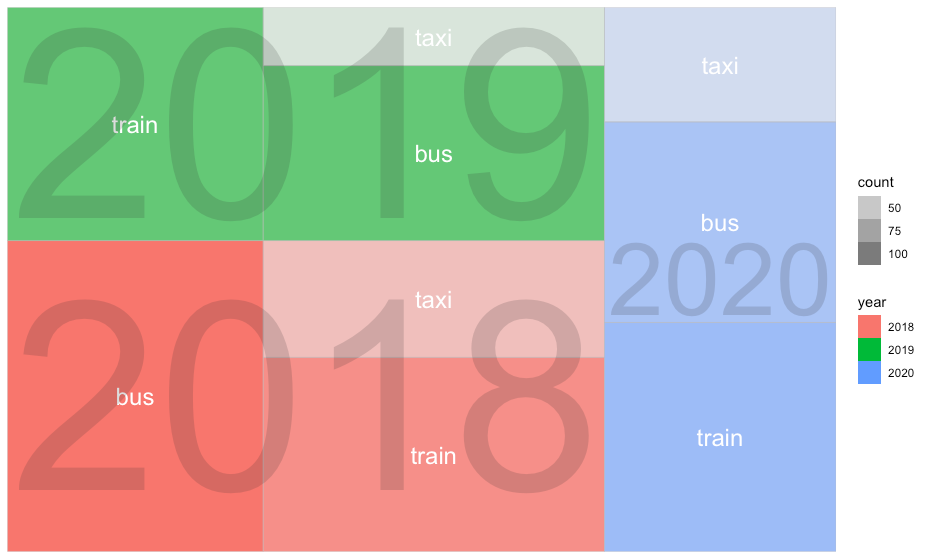
ツリーマップ
- treemapifyを使用
R
library(treemapify)
# データ作成
mobility <- c(rep("train",3),rep("bus",3),rep("taxi",3))
count <- c(c(100, 90, 80), c(120, 90, 70), c(60, 30, 40))
year <- rep(c("2018", "2019", "2020"), 3)
df <- data.frame(mobility, count, year)
ggplot(df, aes(area = count, fill = year, label=mobility, subgroup=year)) +
geom_treemap(aes(alpha = count)) +
geom_treemap_text(colour = "white", place = "centre") +
geom_treemap_subgroup_text(place = "centre", grow = T, alpha = 0.2)
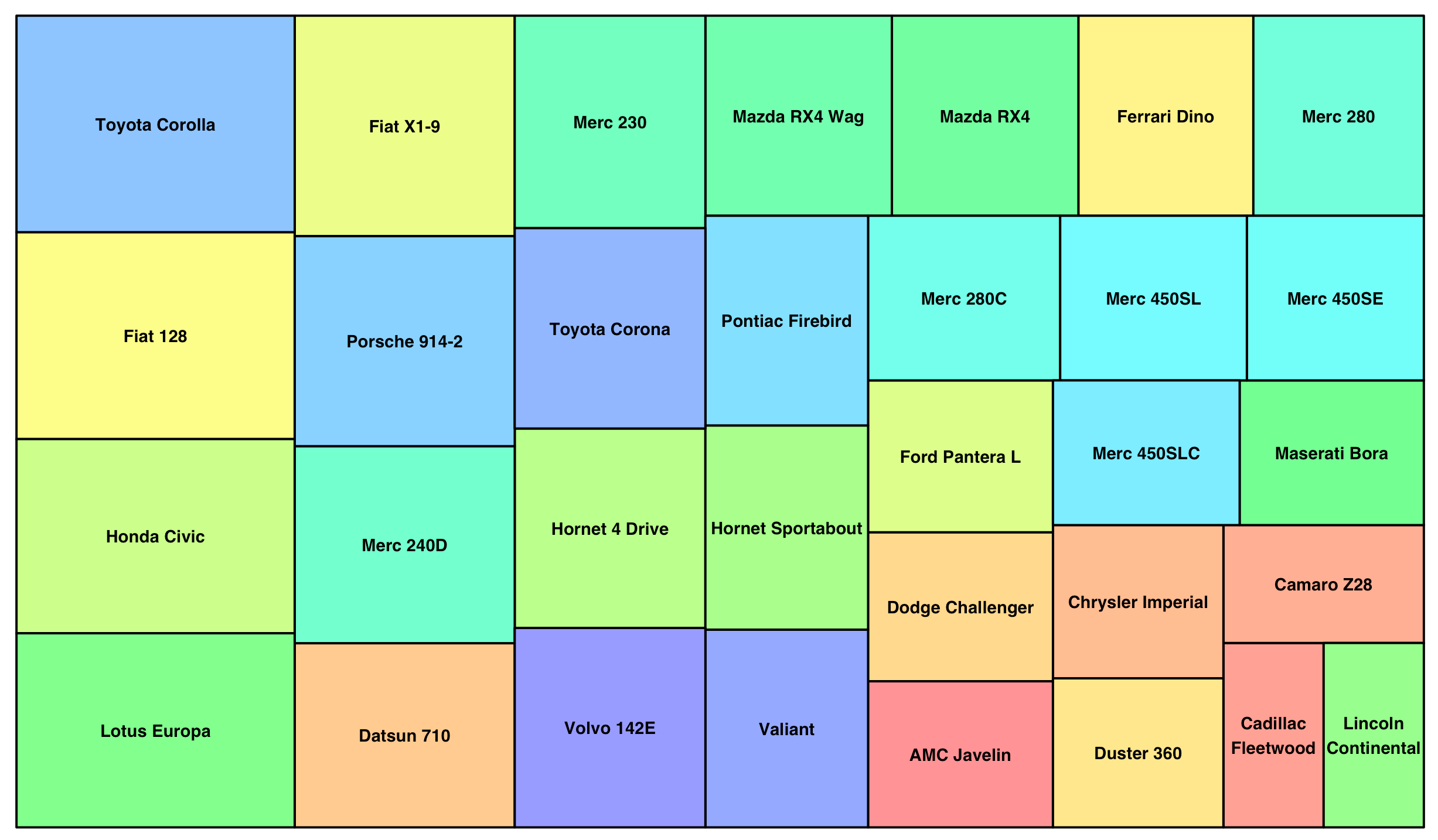
- treemapを使用
R
library(treemap)
data <- data.frame(index=rownames(mtcars),
value=mtcars$mpg)
rainbow_color <- rainbow(47,s=0.4) #set colors
treemap(data,
index=c("index"),
vSize="value",
type="index",
palette = rainbow_color)
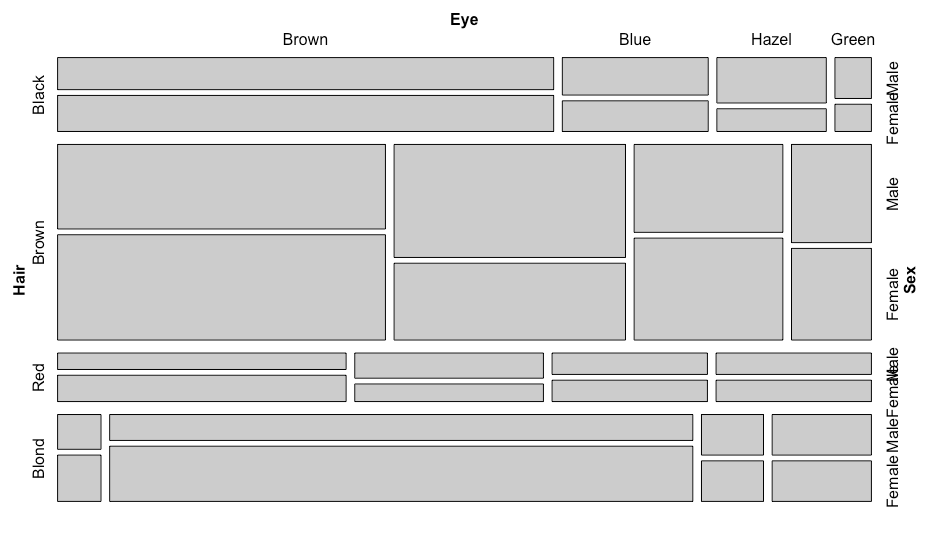
モザイクプロット
R
library(vcd)
mosaic(HairEyeColor)
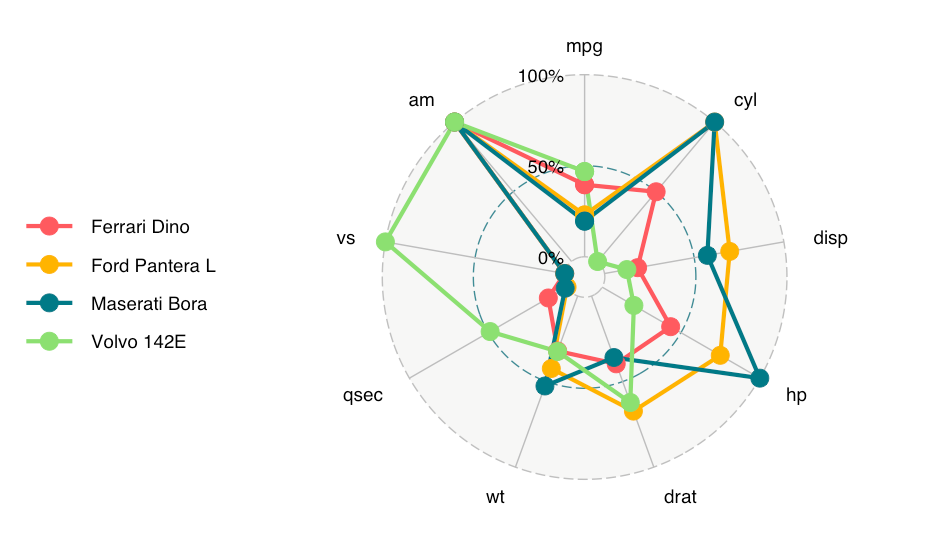
レーダーチャート
R
library(ggradar)
library(scales)
mtcars %>%
tibble::rownames_to_column("group") %>%
mutate_each(funs=rescale, -group) %>%
tail(4) %>% select(1:10) -> mtcars_radar
ggradar(mtcars_radar)
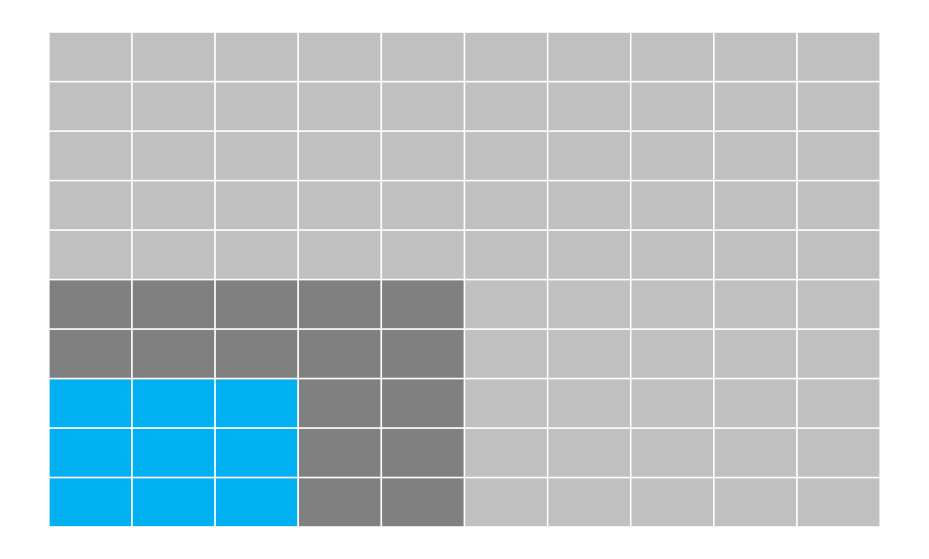
面積グラフ
R
# データ作成
xs <- c()
ys <- c()
ds <- c()
for(x in 1:10){
for(y in 1:10){
xs <- c(xs, x)
ys <- c(ys, y)
if(x <= 3 & y <= 3){
ds <- c(ds, "1")
}else if(x <= 5 & y <=5){
ds <- c(ds, "2")
}else{
ds <- c(ds, "3")
}
}
}
df <- data.frame(x=xs, y=ys, d=ds)
ggplot(df) +
scale_x_continuous(breaks=NULL) +
scale_y_continuous(breaks=NULL) +
theme(axis.title.x = element_blank(),
axis.title.y = element_blank(),
panel.background = element_blank(),
legend.position = 'none') +
geom_tile(aes(x=xs,y=ys,fill=ds), width=1, height=1, size=0.5, colour="white") +
scale_fill_manual(values=c("#00B0F0", "#808080", "#C0C0C0"))
クラスタリング
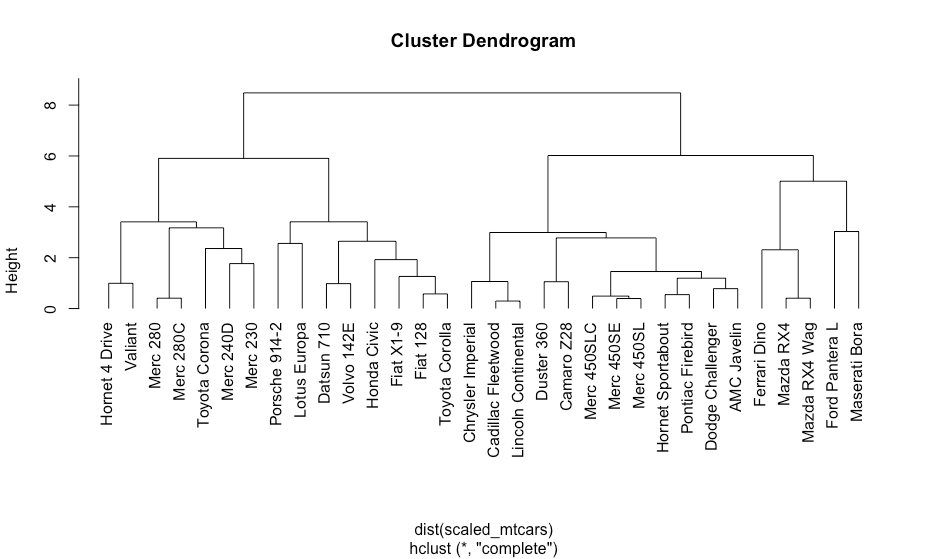
樹形図
R
scaled_mtcars <- scale(mtcars)
hc <- hclust(dist(scaled_mtcars))
plot(hc, hang=-1)
その他
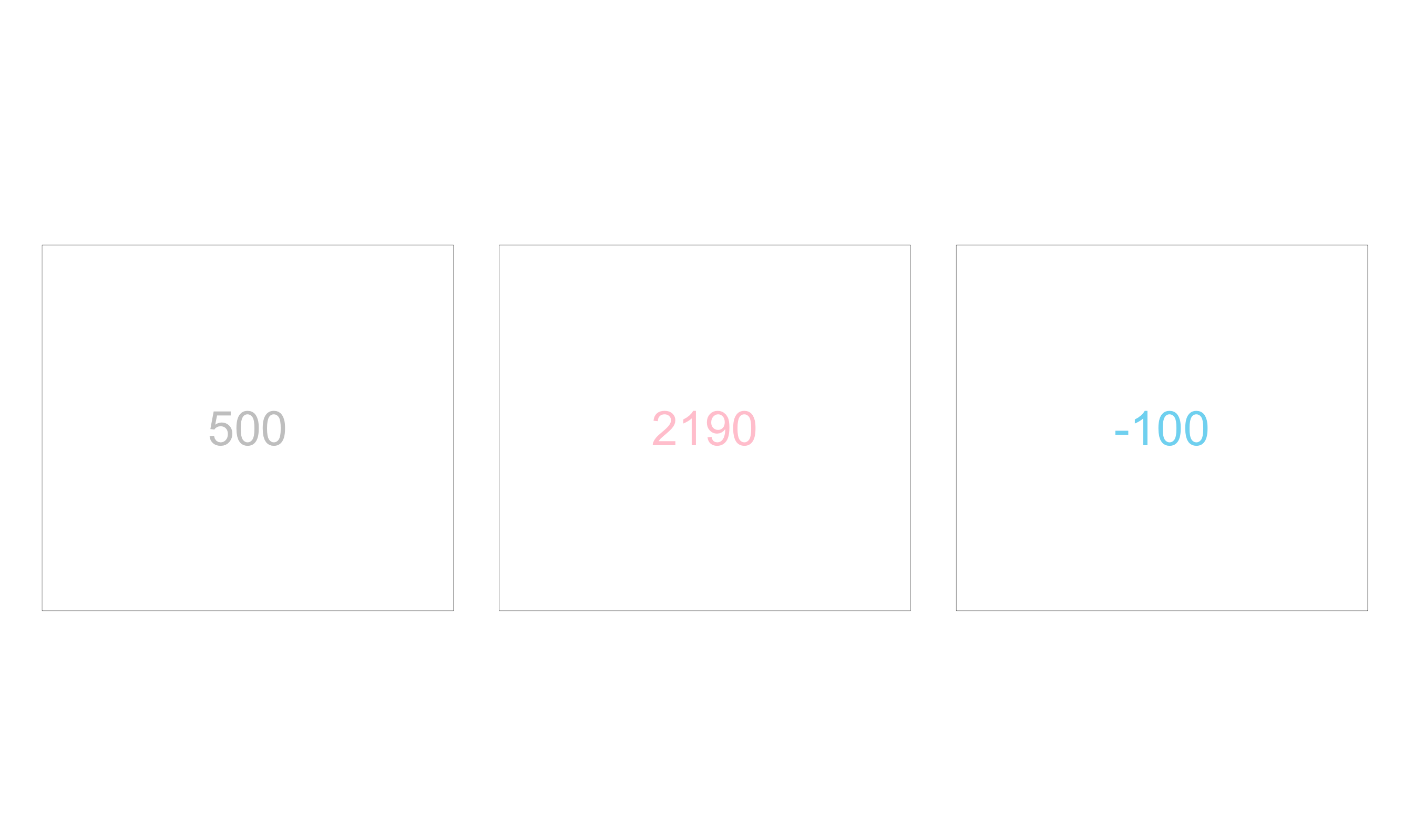
スコアカード(単純なテキスト)
R
rects <- data.frame(x=1:3,
text=c(500, 2190, -100),
colors=c("gray", "pink", "skyblue"))
ggplot(rects, aes(x, y = 0, label = text)) +
geom_tile(width = .9, height = .8, fill="white", colour="black") +
geom_text(aes(color = colors), size=12) +
scale_color_identity(guide = "none") +
coord_fixed() +
theme_void()
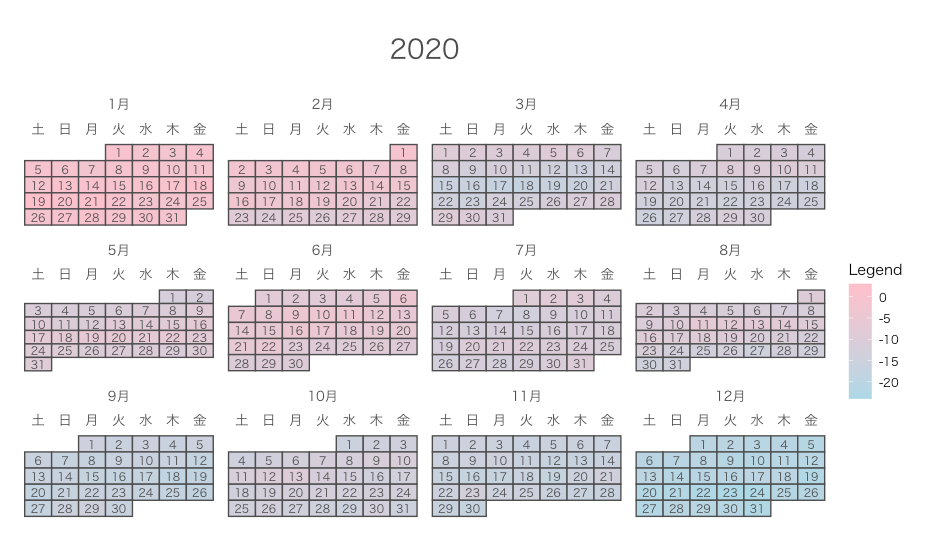
カレンダープロット
R
library(calendR)
# データ作成
date <- seq(as.Date("2020-01-01"), as.Date("2020-12-31"), by="day")
value <- random.walk <- cumsum(rnorm(n=length(date))) #ランダムウォーク
calendR(year=2020,
weeknames = c("日", "月", "火", "水", "木", "金", "土"),
special.days=value,
gradient = TRUE,
special.col = "pink",
low.col = "lightblue",
legend.pos = "right",
legend.title = "Legend",
font.family = "HiraKakuProN-W3") #文字化け対策(MACの場合)
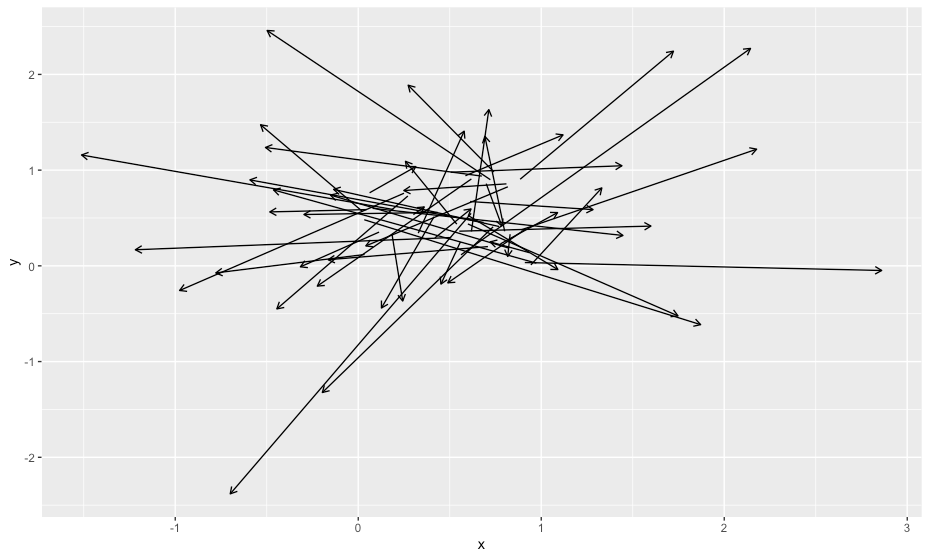
ベクトルフィールド
R
n <- 50
df <- data.frame(x=runif(n),y=runif(n),dx=rnorm(n),dy=rnorm(n))
ggplot(data=df, aes(x=x, y=y)) +
geom_segment(aes(xend=x+dx, yend=y+dy), arrow = arrow(length = unit(0.2,"cm")))
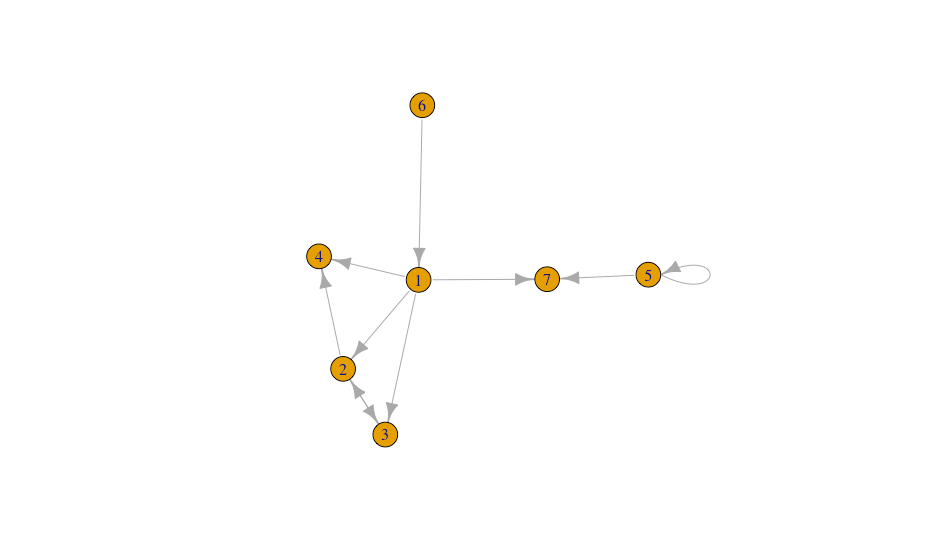
ネットワークグラフ
R
library(igraph)
network_df <- data.frame(from=c(1,2,1,1,3,2,5,6,5,1),
to =c(2,3,3,4,2,4,5,1,7,7))
g <- graph.data.frame(network_df)
plot(g)
ワードクラウド
R
# stopwordsを使いランダム的にサイズ設定して表示していますが、これ自体にはとくに意味はありません。
library(wordcloud2)
library(stopwords)
words <- stopwords::stopwords("ja", source = "marimo")
df <- data.frame(words=words, freq=rnorm(length(words)))
wordcloud2(df)