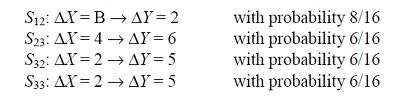はじめに
Differential Cryptanalysis(差分解読法)を説明します。[1]を解説します。
The Basic SPN Cipherおよび記号については[2]を参照ください。
S-Box に対する Differential Characteristics
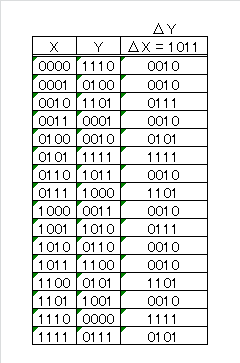
S-Box への入力差分 $\Delta X = X' \oplus X''$ と 出力差分 $\Delta Y = Y' \oplus Y''$の関係を考えます。
例としてΔX = 1011 における ΔYの対応を次に示します。ΔY = 0010b の出現回数が多いことが分かります。
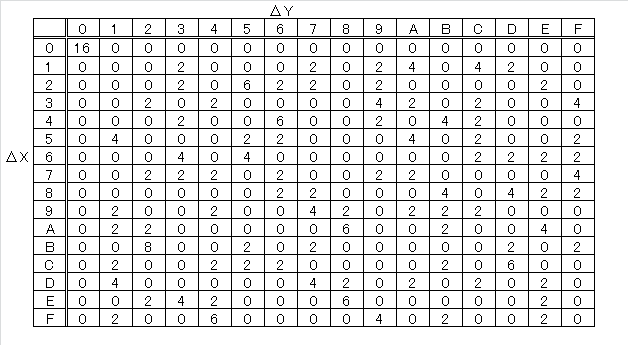
すべての$\Delta X$に対して$\Delta Y$が出現する回数を表にします。Difference Distribution Tableといいます。
(ΔX, ΔY)をDifferentialといいます。(ΔX, ΔY, pd)をDifferential Characteristicといいます。
pdは出現回数を16で割ったものです。
具体的な実装例はCode Example [C1] を参照ください。
The Basic SPN Cipher に対する Differential Characteristics
S-Box に対する Differential Characteristicsを使って
The Basic SPN Cipher に対する Differential Characteristics を構成します。
構成方法はさまざま考えられますが、
ここでは例として、各S-Boxに対して、次のDifferential Characteristicsを考えます。
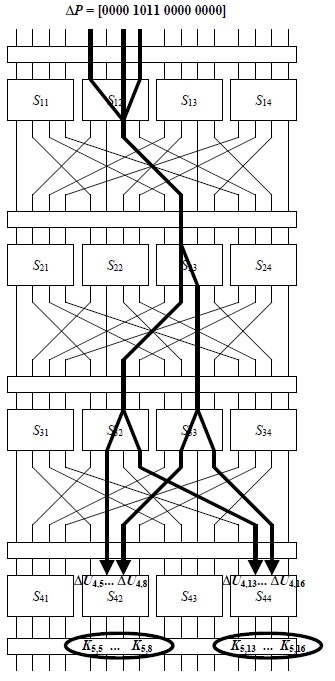
上記をCipher全体に適用します。注目しているbitのデータフローを太線で示します。
ΔP = [0000 1011 000 0000]の時にΔU4 = [0000 0110 0000 0110]となる確率は
S-BoxのDifferential Characteristicsを用いて次のように計算できます。
\frac{8}{16} (\frac{6}{16})^3 = \frac{27}{1024}
上記を計算するには ΔU4 が未知です。これは既知である C5~C8,C13~C16 に対して
K5,5~K5,8 K5,13~K5,16 (16bit) すべてのパターンで CとのXORとS-Boxの逆対応をすることで得られます。
具体的な実装例はCode Example [C2] を参照ください。
正しいKey 0x9A の成立回数が一番多くなっています。
Code Example
Code Exampleを記載します。
CFLAGS=-I. -Wall -Werror -O2
INCS=
OBJS=test.o
LIBS=
TARGET=test
%.o: %.c $(INCS)
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) -c -o $@ $<
$(TARGET): $(OBJS)
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) -o $@ $^ $(LIBS)
clean:
rm -rf $(TARGET) *.o
[C1] Difference Distribution Table
# include <stdio.h>
# include <stdint.h>
# include <string.h>
static uint8_t Sbox[] = { 0xE, 0x4, 0xD, 0x1, 0x2, 0xF, 0xB, 0x8, 0x3, 0xA, 0x6, 0xC, 0x5, 0x9, 0x0, 0x7, };
static void difference_distribution(uint8_t dx, uint8_t* dy /*[16]*/)
{
uint8_t X;
for (X=0; X<0x10; X++) {
dy[Sbox[X^dx] ^ Sbox[X]]++;
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
uint8_t dx, dy[16], i;
printf(" ");
for (i=0; i<0x10; i++) {
printf("%2X ", i);
}
printf("\n");
for (dx=0; dx<0x10; dx++) {
printf("%01X ", dx);
memset(dy, 0, 16);
difference_distribution(dx, dy);
for (i=0; i<0x10; i++) {
printf("%2d ", dy[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
$ gcc --version && make clean && make && ./test.exe
gcc.exe (Rev2, Built by MSYS2 project) 6.2.0
Copyright (C) 2016 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This is free software; see the source for copying conditions. There is NO
warranty; not even for MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
rm -rf test *.o
cc -I. -Wall -Werror -O2 -c -o test.o test.c
cc -I. -Wall -Werror -O2 -o test test.o
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
0 16 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 2 0 2 4 0 4 2 0 0
2 0 0 0 2 0 6 2 2 0 2 0 0 0 0 2 0
3 0 0 2 0 2 0 0 0 0 4 2 0 2 0 0 4
4 0 0 0 2 0 0 6 0 0 2 0 4 2 0 0 0
5 0 4 0 0 0 2 2 0 0 0 4 0 2 0 0 2
6 0 0 0 4 0 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 2 2 2
7 0 0 2 2 2 0 2 0 0 2 2 0 0 0 0 4
8 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 2 0 0 0 4 0 4 2 2
9 0 2 0 0 2 0 0 4 2 0 2 2 2 0 0 0
A 0 2 2 0 0 0 0 0 6 0 0 2 0 0 4 0
B 0 0 8 0 0 2 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 2
C 0 2 0 0 2 2 2 0 0 0 0 2 0 6 0 0
D 0 4 0 0 0 0 0 4 2 0 2 0 2 0 2 0
E 0 0 2 4 2 0 0 0 6 0 0 0 0 0 2 0
F 0 2 0 0 6 0 0 0 0 4 0 2 0 0 2 0
[C2] Differential Cryptanalysis
# include <stdio.h>
# include <stdint.h>
# include <stdbool.h>
# include <string.h>
# include <stdlib.h>
# define COUNT (5000)
# define COUNTER_MAX (256)
//0x0, 0x1, 0x2, 0x3, 0x4, 0x5, 0x6, 0x7, 0x8, 0x9, 0xA, 0xB, 0xC, 0xD, 0xE, 0xF,
static const uint8_t Sbox[] = { 0xE, 0x4, 0xD, 0x1, 0x2, 0xF, 0xB, 0x8, 0x3, 0xA, 0x6, 0xC, 0x5, 0x9, 0x0, 0x7, };
static const uint8_t InvSbox[] = { 0xE, 0x3, 0x4, 0x8, 0x1, 0xC, 0xA, 0xF, 0x7, 0xD, 0x9, 0x6, 0xB, 0x2, 0x0, 0x5, };
static const uint8_t Key[] = { 0x11, 0x22, 0x33, 0x44, 0x55, 0x66, 0x77, 0x88, 0x99, 0xAA, }; // 5 x 16bit = 5 x 2byte = 10byte
static const int round = 4;
static uint16_t counter[COUNTER_MAX];
static void Substitution(uint8_t* S, bool is_inv)
{
uint8_t* box, _S[2];
if (is_inv) {
box = (uint8_t*)InvSbox;
} else {
box = (uint8_t*)Sbox;
}
_S[0] = box[S[0]&0x0F];
_S[0] |= (box[S[0]>>4]<<4);
_S[1] = box[S[1]&0x0F];
_S[1] |= (box[S[1]>>4]<<4);
memcpy(S, _S, 2);
}
static void Permutation(uint8_t* S)
{
uint8_t tmp[2];
/* bit0 */
tmp[0] = (S[0] & 0x80);
tmp[0] |= (S[0] & 0x08)<<3;
tmp[0] |= (S[1] & 0x80)>>2;
tmp[0] |= (S[1] & 0x08)<<1;
/* bit1 */
tmp[0] |= (S[0] & 0x40)>>3;
tmp[0] |= (S[0] & 0x04);
tmp[0] |= (S[1] & 0x40)>>5;
tmp[0] |= (S[1] & 0x04)>>2;
/* bit2 */
tmp[1] = (S[0] & 0x20)<<2;
tmp[1] |= (S[0] & 0x02)<<5;
tmp[1] |= (S[1] & 0x20);
tmp[1] |= (S[1] & 0x02)<<3;
/* bit3 */
tmp[1] |= (S[0] & 0x10)>>1;
tmp[1] |= (S[0] & 0x01)<<2;
tmp[1] |= (S[1] & 0x10)>>3;
tmp[1] |= (S[1] & 0x01);
memcpy(S, tmp, 2);
}
static void cipher(const uint8_t* P, uint8_t* C)
{
int i; bool inv = false;
uint8_t S[2];
memcpy(S, P, 2);
for (i=0; i<round-1; i++) {
S[0] ^= Key[i*2+0]; S[1] ^= Key[i*2+1];
Substitution(S, inv);
Permutation(S);
}
S[0] ^= Key[6]; S[1] ^= Key[7];
Substitution(S, inv);
S[0] ^= Key[8]; S[1] ^= Key[9];
memcpy(C, S, 2);
}
static void part_inv_cipher(uint8_t K, const uint8_t* C, uint8_t* U)
{
// K = K5-K8, K13-K16
U[0] = C[0] ^ (K>>4);
U[1] = C[1] ^ K;
Substitution(U, true /*inv*/);
}
static void count(const uint8_t* C1, const uint8_t* C2)
{
uint16_t K;
for (K=0; K<COUNTER_MAX; K++) {
uint8_t U1[2], U2[2], dU[2];
part_inv_cipher(K, C1, U1);
part_inv_cipher(K, C2, U2);
dU[0] = U1[0] ^ U2[0];
dU[1] = U1[1] ^ U2[1];
if (((dU[0]&0x0F) == 0x06) && ((dU[1]&0x0F) == 0x06)) {
counter[K]++;
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
uint16_t P, dP = 0x00B0;
int i;
for (P=0; P<COUNT; P++) {
uint16_t _P1 = P<<8 | P>>8, _P2 = _P1 ^ dP, C1, C2;
cipher((uint8_t*)&_P1, (uint8_t*)&C1);
cipher((uint8_t*)&_P2, (uint8_t*)&C2);
count((uint8_t*)&C1, (uint8_t*)&C2);
}
for (i=0; i<COUNTER_MAX; i++) {
printf("%03d %02X\n", counter[i], i);
}
return 0;
}
$ make clean && make && ./test.exe | sort -r | head
rm -rf test *.o
cc -I. -Wall -Werror -O2 -c -o test.o test.c
cc -I. -Wall -Werror -O2 -o test test.o
166 9A
091 9F
083 CA
...
references
- [1] A Tutorial on Linear and Differential Cryptanalysis Howard M. Heys
- [2] https://qiita.com/tobira-code/private/1b8511f65dcf4f1b6e79