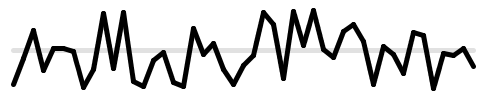
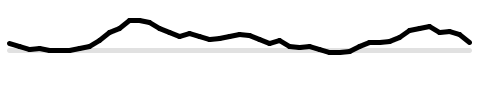
Processingで乱数を取得する関数にrandom()とnoise()がありますが、両者には違いがあります。
random()
乱数を呼び出すたびに取得し、返り値はfloat型になります。 引数に何も記述しないと0.0〜1.0の範囲の乱数を取得します。 random(max); 引数が1つのときは0〜maxの範囲の乱数を取得します。 random(min, max); 引数が2つのときはmin〜maxの範囲の乱数を取得します。random.pde
size(500,100);
background(255);
strokeWeight(5);
smooth();
stroke(0, 30);
line(20,50,480,50);
int step = 10;
float lastx = -999;
float lasty = -999;
float y = 50;
int borderx=20;
int bordery=10;
stroke(0);
for (int x=borderx; x<=width-borderx; x+=step) {
y = bordery + random(height - 2*bordery); //from 10 to 90
if (lastx > -999) {
line(x, y, lastx, lasty);
}
lastx = x;
lasty = y;
}
yの値は10から90の範囲を取得します。
noise()
こちらも乱数を取得しますが、正確にはパーリンノイズという主に自然物を描写する際に使用するノイズ値を取得します。 0.0から1.0の間のfloat型を取得します。noise.pde
size(500, 100);
background(255);
strokeWeight(5);
smooth();
stroke(0, 30);
line(20, 50, 480, 50);
stroke(0);
int step = 10;
float lastx = -999;
float lasty = -999;
float ynoise = random(10);
float y;
for (int x=20; x<=480; x+=step) {
y = 10 + noise(ynoise) * 80; //from 10 to 90
if (lastx > -999) {
line(x, y, lastx, lasty);
}
lastx = x;
lasty = y;
ynoise += 0.1;
}
この例では変数ynoiseをrandom(10)からはじめ、
その値を0.1ずつ増やしてnoise()の引数にしています。パーリンノイズはゲーム開発において炎、雲、水などに使用されているので、random()より自然な動きを作り出すことができます。
パーリンノイズについては奥が深く、今回は触り程度の内容なので、機会があれば続きを投稿したいと思います。