はじめに
Qiitaの競技プログラミング研究月間ということで、アルゴリズムの記事を書いています。
今回は連結リスト問題をまとめました。
JavaScriptでアルゴリズムの勉強をされている方の参考になれば幸いです。
記事を順次まとめていきますので、その他の記事についてはマイページからご覧ください。
連結リスト
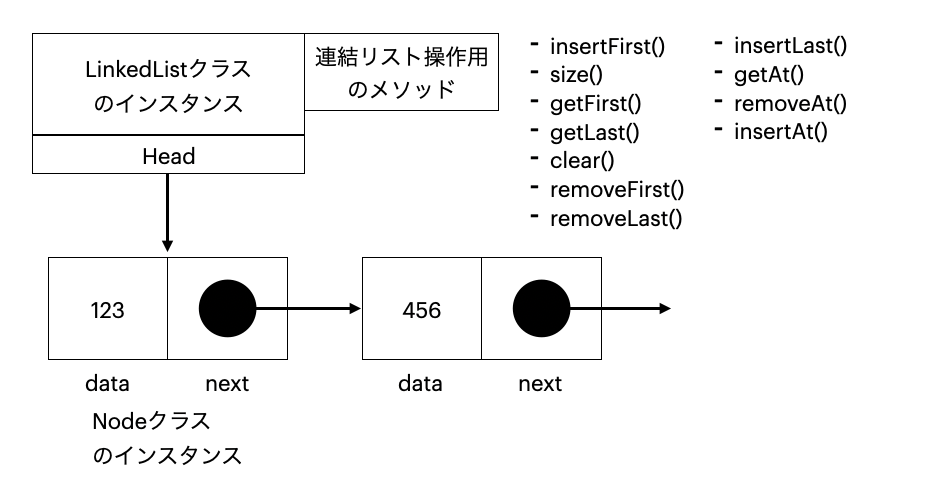
連結リストを構成する、NodeクラスとLinkedListクラスを作成してください。
Nodeクラスのインスタンスプロパティにはdataとnextをもってください。
nextには連結先のノードのデータをもち、連結先がなければnullを返してください。
LinkedListクラスのインスタンスプロパティにはheadをもってください。
headには連結リストの最初のノードのデータを持ち、デフォルトではnullとなります。
また、LinkedListクラスは連結リストを操作する複数のメソッドをもちます。
解答
解答は以下のようになります。
メソッドの役割はノードの追加・削除・取得にわけられ、後は連結リストのどの位置で実行するかどうかの違いとなります。
メソッドを作成する上で、操作するノードがどのノードに連結されるかどうかを意識するのがとても重要です。
class Node {
constructor(data, next = null) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
}
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
}
// 先頭にノードを追加
insertFirst(data) {
this.insertAt(data, 0)
}
// 全ノード数を取得
size() {
let counter = 0;
let node = this.head;
while (node) {
counter++;
node = node.next;
}
return counter;
}
// 先頭のノードを取得
getFirst() {
return this.getAt(0)
}
// 最後のノードを取得
getLast() {
return this.getAt(this.size() - 1)
}
// 全ノードを削除
clear() {
this.head = null;
}
// 先頭のノードを削除
removeFirst() {
if (!this.head) {
return;
}
this.head = this.head.next;
}
// 最後のノードを削除
removeLast() {
// ノードがないとき
if (!this.head) {
return;
}
// ノードが一つしかないとき
if (!this.head.next) {
this.head = null;
return;
}
// ノードが二つ以上のとき
let previous = this.head;
let node = this.head.next;
// previous, nodeを一個ずつずらす
while (node.next) {
previous = node;
node = node.next;
}
previous.next = null;
}
// 最後にノードを追加
insertLast() {
const last = this.getLast();
if (last) {
last.next = new Node(data);
} else {
this.head = new Node(data);
}
}
// 指定したノードを取得
getAt(index) {
if (!this.head) {
return null;
}
let counter = 0;
let node = this.head;
while (node) {
if (counter === index) {
return node;
}
counter++;
node = node.next;
}
return null;
}
// 指定したノードを削除
removeAt(index) {
if (!this.head) {
return;
}
if (index === 0) {
this.head = this.head.next;
return;
}
// 一個前のノードの連結先を変える
const previous = this.getAt(index - 1);
if (!previous || !previous.next) {
return;
}
previous.next = previous.next.next;
}
// 指定位置へのノードの挿入
insertAt(data, index) {
if (!this.head) {
this.head = new Node(data);
return;
}
if (index === 0) {
this.head = new Node(data, this.head); // 前のheadをnextにする
return;
}
const previous = this.getAt(index - 1) || this.getLast();
previous.next = new Node(data, previous.next);
}
}
ノードの取得
指定した位置のノードを取得するメソッドgetAt()は以下のようになります。
まず、headが存在しなければnullを返します。
headが存在していればlet node = this.headでnodeを定義し、while内でcounterの値と同時にnodeの位置をnode = node.nextで移動させます。
そして、counterとindexの値が一致したらnodeを返すようにします。
getAt(index) {
if (!this.head) {
return null;
}
let counter = 0;
let node = this.head;
while (node) {
if (counter === index) {
return node;
}
counter++;
node = node.next;
}
return null;
}
ノードの追加
指定した位置にノードを追加するメソッドinsertAt()は以下のようになります。
headが存在しなければ、this.head = new Node(data)でheadに直接ノードを作成します。
先頭(index = 0)にノードを作成するときは、this.head = new Node(data, this.head)として新しいノードを作成してheadの更新も行います。
また、指定したindex、またはリストの最後にノードを追加する場合には、const previous = this.getAt(index - 1) || this.getLast()で追加したい位置の前のノードpreviousを取得します。
||の演算子を使うことで、this.getAt(index - 1)のノードが存在しない場合に、this.getLast()で最後のノードを取得することができます。
最後にprevious.next = new Node(data, previous.next)とすることで、ノードの矢印の向きを更新します。
insertAt(data, index) {
// 空のリストにノードを追加する場合
if (!this.head) {
this.head = new Node(data);
return;
}
// 先頭にノードを追加する場合
if (index === 0) {
this.head = new Node(data, this.head); // 前のheadをnextにする
return;
}
// リストの中、最後にノードを追加する場合
const previous = this.getAt(index - 1) || this.getLast();
previous.next = new Node(data, previous.next);
}
ノードの削除
最後のノードを削除するメソッドremoveLast()は以下のようになります。
削除したいノードnodeとその一個前のノードpreviousを用意して、これらをnode.nextがnullになるまでwhile (node.next)で更新していきます。
最後のノードnodeが見つかったところで、previousの連結先previous.nextをnullにしてあげれば削除完了です。
removeLast() {
// ノードがないとき
if (!this.head) {
return;
}
// ノードが一つしかないとき
if (!this.head.next) {
this.head = null;
return;
}
// ノードが二つ以上のとき
let previous = this.head;
let node = this.head.next;
// previous, nodeを一個ずつずらす
while (node.next) {
previous = node;
node = node.next;
}
previous.next = null;
}
また、指定したノードを削除するメソッドremoveAt()は以下のようになります。
こちらについても削除したいノードの一個前のノードpreviousに着目し、連結先を変えるような操作previous.next = previous.next.nextを行います。
removeAt(index) {
// ノードが空の場合
if (!this.head) {
return;
}
// 先頭のノードを指定した場合
if (index === 0) {
this.head = this.head.next;
return;
}
// 上記以外の場合
// 一個前のノードpreviousの連結先を変える
const previous = this.getAt(index - 1);
if (!previous || !previous.next) {
return;
}
previous.next = previous.next.next;
}
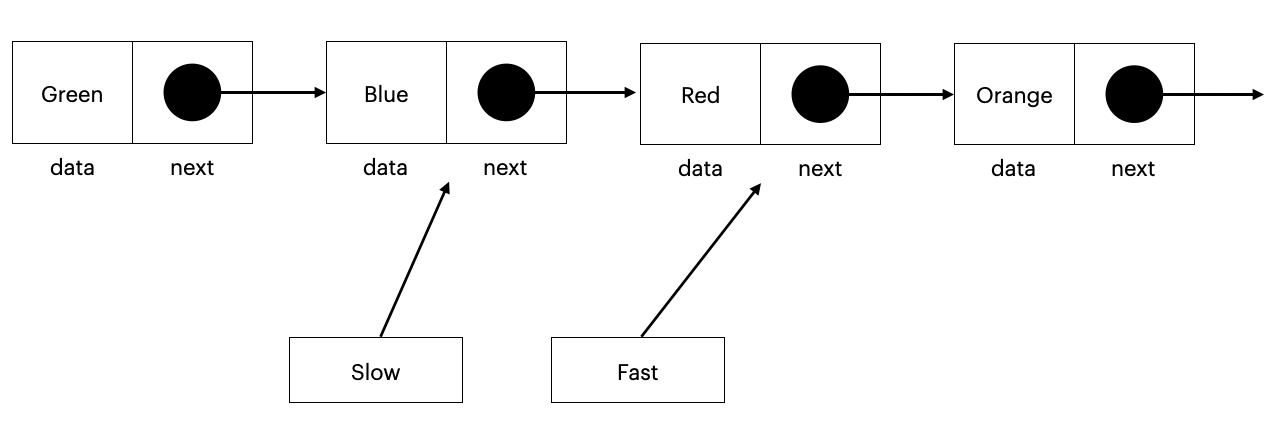
中心ノード探索
連結リストの中心のノードを返してください。
ノードの数が偶数の場合は、リストの前半分の最後のノードを返してください。
*counter変数やsize()メソッドを利用しないでください。
*繰り返しは1回まで許容されます。
const l = new LinkedList();
l.insertLast('a')
l.insertLast('b')
l.insertLast('c')
midpoint(l); // returns { data: 'b' }
解答
初期値が先頭のノードであるslowとfastという変数を用意し、fast.nextとfast.next.nextがnullになるまで、slowは1個、fastは2個ずつノードを更新していきます。
最終的なslowの値がリストの中心ノードとなります。
function midpoint(list) {
let slow = list.getFirst();
let fast = list.getFirst();
while (fast.next && fast.next.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
リスト循環(Circular)
連結リストを引数に与えたときに、リストの一部が循環していたらtrue、循環していなければfalseを返してください。
const l = new List();
const a = new Node('a');
const b = new Node('b');
const c = new Node('c');
l.head = a;
a.next = b;
b.next = c;
c.next = b;
circular(l) // true
解答
中心ノード探索と解き方の方針は同じです。
リストが循環しているとslowとfastが重なるので、そのときにtrueを返すようにします。
function circular(list) {
let slow = list.getFirst();
let fast = list.getFirst();
while (fast.next && fast.next.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow === fast) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
最後からn番目のノード探索
連結リストと整数nを引数に与えたときに、最後からn番目のノードを返してください。
*size()メソッドは使用しないでください。
*nは常にリストの長さ以下であると仮定してください。
const list = new List();
list.insertLast('a');
list.insertLast('b');
list.insertLast('c');
list.insertLast('d');
fromLast(list, 2).data // 'b'
解答
中心ノード探索やリスト循環と同様に、先頭ノードを初期値としたslowとfastを用意します。
次に、while (n > 0)内でfastを更新し、slowとn個分間隔を空けます。
while (fast.next)でslowとfastを1個ずつ更新していき、fast.nextがnullになったとき(fastが最後のノードになったとき)のslowを結果として返します。
function fromLast(list, n) {
let slow = list.getFirst();
let fast = list.getFirst();
// 最初にfastをn移動させる(slowをn個分間隔をあける)
while (n > 0) {
fast = fast.next;
n--;
}
while (fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
参考資料