Tensorboardを使って学習結果をVisualizationする方法を調べてみた。
Tensorboardに出力する方法はここを参考にした。
簡単な例
いきなり複雑なやつだと大変なので、簡単な例を作って試した。
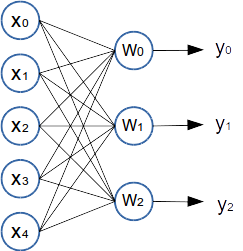
テストデータは下記の図のように、xは5次元、yを3次元とし、xをランダムで生成したあとに、あらかじめ指定しておいたWをかけてbを足してyを生成した。xが5次元、yが3次元なので、Wのサイズは5x3になる。
実行したコードは下記の通り、これはTensorflowのホームページのコードをテストデータに合わせてちょっとだけ変更した。
コードのポイントは下記の通り。
1. writer = tf.train.SummaryWriter("/tmp/tensorflow_log", sess.graph_def)のようにしてSummaryWriterのobjectを作る。そのときにlogを出力するdirectoryを指定する。
2. merged = tf.merge_all_summaries()でsummary dataを生成するoprationをまとめる。operationとはscalar_summaryとかhistogram_summaryのこと。
3. operationをコードに埋め込む。w_hist = tf.histogram_summary("weights", W)こんな感じ。
4. 何回かに1回(コードでは10回に1回)result = sess.run([merged, loss])のようにmergedを実行する。lossの方は、標準出力に出力するためなのでTensorboardに出したいだけであれば実行しなくてもいいと思う。
5. sess.runの戻り値をwriteに渡す。コードでは、mergedとlossをsess.runに渡しているのでresultがlistで戻ってくる。mergedの方なのでresult[0]をwriter.add_summary(summary_str, step)こんな感じで渡す。
6.学習を実行して終わったら、tensorboard --logdir=/tmp/tensorflow_log を実行する。
7.その状態でchromeを起動し、http://localhost:6006 にアクセスするとTensorBoardが表示され、logの出力がうまく行っているとGRAPHが表示される。
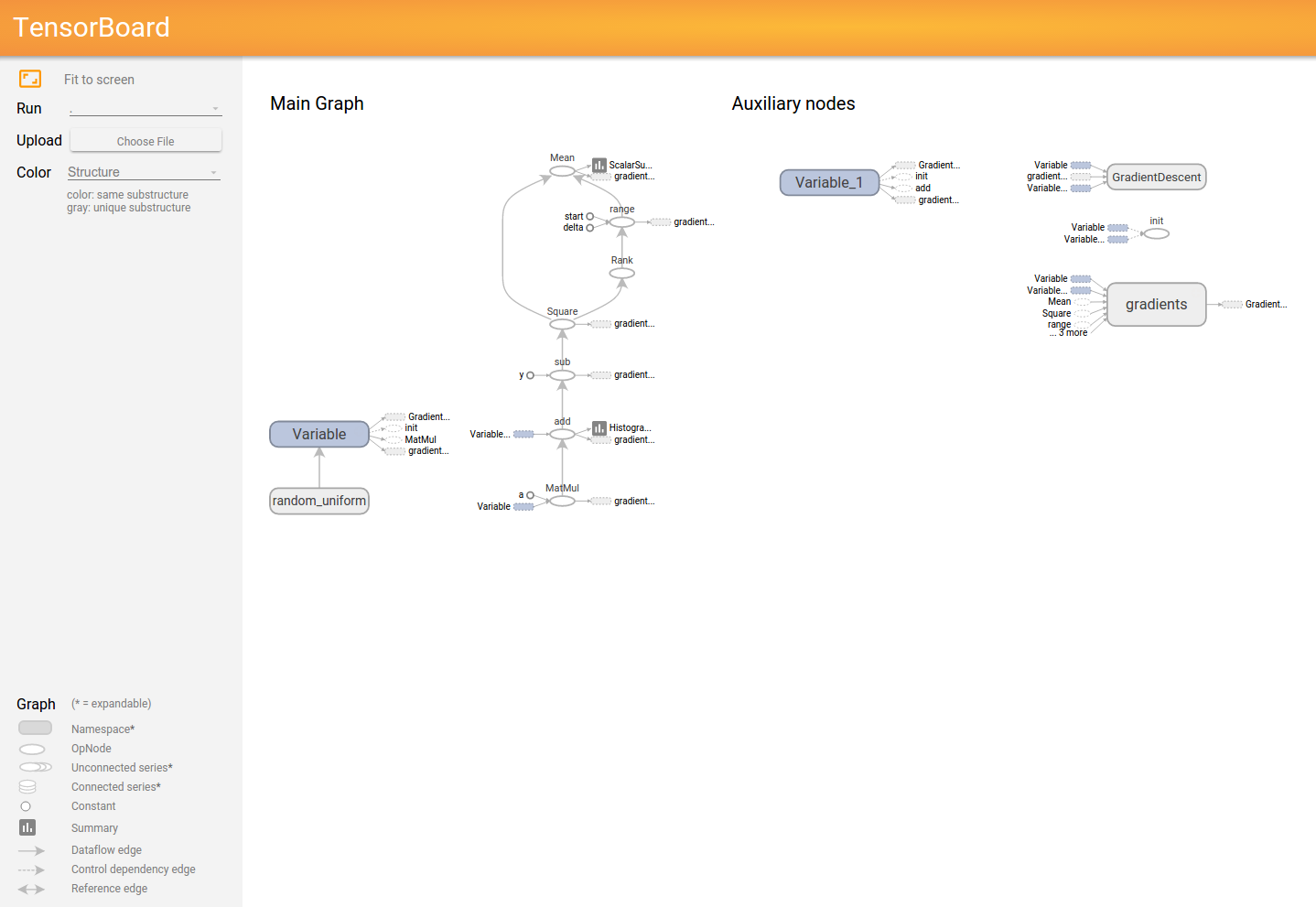
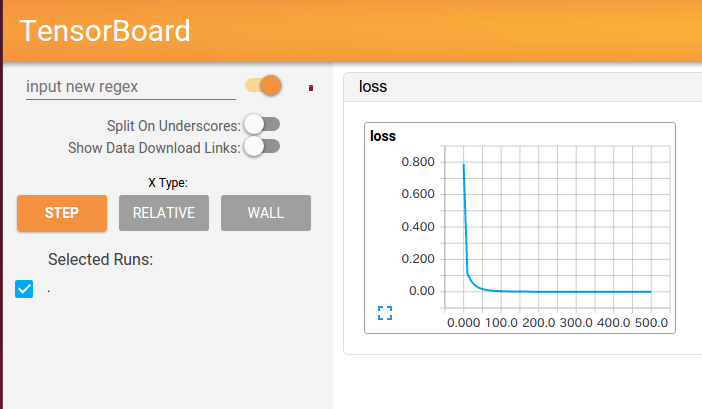
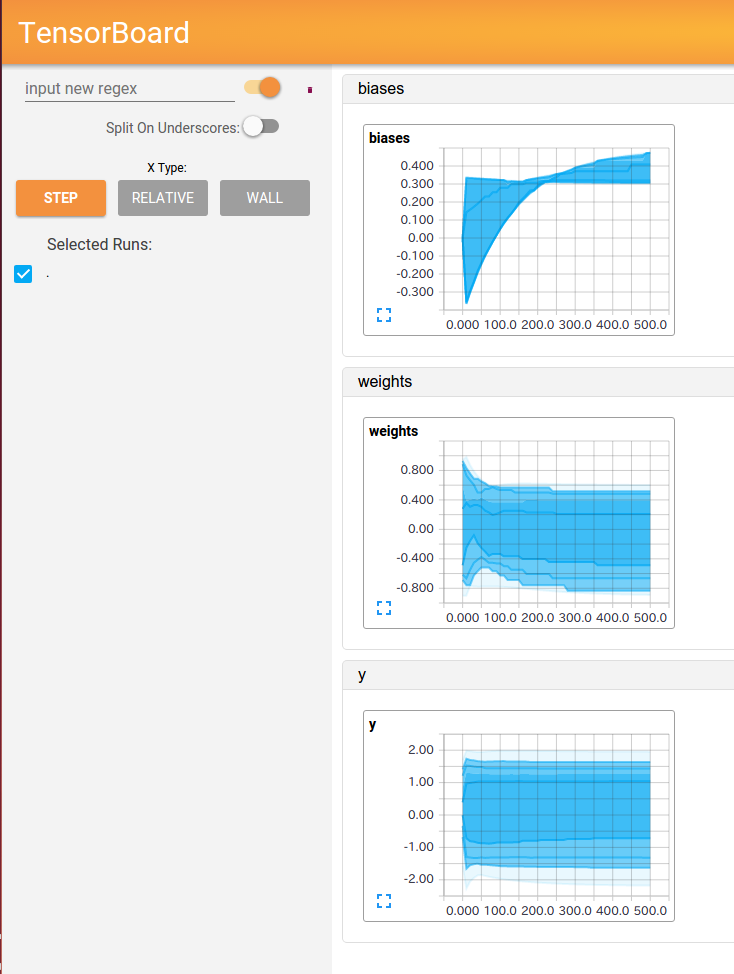
以下にTensorboardの結果と実行したコードを示す。
GRAPH
EVENTS
HISTOGRAMS
Code
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
WW = np.array([[0.1, 0.6, -0.9],
[0.2, 0.5, -0.8],
[0.3, 0.4, -0.7],
[0.4, 0.3, -0.6],
[0.5, 0.2, -0.5]]).astype(np.float32)
bb = np.array([0.3, 0.4, 0.5]).astype(np.float32)
x_data = np.random.rand(100,5).astype(np.float32)
y_data = np.dot(x_data, WW) + bb
with tf.Session() as sess:
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([5,3], -1.0, 1.0))
# The zeros set to zero with all elements.
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([3]))
#y = W * x_data + b
y = tf.matmul(x_data, W) + b
# Add summary ops to collect data
w_hist = tf.histogram_summary("weights", W)
b_hist = tf.histogram_summary("biases", b)
y_hist = tf.histogram_summary("y", y)
# Minimize the mean squared errors.
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y - y_data))
# Outputs a Summary protocol buffer with scalar values
loss_summary = tf.scalar_summary("loss", loss)
# Gradient descent algorithm
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5)
train = optimizer.minimize(loss)
# Before starting, initialize the variables. We will 'run' this first.
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
# Creates a SummaryWriter
# Merges all summaries collected in the default graph
merged = tf.merge_all_summaries()
writer = tf.train.SummaryWriter("/tmp/tensorflow_log", sess.graph_def)
sess.run(init)
# Fit the line
for step in xrange(501):
if step % 10 == 0:
result = sess.run([merged, loss])
summary_str = result[0]
acc = result[1]
writer.add_summary(summary_str, step)
print"step = %s acc = %s W = %s b = %s" % (step, acc, sess.run(W), sess.run(b))
else:
sess.run(train)
もうちょっと複雑な例
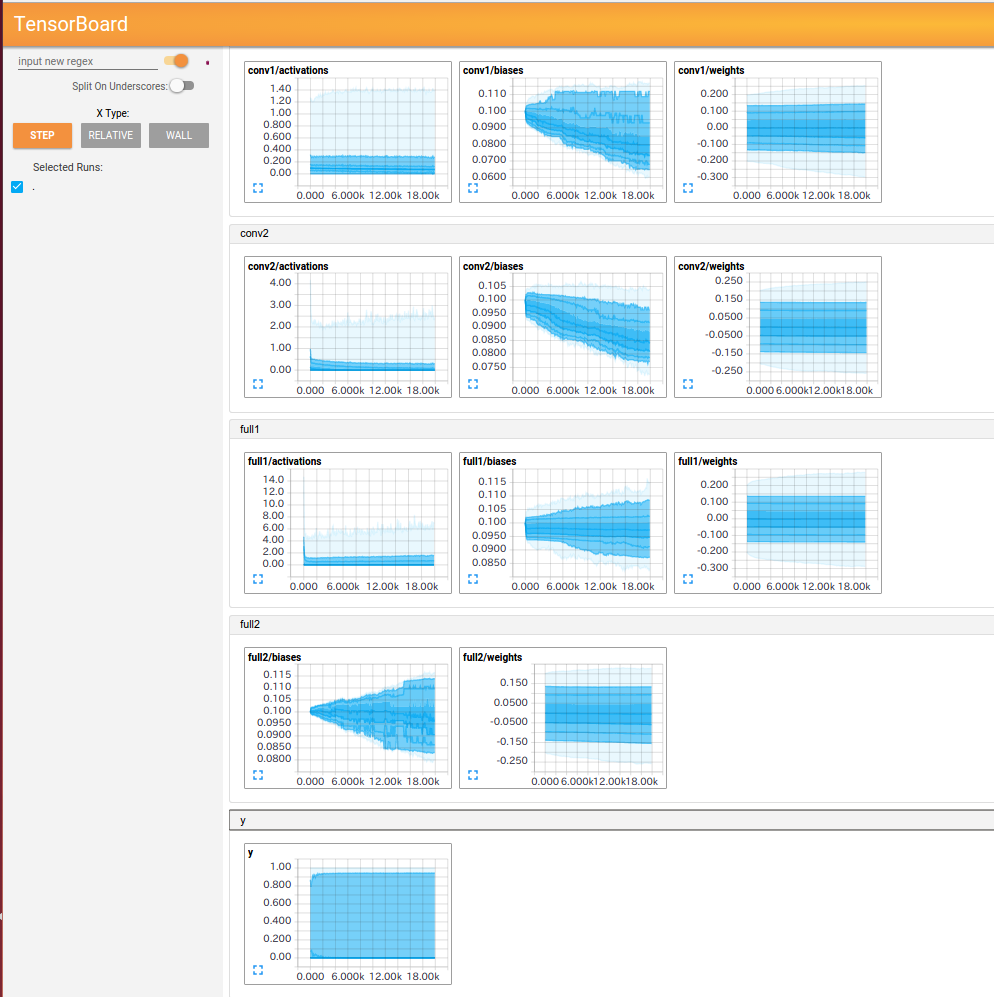
histogramをまとめるときは、tf.histogram_summary("xxx/weights", w), tf.histogram_summary("xxx/biases", b)のようにまとめたいhistogramのxxxを同じにする。
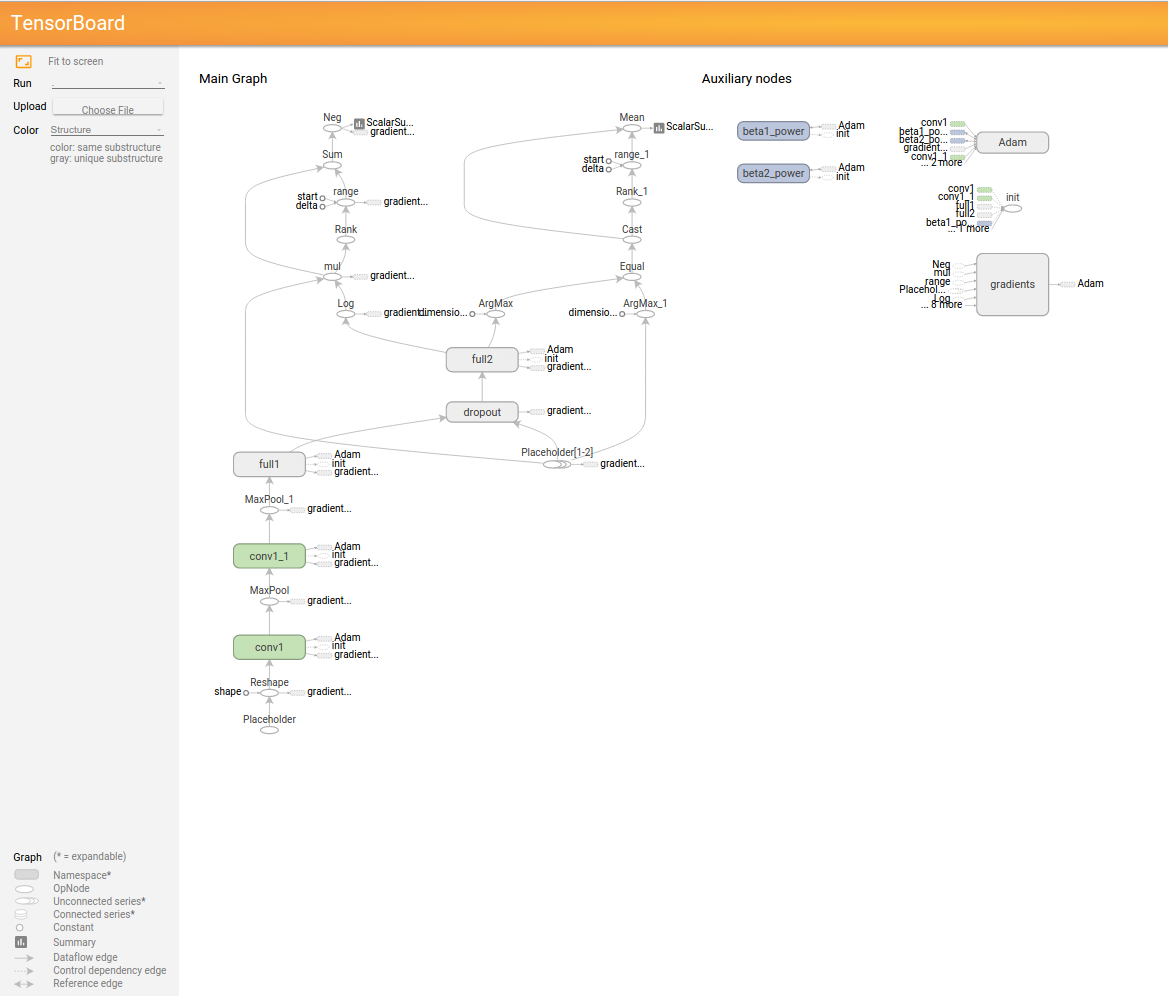
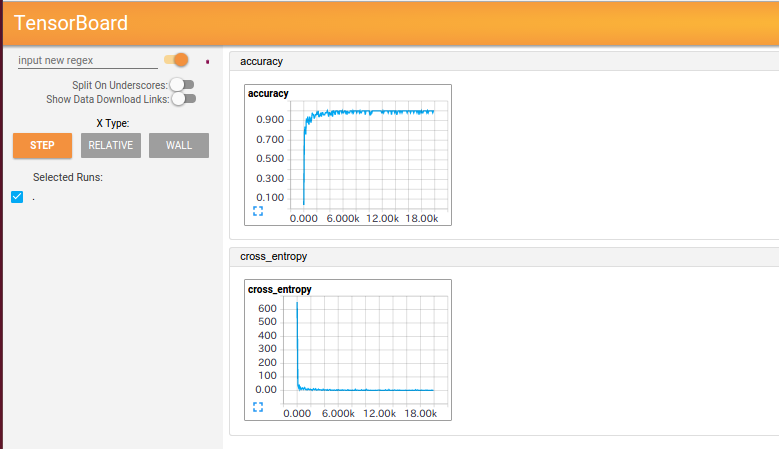
以下にTensorboardの結果と実行したコードを示す。
GRAPH
EVENTS
HISTOGRAMS
Code
import input_data
import tensorflow as tf
print 'load MNIST dataset'
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data", one_hot=True)
def weight_variable(shape):
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.1)
return tf.Variable(initial)
def bias_variable(shape):
initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape = shape)
return tf.Variable(initial)
def conv2d(x, W):
return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1,1,1,1], padding='SAME')
def max_pool_2x2(x):
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1,2,2,1], strides=[1,2,2,1], padding='SAME')
def _write_histogram_summary(parent, infos):
for i in infos:
tf.histogram_summary("%s/%s" % (parent, i[0]), i[1])
with tf.Session() as sess:
x = tf.placeholder("float", [None, 784])
y_ = tf.placeholder("float", [None, 10])
# 1x28x28 -> 32x28x28 -> 32x14x14
x_image = tf.reshape(x, [-1,28,28,1])
with tf.variable_scope('conv1') as scope:
W_conv1 = weight_variable([5, 5, 1, 32])
b_conv1 = bias_variable([32])
h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image, W_conv1) + b_conv1, name=scope.name)
_write_histogram_summary('conv1', [['weights', W_conv1],['biases', b_conv1], ['activations', h_conv1]])
h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1)
# 32x14x14 -> 64x7x7
with tf.variable_scope('conv1') as scope:
W_conv2 = weight_variable([5, 5, 32, 64])
b_conv2 = bias_variable([64])
h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1, W_conv2) + b_conv2, name=scope.name)
_write_histogram_summary('conv2', [['weights', W_conv2],['biases', b_conv2], ['activations', h_conv2]])
h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2)
# 64x7x7 -> 1024
with tf.variable_scope('full1') as scope:
W_fc1 = weight_variable([7 * 7 * 64, 1024])
b_fc1 = bias_variable([1024])
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7*7*64])
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1, name=scope.name)
_write_histogram_summary('full1', [['weights', W_fc1],['biases', b_fc1], ['activations', h_fc1]])
# dropout
keep_prob = tf.placeholder("float")
h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, keep_prob)
# Readout
with tf.variable_scope('full2') as scope:
W_fc2 = weight_variable([1024, 10])
b_fc2 = bias_variable([10])
y_conv=tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop, W_fc2) + b_fc2, name=scope.name)
_write_histogram_summary('full2', [['weights', W_fc2],['biases', b_fc2]])
tf.histogram_summary("y", y_conv)
cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_*tf.log(y_conv))
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cross_entropy)
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_conv,1), tf.argmax(y_,1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float"))
tf.scalar_summary("cross_entropy", cross_entropy)
tf.scalar_summary("accuracy", accuracy)
# Before starting, initialize the variables. We will 'run' this first.
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
# Creates a SummaryWriter
# Merges all summaries collected in the default graph
merged = tf.merge_all_summaries()
writer = tf.train.SummaryWriter("/tmp/tensorflow_log_mnist", sess.graph_def)
sess.run(init)
# training
N = len(mnist.train.images)
N_test = len(mnist.test.images)
n_epoch = 20000
batchsize = 50
for i in range(n_epoch):
batch = mnist.train.next_batch(batchsize)
if i%100 == 0:
summary_str, loss_value = sess.run([merged, accuracy], feed_dict={x: batch[0], y_: batch[1], keep_prob: 0.5})
writer.add_summary(summary_str, i)
print "step %d %.2f" % (i, loss_value)
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x: batch[0], y_: batch[1], keep_prob: 0.5})
tacc = 0
tbatchsize = 1000
for i in range(0,N_test,tbatchsize):
acc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={
x: mnist.test.images[i:i+tbatchsize], y_: mnist.test.labels[i:i+tbatchsize], keep_prob: 1.0})
tacc += acc * tbatchsize
print "test step %d acc = %.2f" % (i//tbatchsize, acc)
tacc /= N_test
print "test accuracy %.2f" % tacc